C++学习笔记:string类的常用函数详解
C++提供了std::string(后面简写为string)类用于字符串的处理。string类定义在C++头文件中,注意和 头文件区分,其实是对C标准库中的
构造函数
//首先粗看一下basic_string类,作为string类的基类,其为一个内容巨大无比。
class basic_string { // null-terminated transparent array of elements
private:
friend _Tidy_deallocate_guard<basic_string>;
friend basic_stringbuf<_Elem, _Traits, _Alloc>;
using _Alty = _Rebind_alloc_t<_Alloc, _Elem>;
using _Alty_traits = allocator_traits<_Alty>;
using _Scary_val = _String_val<conditional_t<_Is_simple_alloc_v<_Alty>, _Simple_types<_Elem>,
_String_iter_types<_Elem, typename _Alty_traits::size_type, typename _Alty_traits::difference_type,
typename _Alty_traits::pointer, typename _Alty_traits::const_pointer, _Elem&, const _Elem&>>>;
static_assert(!_ENFORCE_MATCHING_ALLOCATORS || is_same_v<_Elem, typename _Alloc::value_type>,
_MISMATCHED_ALLOCATOR_MESSAGE("basic_string" , "T"));
static_assert(is_same_v<_Elem, typename _Traits::char_type>,
"N4659 24.3.2.1 [string.require]/3 requires that the supplied "
"char_traits character type match the string's character type.");
static_assert(!is_array_v<_Elem> && is_trivial_v<_Elem> && is_standard_layout_v<_Elem>,
"The character type of basic_string must be a non-array trivial standard-layout type. See N4861 "
"[strings.general]/1.");
public:
using traits_type = _Traits;
using allocator_type = _Alloc;
using value_type = _Elem;
using size_type = typename _Alty_traits::size_type;
using difference_type = typename _Alty_traits::difference_type;
using pointer = typename _Alty_traits::pointer;
using const_pointer = typename _Alty_traits::const_pointer;
using reference = value_type&;
using const_reference = const value_type&;
using iterator = _String_iterator<_Scary_val>;
using const_iterator = _String_const_iterator<_Scary_val>;
using reverse_iterator = _STD reverse_iterator<iterator>;
using const_reverse_iterator = _STD reverse_iterator<const_iterator>;
private:
static constexpr auto _BUF_SIZE = _Scary_val::_BUF_SIZE;
static constexpr auto _ALLOC_MASK = _Scary_val::_ALLOC_MASK;
//。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。此处省略一万个字。
}
//以下列举几种基本的构造函数。
//无参数的string类构造函数。Allocator为用于内存分配的内存分配器。CharT 为字符类型。
basic_string();
explicit basic_string( const Allocator& alloc );
//用指定数目的单个字符初始化,cout字符数(size_type为无符号类型),ch为字符。
basic_string( size_type count,
CharT ch,
const Allocator& alloc = Allocator() );
//用指定字符串初始化。
basic_string( const CharT* s,
const Allocator& alloc = Allocator() );
构造函数测试
char str1[128] = {'h','e','l','l','o'};
str1[10] = 'b';
string test1(str1);
结果为6,15。证明用字符数组初始化string类,实际只使用了首个结束符前的部分,即字符串部分。
cout << "size : " << test1.size() << "capacitt : " << test1.capacity() << endl;
const char* str2 = "hello_world";
string test2(str2);
string test3 = test1 + test2;
string test4 = test1 + str1;
string test5 = test1 + "bye";
析构函数
C++ reference中无析构函数具体内容,默认为销毁字符串。
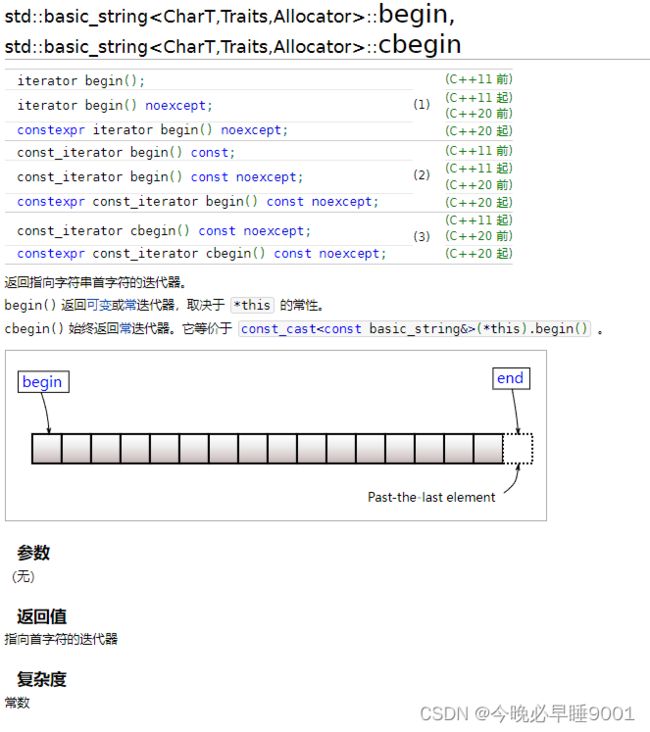
元素访问
迭代器
//一般就使用begin(),end()。
string test = "hello_world";
//可将迭代器想成一个对于c++类和容器的通用指针。操作形同指针。
for (string::iterator it = test.begin(); it != test.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//略略略
for (auto &it : test)
{
cout << it << " ";
}
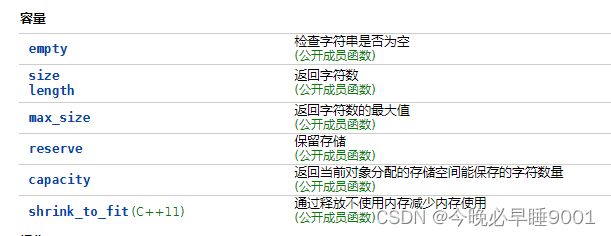
容量操作
int main(void)
{
string test;
int ret = 0;
//empty()为空返回true,不为空返回false
test.empty();
//size()返回CharT字符数
ret = test.size();
//返回可容纳最大的字符数
ret = test.max_size();
/*
void reserve(size_type new_cap = 0);
constexpr void reserve(size_type new_cap);
参数为string的新容量,reserve()会开辟一段内存空间,但并不会产生元素。体现在调用后只对capacity产生了影响。
*/
test.reserve(100);
ret = test.capacity();
ret = test.size();
//请求移除未使用的容量,使capacity()向size()收缩。收缩到以当前size()为基准,系统本应分配的capacity()尺寸。
std::string s;
std::cout << "Default-constructed capacity is " << s.capacity()
<< " and size is " << s.size() << '\n';
for (int i = 0; i < 42; i++)
s.append(" 42 ");
std::cout << "Capacity after a couple of appends is " << s.capacity()
<< " and size is " << s.size() << '\n';
s.clear();
std::cout << "Capacity after clear() is " << s.capacity()
<< " and size is " << s.size() << '\n';
s.shrink_to_fit();
std::cout << "Capacity after shrink_to_fit() is " << s.capacity()
<< " and size is " << s.size() << '\n';
/*
结果为
Default-constructed capacity is 15 and size 0
Capacity after a couple of appends is 240 and size 168
Capacity after clear() is 240 and size 0
Capacity after shrink_to_fit() is 15 and size 0
*/
return 0;
}
操作函数
//这里是解释几个个人常用函数
//操作函数出错一般会抛出std::length_error
//clear()如同通过执行 erase(begin(), end()) 从 string 移除所有字符。
//insert()用法众多,本质是在index索引位置插入字符串。
//1) 移除始于 index 的 min(count, size() - index) 个字符。
basic_string& erase( size_type index = 0, size_type count = npos );
//2) 移除位于 position 的字符。
iterator erase( iterator position );
//3) 移除范围 [first, last) 中的字符。
iterator erase( iterator first, iterator last );
int main()
{
std::string s = "This is an example";
std::cout << s << '\n';
s.erase(0, 5); // 擦除 "This "
std::cout << s << '\n';
s.erase(std::find(s.begin(), s.end(), ' ')); // 擦除 ' '
std::cout << s << '\n';
s.erase(s.find(' ')); // 从 ' ' 到字符串尾裁剪
std::cout << s << '\n';
}
//push_back()在字符串尾部添加,类比入栈。pop_back()从字符串尾部弹出,类比出栈。
//compare()本质和C中一样,比对两个字符串,相同返回0,不相同返回非0。
//substr()返回子串 [pos, pos+count] 。若请求的字串越过字符串的结尾,即 count 大于 size() - pos (例如若 count == npos ),则返回的子串为 [pos, size()] 。
//pos为首位置,count为需要返回的子串长度。
basic_string substr( size_type pos = 0, size_type count = npos ) const;
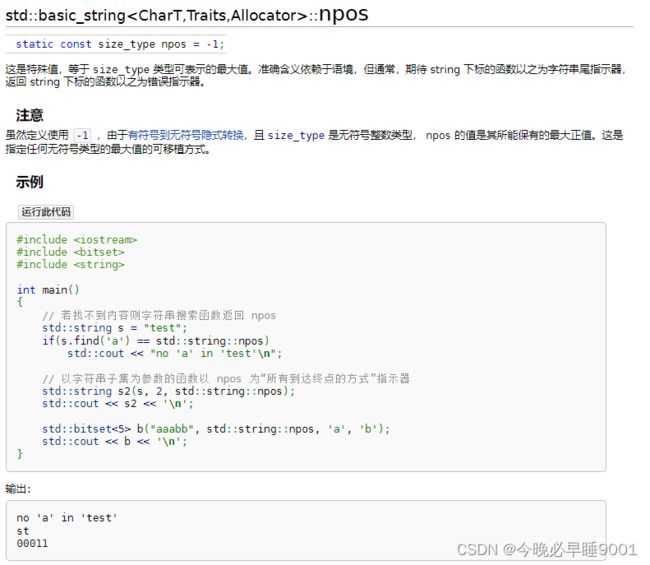
查找
//find() 返回值:找到的子串在主串中首字符位置,未找到返回 npos 。
//1) 寻找等于 str 的首个子串。
size_type find( const basic_string& str, size_type pos = 0 ) const;
//2) 寻找等于范围 [s, s+count) 的首个子串。此范围能含空字符。
size_type find( const CharT* s, size_type pos, size_type count ) const;
//3) 寻找等于 s 所指向的字符串的首个子串。由首个空字符,用 Traits::length(s) 确定字符串长度。
size_type find( const CharT* s, size_type pos = 0 ) const;
//4) 寻找首个字符 ch (由后述规则当作单字节子串)。
size_type find( CharT ch, size_type pos = 0 ) const;
void print(std::string::size_type n, std::string const &s)
{
if (n == std::string::npos) {
std::cout << "not found\n";
} else {
std::cout << "found: " << s.substr(n) << '\n';
}
}
int main()
{
std::string::size_type n;
std::string const s = "This is a string";
// 从 string 开始搜索
n = s.find("is");
print(n, s);
// 从位置 5 开始搜索
n = s.find("is", 5);
print(n, s);
// 寻找单个字符
n = s.find('a');
print(n, s);
// 寻找单个字符
n = s.find('q');
print(n, s);
/*
found: is is a string
found: is a string
found: a string
not found
*/
}
//find_first_of() 返回值:找到的子串在主串中首字符位置,未找到返回 npos 。
//寻找等于子串str中任意一个字符的字符,在主串中第一次出现的位置。常用于字符串去杂质。
size_type find_first_of( const basic_string& str, size_type pos = 0 ) const;
int main()
{
// 被搜索的字符串
const std::string str = "Hello World!";
// 要搜索的字符串和字符
const std::string search_str = "o";
const char* search_cstr = "Good Bye!";
std::cout << str.find_first_of(search_str) << std::endl;
std::cout << str.find_first_of(search_str, 5) << std::endl;
std::cout << str.find_first_of(search_cstr) << std::endl;
std::cout << str.find_first_of(search_cstr, 0, 4) << std::endl;
// 当 'x' 不在 str 中时它将返回 std::string::npos
std::cout << str.find_first_of('x') << '\n';
}
/*
4
7
1
4
18446744073709551615
*/
//find_first_not_of() 返回值:找到的子串在主串中首字符位置,未找到返回 npos 。
//寻找不等于子串str中任意一个字符的字符,在主串中第一次出现的位置。
size_type find_first_not_of( const basic_string& str, size_type pos = 0 ) const;
int main(void)
{
string test = "hello_world";
auto pos = test.find_first_not_of("he");
return 0;
}
//字符串替换案例
int main() {
std::string to_search = "Some data with %MACROS to substitute %asda endl";
std::cout << "Before: " << to_search << '\n';
auto pos = std::string::npos;
while ((pos = to_search.find('%')) != std::string::npos) {
// 宏名中容许大写字母、小写字母和数字
const auto after = to_search.find_first_not_of("ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"
"abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
"0123456789", pos + 1);
// 现在 to_search[pos] == '%' 而 to_search[after] == ' ' (在 'S' 后)
if (after != std::string::npos)
to_search.replace(pos, after - pos, "some very nice macros");
}
std::cout << "After: " << to_search << '\n';
}
后续待补充
内容参考自https://zh.cppreference.com/w/cpp/string/basic_string