Leetcode刷题笔记--Hot61-70
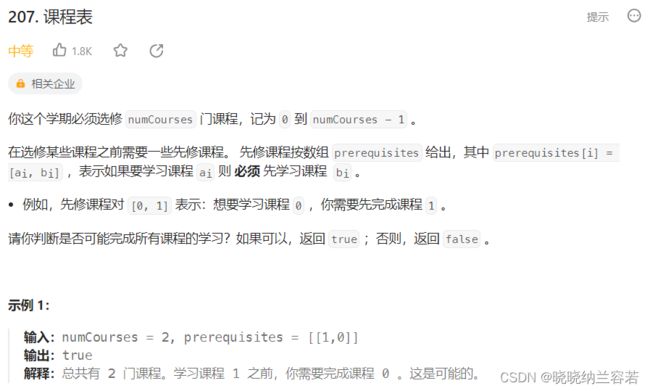
1--课程表(207)
主要思路:
用 in 记录每一门课程剩余的先修课程个数,当剩余先修课程个数为0时,将该课程加入到队列q中。
每修队列q中的课程,以该课程作为先修课程的所有课程,其剩余先修课程个数减1;
不断将剩余先修课程数为0的课程加入到队列q中,当队列为空时,若修的课程数等于总课程数,则返回true,否则返回false;
#include
#include
#include
class Solution {
public:
bool canFinish(int numCourses, std::vector>& prerequisites) {
std::vector> out; // 存储每一个先修课程对应的课程
std::vector in; // 存储每一个课程对应的剩余先修课程的个数
std::queue q; // 存储可以修的课程
out.resize(numCourses);
in.resize(numCourses);
// 初始化
for(auto pair : prerequisites){
int cur = pair[0]; // 当前课程
int pre = pair[1]; // 当前课程的先修课程
out[pre].push_back(cur); // 初始化out
in[cur]++;
}
// 选取可以直接修的课程加入到队列q中
for(int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++){
if(in[i] == 0) q.push(i);
}
int num = 0; // 已经修过的课程数
while(!q.empty()){
int tmp = q.front(); // 修弹出的课程
q.pop();
num++;
// 以tmp作为先修课程的课程,其剩余的先修课程数减1
for(auto course : out[tmp]){
in[course] --;
if(in[course] == 0) q.push(course); // course没有需要先修的课程了,因此可以加入到队列q中
}
}
if(num == numCourses) return true;
else return false;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
// numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0],[0,1]]
std::vector> test = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}};
int numCourses = 2;
Solution S1;
bool res = S1.canFinish(numCourses, test);
if(res) std::cout << "true" << std::endl;
else std::cout << "false" << std::endl;
return 0;
} 2--实现Trie(前缀树)(208)
主要思路:
参考之前的笔记:前缀树的实现
3--数组中的第K个最大的元素(215)
主要思路:
基于随机化的快排(即随机选取基准元素)划分数组,其时间复杂度为O(n);
根据第K个最大的元素在哪一个数组,继续递归随机化快排,直到找到第K个最大的元素。
#include
#include
#include
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(std::vector& nums, int k){
return quickSelect(nums, k);
}
int quickSelect(std::vector& nums, int k){
std::vector large;
std::vector equal;
std::vector less;
// 随机选取基准元素
int pivot = nums[rand() % nums.size()]; // 返回[0, nums.size()-1]范围内的一个随机数
for(int num : nums){
if(num > pivot) large.push_back(num);
else if(num == pivot) equal.push_back(num);
else less.push_back(num);
}
// large, equal, less
// 第k大的元素在large中
if(k <= large.size()) return quickSelect(large, k);
// 第k大的元素在less中
else if(k > (nums.size() - less.size())) return quickSelect(less, k-(nums.size() - less.size()));
else return pivot;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
// [3, 2, 1, 5, 6, 4], k = 2
std::vector test = {3, 2, 1, 5, 6, 4};
int k = 2;
Solution S1;
int res = S1.findKthLargest(test, k);
std::cout << res << std::endl;
return 0;
}
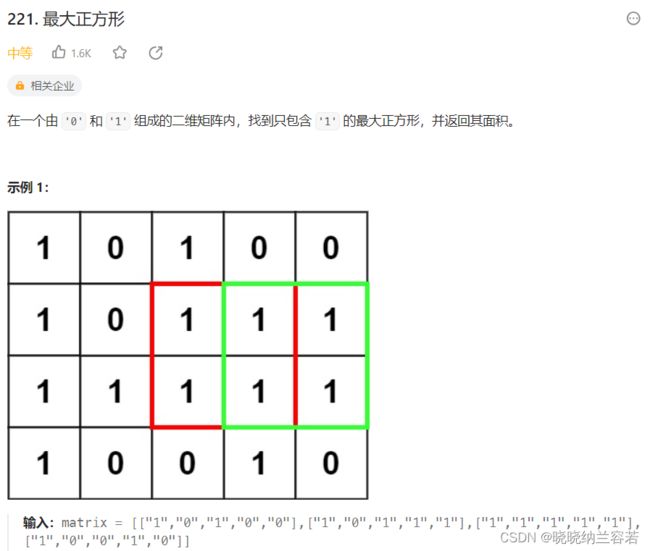
4--最大正方形(221)
主要思路:
基于动态规划,dp[i][j]表示以(i, j)为右下角,所构成正方形的最大边长。
状态转移方程: dp[i][j] = std::min(dp[i-1][j-1], std::min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1])) + 1;
具体推导参考: 统计全为 1 的正方形子矩阵
#include
#include
class Solution {
public:
int maximalSquare(std::vector>& matrix) {
// dp[i][j]表示以(i, j)作为右下角构成正方形的最大边长
std::vector> dp(matrix.size(), std::vector(matrix[0].size(), 0));
// 初始化
int max = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); i++){
if(matrix[i][0] == '1'){
dp[i][0] = 1;
max = 1;
}
}
for(int j = 0; j < matrix[0].size(); j++){
if(matrix[0][j] == '1'){
dp[0][j] = 1;
max = 1;
}
}
for(int i = 1; i < matrix.size(); i++){
for(int j = 1; j < matrix[0].size(); j++){
if(matrix[i][j] == '1'){
dp[i][j] = std::min(dp[i-1][j-1], std::min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1])) + 1;
}
max = std::max(max, dp[i][j]);
}
}
return max * max; // 返回面积
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
// matrix = [["1","0","1","0","0"],["1","0","1","1","1"],["1","1","1","1","1"],["1","0","0","1","0"]]
std::vector> test = {{'1', '0', '1', '0', '0'}, {'1', '0', '1', '1', '1'},
{'1', '1', '1', '1', '1'}, {'1', '0', '0', '1', '0'}};
Solution S1;
int res = S1.maximalSquare(test);
std::cout << res << std::endl;
return 0;
}
5--翻转二叉树(226)
主要思路:
递归交换左右子树即可。
#include
#include
#include
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
return dfs(root);
}
TreeNode* dfs(TreeNode* root){
if(root == nullptr) return nullptr;
TreeNode* left = dfs(root->right);
TreeNode* right = dfs(root->left);
root->left = left;
root->right = right;
return root;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
// root = [4, 2, 7, 1, 3, 6, 9]
TreeNode *Node1 = new TreeNode(4);
TreeNode *Node2 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode *Node3 = new TreeNode(7);
TreeNode *Node4 = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode *Node5 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode *Node6 = new TreeNode(6);
TreeNode *Node7 = new TreeNode(9);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node3;
Node2->left = Node4;
Node2->right = Node5;
Node3->left= Node6;
Node3->right = Node7;
Solution S1;
TreeNode *res = S1.invertTree(Node1);
// 层次遍历打印
std::queue q;
q.push(res);
while(!q.empty()){
TreeNode* top = q.front();
q.pop();
std::cout << top->val << " ";
if(top->left != nullptr) q.push(top->left);
if(top->right != nullptr) q.push(top->right);
}
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}
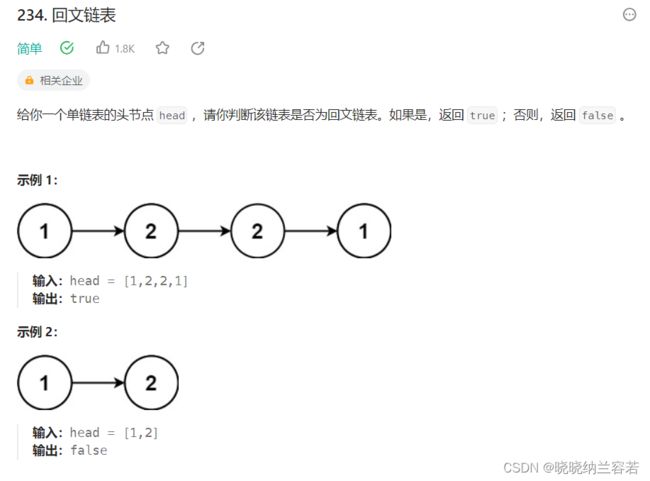
6--回文链表(234)
主要思路:
基于快慢指针,将链表划分为两部分,判断两部分是否相同即可。
其中第一部分为链表的前半部分,在快慢指针遍历的时候需要重构链表,将指针前指。
#include
#include
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
// 1 2 2 1
// 1 2 1 2 1
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head->next;
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
ListNode* next = nullptr;
while(fast != nullptr){
// 前指
next = slow->next;
slow->next = pre;
pre = slow;
slow = next;
fast = fast->next;
if(fast == nullptr){
break;
}
fast = fast->next;
if(fast == nullptr){
slow = slow->next;
}
}
while(slow != nullptr && pre != nullptr){
if(slow->val != pre->val) return false;
slow = slow->next;
pre = pre->next;
}
return true;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
// head = [1, 2, 1, 2, 1]
ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode *Node5 = new ListNode(1);
Node1->next = Node2;
Node2->next = Node3;
Node3->next = Node4;
Node4->next = Node5;
Solution S1;
bool res = S1.isPalindrome(Node1);
if(res) std::cout << "true" << std::endl;
else std::cout << "false" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
7--二叉树的最近公共祖先(236)
主要思路: