数据结构 2 第二章 线性结构 代码实现
头文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include //malloc函数头文件
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
# include 一、单链表
1.单链表
线性表:1.有限的序列 2.序列中的每一个元素都有唯一的前驱和后继,除了开头和结尾的两个节点。
顺序表:分配一块连续的内存去存放这些元素,eg、数组
链表:内存是不连续的,元素会各自被分配一块内存,内存和内存之间用指针进行相连。
顺序表和链表的区别是内存的连续与否
data域 | next指针域 ——> data域 | next指针域 ——> data域 | next指针域 ——> NULL
2.单链表的操作
1.增加 :1>头插法 2>尾插法
1>插入——> data域 | next指针域 ——> data域 | next指针域 ——> data域 | next指针域 ——> NULL
2>data域 | next指针域 ——> data域 | next指针域 ——> data域 | next指针域 ——> 插入——>NULL
2.删除:用前一个节点的指针直接指向对应节点的后一个节点的前驱,只操作一个指针。
为了使操作方便,在操作中添加一个头节点。头节点并不实际存储,只保存链表中的元素个数。
代码实现
1.定义一个结构体
typedef struct Node {//定义一个结构体
int data;
struct Node* next;
}Node;2.初始化一个链表
Node* initList() {//初始化一个链表
Node* list = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
list->data = 0;
list->next = NULL;
return list;
}3.头插法
void headInsert(Node* list,int data){//头插法
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
node->next = list->next;
list->next = node;
list->data++;//代表当前链表之中插入元素
}4.尾插法
void tailInsert(Node* list, int data){//尾插法
Node* head = list;
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
node->next = NULL;
list = list->next;
while (list->next) {
list = list->next;
}
list->next = node;
head->data++;
}5.删除操作
void Delete(Node* list, int data){//删除
Node* head = list;
Node* pre = list;
Node* current = list->next;
list = list->next;
while (current)
{
if (current->data == data)
{
pre->next = current->next;
free(current);
break;
}
pre = current;
current = current->next;
}
list->data--;
}6.遍历打印操作
void printList(Node* list) {//遍历操作
list = list->next;
while (list)
{
printf("%d ", list->data);
list = list->next;
}
printf("\n");
}7.代码实现
typedef struct Node {//定义一个结构体
int data;
struct Node* next;
}Node;
Node* initList() {//初始化一个链表
Node* list = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
list->data = 0;
list->next = NULL;
return list;
}
void headInsert(Node* list,int data){//头插法
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
node->next = list->next;
list->next = node;
list->data++;//代表当前链表之中插入元素
}
void tailInsert(Node* list, int data){//尾插法
Node* head = list;
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
node->next = NULL;
list = list->next;
while (list->next) {
list = list->next;
}
list->next = node;
head->data++;
}
void Delete(Node* list, int data){//删除
Node* head = list;
Node* pre = list;
Node* current = list->next;
list = list->next;
while (current)
{
if (current->data == data)
{
pre->next = current->next;
free(current);
break;
}
pre = current;
current = current->next;
}
list->data--;
}
void printList(Node* list) {//遍历操作
list = list->next;
while (list)
{
printf("%d ", list->data);
list = list->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
Node* list = initList();
headInsert(list, 1);
headInsert(list, 2);
headInsert(list, 3);
headInsert(list, 4);
headInsert(list, 5);
tailInsert(list, 6);
tailInsert(list, 7);
tailInsert(list, 8);
tailInsert(list, 9);
tailInsert(list, 10);
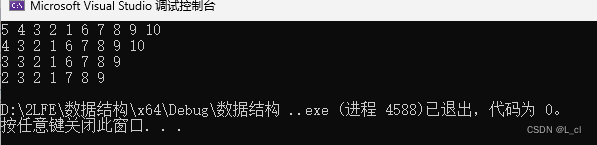
printList(list);
Delete(list, 5);
printList(list);
Delete(list, 10);
printList(list);
Delete(list, 6);
printList(list);
return 0;
}
8.结果
二、单循环链表
1..单循环链表
data|next——>data|next——>data|next——>头节点
1.初始化链表
2.增加节点(头插法、尾插法)
3.删除节点
4.遍历链表
代码实现
1.定义一个结构体
typedef struct Node {//定义一个结构体,存放data域和指针域
int data;//数据域类型
struct Node* next;
}Node;2. 初始化链表
Node* initList() {//初始化链表
Node* L = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
L->data = 0;
L->next = L;
return L;
}3.头插法
void headInsert(Node* L, int data) {//头插法
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
node->next = L->next;
L->next = node;
}4尾插法
void tailInsert(Node* L, int data) {//尾插法
Node* n = L;
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
while (n->next != L) {
n = n->next;
}
node->next = L;
n->next = node;
}5.删除操作
int Delete(Node* L, int data)//删除
{
Node* preNode = L;
Node* node = L->next;
while (node != L)
{
if (node->data == data) {
preNode->next = node->next;
free(node);
return TRUE;
}
preNode = node;
node = node->next;
}
return FALSE;
}6.遍历链表打印
void printList(Node* L) {//遍历链表
Node* node = L->next;
while (node != L) {
printf("%d->", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}7.代码实现
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
typedef struct Node {//定义一个结构体,存放data域和指针域
int data;//数据域类型
struct Node* next;
}Node;
Node* initList() {//初始化链表
Node* L = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
L->data = 0;
L->next = L;
return L;
}
void headInsert(Node* L, int data) {//头插法
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
node->next = L->next;
L->next = node;
}
void tailInsert(Node* L, int data) {//尾插法
Node* n = L;
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
while (n->next != L) {
n = n->next;
}
node->next = L;
n->next = node;
}
int Delete(Node* L, int data)//删除
{
Node* preNode = L;
Node* node = L->next;
while (node != L)
{
if (node->data == data) {
preNode->next = node->next;
free(node);
return TRUE;
}
preNode = node;
node = node->next;
}
return FALSE;
}
void printList(Node* L) {//遍历链表
Node* node = L->next;
while (node != L) {
printf("%d->", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
int main()
{
Node* L = initList();
headInsert(L, 1);
headInsert(L, 2);
headInsert(L, 3);
headInsert(L, 4);
headInsert(L, 5);
tailInsert(L, 6);
tailInsert(L, 7);
tailInsert(L, 8);
tailInsert(L, 9);
tailInsert(L, 10);
printList(L);
Delete(L, 4);
Delete(L, 5);
printList(L);
return 0;
}8.结果
三、双链表
1.双链表
pre指针|data域|next指针<——>pre|data|next<——>pre|data|next
与单链表相比多一个指针域
2.双链表的操作:
1.初始化链表
2.插入节点(头插法、尾插法)
3.删除结点
4.遍历链表
代码实现
1.数据结构的定义
typedef struct Node {//数据结构的定义
int data;//data域
struct Node* pre;//pre指针
struct Node* next;//next指针
}Node;2. 初始化链表
Node* initList() {//初始化链表
Node* L = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));//新建指针变量并开辟空间 返回一个Node*类型指针
L->data = 0;//头节点data域初始化为0
L->pre = NULL;//头指针为NULL
L->next = NULL;//next指针为NULL
return3. 头插法
void headInsert(Node* L, int data) {//头插法
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));//新建一个结点并为他开辟空间
node->data = data;
if (L->data == 0)
{
node->next = L->next;
node->pre = L;
L->next = node;
}
else {
node->pre = L;//node指向的pre指向头节点
node->next = L->next;
L->next->pre = node;
L->next = node;
L->data++;
}
}
4.尾插法
void tailInsert(Node* L,int data) //尾插法
{
Node* node = L;
Node* n = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
n->data = data;
while (node->next) {
node = node->next;
}
n->next = node->next;
node->next = n;
n->pre = node;
L->data++;
}5.删除操作
int Delete(Node* L, int data) //删除
{
Node* node = L->next;
while (node)
{
if (node->data == data)
{
node->pre->next = node->next;
node->next->pre = node->pre;
free(node);
return TRUE;
}
node = node->next;
}
return FALSE;
}6.遍历链表打印
void printList(Node* L)//遍历
{
Node* node = L->next;
while (node) {
printf("%d -> ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}7.代码实现
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
typedef struct Node {//数据结构的定义
int data;//data域
struct Node* pre;//pre指针
struct Node* next;//next指针
}Node;
Node* initList() {//初始化链表
Node* L = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));//新建指针变量并开辟空间 返回一个Node*类型指针
L->data = 0;//头节点data域初始化为0
L->pre = NULL;//头指针为NULL
L->next = NULL;//next指针为NULL
return L;//返回L
}
void headInsert(Node* L, int data) {//头插法
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));//新建一个结点并为他开辟空间
node->data = data;
if (L->data == 0)
{
node->next = L->next;
node->pre = L;
L->next = node;
}
else {
node->pre = L;//node指向的pre指向头节点
node->next = L->next;
L->next->pre = node;
L->next = node;
L->data++;
}
}
void tailInsert(Node* L,int data) //尾插法
{
Node* node = L;
Node* n = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
n->data = data;
while (node->next) {
node = node->next;
}
n->next = node->next;
node->next = n;
n->pre = node;
L->data++;
}
int Delete(Node* L, int data) //删除
{
Node* node = L->next;
while (node)
{
if (node->data == data)
{
node->pre->next = node->next;
node->next->pre = node->pre;
free(node);
return TRUE;
}
node = node->next;
}
return FALSE;
}
void printList(Node* L)//遍历
{
Node* node = L->next;
while (node) {
printf("%d -> ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
int main()
{
Node* L = initList();
headInsert(L, 1);
headInsert(L, 2);
headInsert(L, 3);
headInsert(L, 4);
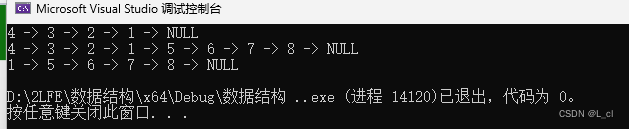
printList(L);
//4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> NULL
tailInsert(L, 5);
tailInsert(L, 6);
tailInsert(L, 7);
tailInsert(L, 8);
printList(L);
//4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> NULL
Delete(L, 2);
Delete(L, 4);
printList(L);
//1 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8->NULL
}8.结果
四、双循环链表
1.双循环链表
pre前指针|data域|next后指针<——>pre|data|next<——>pre|data|next
最后一个节点的next指针和头节点的pre指针相互指向对方,其他节点与双链表相同。
功能:
1.初始化链表
2.插入节点(头插法、尾插法)
3.删除结点
4.遍历链表
代码实现
1.定义一个结构体链表数据节点
typedef struct Node//定义一个结构体类型
{
int data;
struct Node* pre;
struct Node* next;
}Node;2.初始化链表
Node* initList()//初始化链表
{
Node* L = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
L->data = 0;
L->next = L;
L->pre = L;
return L;
}3.头插法
void headInsert(Node* L,int data)//头插法
{
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
if (L->data == 0)
{//链表为空
node->pre = L;
node->next = L->next;
L->next = node;
L->pre = node;
L->data++;
}
else {
//链表不为空
node->next = L->next;
node->pre = L;
L->next->pre = node;
L->next = node;
L->data++;
}
}
4.尾插法
void tailInsert(Node* L,int data)//尾插法
{
Node* node = L;
while (node->next != L)
{
node = node->next;
}
Node* n = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
n->data = data;
n->pre = node;
n->next = L;
L->pre = n;
node->next = n;
L->data++;
}5.删除操作
int Delete(Node* L, int data)//删除
{
Node* node = L->next;
while (node != L)
{
if (node->data == data)
{
node->pre->next = node->next;
node->next->pre = node->pre;
free(node);
L->data--;
return 1;
}
node = node->next;
}
return 0;
}6.遍历链表打印
void printList(Node* L)//遍历
{
Node* node = L->next;
while (node != L) {
printf("%d -> ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}7.代码实现
typedef struct Node//定义一个结构体类型
{
int data;
struct Node* pre;
struct Node* next;
}Node;
Node* initList()//初始化链表
{
Node* L = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
L->data = 0;
L->next = L;
L->pre = L;
return L;
}
void headInsert(Node* L,int data)//头插法
{
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
if (L->data == 0)
{//链表为空
node->pre = L;
node->next = L->next;
L->next = node;
L->pre = node;
L->data++;
}
else {
//链表不为空
node->next = L->next;
node->pre = L;
L->next->pre = node;
L->next = node;
L->data++;
}
}
void tailInsert(Node* L,int data)//尾插法
{
Node* node = L;
while (node->next != L)
{
node = node->next;
}
Node* n = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
n->data = data;
n->pre = node;
n->next = L;
L->pre = n;
node->next = n;
L->data++;
}
int Delete(Node* L, int data)//删除
{
Node* node = L->next;
while (node != L)
{
if (node->data == data)
{
node->pre->next = node->next;
node->next->pre = node->pre;
free(node);
L->data--;
return 1;
}
node = node->next;
}
return 0;
}
void printList(Node* L)//遍历
{
Node* node = L->next;
while (node != L) {
printf("%d -> ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
int main()
{
Node* L = initList();
headInsert(L, 1);
headInsert(L, 2);
headInsert(L, 3);
headInsert(L, 4);
printList(L);
//4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> NULL
tailInsert(L, 5);
tailInsert(L, 6);
tailInsert(L, 7);
tailInsert(L, 8);
printList(L);
//4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> NULL
Delete(L, 2);
Delete(L, 4);
printList(L);
//3 -> 1 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> NULL
}
8.运行结果
五、栈
1.栈
存放:1->2->3 取出:3->2->1 先进后出
应用场景:1.表达式的值 2.解决一些递归问题 3.计算进制转换
栈是一种特殊的线性表,它只能在一端进行存取操作,所以存取的元素有先进后出的特点。
栈的总体特点:先进后出
2.实现的功能:
初始化栈
出栈
入栈
判断栈空
代码实现
1.结构体定义数据结点
typedef struct Node //结构体创建节点
{
int data;//data域
struct Node* next;//next指针
}Node;2.初始化栈
Node* initStack()//初始化栈
{
Node* S = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));//新建一个节点
S->data = 0;
S->next = NULL;
return S;//返回S
}3.出栈
int isEmpty(Node* S)//出栈功能前的判断栈空功能
{
if (S->data == 0 || S->next == NULL)//栈空
{
return 1;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
int getTop(Node* S)//出栈 传入头指针
{
if (isEmpty(S))
{
return -1;
}
else
{
return S->next->data;//不为空的话 S指向第一个节点的data域
}
}4.
六、队
1.队
一种先进先出的特殊线性表,只允许在一端进行存取,在头出,在尾进
2.实现的功能:
1.初始化队
2.出队
3.入队 (尾插法)
代码实现
1.结构体定义数据节点
typedef struct Node //定义数据节点结构体
{
int data;//数据域data
struct Node* next;//next指针
}Node;2.初始化队列
Node* initQueue() //初始化队列
{
Node* Q = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));//新建指针变量
Q->data = 0;
Q->next = NULL;
return Q;
}3. 入队操作 尾插法
void enQueue(Node* Q, int data)//入队操作 尾插法
{
Node* q = Q;//传入头指针
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
for (int i = 0; i < Q->data; i++)//循环遍历队列找到最后一个节点
{
q = q->next;
}
node->next = q->next;
q->next = node;
Q->data++;//!!!!
}4.出队操作,删除队列中第一个结点
int isEmpty(Node* Q)//判空
{
if (Q->data == 0 || Q->next == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
int deQueue(Node* Q) //出队操作 删除队列中的第一个节点
{
if (isEmpty(Q))//判空操作
{
return -1;
}
else
{
Node* node = Q->next;
int data = node->data;
Q->next = node->next;
free(node);
return data;
}
}5.遍历队列打印
void printQueue(Node* Q)//遍历队列打印
{
Node* node = Q->next;//传入第一个节点
while (node)
{
printf("%d -> ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}6.代码实现
typedef struct Node //定义数据节点结构体
{
int data;//数据域data
struct Node* next;//next指针
}Node;
Node* initQueue() //初始化队列
{
Node* Q = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));//新建指针变量
Q->data = 0;
Q->next = NULL;
return Q;
}
void enQueue(Node* Q, int data)//入队操作 尾插法
{
Node* q = Q;//传入头指针
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
for (int i = 0; i < Q->data; i++)//循环遍历队列找到最后一个节点
{
q = q->next;
}
node->next = q->next;
q->next = node;
Q->data++;//!!!!
}
int isEmpty(Node* Q)//判空
{
if (Q->data == 0 || Q->next == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
int deQueue(Node* Q) //出队操作 删除队列中的第一个节点
{
if (isEmpty(Q))//判空操作
{
return -1;
}
else
{
Node* node = Q->next;
int data = node->data;
Q->next = node->next;
free(node);
return data;
}
}
void printQueue(Node* Q)//遍历队列打印
{
Node* node = Q->next;//传入第一个节点
while (node)
{
printf("%d -> ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
int main()
{
Node* Q = initQueue();
enQueue(Q, 1);
enQueue(Q, 2);
enQueue(Q, 3);
enQueue(Q, 4);
printQueue(Q);//1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> NULL
int data = deQueue(Q);
printf("data=%d\n", data);//data=1
printQueue(Q);//2 -> 3 -> 4 -> NULL
data = deQueue(Q);
printQueue(Q);//3 -> 4 -> NULL
data = deQueue(Q);
printQueue(Q);//4 -> NULL
data = deQueue(Q);
printf("data=%d\n", data);//data=4
printQueue(Q);//NULL
return 0;
}7.运行结果
七、循环队列
队列组成一周 需要两个指针指向队列的队首与队尾 当插入一个元素后,队尾指针后移一项,
如何判断队列是空/满:
1.在实际操作中,牺牲掉队列一个空间来判断队列是满/空
2.判断逻辑如下:
1>队空的话,头指针等于尾指针:front==rear
2>队满的话:rear+1%MAXSIZE==front;
实现的功能:
1.初始化队列
2.入队
3.出队
4.遍历循环队列
代码实现
1.定义队列结构体
#define MAXSIZE 5
typedef struct Queue//定义队列结构体
{
int front;//front指针
int rear;//rear指针
int data[MAXSIZE];//data域
}Queue;2.初始化队列
Queue* initQueue()//初始化队列
{
Queue* Q = (Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
Q->front = Q->rear = 0;
return Q;
}3.判满/空操作
int isFull(Queue* Q)//判满操作
{
if ((Q->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE == Q->front)
{
return 1;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
int isEmpty(Queue* Q)//判空操作
{
if (Q->front == Q->rear)
{
return 1;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}4.入队操作
int enQueue(Queue* Q, int data)//插入函数 入队操作
{
if (isFull(Q))
{
return 0;
}
else {
Q->data[Q->rear] = data;
Q->rear = (Q->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE;
return 1;
}
}5。出队操作
int deQueue(Queue* Q)//出队操作
{
if (isEmpty(Q))
{
return -1;
}
else {
int data = Q->data[Q->front];
Q->front = (Q->front + 1) % MAXSIZE;
return data;
}
}6,遍历队列打印
void printQueue(Queue* Q)//遍历队列打印
{
//要知道队列当前有多少个元素
int length = (Q->rear - Q->front + MAXSIZE) % MAXSIZE;
int index = Q->front;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
printf("%d -> ", Q->data[index]);
index = (index + 1) % MAXSIZE;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}7.代码实现
#define MAXSIZE 5
typedef struct Queue//定义队列结构体
{
int front;//front指针
int rear;//rear指针
int data[MAXSIZE];//data域
}Queue;
Queue* initQueue()//初始化队列
{
Queue* Q = (Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
Q->front = Q->rear = 0;
return Q;
}
int isFull(Queue* Q)//判满操作
{
if ((Q->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE == Q->front)
{
return 1;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
int isEmpty(Queue* Q)//判空操作
{
if (Q->front == Q->rear)
{
return 1;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
int enQueue(Queue* Q, int data)//插入函数 入队操作
{
if (isFull(Q))
{
return 0;
}
else {
Q->data[Q->rear] = data;
Q->rear = (Q->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE;
return 1;
}
}
int deQueue(Queue* Q)//出队操作
{
if (isEmpty(Q))
{
return -1;
}
else {
int data = Q->data[Q->front];
Q->front = (Q->front + 1) % MAXSIZE;
return data;
}
}
void printQueue(Queue* Q)//遍历队列打印
{
//要知道队列当前有多少个元素
int length = (Q->rear - Q->front + MAXSIZE) % MAXSIZE;
int index = Q->front;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
printf("%d -> ", Q->data[index]);
index = (index + 1) % MAXSIZE;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
int main()
{
Queue* Q = initQueue();
enQueue(Q, 1);
enQueue(Q, 2);
enQueue(Q, 3);
enQueue(Q, 4);
printQueue(Q);//1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> NULL
deQueue(Q);
printQueue(Q);//2 -> 3 -> 4 -> NULL
return 0;
}