three.js学习-智慧城市
前言
在前面基础知识(摄像机,渲染器,轨道控制器,坐标轴,场景适配,渲染循环、几何体、材质、光等)有了基础了解后,还需要对着色器(坐标)有一定的学习了解
然后就可以做智慧城市的项目了
技术:vite+js
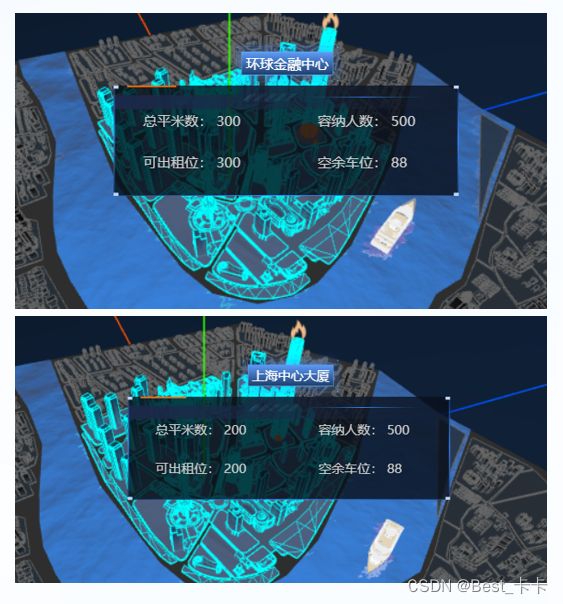
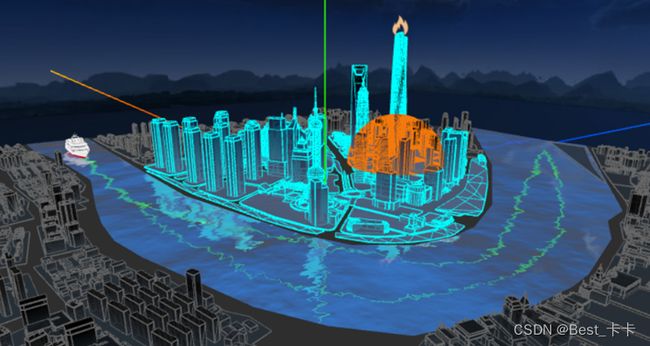
以下是项目预览
1697009690667050
1. 需求
实现智慧城市,对城市数据实时监控,对建筑动效标注和预览
1、城市模型处理(材质颜色、边线效果、着色器白膜效果、水波纹倒影效果、建筑物点击信息查看、产业分布查看)
2、游船(游船移动路线、轮船漫游)
3、火灾和火灾影响范围
4、天空(背景、鸟瞰路线)
5、城市加载优化
模型:
3D 部分:天空背景,城市模型,游船模型,火灾报警,鸟瞰模式,漫游模式
2D 部分:图表统计,城市概况,城市收入,产业分布(与 3D 交互)
项目准备
entry/index.js初始化three.js渲染
import * as THREE from 'three'
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls'
import { CSS2DRenderer } from 'three/examples/jsm/renderers/CSS2DRenderer'
let scene, camera, renderer, control, css2Renderer
// 初始化 3d 基本环境
function init() {
scene = new THREE.Scene()
camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 10000);
camera.position.set(-148, 55, -101)
// 创建渲染器
renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ antialias: true })
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
// 创建2D渲染器
css2Renderer = new CSS2DRenderer()
css2Renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
css2Renderer.domElement.style.position = 'absolute'
css2Renderer.domElement.style.top = '0px'
css2Renderer.domElement.style.pointerEvents = 'none'
// DOM 添加到页面
const canvas = document.getElementById('canvas')
canvas.appendChild(renderer.domElement)
canvas.appendChild(css2Renderer.domElement)
// 轨道控制器
control = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement)
control.update()
// 坐标轴
const axesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper(1500)
scene.add(axesHelper)
}
// 渲染循环
function renderLoop() {
// 这里不再调用轨道控制器 update 方法,会影响摄像机 lookAt
renderer.render(scene, camera)
css2Renderer.render(scene, camera)
requestAnimationFrame(renderLoop)
}
// 灯光
function createLight() {
// 基础光-环境光
const ambientLight = new THREE.AmbientLight('#fff', 3)
scene.add(ambientLight)
}
// 适配
window.addEventListener('resize', function () {
camera.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight;
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
css2Renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
})
// 启动
window.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', function () {
init()
createLight()
renderLoop()
})
utils/eventbus.js 封装eventBus做组件交互
// 发布订阅模式(注入名字和函数)进行调度
export class EventBus {
constructor() {
this.eventMap = {}
}
static getInstance() {
if (!this.instance) {
this.instance = new EventBus()
}
return this.instance
}
on(eventName, fn) {
if (!this.eventMap[eventName]) {
this.eventMap[eventName] = []
}
this.eventMap[eventName].push(fn)
}
emit(eventName, ...args) {
if (!this.eventMap[eventName]) return
this.eventMap[eventName].forEach((fn) => {
fn(...args)
})
}
}
index.html页面静态
Doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, minimum-scale=1, maximum-scale=1, user-scalable=no" />
<title>智慧城市title>
<link href="/style.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div class="index-wrapper">
<div class="header">
<img class="logo" src="/image/park-logo.png" alt="" />
div>
<div class="page-container" ref="container">
<div class="model-container">
<div id="loading" class="loading">
<p id="processing" class="text">园区资源加载中<span id="processing-number">span>…p>
<div id="loading-bar" class="loading-bar">div>
div>
<div id="canvas" class="canvas">div>
<div id="all-charts" class="all-charts" >
<div class="section-one">
<img class="img-header" src="/image/city-gaikuang.png" alt="" />
<div class="icons-container" >
<div class="item">
<div class="icons-item building-icon">
<span id="building-number" class="number">
28
span>
div>
<span class="title">电量峰值span>
<span class="unity">(度)span>
div>
<div class="item">
<div class="icons-item enterprise-icon">
<span id="enterprise-number" class="number">
6
span>
div>
<span class="title"> 实时温度span>
<span class="unity">(度)span>
div>
<div class="item">
<div class="icons-item car-icon">
<span id="car-number" class="number">
1530
span>
div>
<span class="title">出租车运力span>
<span class="unity">(个)span>
div>
<div class="item">
<div class="icons-item rod-icon">
<span id="rod-number" class="number">
48
span>
div>
<span class="title">拥堵程度span>
<span class="unity">(个)span>
div>
div>
div>
<div class="section-two">
<img class="img-header" src="/image/city-shouru.png" alt="" />
<div id="bar-chart" class="bar-chart" >div>
div>
<div class="section-three">
<img class="img-header" src="/image/city-chanye.png" alt="" />
<div id="pie-chart" class="pie-chart" >div>
div>
div>
<div id="right-btns" class="right-btns" style="pointer-events: all;">
<div>
<img id="mode-topView" class="mode-topView" src="/image/city-niaokan.png"
style="pointer-events: all;" alt="">
div>
<div>
<img id="mode-roaming" class="mode-roaming" src="/image/city-manyou.png"
style="pointer-events: all;" alt="">
div>
div>
div>
div>
<div id="tag-1" class="building-name" style="display: none;">东方明珠div>
<div id="tag-2" class="building-info" style="display: none;">
<div>总平米数: 2000div>
<div>容纳人数: 10000div>
<div>可出租位: 50div>
<div>空余车位: 10div>
div>
<div id="tag-3" class="building-fire" style="display: none;">
<div>着火大楼: 东方明珠div>
<div>着火楼层: 18层div>
<div>疏散人数: 1800人div>
div>
div>
<script type="module" src="/main.js">script>
body>
html>
// 样式
import './styles/all.less'
// Three.js 3D 入口
import '@/entry'
all.less
#app {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
html {
height: 100%;
}
body {
margin: 0;
display: flex;
place-items: center;
min-width: 320px;
height: 100%;
}
p {
margin-bottom: 0;
}
.index-wrapper {
position: relative;
height: 100%;
background-color: black;
.header {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
height: 50px;
width: 100%;
margin-bottom: 30px;
z-index: 10;
.logo {
width: 460px;
}
.btn-list {
img {
width: 96px;
margin-right: 24px;
cursor: pointer;
}
}
}
.page-container {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
overflow-x: hidden;
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
scroll-behavior: smooth;
}
}
.model-container {
position: relative;
height: 100%;
background-color: black;
width: 100%;
flex-shrink: 0;
}
.loading {
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 40%;
transform: translateX(-50%);
text-align: center;
.text {
font-size: 14px;
color: #909399;
margin-bottom: 16px;
}
.loading-process {
width: 280px;
height: 4px;
background: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.16);
border-radius: 20px;
overflow: hidden;
}
.loading-bar {
transform: scaleX(0.3);
transform-origin: top left;
width: 280px;
height: 4px;
background: linear-gradient(90deg, #48ffff 0%, #3656ff 100%);
border-radius: 20px;
overflow: hidden;
}
}
.all-charts {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
width: 480px;
padding: 88px 20px 0;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
background: linear-gradient(to left, rgba(0, 6, 15, 0.00) 0%, rgba(0, 6, 15, 0.00) 20%, rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.40) 30%, rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.60) 40%, rgba(1, 4, 11, 1) 70%, #04070d 100%);
img {
width: 100%;
}
}
.right-btns {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
padding: 88px 20px 0;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
background: linear-gradient(to right, rgba(0, 6, 15, 0.00) 0%, rgba(0, 6, 15, 0.00) 20%, rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.40) 70%, rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.60) 80%);
div {
margin-bottom: 48px;
margin-right: 24px;
}
img {
width: 96px;
cursor: pointer;
}
}
.section-one {
flex-basis: 25%;
.icons-container {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
.item {
text-align: center;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
flex: 1;
padding: 10px 0;
.icons-item {
position: relative;
height: 80px;
.number {
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
transform: translateX(-50%);
font-size: 18px;
font-family: FontquanXinYiGuanHeiTi, FontquanXinYiGuanHeiTi-Regular;
color: #ffffff;
}
}
.building-icon {
background: url('./assets/building-icon.png') no-repeat 50% 0 / contain;
}
.enterprise-icon {
background: url('./assets/enterprise-icon.png') no-repeat 50% 0 / contain;
}
.rod-icon {
background: url('./assets/rod-icon.png') no-repeat 50% 0 / contain;
}
.car-icon {
background: url('./assets/car-icon.png') no-repeat 50% 0 / contain;
}
.title,
.unity {
font-size: 14px;
color: #cdd7e1;
}
.title {
margin-top: 8px;
}
}
}
}
.section-two {
flex-basis: 35%;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
.bar-chart {
width: 100%;
// height: 100%;
flex: 1;
}
}
.section-three {
flex-basis: 40%;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
.pie-chart {
position: relative;
margin: 0 auto;
padding-bottom: 20px;
width: 80%;
// height: 100%;
flex: 1;
}
}
.bar-chart-titile {
display: flex;
margin-top: 20px;
justify-content: space-between;
font-size: 14px;
color: #c6d1db;
.bar-icon {
display: inline-block;
width: 12px;
vertical-align: middle;
}
.blue-bar-icon {
background: linear-gradient(to right, #74c0f8, rgba(116, 192, 248, 0));
}
.red-bar-icon {
background: linear-gradient(to right, #ff7152, rgba(255, 113, 82, 0));
}
}
.building-name {
text-align: center;
color: #fff;
font-size: 10px;
background-size: 100% 100%;
background-image: url('./icon/text_select.png');
background-repeat: no-repeat;
padding: 16px;
}
.building-info {
display: flex;
width: 300px;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: flex-end;
flex-wrap: wrap;
text-align: center;
color: #ccc;
font-size: 10px;
padding: 12px;
background-size: 100% 100%;
// text.png
background-image: url('./icon/modal-bg.png');
background-repeat: no-repeat;
margin-top: 60px;
}
.building-info div {
width: 40%;
position: relative;
margin: 10px 0;
}
// 左边
.building-info div:nth-child(odd) {
text-align: right;
padding-right: 12px;
}
.building-info div:nth-child(odd)::after {
position: absolute;
content: '';
width: 10px;
background-color: lightblue;
border-radius: 10px;
top: 33%;
right: 0;
}
// 右边
.building-info div:nth-child(even) {
text-align: left;
// padding-left: 12px;
}
.building-info div:nth-child(even)::before {
position: absolute;
content: '';
width: 10px;
background-color: #00FFFF;
border-radius: 10px;
top: 33%;
left: 0;
}
.building-fire {
color: #ccc;
font-size: 10px;
padding: 12px 28px;
background-size: 100% 100%;
background-image: url('./icon/modal-bg.png');
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}
.building-fire div {
position: relative;
}
.building-fire div::before {
position: absolute;
content: '';
width: 10px;
background-color: red;
border-radius: 10px;
top: 33%;
left: -20px;
}
style.css
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
position: relative;
}
2.模型加载
分析
要加载的模型有city.fbx和ship.gfb,需要两个load加载器
准备专门加载各种模型文件的通用函数,并加载城市和游船模型对象
传入模型文件路径,以及封装成功回调函数

load是异步的
可以通过model.length === pathList.length 来判断是否模型文件都加载完成,完成加载执行suc(model)
import { FBXLoader } from 'three/examples/jsm/loaders/FBXLoader.js'
import { GLTFLoader } from 'three/examples/jsm/loaders/GLTFLoader'
import * as THREE from 'three'
/**
* 专门加载模型文件=>模型对象
* @param {*} pathList 模型文件路径数组
* @param {*} suc 接收成功结果回调函数
*/
export function loadManager(pathList, suc) {
// 定义加载器对象
const gltfLoader = new GLTFLoader(manager)
const fbxLoader = new FBXLoader(manager)
pathList.forEach(path => {
if (path.indexOf('fbx') > -1) {
fbxLoader.load(path, obj => {
// 数据结构
model.push({
model: obj,
url: path
});
(model.length === pathList.length) && suc(model)
})
} else if (path.indexOf('gltf') > -1) {
gltfLoader.load(path, gltf => {
model.push({
model: gltf.scene,
url: path
});
· && suc(model)
})
}
})
}
3.城市加载
分析
创建一个基类(城市、天空、轮船都可以继承基类)
基类:场景、模型、相机、轨道控制器
封装城市类,用于加载并管理城市相关细节和功能
实现:
1.创建 BaseModel.js 基础模型类
2.创建 City.js 城市类并继承 BaseModel
3.判断模型名字并加载模型到网页中

在 src/model/BaseModel.js 准备基类属性和代码
// 基础模型
export class BaseModel {
constructor(model, scene, camera, control) {
this.model = model
this.scene = scene
this.camera = camera
this.control = control
// 子类无需定义 constructor,所以没有地方调用 init 方法,因此在这里调用子类的 init
this.init()
}
}
在 src/model/City.js 新建
// 城市类
import { BaseModel } from "./BaseModel";
import * as THREE from 'three'
export class City extends BaseModel {
init() {
this.scene.add(this.model)
}
}
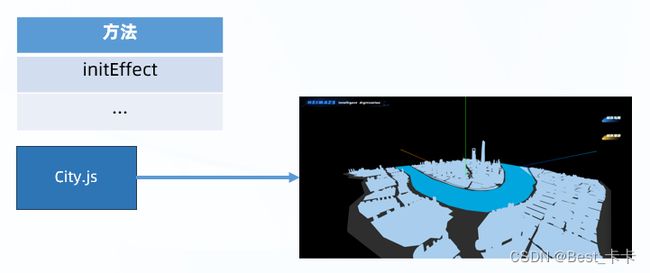
4.城市修改-材质颜色
分析
城市3d模型加载后做些微处理、修改城市模型材质,确认对应物体
实现:在city.js中加入initEffect方法
1.找到模型对象名字
2.隐藏自带的建筑名字
3.排除地面和河水,设置四周和中心模型对象材质
// 初始化城市效果
initEffect() {
// 中心城市建筑材质
const centerMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0xA8CDED,
transparent: true
})
// 外围城市建筑材质
const periphery = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0xA8CDED,
transparent: true
})
this.model.traverse(model => {
if (model.name === 'Text') {
// 隐藏默认建筑名字
model.visible = false
return
}
// 排除地板和河水物体
if (model.name !== 'Shanghai-09-Floor' && model.name !== 'Shanghai-08-River') {
// 修改城市建筑模型材质
if (model.name == 'Shanghai-02' || model.name == 'Shanghai-03' || model.name == 'Shanghai-04' || model.name == 'Shanghai-05' || model.name == 'Shanghai-06' || model.name == 'Shanghai-07') {
// 周围建筑
model.material = periphery
} else {
// 中心建筑
model.material = centerMaterial
}
}
})
}
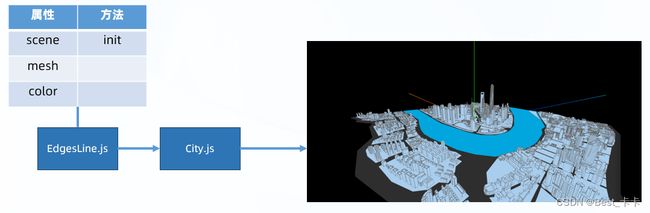
5.城市修改-边线效果
分析
使用three.js提供的边缘几何体为城市模型物体描边边缘几何体
实现
1.创建 EdgesLine.js 边缘几何类
2.基于 three.js 添加边缘线条
3.在 City.js 城市类中引入调用
// 边缘边线效果
import * as THREE from 'three'
export class EdgesLine {
constructor(scene, mesh, color){
this.scene = scene
this.mesh = mesh // 需要添加边线的小物体模型对象
this.color = color // 边线颜色
this.init()
}
init() {
const edgesGeometry = new THREE.EdgesGeometry(this.mesh.geometry)
const material = new THREE.LineBasicMaterial({ color: this.color })
const line = new THREE.LineSegments(edgesGeometry, material)
// 把目标小物体模型对象(位置,旋转角度,缩放)赋予给边线物体
line.position.copy(this.mesh.position)
line.rotation.copy(this.mesh.rotation)
line.scale.copy(this.mesh.scale)
this.scene.add(line)
}
}
在 City.js 中调用
// 修改城市建筑模型材质
if (model.name == 'Shanghai-02' || model.name == 'Shanghai-03' || model.name == 'Shanghai-04' || model.name == 'Shanghai-05' || model.name == 'Shanghai-06' || model.name == 'Shanghai-07') {
// 周围建筑
model.material = periphery
new EdgesLine(this.scene, model, new THREE.Color('#666666'))
} else {
// 中心建筑
model.material = centerMaterial
new EdgesLine(this.scene, model, new THREE.Color('#00ffff'))
}
6.城市修改-着色器
分析
我们要做的是为城市模型添加渐变颜色白膜效果
实现:
1.基于材质对象的 onBeforeCompile 方法修改内置材质
2.查找并使用白膜效果的着色器代码

在src/shader/modifyCityMaterial.js新建
import * as THREE from "three"
// 使用着色器代码 - 修改城市默认细节
export function modifyCityDefaultMaterial(mesh, isCenter) {
// 中心城市物体
if (isCenter) {
// 给现有材质追加着色器内代码
mesh.material.onBeforeCompile = (shader) => {
// 替换片元着色器内代码字符串
// 对混色 dithering_fragment 部分准备改写
// 注意:打印 shader.fragmentShader 发现是类 c 语法,引入了各种插件和实现过程代码(这里对 c 语法做出替换,从而让颜色改变)
shader.fragmentShader = shader.fragmentShader.replace(
"#include " ,
`
#include
//#end#
`
)
// 给物体内着色器代码进行修改和替换,添加过渡颜色
addGradColor(shader, mesh)
}
} else {
// 周围建筑
mesh.material.onBeforeCompile = (shader) => {
shader.fragmentShader = shader.fragmentShader.replace(
"#include " ,
`
#include
//#end#
`
)
addLowGradColor(shader, mesh)
}
}
}
export function addGradColor(shader, mesh) {
// 计算当前几何物体,边缘图形:链接:https://threejs.org/docs/index.html#api/zh/core/BufferGeometry.computeBoundingBox
mesh.geometry.computeBoundingBox()
// 就能拿到这个物体的坐标值
let { min, max } = mesh.geometry.boundingBox
let uHeight = max.z - min.z
let uMaxX = max.x
let uMinX = min.x
// 向 shader 中传入全局参数
shader.uniforms.uTopColor = {
value: new THREE.Color("#1B2569")
};
shader.uniforms.uHeight = {
value: uHeight
};
shader.uniforms.uMaxX = {
value: uMaxX
}
shader.uniforms.uMinX = {
value: uMinX
}
// 顶点着色器代码替换
shader.vertexShader = shader.vertexShader.replace(
// common 包含着色器公共模块(包含常用的数学工具函数以及一些常量定义什么的)
"#include " ,
`
#include
varying vec3 vPosition;
`
)
shader.vertexShader = shader.vertexShader.replace(
// 顶点着色器开始的位置
"#include " ,
`
#include
vPosition = position;
`
)
// 片元着色器代码替换
shader.fragmentShader = shader.fragmentShader.replace(
"#include " ,
`
#include
uniform vec3 uTopColor;
uniform float uHeight;
varying vec3 vPosition;
`
)
shader.fragmentShader = shader.fragmentShader.replace(
"//#end#",
`
vec4 distGradColor = gl_FragColor;
// 设置渐变色比例
float gradMix = (vPosition.z+uHeight/2.0)/uHeight;
// 设置渐变效果 mix(a,b,r) = (1-r)*a + br
vec3 gradMixColor = mix(distGradColor.xyz,uTopColor,gradMix);
// 片元赋色
gl_FragColor = vec4(gradMixColor,0.8);
//#end#
`
)
}
export function addLowGradColor(shader, mesh) {
mesh.geometry.computeBoundingBox()
let { min, max } = mesh.geometry.boundingBox
let uHeight = max.z - min.z
let uMaxX = max.x
let uMinX = min.x
shader.uniforms.uTopColor = {
value: new THREE.Color("#000"),
}
shader.uniforms.uHeight = {
value: uHeight,
}
shader.uniforms.uMaxX = {
value: uMaxX
}
shader.uniforms.uMinX = {
value: uMinX
}
shader.vertexShader = shader.vertexShader.replace(
"#include " ,
`
#include
varying vec3 vPosition;
`
);
shader.vertexShader = shader.vertexShader.replace(
"#include " ,
`
#include
vPosition = position;
`
)
shader.fragmentShader = shader.fragmentShader.replace(
"#include " ,
`
#include
uniform vec3 uTopColor;
uniform float uHeight;
varying vec3 vPosition;
`
)
shader.fragmentShader = shader.fragmentShader.replace(
"//#end#",
`
vec4 distGradColor = vec4(0.4,0.5,0.6,1.0);
float gradMix = (vPosition.z+uHeight/2.0)/uHeight;
vec3 gradMixColor = mix(distGradColor.xyz,uTopColor,gradMix);
gl_FragColor = vec4(gradMixColor,0.8);
//#end#
`
)
}
// 饼状图->点击选择城市效果
export function modifySelectCityMaterial(mesh) {
mesh.material.onBeforeCompile = (shader) => {
shader.fragmentShader = shader.fragmentShader.replace(
"#include " ,
`
#include
//#end#
`
);
addGradColor(shader, mesh);
};
}
在 City.js 中判断引入并使用
import { modifyCityDefaultMaterial } from '@/shader/modifyCityMaterial'
···
// 修改城市建筑模型材质
if (model.name == 'Shanghai-02' || model.name == 'Shanghai-03' || model.name == 'Shanghai-04' || model.name == 'Shanghai-05' || model.name == 'Shanghai-06' || model.name == 'Shanghai-07') {
// 周围建筑
model.material = periphery
new EdgesLine(this.scene, model, new THREE.Color('#666666'))
// 对物体追加混合的着色器代码(渐变色白膜效果)
modifyCityDefaultMaterial(model, false)
} else {
// 中心建筑
model.material = centerMaterial
new EdgesLine(this.scene, model, new THREE.Color('#00ffff'))
modifyCityDefaultMaterial(model, true)
}
7.城市-添加水面效果
分析
实现水面效果
1.使用 three.js 提供附加组件 Water 实现
2.隐藏模型里自带的水物,使用 CityWater 显示
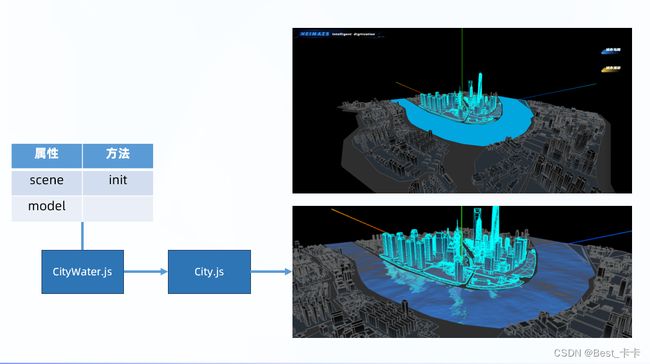
新建 src/effect/CityWater.js 实现水物体效果
import * as THREE from 'three'
import { Water } from 'three/examples/jsm/objects/Water'
export class CityWater {
constructor(model, scene) {
this.scene = scene
this.model = model
this.init()
}
init() {
const modelGeo = this.model.geometry // 先保存原来水模型的几何图形对象
// 新的水模型
this.model = new Water(
modelGeo,
{
textureWidth: 512, // 水贴图的宽度
textureHeight: 512, // 水贴图的高度(值越大细节越多)
waterNormals: new THREE.TextureLoader().load('textures/waternormals.jpg', function (texture) { // 水模型的法线贴图(不同像素点有不同反光效果)
// 纹理图片 UV 环绕到目标物体身上的重复方式
// wrapS这个值定义了纹理贴图在水平方向上将如何包裹,在UV映射中对应于U
// wrapT这个值定义了纹理贴图在垂直方向上将如何包裹,在UV映射中对应于V
// 使用RepeatWrapping,纹理将简单地重复到无穷大
texture.wrapS = texture.wrapT = THREE.RepeatWrapping;
}),
sunDirection: new THREE.Vector3(), // 阳光方向
sunColor: 0xffffff, // 阳光颜色
waterColor: new THREE.Color("#1e90ff"), // 水颜色
distortionScale: 4, // 水倒影分散度(值大越分散)
}
)
this.model.rotation.x = -Math.PI / 2 // 默认模型是垂直于 x 轴,所以翻转
this.scene.add(this.model) // 物体模型添加到场景中
}
// 给水波纹做动画
onTick(t) {
// t的值:渲染循环启动过了多少毫秒时间
// time 全局参数是 Water 内置好的,我们只需要不断传入新的偏移单位数值即可实现水波纹动态效果
this.model.material.uniforms['time'].value = t / 1000
}
}
在 City.js 判断并引入使用
// 针对水物体单独处理
if (model.name === 'Shanghai-08-River') {
// 把原本水物体隐藏
model.visible = false
// 创建更加真实的水面效果物体
const theWater = new CityWater(model, this.scene)
// 把水波纹物体传入到动效管理类当中
EffectManager.getInstance().addObj(theWater)
}
8.添加游船物体
实现
实现游船物体
1.创建 Ship 类,加载和管理游船模型对象
2.设置游船默认位置,旋转角度和缩放大小

在 src/model/Ship.js 新建
// 游船类
import * as THREE from 'three'
import { BaseModel } from './BaseModel'
export class Ship extends BaseModel {
init() {
this.scene.add(this.model)
}
}
在 src/entry/index.js 使用
loadManager(['fbx/city.fbx', 'gltf/ship.glb'], modelList => {
modelList.forEach(async obj => {
if (obj.url === 'fbx/city.fbx') {
const city = new City(obj.model, scene, camera, control)
} else if (obj.url === 'gltf/ship.glb') {
const ship = new Ship(obj.model, scene, camera, control)
}
})
})
在 entry/index.js 加载模型回调函数中
const ship = new Ship(obj.model, scene, camera, control)
ship.model.position.set(150, 0, -80)
ship.model.rotation.set(0, -Math.PI / 2, 0)
ship.model.scale.set(100, 100, 100) // 游船物体很小要与大城市模型匹配需要放大
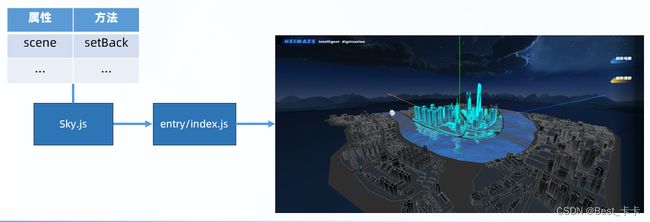
9.项目-天空背景
分析
1.创建 Sky 天空背景类,加载和管理天空背景
2.实例化天空,传入必须要的贴图参数
新建 src/environment/Sky.js
// 天空背景类
import * as THREE from 'three'
export class Sky {
constructor(scene) {
this.scene = scene
}
// 创建并设置天空背景 pathList贴图数组
setBack(publicPath, pathList) {
(new THREE.CubeTextureLoader()).setPath(publicPath).load(pathList, (texture) => {
this.scene.background = texture
})
}
}
在 entry/index.js 中使用
// 初始化天空背景 // 传入6个面的贴图
(new Sky(scene)).setBack('textures/sky/', [
'px.jpg',
'nx.jpg',
'py.jpg',
'ny.jpg',
'pz.jpg',
'nz.jpg'
])
10.城市-火灾标记
分析
创建火灾标记精灵物体
实现:(加载、位置)
1.创建 Fire 火灾标记类,加载和管理火灾标记
2.引入计算物体中心和宽高深的函数,确定火灾标记位置
3.在 City 类中实例化创建火灾标记
回顾
// 区别:
// CSS3D:始终不面向摄像机,场景缩放时跟随着变大/变小,不被模型遮挡,通过 DOM 事件点击
// CSS2D:始终面向摄像机, 场景缩放时不跟随变化, 不被模型遮挡,通过 DOM 事件点击
精灵体:始终面向摄像机, 场景缩放时跟随着变大/变小,被模型遮挡, 通过光射投影交互
// 平面体:始终不面向摄像机,场景缩放时跟随着变大/变小,被模型遮挡, 通过光射投影交互
讲解
新建 src/effect/Fire.js
// 火灾标记类
import * as THREE from 'three'
export class Fire {
constructor(scene, center, size) {
this.scene = scene
this.center = center // 建筑物中心点三维向量对象
this.size = size // 建筑物大小的三维向量对象
this.init()
}
// 初始化火灾标记
init() {
const texture = new THREE.TextureLoader().load('icon/fire.png')
texture.colorSpace = THREE.SRGBColorSpace
const spriteMaterial = new THREE.SpriteMaterial({
map: texture
})
const sprite = new THREE.Sprite(spriteMaterial)
// +3 让精灵物体中心点不在建筑物顶点,再往上移动一些单位
sprite.position.set(this.center.x, this.center.y + this.size.y / 2 + 3, this.center.z)
sprite.scale.set(10, 10, 10)
this.scene.add(sprite)
this.model = sprite
}
}
在 City.js 中 init 方法中调用,并新建 initFire 实例方法
// 随机为01-shanghaizhongxindasha设置火灾标记 后续可以通过接口获取那个建筑火灾了
this.initFire('01-shanghaizhongxindasha')
// 创建火灾标记
// buildName 就是建模师模型中的小物体名字
initFire(buildName) {
const build = this.model.getObjectByName(buildName)
const { center, size } = getBoxCenter(build)
const fire = new Fire(this.scene, center, size)
}
在 utils/getBoxCenter.js新建getBoxCenter函数获取物体中心点坐标
import * as THREE from 'three'
/**
* 获取模型中心点和高度差
* @param {*} mesh 目标模型对象
* @returns { center: 中心点坐标, uHeight: 高度差值 }
*/
// 基于 three.js 的 Box3 可以计算出目标物体的中心点坐标和宽高深大小
export const getBoxCenter = mesh => {
let box = new THREE.Box3()
// expandByObject:包裹在包围盒中的3d对象
box.expandByObject(mesh)
// 计算包围盒的中心点三维坐标对象
let center = new THREE.Vector3()
box.getCenter(center)
// 计算物体宽,高,深(x,y,z)的值
var size = new THREE.Vector3()
box.getSize(size)
return {
center,
size
}
}
11.城市-火灾影响范围
分析
在建筑底部添加火灾影响范围球体标记
实现:
1.创建 FireBall 火灾球体类(半球体),标记火灾影响范围
2.在 City 类中实例化火灾球体,并传入参数
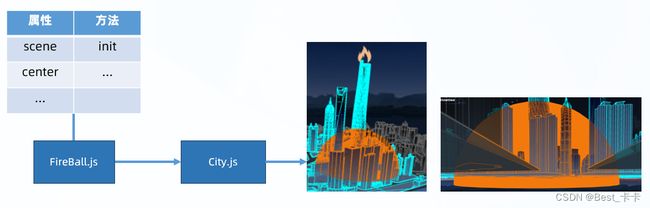
新建 src/effect/FireBall.js 火灾影响范围球体类
// 火灾影响范围-球体标记类
import * as THREE from 'three'
export class FireBall {
constructor(scene, center) {
this.scene = scene
this.center = center
this.init()
}
init() {
// 半球体物体
const geometry = new THREE.SphereGeometry(
25,
32,
16,
0,
Math.PI * 2, // 水平方向扫描角度
0,
Math.PI / 2, // 垂直方向扫描角度(一半)-半球体
)
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: new THREE.Color('#f4790d'),
side: THREE.DoubleSide,
depthTest: false // 关闭深度测试(透视效果)- 多个像素点同时渲染
})
const sphere = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material)
sphere.position.set(this.center.x, 0, this.center.z)
this.scene.add(sphere)
this.nowMesh = sphere
this.nowMesh.scale.set(0, 0, 0) // 缩小成不显示,后续做动效再出现
}
}
在 City.js 中引入并在 initFire 方法中使用
const ball = new FireBall(this.scene, center)
12.城市-建筑物信息
分析
1.创建 BuildInfo 建筑信息类,基于 CSS2D 渲染器,标记建筑物信息
2.在 City 类中实例化使用并传入参数
参数:场景、建筑中心坐标、数据、标题函数、信息函数
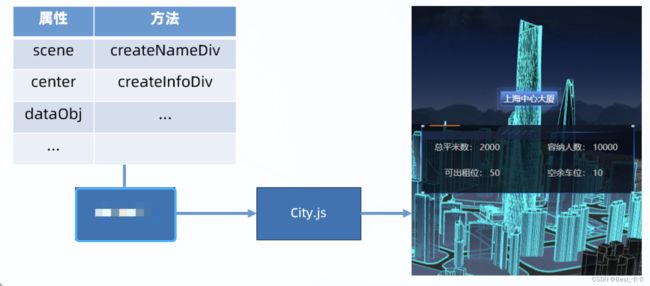
新建 src/dom/BuildInfo.js 类
// 2D 物体 - 建筑信息
import { CSS2DObject } from 'three/examples/jsm/renderers/CSS2DRenderer';
export class BuildInfo {
constructor(scene, center, dataObj) {
this.scene = scene
this.center = center
this.dataObj = dataObj
this.list = [] // 保存名字和信息的 2 个 2D 物体
this.createNameDiv()
this.createInfoDiv()
}
// 建筑名字的 2D 物体
createNameDiv() {
const nameDiv = document.querySelector('#tag-1')
nameDiv.innerHTML = this.dataObj.name // 建筑名字
// 标签虽然有 display:none; 但是转化成 2D 物体后会在 2D 渲染器中直接显示
const nameObject = new CSS2DObject(nameDiv)
nameObject.position.set(this.center.x, this.center.y + 10, this.center.z)
this.scene.add(nameObject)
this.list.push(nameObject)
}
// 建筑信息的 2D 物体
createInfoDiv() {
const infoDiv = document.querySelector('#tag-2')
infoDiv.style.pointerEvents = 'all'
const { squareMeters, accommodate, officesRemain, parkingRemain } = this.dataObj
const textHtml = `
总平米数: ${squareMeters}
容纳人数: ${accommodate}
可出租位: ${officesRemain}
空余车位: ${parkingRemain}
`
infoDiv.innerHTML = textHtml
const infoObject = new CSS2DObject(infoDiv)
infoObject.position.set(this.center.x, this.center.y + 5, this.center.z)
this.scene.add(infoObject)
this.list.push(infoObject)
}
}
在 model/City.js init 中定义数据结构
this.buildNameObj = { // 模型名字和建筑显示名字对应关系
'01-shanghaizhongxindasha': '上海中心大厦',
"02-huanqiujinrongzhongxin": "环球金融中心",
"03-jinmaodasha": "金茂大厦",
"04-dongfangmingzhu": "东方明珠",
}
在 model/City.js initFire 中调用
// 只有单独设置有名字的物体,才能被获取到并绑定事件
new BuildInfo(this.scene, center, {
"squareMeters": "200",
"name": this.buildNameObj[buildName],
"officesRemain": "200",
"accommodate": "500",
"parkingRemain": "88",
"cameraPosition": {
"x": "-27.60404773326758",
"y": "77.6723594934777",
"z": "190.86129619259177"
}
})
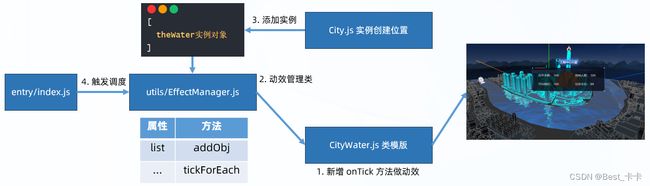
13.项目-水波纹动效
分析
添加水波纹动函数并在渲染循环中不断调度
1、设置EffectManager动效类:
{
list:保存将来要做动效的实例对象
addObj: 添加要做动效的实例对象
tickForEach:将来渲染循环传过来的毫秒级时间数值的动效
}
2、渲染循环中不断调度实例对象的onTick动效函数
实现:
1.水面效果类中,添加 onTick 方法做动效
// 给水波纹做动画
// Water 做动效改变全局参数 time 到着色器代码中,不断影响水物体的像素点位移,从而有波纹效果
onTick(t) {
// t的值:渲染循环启动过了多少毫秒时间
// time 全局参数是 Water 内置好的,我们只需要不断传入新的偏移单位数值即可实现水波纹动态效果
this.model.material.uniforms['time'].value = t / 1000
}
2.创建 EffectManager 动效管理类,管理项目中所有动效实例对象
// 整个项目-动效管理类
// 思路:要做动效的实例对象加入到这里,后续会不断分别调度每个实例对象内置的 onTick 方法
export class EffectManager {
constructor() {
this.list = [] // 保存将来要做动效的实例对象
}
static getInstance() {
if (!this.instance) {
this.instance = new EffectManager()
}
return this.instance
}
// 添加要做动效的实例对象
addObj(obj) {
this.list.push(obj)
}
tickForEach(t) {
// t: 将来渲染循环传过来的毫秒级时间数值
this.list.forEach(obj => {
obj.onTick(t)
})
}
}
3.添加实例物体到动态管理类中
// 针对水物体单独处理
if (model.name === 'Shanghai-08-River') {
// 把原本水物体隐藏
model.visible = false
// 创建更加真实的水面效果物体
const theWater = new CityWater(model, this.scene)
// 把水波纹物体传入到动效管理类当中
EffectManager.getInstance().addObj(theWater)
}
4.渲染循环中不断调度,动效管理类中实例对象们的 onTick 方法,做动效
// 动效是依赖渲染循环,不断重新调度并设置不同变量值来实现动效
// 渲染循环
function renderLoop(t) {
// 这里不再调用轨道控制器 update 方法,会影响摄像机 lookAt
renderer.render(scene, camera)
css2Renderer.render(scene, camera)
// 开始做动效->遍历所有要做动效的实例物体内置的 onTick 方法
EffectManager.getInstance().tickForEach(t)
requestAnimationFrame(renderLoop)
}
14.城市-游船移动效果
分析
游船移动:路径、方向、动画
物体移动路径规划,可以借助三维样条曲线 CatmullRomCurve3 设置几个关键点,就能得到一组很多坐标点数据,让物体不断修改坐标位置实现移动效果
实现:
在 Ship.js 的 init 中新增属性和调用方法
this.pointIndex = 0 // 保存当前游船所在位置坐标的索引
this.generatorMovePath() // 生成游船移动的路径
this.isMoveCamera = false // 开关属性(控制摄像机是否跟随游船移动)
this.onModelAttach() // 鼠标事件
1.游船 Ship 类,新增路径生成方法
// 生成游船行进的路线坐标点集合
generatorMovePath() {
// 设置平滑的三维样条曲线路线坐标点,CatmullRomCurve3
// 设置关键的几个点坐标,其他的构造函数内会帮我们计算
// CatmullRomCurve3(points:Vector3点数组,closed – 该曲线是否闭合,默认值为false,curveType – 曲线的类型,tension – 曲线的张力,默认为0.5)
const shipPath = new THREE.CatmullRomCurve3([
new THREE.Vector3(134.356097129589, 2.0112688541412354, -78.91746888546072),
new THREE.Vector3(13.132075955743915, 2.0112688541412425, -69.85260460470285),
new THREE.Vector3(13.132075955743915, 2.0112688541412425, -69.85260460470285),
new THREE.Vector3(-80.28995611104816, 2.0112688541412282, -12.640254617216172),
new THREE.Vector3(-71.5470123066941, 2.0112688541412354, 25.641138454485144),
new THREE.Vector3(-71.5470123066941, 2.0112688541412354, 25.641138454485144),
new THREE.Vector3(-17.5179164111899, 2.0112688541412354, 139.95062075065943),
new THREE.Vector3(-67.10547001341894, 2.0112688541412354, 64.30494908329582),
new THREE.Vector3(-87.03568940230136, 2.0112688541412354, 20.40776369519459),
new THREE.Vector3(-88.0509634357777, 2.0112688541412425, -32.429601593890354),
new THREE.Vector3(-70.27457116256328, 2.0112688541412425, -50.370253013515836),
new THREE.Vector3(-39.206573479212764, 2.0112688541412425, -64.28841112963838),
new THREE.Vector3(47.33347662423566, 2.0112688541412354, -73.13885409538068),
new THREE.Vector3(134.356097129589, 2.0112688541412354, -78.91746888546072),
])
// getSpacedPoints 等间距的坐标点
this.pointArr = shipPath.getSpacedPoints(3500)
// 要将曲线划分为的分段数 每次移动一个点控制船的速度
// 把坐标点 => 几何图形 => 线段物体显示一下(辅助我们理解)
const geometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry().setFromPoints(this.pointArr)
const material = new THREE.LineBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00, side: THREE.DoubleSide})
const line = new THREE.Line(geometry, material)
// this.scene.add(line)
}
2.游船 Ship 类,新增 onTick 方法做动效
// 游船行进方法-切换坐标点位置
onTick() {
if (this.pointIndex < this.pointArr.length - 1) {
const { x, y, z } = this.pointArr[this.pointIndex + 1]
// 游船移动:
// 取出坐标设置给模型对象
this.model.position.copy(this.pointArr[this.pointIndex])
// 确保船头朝向下一个坐标点位置(前进船头效果)
// 让物体朝着自己 z 轴正方向作为前面
this.model.lookAt(this.pointArr[this.pointIndex + 1])
this.pointIndex += 1
} else {
// 索引回到 0,重新继续做坐标的取值然后做动画效果
this.pointIndex = 0
}
}
3.添加游船实例物体到动态管理类中,在 entery/index.js
// 让游船物体也做动效
EffectManager.getInstance().addObj(ship)
15.城市-查看建筑信息
分析
建筑信息点击显示
three.js 的 3D 物体点击 - 光线投射代码封装起来,需要交互的物体对象和要执行的回调函数传入并映射 Map 数据结构,有交互时回调对应的函数执行
步骤:
1.准备 ClickHandler 类,管理项目的光线投射,在 enter/index.js 中注册
utils/ClickHander.js
// 单击事件管理类
import * as THREE from 'three'
export class ClickHandler {
static getInstance() {
if (!this.instance) {
this.instance = new ClickHandler()
}
return this.instance
}
init(camera) {
this.camera = camera
this.list = [] // 光线投射交互计算的物体
this.map = new Map() // key 可以是 three.js 物体(与点击要执行的回调函数产生一对一关系)
// 光线投射
const rayCaster = new THREE.Raycaster()
const pointer = new THREE.Vector2()
window.addEventListener('click', e => {
e.stopPropagation()
// 鼠标所在uv坐标
pointer.x = (e.clientX / window.innerWidth) * 2 - 1
pointer.y = -(e.clientY / window.innerHeight) * 2 + 1
rayCaster.setFromCamera(pointer, this.camera)
// 获取当前鼠标点击位置所在的物体集合
const resultList = rayCaster.intersectObjects(this.list, false)
// 默认只触发第一个收集到的物体(后面物体不触发交互)
if (resultList.length > 0) {
const targetObj = resultList[0]
const fn = this.map.get(targetObj.object)
// 回调绑定点击事件函数体,并回传当前触发的这个 three.js 物体
fn(targetObj.object)
}
})
}
// 传入要点击物体和函数体
addMesh(mesh, fn) {
this.list.push(mesh)
this.map.set(mesh, fn)
}
}
在 entry/index.js 中
// 光线投射注册
ClickHandler.getInstance().init(camera);
2.City 类中,新增 bindClick 方法给中心建筑绑定事件和显示信息标签逻辑
// 中心 4 个建筑绑定点击事件
bindClick() {
Object.keys(this.buildNameObj).forEach(key => {
const build = this.model.getObjectByName(key)
ClickHandler.getInstance().addMesh(build, (object) => {
// object: 3d 物体
const { center } = getBoxCenter(object)
new BuildInfo(this.scene, center, this.dataObj.buildingsIntroduce[object.name])
})
})
}
16.城市-建筑信息隐藏
分析
点击信息标签隐藏
隐藏 2D / 3D 物体,使用 visible 属性
步骤:
1.修改 BuildInfo 类,新增 list 属性保存标签物体
this.list = [] // 保存名字和信息的 2 个 2D 物体
2.新增 clear 方法,隐藏所有标签物体
// 隐藏信息物体
clear() {
this.list.forEach(obj => obj.visible = false)
}
3.给原生 DOM 绑定点击事件,触发 clear 方法
// DOM 点击事件 => 隐藏此建筑物的信息标签
infoDiv.addEventListener('click', (e) => {
e.stopPropagation()
this.clear.call(this)
})
17.城市-火灾影响动画
分析
完成火灾影响动画
思路:哪个物体要做动效,就新增 onTick 实例方法,把物体加入到动效管理类中,等待渲染循环不断调度触发 onTick 实现物体动效
实现:
1.新增 FireBall 类中 onTick 方法做火灾影响动效(缩放效果)
// 动效
onTick() {
if (this.nowScale < 1) {
this.nowScale += 0.001 // 增加放大的比例
this.nowMesh.scale.set(this.nowScale, this.nowScale, this.nowScale)
} else {
this.nowScale = 0
}
}
2.添加火灾球体实例,到动效管理类中
// 注册动效管理
EffectManager.getInstance().addObj(ball)
18.天空-鸟瞰效果
分析
点击dom标签,在天空设置路径移动一个飞行物体(暂定正方体),摄像机跟随移动完成城市鸟瞰浏览效果

实现:
1.新增 Fly 飞行器类,生成运动路径
// 飞行器
import { BaseModel } from './BaseModel'
import * as THREE from 'three'
export class Fly extends BaseModel {
init() {
this.scene.add(this.model)
this.pointIndex = 0 // 数组下标,用于换取坐标数组里,某个坐标对象
this.isCameraMove = false // 控制摄像机是否跟随切换位置的开关
this.generateMovePath()
}
// 飞行器运动的路径
generateMovePath() {
// EllipseCurve 椭圆曲线
const AirFly_PATH = new THREE.EllipseCurve(
0, 0, // 椭圆中心坐标
110, 110, // x和y轴向上椭圆的半径
0, -2 * Math.PI, // 开始角度和扫描角度
false, // 是否按照顺时针来绘制
0 // 以弧度表示,椭圆从X轴正方向逆时针的旋转角度
);
let tempArr = AirFly_PATH.getPoints(3500)
// 把坐标向 y 轴移动 120 单位(模仿在天空的效果)
let result = []
for (var i = 0; i < tempArr.length; i++) {
// z 轴的坐标位置,是几何图形未旋转之前,垂直于世界坐标系 y 轴的坐标点
let item = new THREE.Vector3(tempArr[i].x, 120, tempArr[i].y)
result.push(item)
}
this.pointsArr = result
}
// 动效-不断切换最新的最标点
onTick() {
if (this.pointIndex < this.pointsArr.length - 1) {
// 重要:如果其他东西也要跟着我的坐标来动
if (this.isCameraMove) {
// 更改摄像机位置
this.camera.position.copy(this.pointsArr[this.pointIndex])
// 让摄像机中心观察点往上偏移一点
this.camera.lookAt(0, 10, 0)
}
this.model.position.copy(this.pointsArr[this.pointIndex]);
this.pointIndex += 1; //调节速度
} else {
this.pointIndex = 0
}
}
}
2.实例化飞行器,实现环绕飞行动效,在 entry/index.js 模型加载的回调函数内
// 生成飞行器对象
const meshObj = new THREE.Mesh(new THREE.BoxGeometry(5, 5, 5), new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 'lightblue' }))
meshObj.visible = false
const fly = new Fly(meshObj, scene, camera, control)
// 注册动效
EffectManager.getInstance().addObj(fly)
// 注册事件-控制摄像机是否移动鸟瞰
EventBus.getInstance().on('mode-topView', (isOpen) => {
fly.control.enabled = !isOpen // 鸟瞰时轨道控制器禁止交互
fly.isCameraMove = isOpen // 控制摄像机是否跟随飞行器切换坐标点位置
})
3.菜单点击切换开关,控制摄像机位置是否跟着移动,实现鸟瞰浏览
新增 src/dom/menu.js
import { EventBus } from '@/utils/EventBus';
// 右上角 2 个按钮
let modeArr = [
{
mode: 'mode-topView', // id 名字,也作为 EventBus 中自定义事件名字
isOpen: false // 当前按钮状态-true开始,false关闭中
},
{
mode: 'mode-roaming',
isOpen: false
},
]
for (var i = 0; i < modeArr.length; i++) {
let item = modeArr[i]
// 获取右上角按钮绑定原生点击事件
document.getElementById(item.mode).onclick = function () {
item.isOpen = !item.isOpen // 控制打开状态等
// 触发这个名字在发布订阅对象里,下属数组里所有方法触发,并传递第二个参数过去
EventBus.getInstance().emit(item.mode, item.isOpen)
}
}
19.游船-漫游模式
分析
摄像机跟随游船移动(同理)
等待 DOM 点击修改开关属性,控制摄像机和游船一起改变坐标位置

实现:
1.修改 Ship 游船类,onTick 方法影响摄像机移动
// 游船行进方法-切换坐标点位置
onTick() {
if (this.pointIndex < this.pointArr.length - 1) {
const { x, y, z } = this.pointArr[this.pointIndex + 1]
if (this.isMoveCamera) { // 移动摄像机
if (!this.isMouseTouching) { // 鼠标没有被按下时,才设置摄像机的 lookAt
// 如果处于漫游模式+鼠标被按下,证明自己要旋转摄像机,那就不能让摄像的 lookAt 执行影响旋转效果
this.camera.lookAt(x, y + 20, z)
}
this.camera.position.set(x, y + 20, z)
}
// 游船移动:
// 取出坐标设置给模型对象
this.model.position.copy(this.pointArr[this.pointIndex])
// 确保船头朝向下一个坐标点位置(前进船头效果)
// 让物体朝着自己 z 轴正方向作为前面
this.model.lookAt(this.pointArr[this.pointIndex + 1])
this.pointIndex += 1
} else {
// 索引回到 0,重新继续做坐标的取值然后做动画效果
this.pointIndex = 0
}
}
2.通过 EventBus 设置摄像机开关模式, 在 entry/index.js
// 订阅改变摄像机跟随游船移动的事件
EventBus.getInstance().on('mode-roaming', isOpen => {
ship.control.enabled = !isOpen // 关闭/开启轨道控制器
ship.isMoveCamera = isOpen // 摄像机跟随移动
})
20.游船-漫游模式-旋转相机
分析
游船的时候,按下鼠标左右移动镜头查看建筑物
思路:点击鼠标后,鼠标移动的点方向上控制相机旋转
实现:
1.Ship 类新增 onModelAttach 方法,绑定/移除鼠标按下,移动,抬起事件
在 init 方法中
init() {
this.scene.add(this.model)
this.pointIndex = 0 // 保存当前游船所在位置坐标的索引
this.generatorMovePath() // 生成游船移动的路径
this.isMoveCamera = false // 开关属性(控制摄像机是否跟随游船移动)
this.onModelAttach() // 鼠标事件
}
// 绑定/移除鼠标事件
onModelAttach() {
// 点击漫游模式 - 绑定/移除鼠标相关事件
EventBus.getInstance().on('mode-roaming', isOpen => {
if (isOpen) {
window.addEventListener('mousedown', this.mousedownFn)
window.addEventListener('mousemove', this.mousemoveFn)
window.addEventListener('mouseup', this.mouseupFn)
} else {
window.removeEventListener('mousedown', this.mousedownFn)
window.removeEventListener('mousemove', this.mousemoveFn)
window.removeEventListener('mouseup', this.mouseupFn)
}
})
}
2.按下和抬起控制 isMouseTouching 属性值 true / false
3.鼠标移动时,旋转摄像机
// 鼠标按下
mousedownFn = () => {
this.isMouseTouching = true // 鼠标已经按下
}
// 鼠标移动
mousemoveFn = (e) => {
if (this.isMouseTouching) { // 只有按下时进入此逻辑代码
// 旋转核心思想:在原有的旋转角度基础上,新增移动的偏移量,乘以 0.01 让旋转弧度降低
// rotateY() 在上一次旋转的角度上继续新增你传入的弧度数值
// rotation.y = 直接赋予一个旋转的最终弧度数值
this.camera.rotateY((this.prePos - e.clientX) * 0.01)
}
this.prePos = e.clientX
}
// 鼠标抬起
mouseupFn = () => {
this.isMouseTouching = false
this.prePos = undefined // 清空上一次记录的坐标点位置
}
4.修改 onTick 方法,鼠标移动旋转摄像机时,摄像机 lookAt 方法不执行
// 游船行进方法-切换坐标点位置
onTick() {
if (this.pointIndex < this.pointArr.length - 1) {
const { x, y, z } = this.pointArr[this.pointIndex + 1]
if (this.isMoveCamera) { // 移动摄像机
if (!this.isMouseTouching) { // 鼠标没有被按下时,才设置摄像机的 lookAt
// 如果处于漫游模式+鼠标被按下,证明自己要旋转摄像机,那就不能让摄像的 lookAt 执行影响旋转效果
this.camera.lookAt(x, y + 20, z)
}
this.camera.position.set(x, y + 20, z)
}
// 游船移动:
// 取出坐标设置给模型对象
this.model.position.copy(this.pointArr[this.pointIndex])
// 确保船头朝向下一个坐标点位置(前进船头效果)
// 让物体朝着自己 z 轴正方向作为前面
this.model.lookAt(this.pointArr[this.pointIndex + 1])
this.pointIndex += 1
} else {
// 索引回到 0,重新继续做坐标的取值然后做动画效果
this.pointIndex = 0
}
}
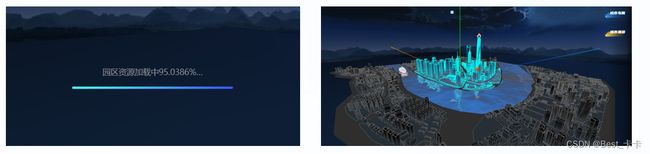
21.城市-模型加载进度
分析
实现模型加载进度条
步骤:
1.基于 three.js 提供的 LoadingManager 管理类,管理模型加载进度
2.实例化管理器对象,传入加载器构造函数中
3.监听进度管理器事件,并实现数字和进度条变化效果
import { FBXLoader } from 'three/examples/jsm/loaders/FBXLoader.js'
import { GLTFLoader } from 'three/examples/jsm/loaders/GLTFLoader'
import * as THREE from 'three'
import gsap from 'gsap'
const manager = new THREE.LoadingManager()
/**
* 专门加载模型文件=>模型对象
* @param {*} pathList 模型文件路径数组
* @param {*} suc 接收成功结果回调函数
*/
export function loadManager(pathList, suc) {
// 定义加载器对象
const gltfLoader = new GLTFLoader(manager)
const fbxLoader = new FBXLoader(manager)
// 保存加载成功模型对象数组
const model = []
let preValue = 0 // 上一次进度值
// 加载器对象关联属性和回调函数
manager.onProgress = (url, loadedNum, totalNum) => {
// url: 当前被加载完成的模型路径
// loadedNum: 当前加载完成的个数
// totalNum: 总共要加载的个数
// * 100 目的:为了让 0.5 进度变成 50 后续添加 % 后缀
// 当前已经加载的进度数字
let progressRatio = Math.floor(loadedNum / totalNum * 100)
gsap.fromTo('#processing-number', {
innerText: preValue // 暂时先传入一个数字(后面再去加 % 字符串)
}, {
innerText: progressRatio,
onUpdate() {
// 详细控制显示的内容
// 取出当前正在做动画的目标对象的属性值(进度数字)
const num = gsap.getProperty(this.targets()[0], 'innerText')
this.targets()[0].innerText = num + '%'
preValue = progressRatio // 把当前最新的加载进度值,赋予到外面变量上
if (num === 100) {
// loader 加载器工作完毕
suc(model)
document.querySelector('.loading').style.display = 'none'
}
}
})
// 对进度条再来做一个动画
// scaleX 范围是 0 - 1 做横向的缩放
gsap.fromTo('#loading-bar', {
scaleX: preValue / 100
}, {
scaleX: progressRatio / 100
})
}
pathList.forEach(path => {
if (path.indexOf('fbx') > -1) {
fbxLoader.load(path, obj => {
// 数据结构
model.push({
model: obj,
url: path
});
// (model.length === pathList.length) && suc(model)
})
} else if (path.indexOf('gltf') > -1) {
gltfLoader.load(path, gltf => {
model.push({
model: gltf.scene,
url: path
});
// (model.length === pathList.length) && suc(model)
})
}
})
}
22.项目-模拟城市数据接口
目标
模mock接口
注意:这里采用 apifox 配合 mock 模拟数据使用
步骤:
1.启动 mock 环境,得到接口地址使用模拟数据
2.获取并使用 DataManager 数据管理类并请求
import { EventBus } from '@/utils/EventBus'
import axios from 'axios'
axios.defaults.baseURL = 'http://127.0.0.1:4523/m1/2896102-0-default'
export class DataManager {
static getInstance() {
if (!this.instance) {
this.instance = new DataManager()
}
return this.instance
}
// 获取数据
getData() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
axios.get("/city").then(response => {
resolve(response.data)
})
})
}
// 模拟轮询请求服务器
refreshData() {
// 15 秒刷新一次数据
setInterval(async () => {
let data = await this.getData()
EventBus.getInstance().emit('refreshHomeCount', data)
}, 15000)
}
}
3.请求接口并设置点击时显示不同建筑的真实数据
模拟json文件在资源里有,下载后导入apifox即可
23.项目-ECharts集成
目标
集成 ECharts 实现 2D 图表
1.获取并使用 charts/index.js 集成图表相关内容
import * as echarts from 'echarts'
import { EventBus } from '@/utils/eventBus'
import { DataManager } from '@/utils/DataManager'
import gsap from 'gsap'
window.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () => {
// 创建柱状图
const myBarChart = echarts.init(document.getElementById('bar-chart'))
// 创建饼状图
const myPieChart = echarts.init(document.getElementById('pie-chart'))
// 开始初始化 ECharts 图表
initChart()
async function initChart() {
// 获取默认数据
let dataJson = await DataManager.getInstance().getData()
// 解构需要的数据
const {
parkIncome: { yIncome },
parkIndustry,
base,
} = dataJson
// ECharts 配置项
const barOption = {
tooltip: {
trigger: 'axis',
axisPointer: {
type: 'shadow',
},
},
grid: {
// 让图表占满容器
top: '10px',
left: '0px',
right: '0px',
bottom: '0px',
containLabel: true,
},
xAxis: [
{
type: 'category',
axisTick: {
alignWithLabel: true,
show: false,
},
data: [
"6月",
"7月",
"8月",
"9月",
"10月",
"11月",
"12月",
"1月",
"2月",
"3月",
"4月",
"5月"
],
},
],
yAxis: [
{
type: 'value',
splitLine: {
show: false,
},
},
],
series: [
{
name: '居民收入情况',
type: 'bar',
barWidth: '10px',
data: yIncome.map((item, index) => {
const color =
index % 2 === 0
? new echarts.graphic.LinearGradient(0, 0, 0, 1, [
{ offset: 0.23, color: '#74c0f8' },
{ offset: 1, color: 'rgba(116,192,248,0.00)' },
])
: new echarts.graphic.LinearGradient(0, 0, 0, 1, [
{ offset: 0.23, color: '#ff7152' },
{ offset: 1, color: 'rgba(255,113,82,0.00)' },
]);
return { value: item, itemStyle: { color } };
}),
},
],
textStyle: {
color: '#B4C0CC',
},
};
const pieOption = {
color: [
'#00B2FF', '#2CF2FF', '#892CFF', '#FF624D', '#FFCF54', '#86ECA2'],
legend: {
itemGap: 20,
bottom: '0',
icon: 'rect',
itemHeight: 10, // 图例icon高度
itemWidth: 10, // 图例icon宽度
textStyle: {
color: '#c6d1db',
},
},
tooltip: {
trigger: 'item'
},
series: [
{
name: '产业分布',
type: 'pie',
radius: ['55%', '60%'], // 设置内圈与外圈的半径使其呈现为环形
center: ['50%', '40%'], // 圆心位置, 用于调整整个图的位置
tooltip: {
trigger: 'item',
formatter: (params) => {
return `${params.seriesName}${params.marker}${params.name}${params.percent}%`;
}
},
label: {
show: false,
position: 'center',
},
data: parkIndustry,
},
],
};
// 给图表设置配置项
myBarChart.setOption(barOption);
myPieChart.setOption(pieOption);
// 饼状图-点击事件
myPieChart.on('click', function (param) {
// 0 素质教育
// 1 医疗健康
// 2 生活服务
// 3 商业娱乐
// 4 其他
if (param.dataIndex == 0) {
EventBus.getInstance().emit('pieClick', "Shanghai-02")
} else if (param.dataIndex == 1) {
EventBus.getInstance().emit('pieClick', "Shanghai-03")
} else if (param.dataIndex == 2) {
EventBus.getInstance().emit('pieClick', "Shanghai-04")
} else if (param.dataIndex == 3) {
EventBus.getInstance().emit('pieClick', "Shanghai-05")
} else if (param.dataIndex == 4) {
EventBus.getInstance().emit('pieClick', "Shanghai-06")
}
// 07 模型暂时没用上
});
// ECharts 适配
window.addEventListener('resize', function () {
myPieChart.resize();
myBarChart.resize();
});
}
// 更新左上角-城市概况数据
EventBus.getInstance().on('refreshHomeCount', (data) => {
console.log('监听')
animateValue(data)
})
// 数据动画更新效果
async function animateValue(data) {
if (data && data.base) {
const { buildingTotal, chargePoleTotal, enterpriseTotal, parkingTotal } = data.base
gsap.to('#building-number', {
duration: 1,
innerText: function () { return buildingTotal.toFixed(0) },
transformOrigin: 'center bottom',
onUpdate: function () {
let n = (gsap.getProperty(this.targets()[0], "innerText"));
this.targets()[0].innerText = n.toFixed(0)
},
})
gsap.to('#enterprise-number', {
duration: 1,
innerText: function () { return chargePoleTotal.toFixed(0) },
transformOrigin: 'center bottom',
onUpdate: function () {
let n = (gsap.getProperty(this.targets()[0], "innerText"));
this.targets()[0].innerText = n.toFixed(0)
},
})
gsap.to('#car-number', {
duration: 1,
innerText: function () { return enterpriseTotal.toFixed(0) },
transformOrigin: 'center bottom',
onUpdate: function () {
let n = (gsap.getProperty(this.targets()[0], "innerText"));
this.targets()[0].innerText = n.toFixed(0)
},
})
gsap.to('#rod-number', {
duration: 1,
innerText: function () { return parkingTotal.toFixed(0) },
transformOrigin: 'center bottom',
onUpdate: function () {
let n = (gsap.getProperty(this.targets()[0], "innerText"));
this.targets()[0].innerText = n.toFixed(0)
},
})
}
}
})
2.在 enter/index.js 注册定时轮询数据接口 - 不断更新城市概况
// 注册轮询的事件,负责间隔 15 秒更新城市概况的数据
DataManager.getInstance().refreshData()
24.城市-产业分布查看
分析
点击饼状图,对应建筑物高亮
实现:
1.饼状图点击事件,并基于 EventBus 传递对应模型名字
2.在 enter/index.js 注册事件,控制对应模型材质
注意:要保留模型原本材质,在点击其他产业时,上一个模型恢复原本材质
把物体本身材质对象保存,回复时把材质对象覆盖回去
// 监听自定义饼状图事件,让模型高亮
city.lastOriginMat = [] // 上一次高亮物体本来的材质
EventBus.getInstance().on('pieClick', buildName => {
// 如果有上一个物体,先把上一个物体的材质恢复一下
let index = 0
if (city.lastClick && city.lastOriginMat.length > 0) {
city.lastClick.traverse(model => {
model.material = city.lastOriginMat[index++]
})
}
// 设置当前点击的物体的高亮材质
const targetBuild = city.model.getObjectByName(buildName)
targetBuild.traverse(model => {
if (model.type === 'Mesh') {
city.lastOriginMat.push(model.material) // 保留小物体中每个细节物体的材质对象
model.material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0x0000ff
})
modifySelectCityMaterial(model) // 再给选中的小物体边线再设置上去
}
})
city.lastClick = targetBuild // 上一次点击的小物体对象
})
25.项目-火灾标记切换
分析
实现:
1.根据接口返回的建筑名字,动态创建火灾标记和范围影响球体
2.15 秒后火灾标记清空(接口轮询时间15秒)
在 Fire.js 新增 clear 方法
clear() {
this.scene.remove(this.model)
}
在 FireBall.js 新增 clear 方法
clear() {
this.nowMesh.geometry.dispose()
this.nowMesh.material.dispose()
this.scene.remove(this.nowMesh)
}
在 EffectManager.js 中新增删除做动效物体
// 移除指定物体,不参与动效
removeObj(obj) {
const index = this.list.findIndex(target => target === obj)
this.list.splice(index, 1)
}
在 City.js 中新建时,暂停 15 秒后消失
// 创建火灾标记
// buildName 就是建模师模型中的小物体名字
initFire(buildName) {
const build = this.model.getObjectByName(buildName)
const { center, size } = getBoxCenter(build)
const fire = new Fire(this.scene, center, size)
const ball = new FireBall(this.scene, center)
// 注册动效管理
EffectManager.getInstance().addObj(ball)
// 过了 15 秒以后清除标记
setTimeout(() => {
fire.clear()
ball.clear()
// 移除动效
EffectManager.getInstance().removeObj(ball)
}, 15000)
}
项目地址
git项目地址
鸣谢-广告
学程序上黑马,黑马程序员成就IT黑马,感谢黑马讲师的视频课程