python 可视化 不同排序_用 Python 构建排序可视化工具
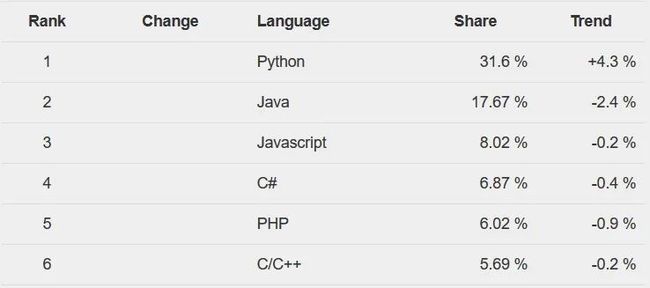
Python 最近在计算机科学领域占据主导地位,其应用领域包括机器学习、数据科学、人工智能、网络开发和软件编程,这些都是21世纪的最新趋势。根据 PYPL 编程语言普及指数,与其他编程语言相比,python 大约占总份额的31.6% 。
python
所以,我想我们可以用最好的方式来学习 python,通过构建一个精彩的项目来掌握任何编程语言中的一个基本原理—— sorting。在本文结束时,你可以用五种不同的算法构建一个令人惊叹的排序可视化工具:
•选择排序•冒泡排序•插入排序•归并排序•快速排序
算法
让我们创建一个名为algorithms.py的文件,在这个文件中,我们将用 python 编写所有的排序算法。导入time模块来告诉用户可视化工具所花费的时间(注意: 显示的时间是系统渲染可视化工具所花费的时间,与排序算法无关)。创建一个称为Algorithm的类,并将这段代码粘贴到这里:
classAlgorithm:
def__init__(self,name):
self.array=random.sample(range(512),512)# Random array of size 512
self.name=name# Get name of the variable
defupdate_display(self,swap1=None,swap2=None):
importvisualizer
visualizer.update(self,swap1,swap2)# pass the indexes to be swapped into the visualizer
defrun(self):# Start the timer and run the algorithm
self.start_time=time.time()
self.algorithm()
time_elapsed=time.time()-self.start_time
returnself.array,time_elapsed
我们最初将创建一个大小为512的随机数组。在 update_display 方法中,我们将调用 visualizer.py 中的 update 函数,稍后将编写这个函数来处理图形。最后,run 方法将启动计时器并调用算法函数,这是每个排序算法的一部分。它返回已排序的数组和运行时间。
选择排序
class SelectionSort(Algorithm):def __init__(self):super().__init__("SelectionSort")def algorithm(self):for i in range(len(self.array)):min_idx = ifor j in range(i+1, len(self.array)):if self.array[j] < self.array[min_idx]:min_idx = jself.array[i], self.array[min_idx] = self.array[min_idx], self.array[i]self.update_display(self.array[i], self.array[min_idx])
Selectionsort 类将继承 Algorithm 类,在其算法方法中我们实现了 Selection sort。每次数组更新时,我们不断调用 update_display 方法并实时呈现数组的排序。类似地,我们也实现了所有其他算法。
冒泡排序
class BubbleSort(Algorithm):def __init__(self):super().__init__("BubbleSort")def algorithm(self):for i in range(len(self.array)):for j in range(len(self.array)-1-i):if self.array[j] > self.array[j+1]:self.array[j], self.array[j+1] = self.array[j+1], self.array[j]self.update_display(self.array[j], self.array[j+1])
插入排序
class InsertionSort(Algorithm):def __init__(self):super().__init__("InsertionSort")def algorithm(self):for i in range(len(self.array)):cursor = self.array[i]idx = iwhile idx > 0 and self.array[idx-1] > cursor:self.array[idx] = self.array[idx-1]idx -= 1self.array[idx] = cursorself.update_display(self.array[idx], self.array[i])
归并排序
classMergeSort(Algorithm):def__init__(self):super().__init__("MergeSort")defalgorithm(self,array=[]):ifarray==[]:array=self.arrayiflen(array)<2:returnarraymid=len(array)// 2left=self.algorithm(array[:mid])right=self.algorithm(array[mid:])returnself.merge(left,right)defmerge(self,left,right):result=[]i,j=0,0whilei
快速排序
classQuickSort(Algorithm):def__init__(self):super().__init__("QuickSort")defalgorithm(self,array=[],start=0,end=0):ifarray==[]:array=self.arrayend=len(array)-1ifstart
可视化工具
祝贺你!你只是写了所有流行的排序算法。最后一步是直观地显示每种排序算法的工作方式。
下面是 visualizer.py 文件的代码。
importalgorithmsimporttimeimportosimportsysimportpygame# Set the window length and breadth (Make sure that the breadth is equal to size of array. [512])dimensions=[1024,512]# List all the algorithms available in the project in dictionary and call the necessary functions from algorithms.pyalgorithms={"SelectionSort":algorithms.SelectionSort(),"BubbleSort":algorithms.BubbleSort(),"InsertionSort":algorithms.InsertionSort(),"MergeSort":algorithms.MergeSort(),"QuickSort":algorithms.QuickSort()}# Check list of all the available sorting techniques using 'list'iflen(sys.argv)>1:ifsys.argv[1]=="list":forkeyinalgorithms.keys():print(key,end=" ")# Display the available algorithmsprint("")sys.exit(0)# Initalise the pygame librarypygame.init()# Set the dimensions of the window and display itdisplay=pygame.display.set_mode((dimensions[0],dimensions[1]))# Fill the window with purple huedisplay.fill(pygame.Color("#a48be0"))defcheck_events():# Check if the pygame window was quitforeventinpygame.event.get():ifevent.type==pygame.QUIT:pygame.quit();sys.exit();defupdate(algorithm,swap1=None,swap2=None,display=display):# The function responsible for drawing the sorted array on each iterationdisplay.fill(pygame.Color("#a48be0"))pygame.display.set_caption("Sorting Visualizer Algorithm: {} Time: {:.3f} Status: Sorting...".format(algorithm.name,time.time()-algorithm.start_time))# Display on title bark=int(dimensions[0]/len(algorithm.array))foriinrange(len(algorithm.array)):colour=(80,0,255)ifswap1==algorithm.array[i]:colour=(0,255,0)elifswap2==algorithm.array[i]:colour=(255,0,0)# The most important step that renders the rectangles to the screen that gets sorted.# pygame.draw.rect(dsiplay_window, color_of_rectangle, size_of_rectangle)pygame.draw.rect(display,colour,(i*k,dimensions[1],k,-algorithm.array[i]))check_events()pygame.display.update()defkeep_open(algorithm,display,time):# Keep the window open until sort completionpygame.display.set_caption("Sorting Visualizer Algorithm: {} Time: {:.3f} Status: Done!".format(algorithm.name,time))whileTrue:check_events()pygame.display.update()defmain():iflen(sys.argv)<2:print("Please select a sorting algorithm.")else:try:algorithm=algorithms[sys.argv[1]]# Pass the algorithm selectedtry:time_elapsed=algorithm.run()[1]keep_open(algorithm,display,time_elapsed)passexcept:passexcept:print("Error.")if__name__=="__main__":main()
太好了!我知道,有很多代码需要消化,但我向您保证,当您按下这个项目的运行按钮时,它将会取得丰硕的成果。同时,让我向您解释一下可视化工具代码。
首先,我们导入我们编写算法的算法 python 文件。然后,在 python 中导入 pygame 模块来处理我们项目中的图形。
另外,通过在终端中执行 pip install pygame 来安装 pygame。
设置维数组中的窗口大小,并确保保留第二个参数512,因为这是我们正在使用的随机样本数。
接下来的几行命令将向用户显示可用算法列表,并提示他们选择一个并在运行代码时输入。
然后,初始化 pygame 模块,设置窗口的尺寸,并用颜色填充显示器。
检查事件函数用于在关闭窗口时退出程序。
其次是整个程序更新方法中最重要的功能。这个方法在每次迭代之后接受数组,并且手头有两个交换变量,swap1和 swap2变量。这些变量被赋予不同的颜色。
然后我们使用 pygame.draw.rect()函数将这些数组元素渲染到窗口并更新它。
只要 pygame 窗口仍在运行,而且窗口没有被终止,那么保持 open 函数就会保持 pygame 窗口处于打开状态。
最后,主函数将用户选择算法作为输入,并调用具体算法及其定时器。
结果
最终,是时候运行我们的项目了。在 project 目录中打开终端,执行 python visualizer.py 列表以获得所有可用算法的列表。