Spring国际化i18n
一、国际化(i18n)介绍
国际化也称作i18n,其来源是英文单词 internationalization的首末字符i和n,18为中间的字符数。由于软件发行可能面向多个国家,对于不同国家的用户,软件显示不同语言的过程就是国际化(举个例子,人们玩的电子游戏,通常可以选择多个语言版本,适应于多个国家的玩家)。通常来讲,软件中的国际化是通过配置文件来实现的,假设某个软件要支撑两种语言,那么就需要两个版本的配置文件。
实现国际化,归根结底就是根据语言类型去定义好字符串模板而已。
下表列举了一些常见国家、地区的语言编码:
| 国家/地区 |
语言编码 |
国家/地区 |
语言编码 |
| 简体中文(中国) |
zh-cn |
繁体中文(台湾地区) |
zh-tw |
| 繁体中文(香港) |
zh-hk |
英语(香港) |
en-hk |
| 英语(美国) |
en-us |
英语(英国) |
en-gb |
| 英语(全球) |
en-ww |
英语(加拿大) |
en-ca |
| 英语(澳大利亚) |
en-au |
英语(爱尔兰) |
en-ie |
| 英语(芬兰) |
en-fi |
芬兰语(芬兰) |
fi-fi |
| 英语(丹麦) |
en-dk |
丹麦语(丹麦) |
da-dk |
| 英语(以色列) |
en-il |
希伯来语(以色列) |
he-il |
| 英语(南非) |
en-za |
英语(印度) |
en-in |
| 英语(挪威) |
en-no |
英语(新加坡) |
en-sg |
| 英语(新西兰) |
en-nz |
英语(印度尼西亚) |
en-id |
| 英语(菲律宾) |
en-ph |
英语(泰国) |
en-th |
| 英语(马来西亚) |
en-my |
英语(阿拉伯) |
en-xa |
| 韩文(韩国) |
ko-kr |
日语(日本) |
ja-jp |
| 荷兰语(荷兰) |
nl-nl |
荷兰语(比利时) |
nl-be |
| 葡萄牙语(葡萄牙) |
pt-pt |
葡萄牙语(巴西) |
pt-br |
| 法语(法国) |
fr-fr |
法语(卢森堡) |
fr-lu |
| 法语(瑞士) |
fr-ch |
法语(比利时) |
fr-be |
| 法语(加拿大) |
fr-ca |
西班牙语(拉丁美洲) |
es-la |
| 西班牙语(西班牙) |
es-es |
西班牙语(阿根廷) |
es-ar |
| 西班牙语(美国) |
es-us |
西班牙语(墨西哥) |
es-mx |
| 西班牙语(哥伦比亚) |
es-co |
西班牙语(波多黎各) |
es-pr |
| 德语(德国) |
de-de |
德语(奥地利) |
de-at |
| 德语(瑞士) |
de-ch |
俄语(俄罗斯) |
ru-ru |
| 意大利语(意大利) |
it-it |
希腊语(希腊) |
el-gr |
| 挪威语(挪威) |
no-no |
匈牙利语(匈牙利) |
hu-hu |
| 土耳其语(土耳其) |
tr-tr |
捷克语(捷克共和国) |
cs-cz |
| 斯洛文尼亚语 |
sl-sl |
波兰语(波兰) |
pl-pl |
| 瑞典语(瑞典) |
sv-se |
|
|
二、Java国际化
定义properties
Java 中的多语言字符串模板一般保存在properties资源文件中。
它必须遵照以下的命名规范:
<资源名>_<语言代码>_<国家/地区代码>.properties
其中,语言代码和国家/地区代码都是可选的。
<资源名>.properties命名的国际化资源文件是默认的资源文件,即某个本地化类型在系统中找不到对应的资源文件,就采用这个默认的资源文件。
例:
定义中英文两种多语言资源文件,将其置于resources 路径下。
content_en_US.properties:
helloWorld = HelloWorld! time = Thecurrenttimeis%s.
content_zh_CN.properties
helloWorld = \u4e16\u754c\uff0c\u4f60\u597d\uff01 time = \u5f53\u524d\u65f6\u95f4\u662f\u0025\u0073\u3002
可以看到,两种语言的Key 完全一致,只是 Value 是对应语言的字符串。
本地化不同的同一资源文件,虽然属性值各不相同,但属性名却是相同的,这样应用程序就可以通过Locale对象和属性名精确调用到某个具体的属性值了。
为了达到跨编码也正常显示的目的,有必要将非ASCII 字符转为 Unicode 编码。上面的中文资源文件就是中文转为 Unicode 的结果。
Unicode 转换工具
JDK在bin目录下为我们提供了一个Unicode 转换工具:native2ascii。
它可以将中文字符的资源文件转换为Unicode代码格式的文件,命令格式如下:
native2ascii [-reverse] [-encoding 编码] [输入文件 [输出文件]]
例:
假设content_zh_CN.properties 在d:\ 目录。执行以下命令可以新建 content_zh_CN_new.properties ,其中的内容就所有中文字符转为 UTF-8 编码格式的结果。
native2ascii -encoding utf-8 d:\content_zh_CN.properties d:\content_zh_CN_new.properties
加载资源文件
定义了多语言资源文件,下一步就是加载资源文件了。
Java为我们提供了用于加载本地化资源文件的工具类:java.util.ResourceBoundle。
使用方式见下例:
Locale localeEn = new Locale("en", "US");
Locale localeZh = new Locale("zh", "CN");
ResourceBundle rbEn = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.locale.resources.content", localeEn);
ResourceBundle rbZh = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.locale.resources.content", localeZh);
System.out.println("us-US:" + rbEn.getString("helloWorld"));
System.out.println("us-US:" + String.format(rbEn.getString("time"), "08:00"));
System.out.println("zh-CN:" + rbZh.getString("helloWorld"));
System.out.println("zh-CN:" + String.format(rbZh.getString("time"), "08:00"));
需要说明的是:ResourceBundle类的 getBundle方法第一个参数 baseName需要输入的是资源文件的package路径 + 文件前缀。
在加载资源时,如果指定的本地化资源文件不存在,它会尝试按下面的顺序加载其他的资源:本地系统默认本地化对象对应的资源-> 默认的资源。如果指定错误,Java 会提示找不到资源文件。
支持国际化的国际化工具类
Java 中也提供了几个支持国际化的格式化工具类。例如:NumberFormat、DateFormat、MessageFormat
1、NumberFormat
NumberFormat 是所有数字格式类的基类。它提供格式化和解析数字的接口。它也提供了决定数字所属语言类型的方法。
Locale locale = new Locale("en", "US");
NumberFormat format = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(locale);
doublenum = 123456.78;
System.out.println("51423.45 Format:");
System.out.println(String.format("%s : %s", locale.toString(), format.format(num)));
2、DateFormat
DateFormat 是日期、时间格式化类的抽象类。它支持基于语言习惯的日期、时间格式。
Date date = new Date();
DateFormat df = DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.MEDIUM, new Locale("zh", "CN"));
DateFormat df2 = DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.MEDIUM, new Locale("en", "US"));
System.out.println(df.format(date));
System.out.println(df2.format(date));
3、MessageFormat
Messageformat 提供一种与语言无关的拼接消息的方式。通过这种拼接方式,将最终呈现返回给使用者。
String pattern1 = "{0},你好!你于 {1} 消费 {2} 元。";
String pattern2 = "At {1,time,short} On {1,date,long},{0} paid {2,number, currency}.";
Object[] params = { "Jack", new GregorianCalendar().getTime(), 8888 };
String msg1 = MessageFormat.format(pattern1, params);
MessageFormat mf = new MessageFormat(pattern2, Locale.US);
String msg2 = mf.format(params);
System.out.println(msg1);
System.out.println(msg2);
三、Spring国际化
spring使用MessageSource接口实现国际化。两个实现类为:
- ResourceBundleMessageSource:基于java的ResourceBundle实现了国际化,配置文件必须放在classpath下。
- ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource:直接使用读取文件的方式实现国际化,规则跟java的相同,支持动态修改后刷新配置,避免在业务不能中断的情况下重启进程。配置文件可以放在任意目录下,指定目录后,该类会去指定目录中加载配置文件。
创建国际化资源文件
在resource下新建i18n目录,目录下文件有:
message.properties
foo.test = 您好, {1} {0}
foo.message = 这是缺省消息,参数: {0}, {1}, {2}.
message_en.properties
foo.test = Hello, {0} {1}
foo.message = This is the default message. Args: {0}, {1}, {2}.
message_zh.properties
foo.test = 您好, {1} {0}
foo.message = 这是缺省消息,参数: {0}, {1}, {2}.
配置MessageSource Bean
@Bean //【注意】这个bean的名字必须叫messageSource,否则无效
public MessageSource messageSource() {
ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource();
//如果设置为-1,表示Cache forever。一般生产环境下采用-1,开发环境为了方便调测采用某个正整数,规范地我们可通过profile来定义
messageSource.setCacheSeconds(5);
messageSource.setDefaultEncoding(StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name());
//设置properties文件的basename,以便找到响应的资源文件
messageSource.setBasenames("classpath:i18n/message", "classpath:i18n/default");
return messageSource;
}
创建国际化工具类I18nMessageUtil
import java.util.Locale;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils;
@Component
public class I18nMessageUtil implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static MessageSource messageSource;
private static Locale currentLocale = new Locale("en");
public static String getMessage(String key) {
return messageSource.getMessage(key, null, key, currentLocale);
}
public static String getMessage(String key, Locale locale) {
return messageSource.getMessage(key, null, key, locale == null ? currentLocale : locale);
}
public static String getMessage(String key, String defaultMessage) {
return messageSource.getMessage(key, null, defaultMessage == null ? key : defaultMessage, currentLocale);
}
public static String getMessage(String key, String defaultMessage, Locale locale) {
return messageSource.getMessage(key, null, defaultMessage == null ? key : defaultMessage, locale == null ? currentLocale : locale);
}
public static String getMessage(String key, Object[] placeHolders) {
return messageSource.getMessage(key, placeHolders, key, currentLocale);
}
public static String getMessage(String key, Object[] placeHolders, String defaultMessage) {
return messageSource.getMessage(key, placeHolders, defaultMessage == null ? key : defaultMessage, currentLocale);
}
public static String getMessage(String key, Object[] placeHolders, Locale locale) {
return messageSource.getMessage(key, placeHolders, key, locale == null ? currentLocale : locale);
}
public static String getMessage(String key, Object[] placeHolders, String defaultMessage, Locale locale) {
return messageSource.getMessage(key, placeHolders, defaultMessage == null ? key : defaultMessage, locale == null ? currentLocale : locale);
}
public static void setCurrentLocale(Locale currentLocale) {
I18nMessageUtil.currentLocale = currentLocale;
}
public static void setCurrentLocale(HttpServletRequest request) {
I18nMessageUtil.currentLocale = RequestContextUtils.getLocale(request);
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
if (null == messageSource) {
messageSource = applicationContext.getBean(MessageSource.class);
}
}
}
代码测试
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@WebAppConfiguration
@ContextHierarchy({
@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class),
@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringMVCConfig.class)
})
public class I18nTest {
@Test
public void testI18n() {
String msg = I18nMessageUtil.getMessage("foo.message", new Object[]{"One", "Two", "Three"}, Locale.ENGLISH);
System.out.println("msg == " + msg);
msg = I18nMessageUtil.getMessage("foo.message", new Object[]{"一", "二", "三"}, Locale.getDefault());
System.out.println("msg == " + msg);
msg = I18nMessageUtil.getMessage("foo.lable", new Object[]{"Hi"}, "{0}, my friend", Locale.ENGLISH);
System.out.println("msg == " + msg);
}
}
消息格式
消息格式(java.text.MessageFormat)含有占位模板,在运行时被替换。例子如下:
There are {0} cats on the farm.
There are {0,number,integer} cats on the farm.
The value of Pi to seven significant digits is {0,number,#.######}.
My birthdate: {0,date,short}. Today is {1,date,long} at {1,time,long}.
My birth day: {0,date,MMMMMM-d}. Today is {1,date,MMM d, YYYY} at {1,time,hh:mma).
There {0,choice,0#are no cats|1#is one cat|1
这些占位符号(placeholder)是有顺序的,替换是按这个顺序,而不是语句中出现的顺序(语句中的顺序本来就是要本地化)。
With a {0,number,percentage} discount, the final price is {1,number,currency}。
占位符是可以带格式的,下面#表示序号,斜体表示用户自定义的格式值:
{#}
{#,number}
{#,number,integer}
{#,number,percent}
{#,number,currency}
{#,number,自定义格式,遵循java.text.DecimalFormat}
{#,date}
{#,date,short}
{#,date,medium}
{#,date,long}
{#,date,full}
{#,date,自定义格式,遵循java.text.SimpleDateFormat}
{#,time}
{#,time,short}
{#,time,medium}
{#,time,long}
{#,time,full}
{#,time,自定义格式,遵循java.text.SimpleDateFormat}
{#,choice,自定义格式,遵循java.text.ChoiceFormat}
resource bundle的命名规则
resource bundle是这些message format的集合,一般采用properties文件的方式,key就是message code,value就是message format。例如:
alerts.current.date=Current Date and Time: {0,date,full} {0,time,full}
文件的命名规则如下:
[baseName]_[language]_[script]_[region]_[variant]
[baseName]_[language]_[script]_[region]
[baseName]_[language]_[script]
[baseName]_[language]_[region]_[variant]
[baseName]_[language]_[region] 例如labels_en_US.properties
[baseName]_[language] 例如labels_en.properties
以上前面的比后面具有优先权。如果只有baseName,language和variant,最匹配的是第4个,例子为:baseName_en__JAVA
四、扩展:页面国际化
使用 jQuery.i18n.properties 实现 Web 前端的国际化
jQuery.i18n.properties 是一款轻量级的 jQuery 国际化插件。与 Java 里的资源文件类似,jQuery.i18n.properties 采用 .properties 文件对 JavaScript 进行国际化。jQuery.i18n.properties 插件根据用户指定的(或浏览器提供的 )语言和国家编码(符合 ISO-639 和 ISO-3166 标准)来解析对应的以”.properties”为后缀的资源文件。
利用资源文件实现国际化是一种比较流行的方式,例如 Android 应用就可以采用以语言和国家编码命名的资源文件来实现国际化。jQuery.i18n.properties 插件中的资源文件以”.properties”为后缀,包含了区域相关的键值对。我们知道,Java 程序也可以使用以 .properties 为后缀的资源文件来实现国际化,因此,当我们要在 Java 程序和前端 JavaScript 程序中共享资源文件时,这种方式就显得特别有用。jQuery.i18n.properties 插件首先加载默认的资源文件(例如:strings.properties),然后加载针对特定语言环境的资源文件(例如:strings_zh.properties),这就保证了在未提供某种语言的翻译时,默认值始终有效。开发人员可以以 JavaScript 变量(或函数)或 Map 的方式使用资源文件中的 key。
jQuery.i18n.properties 有一下一些特点:
- 使用 Java 标准的 .properties 文件作为资源文件,资源文件命名有以下三种格式:
- basename_properties
- basename_language.properties
- basename_language_country.properties
- 使用 ISO-639 作为语言编码标准,ISO-3166 作为国家名称编码标准
- 按顺序加载默认资源文件和指定语言环境的资源文件,保证默认值始终可用
- 未指定语言环境时使用浏览器提供的语言
- 可以在资源字符串中使用占位符(例如:hello= 你好 {0}! 今天是 {1}。)
- 资源文件中的 Key 支持命名空间(例如:com.company.msgs.hello = Hello!)
- 支持跨行的值
- 可以以 JavaScript 变量(或函数)或 Map 的方式使用资源文件中的 Key
jQuery.i18n.properties API
jQuery.i18n.properties 的 API 非常简单,只有少数几个 API,即 jQuery.i18n.properties()、jQuery.i18n.prop()、jQuery.i18n.browserLang()。当然,和其他 jQuery 插件一样,我们也可以采用 $.i18n.properties()、$.i18n.prop() 和 $.i18n.browserLang() 的形式使用这用这些 API。
1、jQuery.i18n.properties(settings)
该方法加载资源文件,其中 settings 是配置加载选项的一系列键值对,各配置项的具体描述如下:
选项
描述
类型
可选?
name
资源文件的名称,例如 strings 或 [strings1,strings2],前者代表一个资源文件,后者代表资源文件数组。
String 或 String[]
否
path
资源文件所在目录的路径
String
是
mode
加载模式:”vars”表示以 JavaScript 变量或函数的形式使用资源文件中的 Key,”map”表示以 Map 的方式使用资源文件中的 Key,”both”表示可以同时使用两种方式。如果资源文件中的 Key 包含 JavaScript 的关键字,则只能采用”map”。默认值是”vars”。
String
是
language
ISO-639 指定的语言编码(如:”en”表示英文、”zh”表示中文),或同时使用 ISO-639 指定的语言编码和 ISO-3166 指定的国家编码(如:”en_US”,”zh_CN”等)。如果不指定,则采用浏览器报告的语言编码。
String
是
cache
指定浏览器是否对资源文件进行缓存,默认为 false。
boolean
是
encoding
加载资源文件时使用的编码。默认为 UTF-8。
String
是
callback
代码执行完成时运行的回调函数
function
是
使用如下:
jQuery.i18n.properties({
name:'strings',// 资源文件名称
path:'bundle/',// 资源文件所在目录路径
mode:'both',// 模式:变量或 Map
language:'pt_PT',// 对应的语言
cache:false,
encoding: 'UTF-8',
callback: function() {// 回调方法
}
});
2、jQuery.i18n.prop(key)
该方法以 map 的方式使用资源文件中的值,其中 key 指的是资源文件中的 key。当 key 指定的值含有占位符时,可以使用 jQuery.i18n.prop(key,var1,var2… ) 的形式,其中 var1,var2…对各占位符依次进行替换。例如资源文件中有”msg_hello= 您好 {0},今天是 {1}。”的键值对,则我们可以采用”jQuery.i18n.prop( ‘ msg_hello ‘ , ‘小明’ , ‘星期一’ );”的形式使用 msg_hello。
jQuery.i18n.browserLang() 用于获取浏览浏览器的语言信息。
具体示例
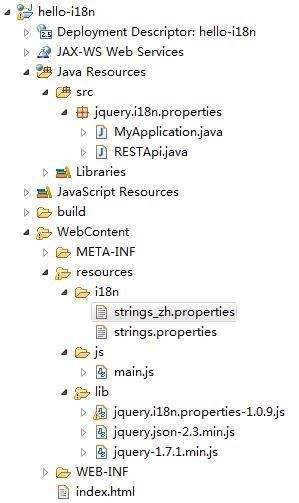
项目组织结构
在项目根路径下创建resource/i18n目录,新建strings.properties 和,stirngs_zh.properties 两个资源文件,其中 strings.properties 对应默认翻译。
strings.properties
string_username=User name
string_password=Password
string_login=Login
string_hello=Hello {0},Welcome to jQuery.i18n.properties,your token is {1}。
string_usernotexist=User does not exist
string_wrongpassword=Wrong Password
strings_zh.properties
string_username= 用户名
string_password= 密码
string_login= 登陆
string_hello= 您好 {0},欢迎使用 jQuery.i18n.properties,您的密钥是:{1}。
string_usernotexist= 用户不存在
string_wrongpassword= 密码错误
index .html
引用 jQuery.i18n.properties 插件
使用 jQuery.i18n.properties 插件
在 main.js加载资源文件,其中未指定”language”参数选项,表示使用浏览器语言。除了在 jQuery.i18n.properties() 定义的回调函数中使用资源文件中的定义的值外,成功加载资源文件后,我们也可以在其它地方使用这些值。
function loadProperties(){
jQuery.i18n.properties({// 加载资浏览器语言对应的资源文件
name:'strings', // 资源文件名称
path:'resources/i18n/', // 资源文件路径
mode:'map', // 用 Map 的方式使用资源文件中的值
callback: function() {// 加载成功后设置显示内容
// 显示"用户名”
$('#label_username').html($.i18n.prop('string_username'));
// 显示"密码”
$('#label_password').html($.i18n.prop('string_password'));
// 显示"登录”
$('#button_login').val($.i18n.prop('string_login'));
}
});
}
当用户点击登录按钮后,我们使用 REST 请求将用户信息发送到前文定义的 RESTFul Web 服务,若用户信息验证成功,则显示欢迎信息和 Web 服务返回的密钥,若验证失败则显示错误信息。
$('#button_login').click(function(){// 点击登录按钮后验证用户信息
var id = $('#username').val();// 用户名
var payload = {};
payload['password']=$('#password').val();
payload = $.toJSON(payload);
$.ajax({
url : 'rest/users/' + id + '/tokens',//REST URI
type : 'POST',
data: payload, // Request body
contentType : 'application/json',
dataType:'json',
success : function(data) {
// 验证成功则显示欢迎信息和密钥
// 使用含占位符的值
$('#content').html($.i18n.prop('string_hello',id,data.token));
},
error : function(jqXHR, textStatus, errorThrown) {
if(jqXHR.status == 403){
// 用户不存在
alert($.i18n.prop('string_usernotexist'));
}else if(jqXHR.status == 401){
// 密码错误
alert($.i18n.prop('string_wrongpassword'));
}else{
// 其他异常信息
alert(errorThrown);
}
}
});
});
五、扩展:Intellij IDEA Resource Bundle
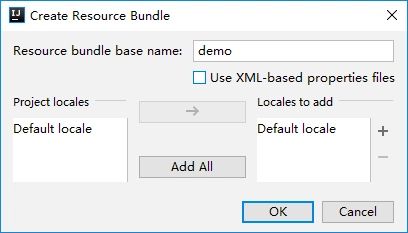
创建Resource Bundle
- 选中要创建Resource Bundle的目录,右键 - New - Resource Bundle。打开创建Resource Bundle的对话框。
- 填写Resource Bundle的基础名称
- 勾选User XML-based properties files则会创建XML格式的属性文件。
- Project locale表示项目里已经存在的区域。
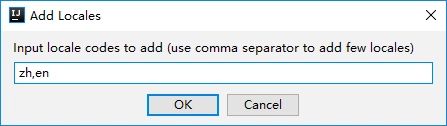
- Locales to add表示添加相应的区域,添加右边的+号即可添加,多个区域用,隔开。
以创建一个基础名称为demo的Resource Bundle为例
点击+号添加多个区域,这里以添加zh和en为例。
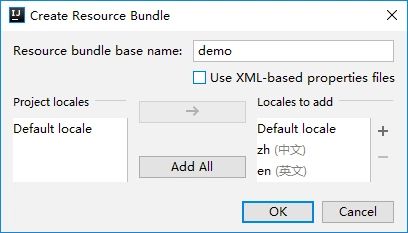
添加完成后,可以在Locales to add看到已经添加的区域。
点击OK生成Resource Bundle。
合并或拆分Resource Bundle
- 添加新的属性文件:直接在Resource Bundle 'demo'目录右键 - Add Property Files to Resource Bundle,点击+添加新的区域即可生成新的属性文件
- 拆分:如果不想使用Resource Bundle管理属性文件,可以在Resource Bundle目录右键 - Dissociate Resource Bundle 'demo'
- 合并:在同一个目录下创建多个符合相同前缀、不同语言后缀名称的属性文件时,Intellij IDEA会自动创建Resource Bundle管理这些文件
转自:Spring国际化i18n - codedot - 博客园