FLink学习笔记:13-Flink 的Table API的Window和UDF
文章目录
- Table API的Window操作
-
- Group Windows
-
- 时间语义的设定和watermark的生成
- 分组滚动窗口
-
- 方式一:Table API的实现
- 方式二:SQL实现
- 完整示例
- 分组滑动窗口
-
- 方式一:Table Api实现
- 方式二:SQL实现
- 分组会话窗口
-
- 方式一:Table API 实现
- 方式二:SQL实现
- OverWindow
-
- 方式一:Table Api实现
- 方式二:SQL实现
- Flink Table的函数和UDF
-
- 常用的系统内置函数
-
- 数学计算函数
- 字符串处理函数
- 时间处理函数
- 类型转换函数
- 自定义函数UDF
-
- 标量函数 ScalarFunction
-
- 概述
- 示例 实现自定义函数实现截取字符串
- 表值函数 TableFunction
-
- 概述
- 示例:实现自定义表函数实现拆分字段
- 聚合函数 UDAGG
-
- 示例:自定义聚合函数,求平均值
- 表值聚合函数 TableAggregateFunction
-
- 示例:实现top-2 表值聚合函数
Table API的Window操作
时间语义,要配合窗口操作才能发挥作用。最主要的用途,当然就是开窗口、根据时间 段做计算了。下面我们就来看看 Table API 和 SQL 中,怎么利用时间字段做窗口操作。 在 Table API 和 SQL 中,主要有两种窗口:Group Windows 和 Over Windows
Group Windows
分组窗口(Group Windows)会根据时间或行计数间隔,将行聚合到有限的组(Group) 中,并对每个组的数据执行一次聚合函数。
Table API 中的 Group Windows 都是使用.window(w:GroupWindow)子句定义的,并且 必须由 as 子句指定一个别名。为了按窗口对表进行分组,窗口的别名必须在 group by 子句 中,像常规的分组字段一样引用。
时间语义的设定和watermark的生成
在使用时间窗口时,也需要通DataStream API一样设定时间语义,以及对乱序数据流的watermark设定。在上一篇笔记中已经有了详细的说明。
分组滚动窗口
语法: .window(Tumble over [窗口Size].[时间单位] on [时间字段] as [窗口的别名])
- over: 定义窗口大小
- 时间单位:seconds,minutes,hours,days,months,years
- 时间字段:在表schema中定义的时间字段
- as:别名,必须出现在构面的groupBy中
- on:用来分组(可以按照时间间隔或者按照行数)的时间间断,按照行数时只能用于processTime的字段。
方式一:Table API的实现
val inputTable = tableEnv.fromDataStream(
datastream,
Schema
.newBuilder()
.column("id", DataTypes.STRING().notNull())
.column("timestamp", DataTypes.BIGINT().notNull())
.column("temperature", DataTypes.DOUBLE())
.columnByExpression(
"rowtime",
"CAST(TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(`timestamp`)) AS TIMESTAMP(3))")
.watermark("rowtime", "rowtime - interval '5' SECONDS ")
.build()
)
//滚动时间窗口
val result = inputTable
.window(Tumble over 5.seconds on 'rowtime as 'w)
.groupBy('w, 'id)
.select($"id",
$"temperature".max() as "max_temperature",
$"w".start() as "start",
$"w".end() as "end",
$"w".rowtime())
方式二:SQL实现
sql中语法:tumble(时间字段,interval ‘[窗口大小]’ [时间单位])
另外还提供一些辅助方法,如:
- TUMBLE_START(rowtime,interval ‘10’ second)
- TUMBLE_END(rowtime,interval ‘10’ second)
- TUMBLE_ROWTIME(rowtime,interval ‘10’ second)
- TUMBLE_PROCTIME(rowtime,interval ‘10’ second)
定义一个滚动窗口,第一个参数是时间字段,第二个参数是窗口长度。
val inputTable = tableEnv.fromDataStream(
datastream,
Schema
.newBuilder()
.column("id", DataTypes.STRING().notNull())
.column("timestamp", DataTypes.BIGINT().notNull())
.column("temperature", DataTypes.DOUBLE())
.columnByExpression(
"rowtime",
"CAST(TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(`timestamp`)) AS TIMESTAMP(3))")
.watermark("rowtime", "rowtime - interval '5' SECONDS ")
.build()
)
//方式二:SQL查询
tableEnv.createTemporaryView("sensor_view", inputTable)
val strSql =
"""
|SELECT
|id,
|tumble_start(rowtime, interval '5' second) as w_start,
|tumble_end(rowtime,interval '5' second) as w_end,
|max(temperature) as max_temperature
|from sensor_view
|group by
|id,
|tumble(rowtime, interval '5' second)
""".stripMargin
val sqlResult = tableEnv.sqlQuery(strSql)
完整示例
package com.hjt.yxh.hw.tableapitest
import java.time.Duration
import com.hjt.yxh.hw.apitest.SensorReading
import org.apache.flink.api.common.eventtime.{
SerializableTimestampAssigner,
WatermarkStrategy
}
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala.StreamExecutionEnvironment
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._
import org.apache.flink.table.api._
import org.apache.flink.table.api.EnvironmentSettings
import org.apache.flink.table.api.bridge.scala.StreamTableEnvironment
object TimeWindowTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//构建环境
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val datastream = env
.readTextFile(
"D:\\LearnWorkSpace\\FlinkDemo\\src\\main\\resources\\Data\\sensor.txt")
.filter(_.nonEmpty)
.map(data => {
val array = data.split(",")
SensorReading(array(0), array(1).toLong, array(2).toDouble)
})
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(
WatermarkStrategy
.forBoundedOutOfOrderness[SensorReading](Duration.ofSeconds(3))
.withTimestampAssigner(
new SerializableTimestampAssigner[SensorReading] {
override def extractTimestamp(element: SensorReading,
recordTimestamp: Long): Long = {
element.timestamp * 1000L
}
})
)
//构建table环境
val tableEnvironmentSettings = EnvironmentSettings
.newInstance()
.inStreamingMode()
.build()
val tableEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env, tableEnvironmentSettings)
val inputTable = tableEnv.fromDataStream(
datastream,
Schema
.newBuilder()
.column("id", DataTypes.STRING().notNull())
.column("timestamp", DataTypes.BIGINT().notNull())
.column("temperature", DataTypes.DOUBLE())
.columnByExpression(
"rowtime",
"CAST(TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(`timestamp`)) AS TIMESTAMP(3))")
.watermark("rowtime", "rowtime - interval '5' SECONDS ")
.build()
)
// val inputTable = tableEnv
// .fromDataStream(datastream,
// $"id",
// $"timestamp",
// $"temperature",
// $"timestamp".rowtime as "rowtime")
// inputTable.printSchema()
//滚动窗口
val result = inputTable
.window(Tumble over 5 on 'rowtime as 'w)
.groupBy('w, 'id)
.select($"id",
$"temperature".max() as "max_temperature",
$"w".start() as "start",
$"w".end() as "end",
$"w".rowtime())
//方式二:SQL查询
tableEnv.createTemporaryView("sensor_view", inputTable)
val strSql =
"""
|SELECT
|id,
|tumble_start(rowtime, interval '5' second) as w_start,
|tumble_end(rowtime,interval '5' second) as w_end,
|max(temperature) as max_temperature
|from sensor_view
|group by
|id,
|tumble(rowtime, interval '5' second)
""".stripMargin
println(strSql)
//滑动窗口
val sqlResult = tableEnv.sqlQuery(strSql)
tableEnv.toDataStream(result).print("table_api")
tableEnv.toDataStream(sqlResult).print("sql")
env.execute()
}
}
分组滑动窗口
滑动窗口(Sliding windows)要用 Slide 类来定义,另外还有四个方法:
- over:定义窗口长度
- every:定义滑动步长
- on:用来分组(按时间间隔)或者排序(按行数)的时间字段
- as:别名,必须出现在后面的 groupBy 中
eg: Slide over 15.seconds() every 5.seconds() on
方式一:Table Api实现
val result = inputTable
.window(Slide over 15.seconds() every 5.seconds() on 'rowtime as 'w)
.groupBy('w, 'id)
.select($"id",
$"temperature".max() as "max_temperature",
$"w".start() as "start",
$"w".end() as "end",
$"w".rowtime())
方式二:SQL实现
SQL中使用Hop(时间字段,interval1,interval2)定义一个滑动窗口
-
第一个参数是时间字段
-
第二个参数是窗口滑动步长
-
第三个是窗口长度
另外还提供一些辅助方法,如: -
HOP_START(rowtime,interval ‘10’ second,INTERVAL ‘5’ second)
-
HOP_END(rowtime,interval ‘10’ second,INTERVAL ‘5’ second)
-
HOP_ROWTIME(rowtime,interval ‘10’ second,INTERVAL ‘5’ second)
-
HOP_PROCTIME(rowtime,interval ‘10’ second,INTERVAL ‘5’ second)
tableEnv.createTemporaryView("sensor_view", inputTable)
val strSql =
"""
|SELECT
|id,
|max(temperature) as max_temperature,
|hop_start(rowtime, interval '5' second, interval '15' second) as w_start,
|hop_end(rowtime, interval '5' second, interval '15' second) as w_end,
|hop_rowtime(rowtime, interval '5' second, interval '15' second)
|from sensor_view
|group by
|id,
|hop(rowtime, interval '5' second, interval '15' second)
""".stripMargin
val sqlResult = tableEnv.sqlQuery(strSql)
分组会话窗口
方式一:Table API 实现
//会话窗口
val result = inputTable
.window(Session withGap 10.seconds() on 'rowtime as 'w)
.groupBy('w, 'id)
.select($"id",
$"temperature".max() as "max_temperature",
$"w".start() as "start",
$"w".end() as "end",
$"w".rowtime())
方式二:SQL实现
SQL中使用Session(rowtime, interval ‘10’ second)来定义一个会话窗口,
另外还提供一些辅助方法,如:
- SESSION_START(rowtime,interval ‘10’ second)
- SESSION_END(rowtime,interval ‘10’ second)
- SESSION_ROWTIME(rowtime,interval ‘10’ second)
- SESSION_PROCTIME(rowtime,interval ‘10’ second)
//方式二:SQL查询
tableEnv.createTemporaryView("sensor_view", inputTable)
val strSql =
"""
|SELECT
|id,
|max(temperature) as max_temperature,
|Session_start(rowtime, interval '10' second) as w_start,
|Session_end(rowtime, interval '10' second) as w_end
|from sensor_view
|group by
|id,
|Session(rowtime, interval '10' second)
""".stripMargin
val sqlResult = tableEnv.sqlQuery(strSql)
OverWindow
Over window 聚合是标准 SQL 中已有的(Over 子句),可以在查询的 SELECT 子句中定义。
Over window 聚合,会针对每个输入行,计算相邻行范围内的聚合。
Over windows 使用.window(w:overwindows*)子句定义,并在 select()方法中通过别名来引用。
方式一:Table Api实现
//Over窗口
val result = inputTable
.window(Over partitionBy 'id orderBy 'rowtime preceding 5.seconds() as 'w)
.select($"id",
$"temperature".max() over $"w" as "max_temperature"
)
方式二:SQL实现
语法:Over(partition by [分区字段] order by [排序字段] range [Range Definitions])
- partition by 按照某个字段分组
- order by 排序字段,如果间隔是时间区间,必须按照时间字段排序
- Range Definitions 区间定义
- Range intevals 按照时间切分区间
RANGE BETWEEN INTERVAL '30' MINUTE PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW - ROW intervals 按照行数定义区间
ROWS BETWEEN 10 PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW WINDOW
- Range intevals 按照时间切分区间
//方式二:SQL查询
tableEnv.createTemporaryView("sensor_view", inputTable)
val strSql =
"""
|SELECT
|id,
|max(temperature) over(
|partition by id
|order by rowtime
|range between INTERVAL '5' SECOND PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW
|)as max_temperature
|from sensor_view
""".stripMargin
val sqlResult = tableEnv.sqlQuery(strSql)
Flink Table的函数和UDF
常用的系统内置函数
数学计算函数
| SQL函数 | Table API | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| POWER(num1,num2) | num1.power(num2) | 返回num1的num2次方 |
| ABS(num1) | num1.abs() | 返回num1的绝对值 |
| SQRT(num1) | num1.sqrt() | 返回num1的平方根 |
| RAND() | rand() | 返回[0.0,1.0)之间的伪随机双精度值。 |
| RAND(INT) | rand(Int) | 返回[0.0,1.0)之间的伪随机双精度值,初始种子是INT。 |
| RAND_INTEGER(INT) | randInteger(Int) | 返回[0,INT)范围内的伪随机整数。 |
| RAND_INTEGER(INT1,INT2) | randInteger(Int1,INT2) | 返回[0,INT2)范围内的伪随机整数,初始种子是INT1。 |
字符串处理函数
| SQL函数 | Table API | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| str1 || str2 | str1+str2 | 返回str1和str2的连接 |
| REPLACE(str1,str2,str3) | str1.replace(str2,str3) | 使用str3替换str1中所有出现的str2 |
| UPPER(string) | STRING.upperCase() | 以大写形式返回字符串。 |
| LOWER(string) | STRING.lowerCase() | 以小写形式返回字符串。 |
| CHAR_LENGTH(string) | STRING.charLength() | 返回字符串中的字符数。 |
| CHARACTER_LENGTH(string) | STRING.charLength() | 返回字符串中的字符数。 |
| LTRIM(string) | STRING.ltrim() | 返回从STRING中删除左边空格的字符串。 |
| RTRIM(string) | STRING.rtrim() | 返回从 STRING 中删除右边空格的字符串. |
时间处理函数
| SQL函数 | Table API | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| DATE string | STRING.toDate() | 以“yyyy-MM-dd”的形式返回从字符串解析的 SQL 日期。 |
| TIME string | STRING.toTime() | 以“HH:mm:ss”的形式返回从字符串解析的 SQL 时间。 |
| TIMESTAMP string | STRING.toTimestamp() | 以“yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss[.SSS]”的形式返回从字符串解析的 SQL 时间戳。 |
| LOCALTIME | localTime() | 返回本地时区的当前 SQL 时间,返回类型为 TIME(0)。在流模式下为每条记录进行取值。 但在批处理模式下,它在查询开始时计算一次,并对每一行使用相同的结果。 |
| LOCALTIMESTAMP | localTimestamp() | 返回本地时区的当前 SQL 时间,返回类型为 TIMESTAMP(3)。在流模式下为每条记录进行取值。 但在批处理模式下,它在查询开始时计算一次,并对每一行使用相同的结果。 |
| CURRENT_TIME | currentTime() | 返回本地时区的当前 SQL 时间,这是 LOCAL_TIME 的同义词。 |
| CURRENT_DATE | currentDate() | 返回本地时区中的当前 SQL 日期。在流模式下为每条记录进行取值。 但在批处理模式下,它在查询开始时计算一次,并对每一行使用相同的结果。 |
| CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | currentTimestamp() | 返回本地时区的当前 SQL 时间戳,返回类型为 TIMESTAMP_LTZ(3)。在流模式下为每条记录进行取值。 但在批处理模式下,它在查询开始时计算一次,并对每一行使用相同的结果。 |
类型转换函数
| SQL函数 | Table API | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| CAST(value AS type) | ANY.cast(TYPE) | 返回被强制转换为类型 type 的新值。例如 CAST(‘42’ AS INT) 返回 42; CAST(NULL AS VARCHAR) 返回 VARCHAR 类型的 NULL。 |
| TYPEOF(input) | call(“TYPEOF”, input) | 返回输入表达式的数据类型的字符串表示形式。默认情况下返回的字符串是一个摘要字符串,可能会为了可读性而省略某些细节 |
| TYPEOF(input, force_serializable) | call(“TYPEOF”, input,force_serializable) | 。 如果 force_serializable 设置为 TRUE,则字符串表示可以保留在目录中的完整数据类型。请注意, 特别是匿名的内联数据类型没有可序列化的字符串表示。在这种情况下返回 NULL。 |
自定义函数UDF
自定义函数(UDF)是一种扩展开发机制,可以用来在查询语句里调用难以用其他方式表达的频繁使用或自定义的逻辑。
当前 Flink 有如下几种函数:
- 标量函数 将标量值转换成一个新标量值;
- 表值函数 将标量值转换成新的行数据;
- 聚合函数 将多行数据里的标量值转换成一个新标量值;
- 表值聚合函数 将多行数据里的标量值转换成新的行数据;
- 异步表值函数 是异步查询外部数据系统的特殊函数。
标量函数 ScalarFunction
概述
用户定义的标量函数,可以将 0、1 或多个标量值,映射到新的标量值。
为了定义标量函数,必须在 org.apache.flink.table.functions 中扩展基类 Scalar Function, 并实现(一个或多个)求值(evaluation,eval)方法。
标量函数的行为由求值方法决定, 求值方法必须公开声明并命名为 eval(直接 def 声明,没有 override)。求值方法的参数类型和返回类型,确定了标量函数的参数和返回类型。
示例 实现自定义函数实现截取字符串
package com.hjt.yxh.hw.tableapitest
import com.hjt.yxh.hw.apitest.SensorReading
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._
import org.apache.flink.table.annotation.{DataTypeHint, FunctionHint}
import org.apache.flink.table.api.{DataTypes, EnvironmentSettings, Schema}
import org.apache.flink.table.api.bridge.scala._
import org.apache.flink.table.api._
import org.apache.flink.table.functions.{ScalarFunction, TableFunction}
import org.apache.flink.types.Row
class MySubString extends ScalarFunction {
def eval(s: String, begin: Integer, end: Integer): String = {
return s.substring(begin, end)
}
def eval(s: String, begin: Integer): String = {
s.substring(begin)
}
}
object UDFTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//构建环境
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setMaxParallelism(12)
val datastream = env
.readTextFile(
"D:\\LearnWorkSpace\\FlinkDemo\\src\\main\\resources\\Data\\sensor.txt")
.filter(_.nonEmpty)
.map(data => {
val array = data.split(",")
SensorReading(array(0), array(1).toLong, array(2).toDouble)
})
//构建table环境
val tableEnvironmentSettings = EnvironmentSettings
.newInstance()
.inStreamingMode()
.build()
val tableEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env, tableEnvironmentSettings)
val inputTable = tableEnv.fromDataStream(
datastream,
Schema
.newBuilder()
.column("id", DataTypes.STRING().notNull())
.column("timestamp", DataTypes.BIGINT().notNull())
.column("temperature", DataTypes.DOUBLE())
.columnByExpression(
"rowtime",
"CAST(TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(`timestamp`)) AS TIMESTAMP(3))")
.watermark("rowtime", "rowtime - interval '5' SECONDS ")
.build()
)
//注册表
tableEnv.createTemporaryView("sensor",inputTable)
//注册函数--标量函数
tableEnv.createTemporaryFunction("mySubstr", classOf[MySubString])
val mySplit = new MySplit(" ")
tableEnv.createTemporaryFunction("mySplit",mySplit)
//tableApi 调用方式
val result1 = inputTable.select(call(classOf[MySubString],$"id",2,5),$"timestamp")
tableEnv.toDataStream(result1).print("result1")
//SQL調用方式
val result = tableEnv.sqlQuery("SELECT mySubstr(id,2,5),`timestamp` from sensor")
tableEnv.toDataStream(result).print("result")
env.execute("UDF test")
}
}
表值函数 TableFunction
概述
与用户定义的标量函数类似,用户定义的表函数,可以将 0、1 或多个标量值作为输入参数;与标量函数不同的是,它可以返回任意数量的行作为输出,而不是单个值。为了定义一个表函数,必须扩展org.apache.flink.table.functions 中的基类
TableFunction并实现(一个或多个)求值方法。表函数的行为由其求值方法决定,求值方法必须是 public 的,并命名为 eval。求值方法的参数类型,决定表函数的所有有效参数。 返回表的类型由 TableFunction 的泛型类型确定。求值方法使用 protected collect(T)方 法发出输出行。
在 Table API 中,Table函数需要与.joinLateral或.leftOuterJoinLateral 一起使用。 joinLateral算子,会将外部表中的每一行,与表函数(TableFunction,算子的参数是它 的表达式)计算得到的所有行连接起来。 而 leftOuterJoinLateral算子,则是左外连接,它同样会将外部表中的每一行与表函数计 算生成的所有行连接起来;并且,对于表函数返回的是空表的外部行,也要保留下来。
示例:实现自定义表函数实现拆分字段
package com.hjt.yxh.tableapi.udf
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._
import org.apache.flink.table.api.{DataTypes, EnvironmentSettings, Schema}
import org.apache.flink.table.api.bridge.scala._
case class SensorReading(id: String, timestamp: Long, temperature: Double)
import org.apache.flink.table.annotation.DataTypeHint
import org.apache.flink.table.annotation.FunctionHint
import org.apache.flink.table.api._
import org.apache.flink.table.functions.TableFunction
import org.apache.flink.types.Row
@FunctionHint(output = new DataTypeHint("ROW" ))
class MySplit(separator: String) extends TableFunction[Row] {
def eval(s: String): Unit = {
s.split(separator).foreach(word => collect(Row.of(word, Int.box(word.length))))
}
}
object UDFTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//构建环境
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setMaxParallelism(12)
val datastream = env
.readTextFile(
"D:\\java_workspace\\hadoop\\FlinkDemo\\src\\main\\resources\\Data\\sensor.txt")
.filter(_.nonEmpty)
.map(data => {
val array = data.split(",")
SensorReading(array(0), array(1).toLong, array(2).toDouble)
})
//构建table环境
val tableEnvironmentSettings = EnvironmentSettings
.newInstance()
.inStreamingMode()
.build()
val tableEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env, tableEnvironmentSettings)
val inputTable = tableEnv.fromDataStream(
datastream,
Schema
.newBuilder()
.column("id", DataTypes.STRING().notNull())
.column("timestamp", DataTypes.BIGINT().notNull())
.column("temperature", DataTypes.DOUBLE())
.columnByExpression(
"rowtime",
"CAST(TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(`timestamp`)) AS TIMESTAMP(3))")
.watermark("rowtime", "rowtime - interval '5' SECONDS ")
.build()
)
//注册表
tableEnv.createTemporaryView("sensor", inputTable)
//注册函数
tableEnv.createTemporaryFunction("mySplit", new MySplit("_"))
//tableApi 调用方式
val result1 = inputTable
.leftOuterJoinLateral(call("mySplit", $"id")).select($"word", $"len", $"id")
tableEnv.toDataStream(result1).print("result1")
//SQL調用方式
val result = tableEnv.sqlQuery("SELECT id,word,len from sensor left join lateral table(mySplit(id)) on true ")
//SQL重命名
val result2 = tableEnv.sqlQuery("SELECT id,newWord,newLen from sensor left join lateral table(mySplit(id)) AS T(newWord,newLen) on true ")
tableEnv.toDataStream(result).print("result2")
env.execute("UDF test")
}
}
聚合函数 UDAGG
自定义聚合函数(UDAGG)是把一个表(一行或者多行,每行可以有一列或者多列)聚合成一个标量值。

上面的图片展示了一个聚合的例子。假设你有一个关于饮料的表。表里面有三个字段,分别是 id、name、price,表里有 5 行数据。假设你需要找到所有饮料里最贵的饮料的价格,即执行一个 max() 聚合。你需要遍历所有 5 行数据,而结果就只有一个数值。
自定义聚合函数是通过扩展 AggregateFunction 来实现的。AggregateFunction 的工作过程如下。首先,它需要一个 accumulator,它是一个数据结构,存储了聚合的中间结果。通过调用 AggregateFunction 的 createAccumulator() 方法创建一个空的 accumulator。接下来,对于每一行数据,会调用 accumulate() 方法来更新 accumulator。当所有的数据都处理完了之后,通过调用 getValue 方法来计算和返回最终的结果。
下面几个方法是每个 AggregateFunction 必须要实现的:
- createAccumulator()
- accumulate()
- getValue()
Flink 的类型推导在遇到复杂类型的时候可能会推导出错误的结果,比如那些非基本类型和普通的 POJO 类型的复杂类型。所以跟 ScalarFunction 和 TableFunction 一样,AggregateFunction 也提供了 AggregateFunction#getResultType() 和 AggregateFunction#getAccumulatorType() 来分别指定返回值类型和 accumulator 的类型,两个函数的返回值类型也都是 TypeInformation。
除了上面的方法,还有几个方法可以选择实现。这些方法有些可以让查询更加高效,而有些是在某些特定场景下必须要实现的。例如,如果聚合函数用在会话窗口(当两个会话窗口合并的时候需要 merge 他们的 accumulator)的话,merge() 方法就是必须要实现的。
AggregateFunction 的以下方法在某些场景下是必须实现的:
- retract() 在 bounded OVER 窗口中是必须实现的。
- merge() 在许多批式聚合和会话以及滚动窗口聚合中是必须实现的。除此之外,这个方法对于优化也很多帮助。例如,两阶段聚合优化就需要所有的 AggregateFunction 都实现 merge 方法。
- resetAccumulator() 在许多批式聚合中是必须实现的。
AggregateFunction 的所有方法都必须是 public 的,不能是static的,而且名字必须跟上面写的一样。createAccumulator、getValue、getResultType 以及 getAccumulatorType 这几个函数是在抽象类AggregateFunction中定义的,而其他函数都是约定的方法。如果要定义一个聚合函数,你需要扩展org.apache.flink.table.functions.AggregateFunction,并且实现一个(或者多个)accumulate 方法。accumulate 方法可以重载,每个方法的参数类型不同,并且支持变长参数。
示例:自定义聚合函数,求平均值
package com.hjt.yxh.hw.tableapitest.udf
import com.hjt.yxh.hw.apitest.SensorReading
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._
import org.apache.flink.table.api.bridge.scala._
import org.apache.flink.table.api._
import org.apache.flink.table.functions.AggregateFunction
import org.apache.flink.table.planner.{JDouble, JInt}
class AvgAcc {
var sum: JDouble = 0.00
var count: JInt = 0
}
class MyAvgFunction extends AggregateFunction[JDouble, AvgAcc] {
override def getValue(accumulator: AvgAcc): JDouble = {
accumulator.sum / accumulator.count
}
override def createAccumulator(): AvgAcc = {
new AvgAcc
}
def accumulate(accumulator: AvgAcc, temperature: JDouble): Unit = {
accumulator.count += 1
accumulator.sum += temperature
}
}
object AggUDFTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val tableSettings =
EnvironmentSettings.newInstance().inBatchMode().build()
val tableEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env, tableSettings)
val inputPath =
"D:\\LearnWorkSpace\\FlinkDemo\\src\\main\\resources\\Data\\sensor.txt"
val dataStream = env
.readTextFile(inputPath)
.filter(_.nonEmpty)
.map(data => {
val arr = data.split(",")
SensorReading(arr(0), arr(1).toLong, arr(2).toDouble)
})
//创建表
val inputTable = tableEnv.fromDataStream(
dataStream,
Schema
.newBuilder()
.column("id", DataTypes.STRING())
.column("timestamp", DataTypes.BIGINT())
.column("temperature", DataTypes.DOUBLE())
.columnByExpression(
"rowtime",
"CAST(TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(`timestamp`)) AS TIMESTAMP(3))")
.watermark("rowtime", "rowtime - INTERVAL '5' SECOND")
.build()
)
//注册表
tableEnv.createTemporaryView("sensor", inputTable)
//注册自定义函数
tableEnv.createTemporaryFunction("myAvg", new MyAvgFunction)
//使用自定义函数
val result1 = inputTable
.groupBy($"id")
.aggregate(call("myAvg", $"temperature") as "avg_temperature")
.select($"id", $"avg_temperature")
tableEnv.toDataStream(result1).print("table")
//SQL中使用
val result2 = tableEnv.sqlQuery("""
|SELECT
| id,
| myAvg(temperature) as avg_temperature
|FROM sensor group by id
""".stripMargin)
tableEnv.toDataStream(result2).print("sql")
env.execute("UDF Test")
}
}
表值聚合函数 TableAggregateFunction
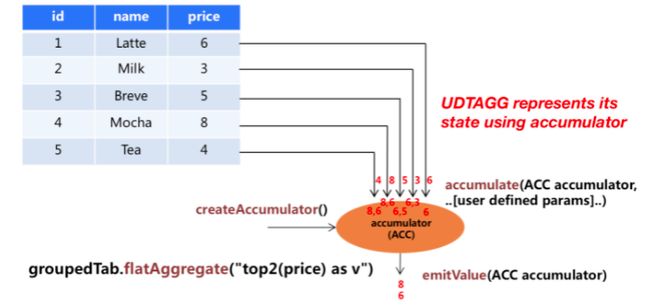
自定义表值聚合函数(UDTAGG)可以把一个表(一行或者多行,每行有一列或者多列)聚合成另一张表,结果中可以有多行多列。
上图展示了一个表值聚合函数的例子。假设你有一个饮料的表,这个表有 3 列,分别是 id、name 和 price,一共有 5行。假设你需要找到价格最高的两个饮料,类似于 top2()表值聚合函数。你需要遍历所有 5 行数据,结果是有 2 行数据的一个表。
用户自定义表值聚合函数是通过扩展 TableAggregateFunction 类来实现的。一个 TableAggregateFunction 的工作过程如下。首先,它需要一个 accumulator,这个 accumulator 负责存储聚合的中间结果。 通过调用 TableAggregateFunction 的 createAccumulator 方法来构造一个空的accumulator。接下来,对于每一行数据,会调用 accumulate 方法来更新 accumulator。当所有数据都处理完之后,调用 emitValue 方法来计算和返回最终的结果。
下面几个 TableAggregateFunction 的方法是必须要实现的:
- createAccumulator()
- accumulate()
Flink 的类型推导在遇到复杂类型的时候可能会推导出错误的结果,比如那些非基本类型和普通的 POJO 类型的复杂类型。所以类似于 ScalarFunction 和TableFunction,TableAggregateFunction 也提供了TableAggregateFunction#getResultType() 和TableAggregateFunction#getAccumulatorType() 方法来指定返回值类型和accumulator 的类型,这两个方法都需要返回 TypeInformation。
除了上面的方法,还有几个其他的方法可以选择性的实现。有些方法可以让查询更加高效,而有些方法对于某些特定场景是必须要实现的。比如,在会话窗口(当两个会话窗口合并时会合并两个 accumulator)中使用聚合函数时,必须要实现merge() 方法。
下面几个 TableAggregateFunction 的方法在某些特定场景下是必须要实现的:
- retract() 在 bounded OVER 窗口中的聚合函数必须要实现。
- merge() 在许多批式聚合和以及流式会话和滑动窗口聚合中是必须要实现的。
- resetAccumulator() 在许多批式聚合中是必须要实现的。
- emitValue() 在批式聚合以及窗口聚合中是必须要实现的。
下面的 TableAggregateFunction 的方法可以提升流式任务的效率:
emitUpdateWithRetract() 在 retract 模式下,该方法负责发送被更新的值。
emitValue 方法会发送所有 accumulator 给出的结果。拿 TopN 来说,emitValue 每次都会发送所有的最大的 n 个值。这在流式任务中可能会有一些性能问题。为了提升性能,用户可以实现 emitUpdateWithRetract 方法。这个方法在 retract 模式下会增量的输出结果,比如有数据更新了,我们必须要撤回老的数据,然后再发送新的数据。如果定义了 emitUpdateWithRetract 方法,那它会优先于 emitValue 方法被使用,因为一般认为 emitUpdateWithRetract 会更加高效,因为它的输出是增量的。
TableAggregateFunction 的所有方法都必须是 public 的、非 static 的,而且名字必须跟上面提到的一样。createAccumulator、getResultType 和 getAccumulatorType 这三个方法是在抽象父类 TableAggregateFunction 中定义的,而其他的方法都是约定的方法。要实现一个表值聚合函数,你必须扩展 org.apache.flink.table.functions.TableAggregateFunction,并且实现一个(或者多个)accumulate 方法。accumulate 方法可以有多个重载的方法,也可以支持变长参数。
示例:实现top-2 表值聚合函数
package com.hjt.yxh.hw.tableapitest.udf
import com.hjt.yxh.hw.apitest.SensorReading
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._
import org.apache.flink.table.annotation.{DataTypeHint, FunctionHint}
import org.apache.flink.table.api.bridge.scala.StreamTableEnvironment
import org.apache.flink.table.api._
import org.apache.flink.table.functions.TableAggregateFunction
import org.apache.flink.table.planner.JDouble
import org.apache.flink.types.Row
import org.apache.flink.util.Collector
class Top2Acc {
var first: JDouble = Double.MinValue
var second: JDouble = Double.MinValue
}
//提取所有温度中温度值最高的两个温度,
@FunctionHint(output = new DataTypeHint("ROW" ))
class Top2AggFunction extends TableAggregateFunction[Row, Top2Acc] {
override def createAccumulator(): Top2Acc = {
new Top2Acc
}
def accumulate(acc: Top2Acc, temperature: JDouble): Unit = {
if (temperature > acc.first) {
acc.second = acc.first
acc.first = temperature
} else if (temperature > acc.second) {
acc.second = temperature
}
}
def emitValue(acc: Top2Acc, out: Collector[Row]): Unit = {
out.collect(Row.of(acc.first, Int.box(1)))
out.collect(Row.of(acc.second, Int.box(2)))
}
}
object TableUAggTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val tableSettings =
EnvironmentSettings
.newInstance()
.inStreamingMode()
.build()
val tableEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env, tableSettings)
val inputPath =
"D:\\LearnWorkSpace\\FlinkDemo\\src\\main\\resources\\Data\\sensor.txt"
val dataStream = env
.readTextFile(inputPath)
.filter(_.nonEmpty)
.map(data => {
val arr = data.split(",")
SensorReading(arr(0), arr(1).toLong, arr(2).toDouble)
})
//创建表
val inputTable = tableEnv.fromDataStream(
dataStream,
Schema
.newBuilder()
.column("id", DataTypes.STRING())
.column("timestamp", DataTypes.BIGINT())
.column("temperature", DataTypes.DOUBLE().notNull())
.columnByExpression(
"rowtime",
"CAST(TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(`timestamp`)) AS TIMESTAMP(3))")
.watermark("rowtime", "rowtime - INTERVAL '5' SECOND")
.build()
)
//注册表
tableEnv.createTemporaryView("sensor", inputTable)
//注册自定义函数
tableEnv.createTemporaryFunction("myTop2", new Top2AggFunction)
//使用自定义函数
val result1 = inputTable
.groupBy($"id")
.flatAggregate(call("myTop2", $"temperature"))
.select($"id", $"tempera", $"rank")
tableEnv.toRetractStream[Row](result1).print("table").setParallelism(1)
env.execute("UDF Test")
}
}