CompletableFuture使用方法详细说明
异步执行一个任务时,我们一般是使用自定义的线程池Executor去创建执行的。如果不需要有返回值, 任务实现Runnable接口;如果需要有返回值,任务实现Callable接口,调用Executor的submit方法,再使用Future获取即可。
如果多个线程存在前后依赖的话,我们怎么处理呢?可使用同步组件CountDownLatch、CyclicBarrier等,但是比较麻烦。
其实还有比较简单的方法, 那就是使用CompeletableFuture。

本文涉及知识点,参考了这里
1.回顾Future
因为CompletableFuture实现了Future接口,我们先来回顾Future吧。
Future是Java5新加的一个接口,它提供了一种异步并行计算的功能。
如果主线程需要执行一个很耗时的计算任务,我们就可以通过future把这个任务放到异步线程中执行。
主线程继续处理其他任务,处理完成后,再通过Future获取计算结果。
来看个简单例子吧,假设我们有两个任务服务(模拟实际业务),一个获取当前时间,一个是获取用户名。如下:
/**
* @author jiangkd
* @date 2022/8/25 16:37:45
*/
@Service
public class DateService {
/**
* 模拟接口调用
*
* @return value
*/
public String getDate() {
// 模拟处理
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "现在的时间是" + DateUtil.now();
}
}
/**
* @author jiangkd
* @date 2022/8/25 16:37:57
*/
@Service
public class UserService {
/**
* 模拟接口调用
*
* @return value
*/
public String getName() {
// 模拟处理
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "Tom";
}
}
接下来,我们来演示下,在主线程中是如何使用Future来进行异步调用的。
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = DemoExampleSpringbootApplication.class)
public class FutureTest {
@Resource
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Resource
DateService dateService;
@Resource
UserService userService;
/**
* 使用Future来进行异步调用的
*/
@Test
public void test() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
//
final StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
// getDate
final Future getDateFutureTask = threadPoolTaskExecutor.submit(() -> dateService.getDate());
//模拟主线程其它操作耗时
Thread.sleep(2000);
// getName
final Future getNameFutureTask = threadPoolTaskExecutor.submit(() -> userService.getName());
// 获取两个线程执行的结果
final String getDate = getDateFutureTask.get(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
final String getName = getNameFutureTask.get();
stopWatch.stop();
log.info("date:{}", getDate);
log.info("name:{}", getName);
//
log.info(stopWatch.prettyPrint());
}
}
运行结果:
2022-08-25 16:50:36.968 INFO 21692 --- [ main] example.demo.jiangkd.thread.FutureTest : date:现在的时间是2022-08-25 16:50:36
2022-08-25 16:50:36.970 INFO 21692 --- [ main] example.demo.jiangkd.thread.FutureTest : name:Tom
2022-08-25 16:50:36.970 INFO 21692 --- [ main] example.demo.jiangkd.thread.FutureTest : StopWatch '': running time (millis) = 3048
-----------------------------------------
ms % Task name
-----------------------------------------
03048 100%
如果我们不使用Future进行并行异步调用,而是在主线程串行进行的话,耗时大约为3000+2000+1000 = 6000ms左右。可以发现,future+线程池异步配合,提高了程序的执行效率。
注意: 代码中的 threadPoolTaskExecutor 是我自己定义的线程池。 详情请参考 ThreadPoolTaskExecutor线程池创建
这里有个注意点, 代码中 getDataFutureTask.get(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS) 并没有报出TimeoutException, getDate方法中睡眠了3s, 这里get的时候, 如果超过2s线程没有结束, 是要报错的, 那么为什么没有报错呢? 因为主线程中我们 Thread.sleep(2000) 睡眠了2s, 此时getDataFutureTask的线程已经开始执行了, 睡眠2s后才进行get阻塞, 此时只等待了大概1s左右的时间线程就执行完了, 所以没有报错, 如果把 Thread.sleep(2000) 注释掉, 就会报错了, 可以自行试一试。
但是Future对于结果的获取,不是很友好,只能通过阻塞或者轮询的方式得到任务的结果。
- Future.get() 就是阻塞调用,在线程获取结果之前get方法会一直阻塞。
- Future提供了一个isDone方法,可以在程序中轮询这个方法查询执行结果。
阻塞的方式和异步编程的设计理念相违背,而轮询的方式会耗费无谓的CPU资源。因此,JDK8设计出CompletableFuture。CompletableFuture提供了一种观察者模式类似的机制,可以让任务执行完成后通知监听的一方。
2.走进CompletableFuture
我们还是基于以上Future的例子,改用CompletableFuture 来实现
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = DemoExampleSpringbootApplication.class)
public class CompletableFutureTest {
@Resource
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Resource
DateService dateService;
@Resource
UserService userService;
/**
* 基于FutureTest中的方法test的例子,改用CompletableFuture 来实现
*
* @throws InterruptedException e
* @throws ExecutionException e
* @throws TimeoutException e
*/
@Test
public void test() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
//
final StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
// getDate
final CompletableFuture getDateCompletableFuture =
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> dateService.getDate(), threadPoolTaskExecutor);
//模拟主线程其它操作耗时
Thread.sleep(2000);
// getName
final CompletableFuture getNameCompletableFuture =
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> userService.getName(), threadPoolTaskExecutor);
// 获取两个线程执行的结果
final String getDate = getDateCompletableFuture.get(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
final String getName = getNameCompletableFuture.get();
stopWatch.stop();
log.info("date:{}", getDate);
log.info("name:{}", getName);
//
log.info(stopWatch.prettyPrint());
}
}
可以发现,使用CompletableFuture,并没有让代码简洁多少,这里都是用了lambda表达式进行简化,更多CompletableFuture的使用继续往下看就行。
CompletableFuture的supplyAsync方法,提供了异步执行的功能,如果第二个参数不传的话,线程池也不用单独创建了。实际上,CompletableFuture使用了默认线程池是ForkJoinPool.commonPool。
CompletableFuture提供了几十种方法,辅助我们的异步任务场景。这些方法包括创建异步任务、任务异步回调、多个任务组合处理等方面。我们一起来学习吧
3.CompletableFuture的使用场景
3.1.创建异步任务
CompletableFuture创建异步任务,一般有supplyAsync和runAsync两个方法

- supplyAsync: 执行CompletableFuture任务,支持返回值。
- runAsync: 执行CompletableFuture任务,没有返回值。
3.1.1.supplyAsync方法
// 使用默认内置线程池ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根据supplier构建执行任务
public static CompletableFuture supplyAsync(Supplier supplier)
// 自定义线程,根据supplier构建执行任务
public static CompletableFuture supplyAsync(Supplier supplier, Executor executor)
示例代码如下:
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = DemoExampleSpringbootApplication.class)
public class SupplyAsyncTest {
@Resource
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Resource
DateService dateService;
@Resource
UserService userService;
/**
* 自定义线程,根据runnable构建执行任务
*/
@Test
public void test() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 使用自定义线程池, 线程中打印线程名称
final CompletableFuture completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("执行线程, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
return dateService.getDate();
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor);
// 使用默认的线程池, 线程中打印线程名称
final CompletableFuture completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("执行线程, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
return userService.getName();
});
// 分别获取两个线程的返回值
final String date = completableFuture1.get();
log.info("getDate:{}", date);
final String name = completableFuture2.get();
log.info("getName:{}", name);
}
}
运行结果
2022-08-27 08:54:06.444 INFO 5968 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.c.SupplyAsyncTest : 执行线程, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 08:54:06.445 INFO 5968 --- [onPool-worker-9] e.d.j.t.c.SupplyAsyncTest : 执行线程, 线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
2022-08-27 08:54:09.506 INFO 5968 --- [ main] e.d.j.t.c.SupplyAsyncTest : getDate:现在的时间是2022-08-27 08:54:09
2022-08-27 08:54:09.507 INFO 5968 --- [ main] e.d.j.t.c.SupplyAsyncTest : getName:Tom
通过运行结果发现, 两个线程执行打印的线程名称是不同的, 第一个getDate的线程使用的是我们自己定义的线程池, 自定义的线程池的线程前缀是demo-example-task-, 而第二个getName的线程使用的就是默认的内置线程池ForkJoinPool.commonPool()。
再说一遍, 自定义的线程池参考 ThreadPoolTaskExecutor线程池创建。
运行结果中也打印出了两个线程的返回结果。
3.1.2.runAsync方法
// 使用默认内置线程池ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根据runnable构建执行任务
public static CompletableFuture runAsync(Runnable runnable)
// 自定义线程,根据runnable构建执行任务
public static CompletableFuture runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)

从上图看出, 如果此时使用了runAsync方法, 线程中不可以用return返回值, 否则会报错。
示例代码如下:
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = DemoExampleSpringbootApplication.class)
public class RunAsyncTest {
@Resource
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Resource
DateService dateService;
@Resource
UserService userService;
@Test
public void test() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 使用自定义线程池, 线程中打印线程名称
final CompletableFuture completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
log.info("执行线程, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
dateService.getDate();
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor);
// 使用默认的线程池, 线程中打印线程名称
final CompletableFuture completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
log.info("执行线程, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
userService.getName();
});
// 分别获取两个线程的返回值
final Void unused1 = completableFuture1.get();
log.info("getDate:{}", unused1);
final Void unused2 = completableFuture2.get();
log.info("getName:{}", unused2);
}
}
执行结果:
2022-08-27 09:06:06.527 INFO 30060 --- [onPool-worker-9] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.RunAsyncTest : 执行线程, 线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
2022-08-27 09:06:06.527 INFO 30060 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.RunAsyncTest : 执行线程, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 09:06:09.588 INFO 30060 --- [ main] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.RunAsyncTest : getDate:null
2022-08-27 09:06:09.588 INFO 30060 --- [ main] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.RunAsyncTest : getName:null
示例代码中我们将supplyAsync改为了runAsync方法,线程中也没有使用return(否则会报错,,如面上的截图),最后通过get方法获取两个线程的执行结果也都是null。
和supplyAsync的示例一样, getDate线程依然使用了自定义的线程池,getName使用了默认内置的, 通过执行结果可知。
细心的你有没有发现,runAsync示例中,CompletableFuture的泛型是Void,所以get方法得到的返回就是Void,Void是什么呢? java.lang.Void是void 关键字的包装类。Void类是一个不可实例化的占位符类,如果方法返回值是Void类型,那么该方法只能返回null类型。
3.2.任务异步回调
3.2.1.thenRun/thenRunAsync
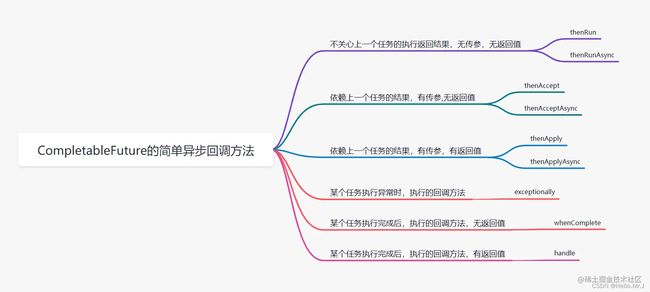
CompletableFuture的thenRun/thenRunAsync方法,通俗点讲就是,做完第一个任务后,再做第二个任务。也就是说某个任务执行完成后,执行回调方法;但是前后两个任务没有参数传递,第二个任务也没有返回值。
public CompletableFuture thenRun(Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture thenRunAsync(Runnable action);
thenRun 和thenRunAsync有什么区别呢? 可以看下源码:
private static final Executor asyncPool = useCommonPool ?
ForkJoinPool.commonPool() : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor();
public CompletableFuture thenRun(Runnable action) {
return uniRunStage(null, action);
}
public CompletableFuture thenRunAsync(Runnable action) {
return uniRunStage(asyncPool, action);
}
如果执行第一个任务的时候,没有传入自定义的线程池,那么thenRun/thenRunAsync理所当然的都是用默认内置的ForkJoin线程池,可能都是用的同一个线程。
相反如果你执行第一个任务的时候,传入了一个自定义线程池:
- 调用thenRun方法执行第二个任务时,则第二个任务和第一个任务是共用同一个线程池,所以可能用到的是同一个线程。
- 调用thenRunAsync执行第二个任务时,则第一个任务使用的是你自己传入的线程池,第二个任务使用的是ForkJoin线程池。
thenRun示例代码如下:
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = DemoExampleSpringbootApplication.class)
public class ThenRunAndThenRunAsyncTest {
@Resource
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Resource
DateService dateService;
/**
* thenRun方法测试, 链式调用, 执行supplyAsync后接着执行thenRun
*/
@Test
public void thenRunTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
/*
1.thenRun, 使用自定义线程池
*/
final CompletableFuture completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 使用了supplyAsync,返回值
return dateService.getDate();
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor).thenRun(() -> {
//
log.info("thenRun线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
final Void unused1 = completableFuture1.get();
log.info("completableFuture1返回结果:{}", unused1);
log.info("=====================================================");
/*
2.thenRun, 不使用自定义线程池
*/
final CompletableFuture completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 使用了supplyAsync,返回值
return dateService.getDate();
}).thenRun(() -> {
//
log.info("thenRun线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
final Void unused2 = completableFuture2.get();
log.info("completableFuture1返回结果:{}", unused2);
}
}
运行结果:
2022-08-27 09:42:39.668 INFO 35820 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.c.ThenRunAndThenRunAsyncTest : supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 09:42:42.725 INFO 35820 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.c.ThenRunAndThenRunAsyncTest : thenRun线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 09:42:42.725 INFO 35820 --- [ main] e.d.j.t.c.ThenRunAndThenRunAsyncTest : completableFuture1返回结果:null
2022-08-27 09:42:42.725 INFO 35820 --- [ main] e.d.j.t.c.ThenRunAndThenRunAsyncTest : =====================================================
2022-08-27 09:42:42.726 INFO 35820 --- [onPool-worker-9] e.d.j.t.c.ThenRunAndThenRunAsyncTest : supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
2022-08-27 09:42:45.738 INFO 35820 --- [onPool-worker-9] e.d.j.t.c.ThenRunAndThenRunAsyncTest : thenRun线程执行, 线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
2022-08-27 09:42:45.738 INFO 35820 --- [ main] e.d.j.t.c.ThenRunAndThenRunAsyncTest : completableFuture1返回结果:null
thenRunAsync示例代码如下:
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = DemoExampleSpringbootApplication.class)
public class ThenRunAndThenRunAsyncTest {
@Resource
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Resource
DateService dateService;
/**
* thenRunAsync方法测试, 链式调用, 执行supplyAsync后接着执行thenRunAsync
*/
@Test
public void thenRunAsyncTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
/*
1.thenRunAsync, 使用自定义线程池
*/
final CompletableFuture completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 使用了supplyAsync,返回值
return dateService.getDate();
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor).thenRunAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("thenRunAsync线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
final Void unused1 = completableFuture1.get();
log.info("completableFuture1返回结果:{}", unused1);
log.info("=====================================================");
/*
2.thenRunAsync, 不使用自定义线程池
*/
final CompletableFuture completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 使用了supplyAsync,返回值
return dateService.getDate();
}).thenRunAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("thenRunAsync线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
final Void unused2 = completableFuture2.get();
log.info("completableFuture1返回结果:{}", unused2);
}
}
执行结果
2022-08-27 09:48:03.013 INFO 776 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.c.ThenRunAndThenRunAsyncTest : supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 09:48:06.078 INFO 776 --- [onPool-worker-9] e.d.j.t.c.ThenRunAndThenRunAsyncTest : thenRunAsync线程执行, 线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
2022-08-27 09:48:06.078 INFO 776 --- [ main] e.d.j.t.c.ThenRunAndThenRunAsyncTest : completableFuture1返回结果:null
2022-08-27 09:48:06.078 INFO 776 --- [ main] e.d.j.t.c.ThenRunAndThenRunAsyncTest : =====================================================
2022-08-27 09:48:06.078 INFO 776 --- [onPool-worker-9] e.d.j.t.c.ThenRunAndThenRunAsyncTest : supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
2022-08-27 09:48:09.090 INFO 776 --- [onPool-worker-9] e.d.j.t.c.ThenRunAndThenRunAsyncTest : thenRunAsync线程执行, 线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
2022-08-27 09:48:09.090 INFO 776 --- [ main] e.d.j.t.c.ThenRunAndThenRunAsyncTest : completableFuture1返回结果:null
注意:后面介绍的thenAccept和thenAcceptAsync,thenApply和thenApplyAsync等,它们之间的区别也和thenRun和thenRunAsync相同。
3.2.2.thenAccept/thenAcceptAsync
CompletableFuture的thenAccept/thenAcceptAsync方法表示,第一个任务执行完成后,执行第二个回调方法任务,但是会将第一个任务的执行结果,作为入参,传递到回调方法中,但是回调方法是没有返回值的。
示例代码如下:
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = DemoExampleSpringbootApplication.class)
public class ThenAcceptAndThenAcceptAsyncTest {
@Resource
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Resource
DateService dateService;
/**
* thenAccept
*/
@Test
public void thenAcceptTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//
final CompletableFuture completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
final String date = dateService.getDate();
log.info("supplyAsync线程执行, 返回值:{}", date);
return date;
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor).thenAccept((value) -> {
//
log.info("thenAccept线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
log.info("thenAccept线程执行, 获取supplyAsync线程的返回值:{}", value);
});
final Void unused = completableFuture.get();
log.info("返回结果:{}", unused);
}
/**
* thenAcceptAsync
*/
@Test
public void thenAcceptAsyncTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//
final CompletableFuture completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
final String date = dateService.getDate();
log.info("supplyAsync线程执行, 返回值:{}", date);
return date;
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor).thenAcceptAsync((value) -> {
//
log.info("thenAcceptAsync线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
log.info("thenAcceptAsync线程执行, 获取supplyAsync线程的返回值:{}", value);
});
final Void unused = completableFuture.get();
log.info("返回结果:{}", unused);
}
}
thenAcceptTest执行结果:
2022-08-27 10:05:40.741 INFO 37528 --- [-example-task-1] d.j.t.c.ThenAcceptAndThenAcceptAsyncTest : supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 10:05:43.793 INFO 37528 --- [-example-task-1] d.j.t.c.ThenAcceptAndThenAcceptAsyncTest : supplyAsync线程执行, 返回值:现在的时间是2022-08-27 10:05:43
2022-08-27 10:05:43.803 INFO 37528 --- [-example-task-1] d.j.t.c.ThenAcceptAndThenAcceptAsyncTest : thenAccept线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 10:05:43.803 INFO 37528 --- [-example-task-1] d.j.t.c.ThenAcceptAndThenAcceptAsyncTest : thenAccept线程执行, 获取supplyAsync线程的返回值:现在的时间是2022-08-27 10:05:43
2022-08-27 10:05:43.803 INFO 37528 --- [ main] d.j.t.c.ThenAcceptAndThenAcceptAsyncTest : 返回结果:null
thenAcceptAsyncTest执行结果
2022-08-27 10:06:55.593 INFO 20144 --- [-example-task-1] d.j.t.c.ThenAcceptAndThenAcceptAsyncTest : supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 10:06:58.641 INFO 20144 --- [-example-task-1] d.j.t.c.ThenAcceptAndThenAcceptAsyncTest : supplyAsync线程执行, 返回值:现在的时间是2022-08-27 10:06:58
2022-08-27 10:06:58.641 INFO 20144 --- [onPool-worker-9] d.j.t.c.ThenAcceptAndThenAcceptAsyncTest : thenAcceptAsync线程执行, 线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
2022-08-27 10:06:58.641 INFO 20144 --- [onPool-worker-9] d.j.t.c.ThenAcceptAndThenAcceptAsyncTest : thenAcceptAsync线程执行, 获取supplyAsync线程的返回值:现在的时间是2022-08-27 10:06:58
2022-08-27 10:06:58.641 INFO 20144 --- [ main] d.j.t.c.ThenAcceptAndThenAcceptAsyncTest : 返回结果:null
3.2.3. thenApply/thenApplyAsync
CompletableFuture的thenApply/thenApplyAsync方法表示,第一个任务执行完成后,执行第二个回调方法任务,但是会将第一个任务的执行结果,作为入参,传递到回调方法中,并且回调方法是有返回值的。
示例代码如下:
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = DemoExampleSpringbootApplication.class)
public class ThenApplyAndThenApplyAsyncTest {
@Resource
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Resource
UserService userService;
/**
* thenApply
*/
@Test
public void thenApplyTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//
final CompletableFuture completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
final String name = userService.getName();
log.info("supplyAsync线程执行, 返回值:{}", name);
return name;
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor).thenApply((value) -> {
//
log.info("thenApply线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
log.info("thenApply线程执行, 获取supplyAsync线程的返回值:{}", value);
return "thenApply返回, value是supplyAsync的结果, " + value;
});
final String name = completableFuture.get();
log.info("返回结果:{}", name);
}
/**
* thenApplyAsync
*/
@Test
public void thenApplyAsyncTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//
final CompletableFuture completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
final String name = userService.getName();
log.info("supplyAsync线程执行, 返回值:{}", name);
return name;
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor).thenApplyAsync((value) -> {
//
log.info("thenApplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
log.info("thenApplyAsync线程执行, 获取supplyAsync线程的返回值:{}", value);
return "thenApplyAsync返回, value是supplyAsync的结果, " + value;
});
final String name = completableFuture.get();
log.info("返回结果:{}", name);
}
}
thenApplyTest的执行结果:
2022-08-27 10:14:16.608 INFO 38224 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.c.ThenApplyAndThenApplyAsyncTest : supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 10:14:17.618 INFO 38224 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.c.ThenApplyAndThenApplyAsyncTest : supplyAsync线程执行, 返回值:Tom
2022-08-27 10:14:17.618 INFO 38224 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.c.ThenApplyAndThenApplyAsyncTest : thenApply线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 10:14:17.618 INFO 38224 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.c.ThenApplyAndThenApplyAsyncTest : thenApply线程执行, 获取supplyAsync线程的返回值:Tom
2022-08-27 10:14:17.619 INFO 38224 --- [ main] e.d.j.t.c.ThenApplyAndThenApplyAsyncTest : 返回结果:thenApply返回, value是supplyAsync的结果, Tom
thenApplyAsyncTest的执行结果:
2022-08-27 10:14:35.846 INFO 47200 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.c.ThenApplyAndThenApplyAsyncTest : supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 10:14:36.859 INFO 47200 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.c.ThenApplyAndThenApplyAsyncTest : supplyAsync线程执行, 返回值:Tom
2022-08-27 10:14:36.860 INFO 47200 --- [onPool-worker-9] e.d.j.t.c.ThenApplyAndThenApplyAsyncTest : thenApplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
2022-08-27 10:14:36.861 INFO 47200 --- [onPool-worker-9] e.d.j.t.c.ThenApplyAndThenApplyAsyncTest : thenApplyAsync线程执行, 获取supplyAsync线程的返回值:Tom
2022-08-27 10:14:36.861 INFO 47200 --- [ main] e.d.j.t.c.ThenApplyAndThenApplyAsyncTest : 返回结果:thenApplyAsync返回, value是supplyAsync的结果, Tom
3.2.4.exceptionally
CompletableFuture的exceptionally方法表示,某个任务执行异常时,执行的回调处理方法,并且有抛出异常作为参数,传递到回调方法,回调方法有返回值。
示例代码如下:
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = DemoExampleSpringbootApplication.class)
public class ExceptionallyTest {
@Resource
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Resource
UserService userService;
/**
* exceptionally
*/
@Test
public void exceptionallyTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//
final CompletableFuture completedFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 异常触发
int i = 1 / 0;
return userService.getName();
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor).exceptionally((e) -> {
log.info("exceptionally线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
log.error("exceptionally线程执行, 得到supplyAsync中的异常堆栈信息", e);
return "exceptionally得到supplyAsync的异常信息, " + e.getMessage();
});
final String value = completedFuture.get();
log.info("返回值:{}", value);
}
}
执行结果如下:
2022-08-27 10:21:44.440 INFO 44716 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.c.ExceptionallyTest : supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 10:21:44.440 INFO 44716 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.c.ExceptionallyTest : exceptionally线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 10:21:44.444 ERROR 44716 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.c.ExceptionallyTest : exceptionally线程执行, 得到supplyAsync中的异常堆栈信息
java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.encodeThrowable(CompletableFuture.java:273) ~[na:1.8.0_151]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.completeThrowable(CompletableFuture.java:280) ~[na:1.8.0_151]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture$AsyncSupply.run(CompletableFuture.java:1592) ~[na:1.8.0_151]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1149) ~[na:1.8.0_151]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:624) ~[na:1.8.0_151]
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748) ~[na:1.8.0_151]
Caused by: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at example.demo.jiangkd.thread.completablefuture.ExceptionallyTest.lambda$exceptionallyTest$0(ExceptionallyTest.java:45) ~[test-classes/:na]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture$AsyncSupply.run(CompletableFuture.java:1590) ~[na:1.8.0_151]
... 3 common frames omitted
2022-08-27 10:21:44.444 INFO 44716 --- [ main] e.d.j.t.c.ExceptionallyTest : 返回值:exceptionally得到supplyAsync的异常信息, java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
3.2.5.whenComplete
CompletableFuture的whenComplete方法表示,某个任务执行完成后,执行的回调方法,并且任务结果作为回调方法的入参,回调方法无返回值,并且whenComplete方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是第一个任务的结果。
示例代码如下:
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = DemoExampleSpringbootApplication.class)
public class WhenCompleteTest {
@Resource
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Resource
UserService userService;
@Test
public void whenCompleteTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//
final CompletableFuture completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
return userService.getName();
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor).whenComplete((value, throwable) -> {
//
log.info("whenComplete线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
log.info("whenComplete线程执行, 得到supplyAsync的返回结果:{}", value);
});
// 得到的value是supplyAsync的结果
final String value = completableFuture.get();
log.info("返回结果:{}", value);
}
}
执行结果:
2022-08-27 10:30:58.969 INFO 47592 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.c.WhenCompleteTest : supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 10:30:59.981 INFO 47592 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.c.WhenCompleteTest : whenComplete线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 10:30:59.981 INFO 47592 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.c.WhenCompleteTest : whenComplete线程执行, 得到supplyAsync的返回结果:Tom
2022-08-27 10:30:59.982 INFO 47592 --- [ main] e.d.j.t.c.WhenCompleteTest : 返回结果:Tom
3.2.6.handle
CompletableFuture的handle方法表示,某个任务执行完成后,执行回调方法,并且任务结果作为回调方法的入参,回调方法是有返回值的,并且handle方法返回的CompletableFuture的result就是回调方法执行的结果。
示例代码:
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = DemoExampleSpringbootApplication.class)
public class HandleTest {
@Resource
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Resource
UserService userService;
@Test
public void handleTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//
final CompletableFuture completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
return userService.getName();
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor).handle((value, throwable) -> {
//
log.info("handle线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
log.info("handle线程执行, 得到supplyAsync的返回结果:{}", value);
return "handle的返回结果" + value;
});
// 得到的value是handle的结果
final String value = completableFuture.get();
log.info("返回结果:{}", value);
}
}
执行结果:
2022-08-27 10:35:50.796 INFO 41200 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.HandleTest : supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 10:35:51.812 INFO 41200 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.HandleTest : handle线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 10:35:51.813 INFO 41200 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.HandleTest : handle线程执行, 得到supplyAsync的返回结果:Tom
2022-08-27 10:35:51.813 INFO 41200 --- [ main] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.HandleTest : 返回结果:handle的返回结果Tom
3.3.多个任务组合处理
3.3.1.AND组合关系
thenCombine/thenCombineAsync、thenAcceptBoth/thenAcceptBothAsync、runAfterBoth/runAfterBothAsync都表示:将两个CompletableFuture组合起来,只有这两个都正常执行完了,才会执行某个指定任务。
区别在于:
- thenCombine/thenCombineAsync:会将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,传递到指定任务中,且指定方法有返回值。
- thenAcceptBoth/thenAcceptBothAsync:会将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,传递到指定任务中,且指定方法无返回值。
- runAfterBoth/runAfterBothAsync:不会把执行结果当做任务方法入参,也就是指定任务没有入参,且没有返回值。
thenCombine/thenCombineAsync示例代码:
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = DemoExampleSpringbootApplication.class)
public class AndTest {
@Resource
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Resource
DateService dateService;
@Resource
UserService userService;
/**
* thenCombine/thenCombineAsync
*
* 会将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,传递到指定任务中,且指定方法有返回值。
*/
@Test
public void thenCombineAndThenCombineAsyncTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//
final CompletableFuture dateCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync getDate线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 第一个CompletableFuture的返回
return dateService.getDate();
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor);
//
final CompletableFuture completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync getName线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 第二个CompletableFuture的返回
return userService.getName();
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor).thenCombine(dateCompletableFuture, (nameValue, dateValue) -> {
//
log.info("thenCombine线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
log.info("第一个CompletableFuture的执行结果:{}", dateValue);
log.info("第二个CompletableFuture的执行结果:{}", nameValue);
return "两个异步任务的组合结果";
});
final String value = completableFuture.get();
log.info("返回结果:{}", value);
}
}
thenCombine/thenCombineAsync执行结果:
2022-08-27 11:02:59.442 INFO 39580 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.AndTest : supplyAsync getDate线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 11:02:59.442 INFO 39580 --- [-example-task-2] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.AndTest : supplyAsync getName线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-2
2022-08-27 11:03:02.502 INFO 39580 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.AndTest : thenCombine线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 11:03:02.502 INFO 39580 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.AndTest : 第一个CompletableFuture的执行结果:现在的时间是2022-08-27 11:03:02
2022-08-27 11:03:02.502 INFO 39580 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.AndTest : 第二个CompletableFuture的执行结果:Tom
2022-08-27 11:03:02.502 INFO 39580 --- [ main] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.AndTest : 返回结果:两个异步任务的组合结果
注意:示例代码中thenCombine的参数中,第一个参数是执行的第一个CompletableFuture异步任务对象,第二个参数是BiFunction对象,BiFunction的两个入参就是两个CompletableFuture的执行结果,第一个入参是第二个CompletableFuture的结果,第二个入参是第一个CompletableFuture(也就是代码中的dateCompletableFuture)的结果。
thenAcceptBoth/thenAcceptBothAsync示例代码如下:
/**
* thenAcceptBoth/thenAcceptBothAsync
*
* 会将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,传递到指定任务中,且指定方法无返回值。
*/
@Test
public void thenAcceptBothAndthenAcceptBothAsyncTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//
final CompletableFuture dateCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync getDate线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 第一个CompletableFuture的返回
return dateService.getDate();
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor);
//
final CompletableFuture completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync getName线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 第二个CompletableFuture的返回
return userService.getName();
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor).thenAcceptBoth(dateCompletableFuture, (nameValue, dateValue) -> {
//
log.info("thenCombine线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
log.info("第一个CompletableFuture的执行结果:{}", dateValue);
log.info("第二个CompletableFuture的执行结果:{}", nameValue);
log.info("两个异步任务的组合结果");
});
final Void unused = completableFuture.get();
log.info("返回结果:{}", unused);
}
thenAcceptBoth/thenAcceptBothAsync执行结果:
2022-08-27 11:12:34.153 INFO 35832 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.AndTest : supplyAsync getDate线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 11:12:34.153 INFO 35832 --- [-example-task-2] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.AndTest : supplyAsync getName线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-2
2022-08-27 11:12:37.202 INFO 35832 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.AndTest : thenCombine线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 11:12:37.202 INFO 35832 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.AndTest : 第一个CompletableFuture的执行结果:现在的时间是2022-08-27 11:12:37
2022-08-27 11:12:37.202 INFO 35832 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.AndTest : 第二个CompletableFuture的执行结果:Tom
2022-08-27 11:12:37.202 INFO 35832 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.AndTest : 两个异步任务的组合结果
2022-08-27 11:12:37.202 INFO 35832 --- [ main] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.AndTest : 返回结果:null
runAfterBoth/runAfterBothAsync的示例代码如下:
/**
* runAfterBoth/runAfterBothAsync
*
* 不会把执行结果当做任务方法入参,也就是指定任务没有入参,且没有返回值。
*/
@Test
public void runAfterBothAndRunAfterBothAsyncTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//
final CompletableFuture dateCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync getDate线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 第一个CompletableFuture的返回
return dateService.getDate();
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor);
//
final CompletableFuture completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync getName线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 第二个CompletableFuture的返回
return userService.getName();
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor).runAfterBoth(dateCompletableFuture, () -> {
//
log.info("thenCombine线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
log.info("两个异步任务的组合结果");
});
final Void unused = completableFuture.get();
log.info("返回结果:{}", unused);
}
runAfterBoth/runAfterBothAsync的执行结果
2022-08-27 11:15:25.858 INFO 19876 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.AndTest : supplyAsync getDate线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 11:15:25.858 INFO 19876 --- [-example-task-2] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.AndTest : supplyAsync getName线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-2
2022-08-27 11:15:28.924 INFO 19876 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.AndTest : thenCombine线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 11:15:28.924 INFO 19876 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.AndTest : 两个异步任务的组合结果
2022-08-27 11:15:28.924 INFO 19876 --- [ main] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.AndTest : 返回结果:null
3.3.2.OR 组合的关系
applyToEither/applyToEitherAsync、acceptEither/acceptEitherAsync、runAfterEither/runAfterEitherAsync 都表示:将两个CompletableFuture组合起来,只要其中一个执行完了,就会执行某个指定任务。
区别在于
- applyToEither/applyToEitherAsync:会将已经执行完成的任务的结果,作为方法入参,传递到指定任务中,且指定任务有返回值。
- acceptEither/acceptEitherAsync:会将已经执行完成的任务的结果,作为方法入参,传递到指定任务中,且指定任务无返回值。
- runAfterEither/runAfterEitherAsync:不会把执行结果当做指定任务的入参,且指定任务没有返回值。
applyToEither/applyToEitherAsync的示例代码如下:
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = DemoExampleSpringbootApplication.class)
public class OrTest {
@Resource
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Resource
DateService dateService;
@Resource
UserService userService;
/**
* applyToEither/applyToEitherAsync
*/
@Test
public void applyToEitherAndApplyToEitherTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//
final CompletableFuture dateCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync getDate线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 第一个CompletableFuture的返回
return dateService.getDate();
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor);
//
final CompletableFuture completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync getName线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 第二个CompletableFuture的返回
return userService.getName();
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor).applyToEither(dateCompletableFuture, value-> {
//
log.info("applyToEither线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
log.info("获取到某个CompletableFuture的执行结果:{}", value);
return "获取到先执行完的CompletableFuture的结果";
});
final String value = completableFuture.get();
log.info("返回结果:{}", value);
}
}
applyToEither/applyToEitherAsync执行结果
2022-08-27 11:26:50.093 INFO 49780 --- [-example-task-2] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.OrTest : supplyAsync getName线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-2
2022-08-27 11:26:50.093 INFO 49780 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.OrTest : supplyAsync getDate线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 11:26:51.110 INFO 49780 --- [-example-task-2] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.OrTest : applyToEither线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-2
2022-08-27 11:26:51.110 INFO 49780 --- [-example-task-2] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.OrTest : 获取到某个CompletableFuture的执行结果:Tom
2022-08-27 11:26:51.111 INFO 49780 --- [ main] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.OrTest : 返回结果:获取到先执行完的CompletableFuture的结果
注意:因为我们这里的DateService中的getDate方法睡眠了3s,而UserService的getName睡眠了1s, 所以每次执行一般都是getName先执行完,所以applyToEither获取到的总是第二个CompletableFuture的返回结果,你也可以改改睡眠时间试一试。
acceptEither/acceptEitherAsync的示例代码如下:
/**
* acceptEither/acceptEitherAsync
*/
@Test
public void acceptEitherAndAcceptEitherTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//
final CompletableFuture dateCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync getDate线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 第一个CompletableFuture的返回
return dateService.getDate();
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor);
//
final CompletableFuture completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync getName线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 第二个CompletableFuture的返回
return userService.getName();
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor).acceptEither(dateCompletableFuture, value-> {
//
log.info("applyToEither线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
log.info("获取到某个CompletableFuture的执行结果:{}", value);
});
final Void unused = completableFuture.get();
log.info("返回结果:{}", unused);
}
acceptEither/acceptEitherAsync执行结果:
2022-08-27 13:22:17.330 INFO 28552 --- [-example-task-2] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.OrTest : supplyAsync getName线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-2
2022-08-27 13:22:17.330 INFO 28552 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.OrTest : supplyAsync getDate线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 13:22:18.344 INFO 28552 --- [-example-task-2] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.OrTest : applyToEither线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-2
2022-08-27 13:22:18.344 INFO 28552 --- [-example-task-2] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.OrTest : 获取到某个CompletableFuture的执行结果:Tom
2022-08-27 13:22:18.345 INFO 28552 --- [ main] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.OrTest : 返回结果:null
runAfterEither/runAfterEitherAsync的示例代码如下:
/**
* runAfterEither/runAfterEitherAsync
*/
@Test
public void runAfterEitherAndRunAfterEitherTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//
final CompletableFuture dateCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync getDate线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 第一个CompletableFuture的返回
return dateService.getDate();
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor);
//
final CompletableFuture completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//
log.info("supplyAsync getName线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 第二个CompletableFuture的返回
return userService.getName();
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor).runAfterEither(dateCompletableFuture, () -> {
//
log.info("applyToEither线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
final Void unused = completableFuture.get();
log.info("返回结果:{}", unused);
}
runAfterEither/runAfterEitherAsync的执行结果:
2022-08-27 13:25:07.001 INFO 51980 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.OrTest : supplyAsync getDate线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 13:25:07.001 INFO 51980 --- [-example-task-2] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.OrTest : supplyAsync getName线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-2
2022-08-27 13:25:08.010 INFO 51980 --- [-example-task-2] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.OrTest : applyToEither线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-2
2022-08-27 13:25:08.010 INFO 51980 --- [ main] e.d.j.thread.completablefuture.OrTest : 返回结果:null
3.4.AllOf
所有任务都执行完成后,才执行 allOf返回的CompletableFuture。如果任意一个任务异常,allOf的CompletableFuture,执行get方法,会抛出异常。
和上面3.3.1.AND组合关系不同,这里的allOf方法可以是多个CompletableFuture完成后再执行某个依赖线程,而AND组合只是两个CompletableFuture。
allOf的示例代码如下:
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = DemoExampleSpringbootApplication.class)
public class AllOfTest {
@Resource
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Test
public void allOfTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//
final CompletableFuture c1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("supplyAsync1线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "completableFuture1";
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor);
//
final CompletableFuture c2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("supplyAsync2线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "completableFuture2";
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor);
//
final CompletableFuture c3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("supplyAsync3线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "completableFuture3";
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor);
final CompletableFuture completableFuture = CompletableFuture.allOf(c1, c2, c3).thenRun(() -> {
log.info("thenRun线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
log.info("c1, c2, c3全部执行完毕, 执行了thenRun线程");
});
final Void unused = completableFuture.get();
log.info("返回值:{}", unused);
}
}
执行结果
2022-08-27 13:46:57.905 INFO 50628 --- [-example-task-3] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.AllOfTest : supplyAsync3线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-3
2022-08-27 13:46:57.905 INFO 50628 --- [-example-task-2] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.AllOfTest : supplyAsync2线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-2
2022-08-27 13:46:57.905 INFO 50628 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.AllOfTest : supplyAsync1线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 13:46:57.907 INFO 50628 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.AllOfTest : thenRun线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 13:46:57.907 INFO 50628 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.AllOfTest : c1, c2, c3全部执行完毕, 执行了thenRun线程
2022-08-27 13:46:57.907 INFO 50628 --- [ main] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.AllOfTest : 返回值:null
3.5.AnyOf
任意一个任务执行完,就执行anyOf返回的CompletableFuture。如果执行的任务异常,anyOf的CompletableFuture执行get方法,会抛出异常。
anyOf的示例代码如下:
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = DemoExampleSpringbootApplication.class)
public class AnyOfTest {
@Resource
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Test
public void anyOfTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//
final CompletableFuture c1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("supplyAsync1线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "completableFuture1";
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor);
//
final CompletableFuture c2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("supplyAsync2线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "completableFuture2";
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor);
//
final CompletableFuture c3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("supplyAsync3线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "completableFuture3";
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor);
final CompletableFuture 执行结果:
2022-08-27 13:57:58.395 INFO 50456 --- [-example-task-3] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.AnyOfTest : supplyAsync3线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-3
2022-08-27 13:57:58.395 INFO 50456 --- [-example-task-2] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.AnyOfTest : supplyAsync2线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-2
2022-08-27 13:57:58.395 INFO 50456 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.AnyOfTest : supplyAsync1线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 13:57:58.396 INFO 50456 --- [-example-task-3] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.AnyOfTest : whenComplete线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-3
2022-08-27 13:57:58.396 INFO 50456 --- [-example-task-3] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.AnyOfTest : c1, c2, c3任意一个执行完毕, 执行了whenComplete线程, 获取执行完的线程的结果值:completableFuture3
2022-08-27 13:57:58.396 INFO 50456 --- [ main] e.d.j.t.completablefuture.AnyOfTest : 返回值:completableFuture3
3.6.thenCompose
thenCompose方法会在某个任务执行完成后,将该任务的执行结果作为方法入参,去执行指定的方法。该指定方法会返回一个新的CompletableFuture实例。
- 如果该CompletableFuture实例的result不为null,则thenCompose返回一个基于该result新的CompletableFuture实例。
- 如果该CompletableFuture实例为null,然后就执行这个thenCompose新任务。
示例代码如下:
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = DemoExampleSpringbootApplication.class)
public class ThenComposeTest {
@Resource
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Test
public void thenComposeTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 获取thenCompose返回的CompletableFuture
final CompletableFuture completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "Hello";
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor).thenCompose(value -> {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("thenCompose中获取supplyAsync的返回值:{}", value);
return value + " World!";
});
});
final String value = completableFuture.get();
log.info("返回值:{}", value);
log.info("=======================================================");
// 只是执行thenCompose
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "Hello";
}, threadPoolTaskExecutor).thenCompose(v -> {
log.info("只是打印一下supplyAsync的返回值:{}", v);
return null;
});
}
}
执行结果:
2022-08-27 14:39:16.178 INFO 5216 --- [-example-task-1] e.d.j.t.c.ThenComposeTest : supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-1
2022-08-27 14:39:16.180 INFO 5216 --- [onPool-worker-9] e.d.j.t.c.ThenComposeTest : thenCompose中获取supplyAsync的返回值:Hello
2022-08-27 14:39:16.180 INFO 5216 --- [ main] e.d.j.t.c.ThenComposeTest : 返回值:Hello World!
2022-08-27 14:39:16.181 INFO 5216 --- [ main] e.d.j.t.c.ThenComposeTest : =======================================================
2022-08-27 14:39:16.181 INFO 5216 --- [-example-task-2] e.d.j.t.c.ThenComposeTest : supplyAsync线程执行, 线程名称:demo-example-task-2
2022-08-27 14:39:16.181 INFO 5216 --- [-example-task-2] e.d.j.t.c.ThenComposeTest : 只是打印一下supplyAsync的返回值:Hello
4.CompletableFuture使用注意点
CompletableFuture 使我们的异步编程更加便利的、代码更加优雅的同时,我们也要关注下它,使用的一些注意点。

4.1.Future需要获取返回值,才能获取异常信息
CompletableFuture future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int a = 0;
int b = 68;
int c = b / a;
return true;
}, executorService).thenAccept(System.out::println);
// 如果不加 get()方法这一行,看不到异常信息
future.get();
Future需要获取返回值,才能获取到异常信息。如果不加 get()/join()方法,看不到异常信息。所以使用的时候,注意一下考虑是否加try…catch…或者使用exceptionally方法。
4.2.CompletableFuture的get()方法是阻塞的
CompletableFuture的get()方法是阻塞的,如果使用它来获取异步调用的返回值,需要添加超时时间。
// 阻塞
CompletableFuture.get();
// 添加超时时间
CompletableFuture.get(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
4.3.线程池的注意点
CompletableFuture代码中可能会使用默认的线程池。在大量请求过来的时候,处理逻辑复杂的话,响应会很慢。一般建议使用自定义线程池,优化线程池配置参数。
4.4.自定义线程池注意饱和策略
CompletableFuture的get()方法是阻塞的,我们一般建议使用future.get(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)。并且一般建议使用自定义线程池。
但是如果线程池拒绝策略是DiscardPolicy或者DiscardOldestPolicy,当线程池饱和时,会直接丢弃任务,不会抛弃异常。因此建议,CompletableFuture线程池策略最好使用AbortPolicy,然后耗时的异步线程,做好线程池隔离。