【PAT】01 字符串处理
01 字符串处理
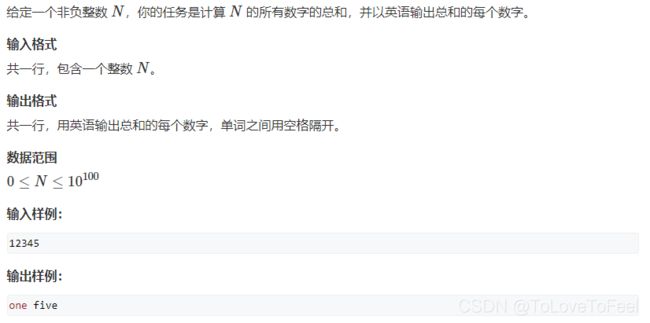
AcWing 1473. A + B 格式
问题描述
分析
- 相加得到结果后,转为指定形式的字符串输出即可。
代码
- C++
#include AcWing 1477. 拼写正确
问题描述
分析
- 以字符串的形式读入数据,然后将每位相加,最后打表输出即可。
代码
- C++
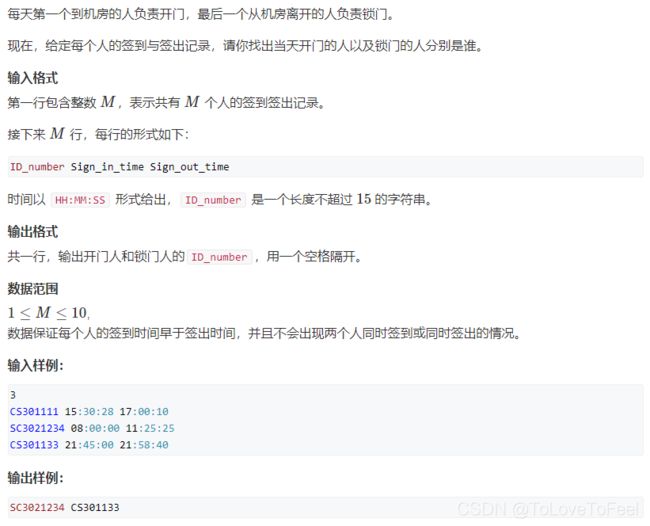
#include AcWing 1478. 签到与签出
问题描述
分析
- 本题相当于求解一个最小值和一个最大值,每次读取一条记录更新答案即可。
代码
- C++
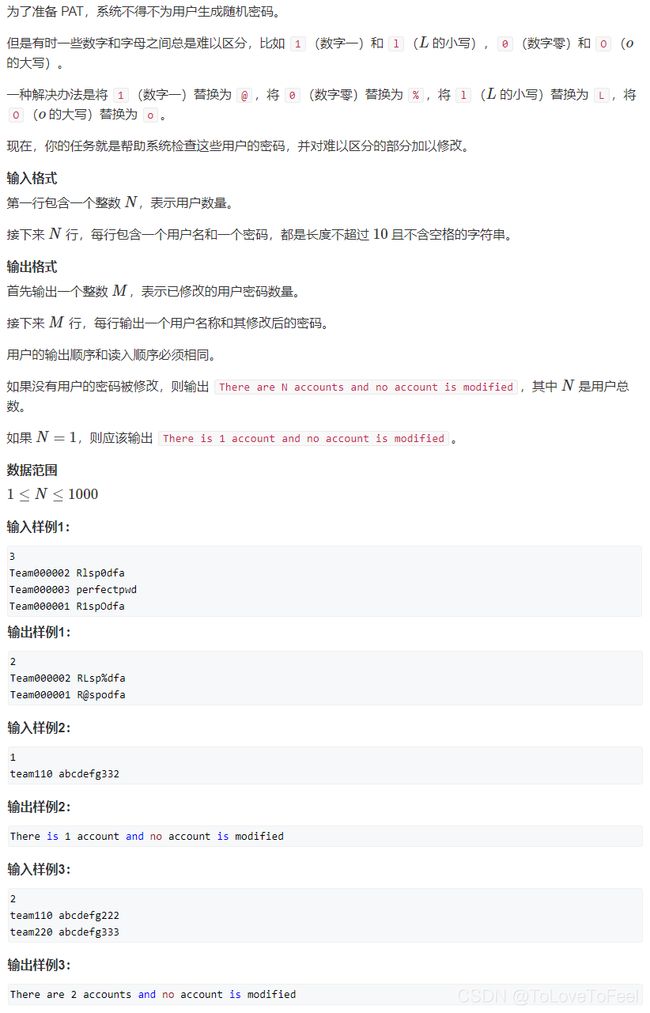
#include AcWing 1519. 密码
问题描述
分析
- 按照题目要求模拟一遍即可。
代码
- C++
#include AcWing 1520. 男孩 vs 女孩
问题描述
分析
- 按照题目要求模拟一遍即可。
代码
- C++
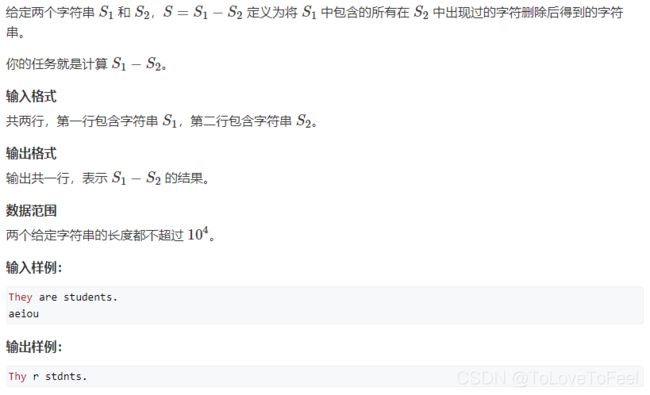
#include AcWing 1534. 字符串减法
问题描述
分析
- 使用哈希表统计出字符串
b中存在的字符,然后遍历字符串a中的所有字符c,如果c在哈希表中没有出现,则将c加到结果中即可。
代码
- C++
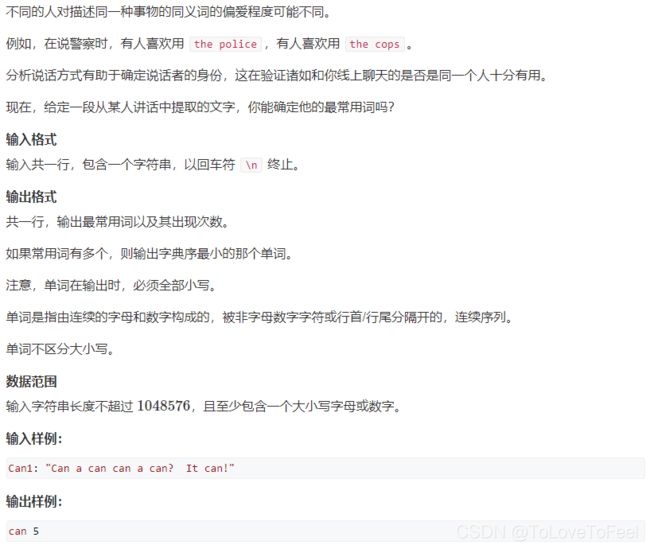
#include AcWing 1557. 说话方式
问题描述
分析
-
将每个单词切分出来,然后全部转化为小写,与此同时使用哈希表统计每个单词出现的次数。
-
之后遍历哈希表,找到出现次数最多且字典序最小的单词输出即可。
代码
- C++
#include AcWing 1547. 约会
问题描述
分析
- 按照题目要求模拟一遍即可。
代码
- C++
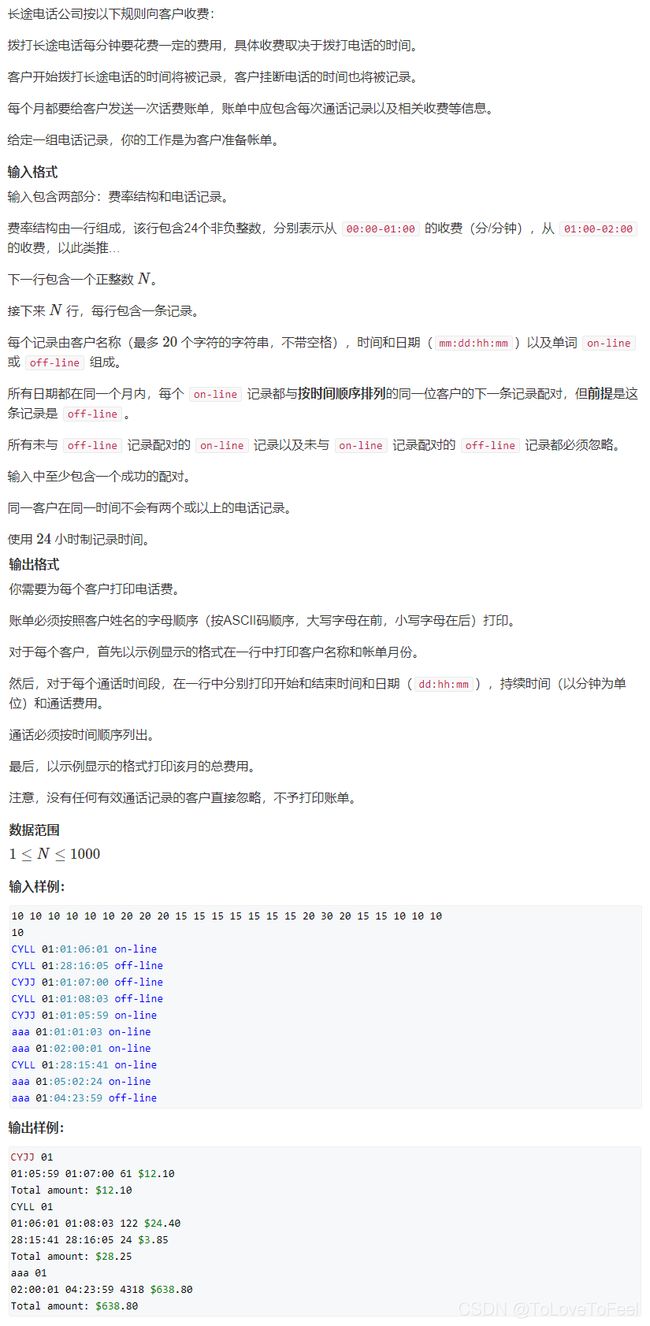
#include AcWing 1493. 电话账单
问题描述
分析
-
因为需要按照人名的字典序输出每个人的信息,因此可以使用
map记录每个人的信息,每个人可能有多条通话记录,使用vector记录这些信息,每条信息用一个结构体存储。 -
为了方便计算时间之差,这里将所有时间转化为相对于当月零时零分过去的时间。这样也方便排序。
-
为了方便计算任意两个时刻的花费,可以使用前缀和数组的技巧。
-
另外还需要将美分转化为美元。
代码
- C++
#include AcWing 1494. 银行排队
问题描述
分析
-
使用一个优先队列存储
m个窗口的空闲时间点 。 -
读入所有的人,按照到达时间进行排序,然后依次处理每个人,每次 从优先队列中弹出一个时间
w,这代表在w时刻有一个窗口空闲,此时可以有一个人到这个窗口,计算该人的等待时间,加到答案中。 -
如果当前考虑的人达到的时间超过了下午五点,后面的人就不需要考察了。
-
另外需要注意即使有窗口空闲,但可能人还没来,因此窗口此时需要等待顾客。
代码
- C++
#include AcWing 1503. 乒乓球
问题描述
分析
代码
- C++
AcWing 1546. 它们是否相等
问题描述
分析
-
总体思路是首先将两个字符串转为题目对应形式,然后对比是否相同后输出。具体转化步骤如下:
(1)找到小数点的位置,并将小数点去掉;
(2)去掉前导0;
(3)对齐到n位;
(4)拼接成题目要求字符串返回
代码
- C++
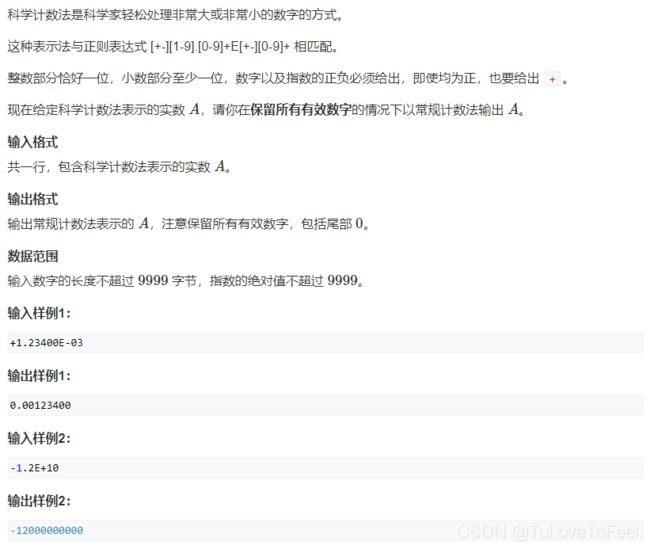
#include AcWing 1559. 科学计数法
问题描述
分析
-
分为如下步骤:
(1)如果是负数,先输出一个负号;
(2)得到底数和指数部分,并让小数点向前移动一位,指数加一;
(3)根据指数的整数得到结果。
代码
- C++
#include AcWing 1563. Kuchiguse
问题描述
分析
-
我们需要求出给定多个字符串的最长公共后缀。
-
可以从后向前遍历第一个字符串,然后考察其他字符串对应位置是否和第一个字符串对应位置相同。
代码
- C++
#include AcWing 1568. 中文读数字
问题描述
分析
-
因为最多九位,我们将其拆为三个数字进行读,使用
work函数返回一个四位数的读法。 -
两个四位数之间,如果后面一个四位数小于
1000,说明该四位数千位是0,如果此时答案的结尾不是0,这加上0。
代码
- C++
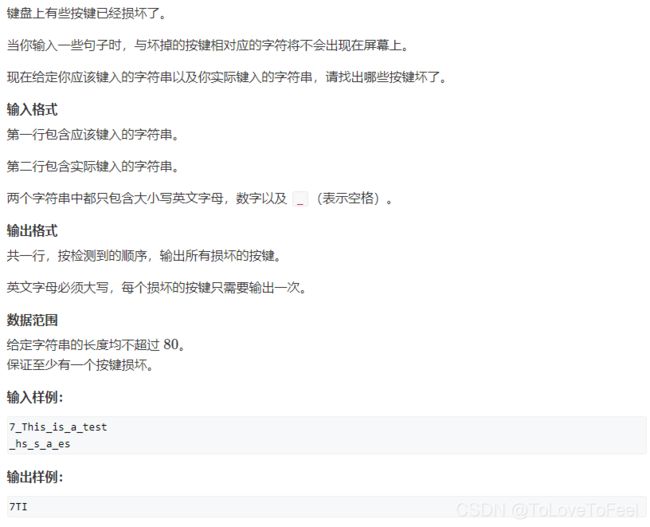
#include AcWing 1570. 坏掉的键盘
问题描述
分析
- 同时遍历两个字符串
a、b,当a中存在某个字符,但b中不存在时,说明该字符对应的键损坏,输出即可,并标记为已经输出,防止多次输出。
代码
- C++
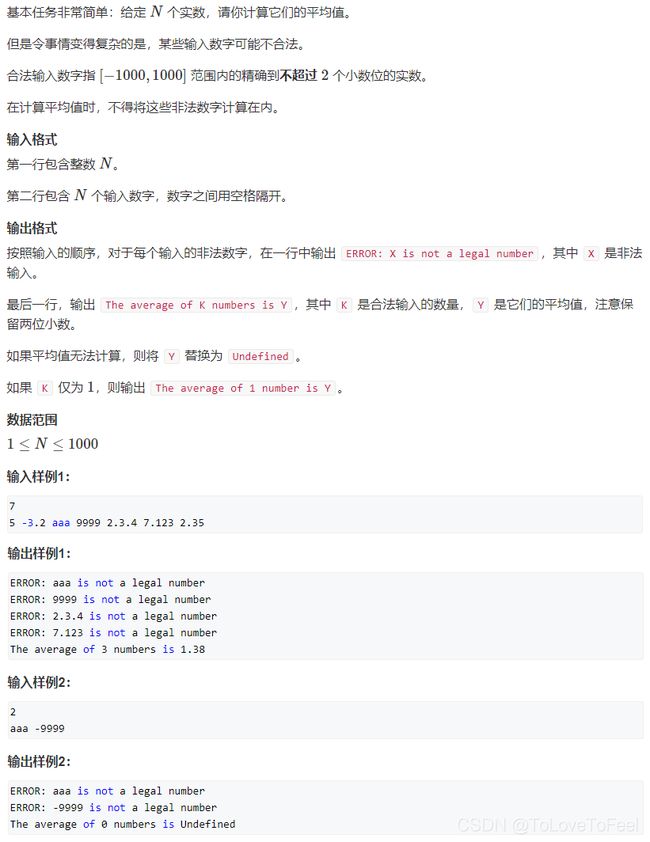
#include AcWing 1598. 求平均值
问题描述
分析
- 本题实质上是一个语法题。使用
try catch解决。
代码
- C++
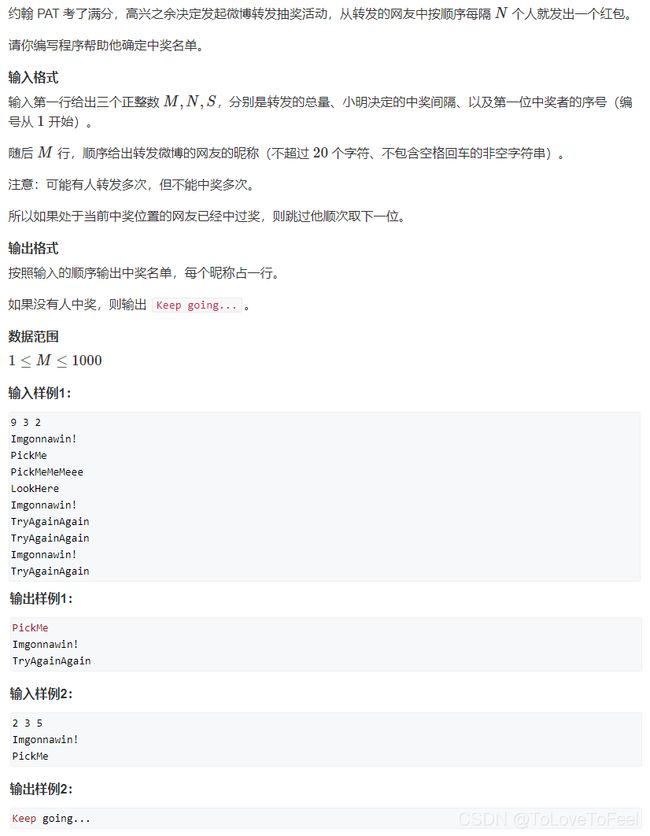
#include AcWing 1617. 微博转发抽奖
问题描述
分析
- 按照题目要求模拟一遍即可。可以使用哈希表存储已经中奖的同学,防止重复输出。
代码
- C++
#include AcWing 1634. PAT单位排行
问题描述
分析
- 首先使用哈希表统计出每个学校的记录。然后将这些记录存放到
vector中,排序后输出即可。
代码
- C++
#include AcWing 1647. 解码PAT准考证
问题描述
分析
-
使用结构体存储每一条记录,使用
vector存储所有记录。 -
对于不同类型的查询,直接遍历一遍所有记录,将符合条件的记录存储下来,最后得到统计结果输出即可。
代码
- C++
#include