C++ Primer plus学习总结(未完成)
文章目录
- 2开始学习C++
-
- 2.1复习题
-
- 2.1.1 1C++的程序模块叫上面
- 2.2.预处理编译指令的作用
- 2.2编程题
-
- 2.2.5 将摄氏温度转换为华氏温度
- 2.2.7 输出特定格式的时间
- 总结
- 3 处理数据
-
- 3.1contenet
-
- 3.1.1 std::hex在cout中作用
- 3.3编程题
-
- 3.3.5
- 总结
- 4 符合类型
-
- 4.1content
-
- 4.1.1字符串长度超过定义
- 4.1.2给字符数组赋值
- 4.2复习题
-
- 4.2.1如何申明小列数据
- 4.2.2使用模板类array而不是数组来完成问题1
- 4.2.5编写一个语句来显示float数组ideas中第二个元素的值
- 4.2.8 设计一个结构
- 4.2.11假设ted是一个double变量,请声明一个指向ted的指针,并用该指针来显示ted的值
- 4.2.14(int*)"hone sojdoa "s是否有效,如果有效打印出结果
- 4.2.15根据8的结构动态分配内存
- 4.2.17 vector and array
- 4.3编程练习
-
- 4.3.1 读取一行输入
- 4.3.2使用string类进行输入输出
- 4.3.6
- 4.3.10 new struct
- 总结
- 5循环和关系表达式
-
- 5.1 content
- 5.2复习题
-
- 5.2.1入口条件循环和出口用条件循环区别是上面?
- 5.2.3 for循环
- 5.2.5 do while
- 5.2.6
- 5.2.7如何在循环体中包括多条语句
- 5.2.8 int =(1,024)是否有效
- 5.3编程练习
-
- 5.3.1 习题一 求两个整数之间所有整数的和
- 5.3.2 求阶乘 array
- 5.3.3
- 5.3.8 strcmp
- 5.3.9 在8的基础上用string
- 7函数
-
- 7.1content
- 7.2复习题
- 7.2.1函数使用的三个步骤
- 7.2.2定义函数
- 7.2.4 函数编写
- 7.2.6为什么不对类型为基础类型的函数使用const限定符
- 7.2.13
- 9内存模型和名称控件
-
- 9.1content
-
- 9.1.1定义赋值不会重复赋值
- 9.2复习题
-
- 9.2.1变量存储方式
- 9.2.2using申明和using编译指令
- 9.2.3 不用using申明和编译指令
- 9.2.4 using申明
- 9.2.7
- 9.3 编程练习
-
- 9.3.1含有多文件的编译
-
-
- 知识点
-
- 9.2.4名称空间
- 10对象和类
-
- 10.1 content
- 10.2复习题
-
- 10.2.1什么是类
- 10.2.2类是如何实现抽象、封装和数据隐藏的
- 10.2.5
- 10.2.6类的构造函数何时被调用?类析构函数呢?
- 10.2.10 this和 *this
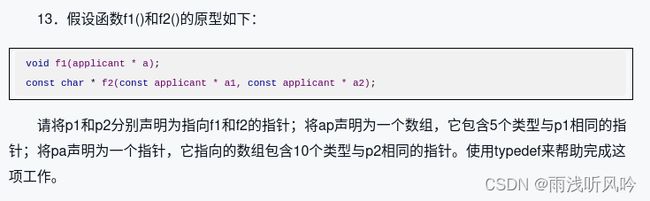
- 10.3 编程练习
2开始学习C++
2.1复习题
2.1.1 1C++的程序模块叫上面
函数
2.2.预处理编译指令的作用
#include在最终编译之前,用iostream文件替换替换该编译指令
2.2编程题
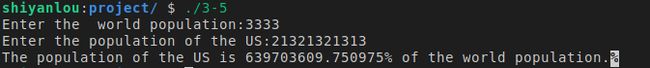
2.2.5 将摄氏温度转换为华氏温度
#include2.2.7 输出特定格式的时间
#includestd::cin>>val1>>val2; 可以输入多个数据。
#include总结
在 C++ 中,函数和变量一样都需要先定义后使用;
std::cout 可以输出多个变量,std::cin 可以输入多个变量;
C++ 的标准输入输出被定义在 iostream 中,需要先包含头文件才可以输入输出;
cin 和 cout 位于 std 命名空间下。
3 处理数据
3.1contenet
3.1.1 std::hex在cout中作用
#include3.3编程题
3.3.5
![]()
#includecout.setf(ios_base::fixed,ios_base::floatfield)
总结
强制类型转换的优先级为 2,高于乘除运算;使用 cin 读取数据产生错误,如果不进行特殊处理,则之后调用 cin 也无法正常读取缓冲区或触发用户输入;cin.clear() 可以清除错误。
4 符合类型
4.1content
4.1.1字符串长度超过定义
这里字符串长度要为定义的+1,即char[3]只能定义两个字符

#include若是超出字符,会提示出错,编译的化也会报错
![]()
若是短与定义会加入/0
#include4.1.2给字符数组赋值
#include4.2复习题
4.2.1如何申明小列数据
char actor[30]
short betsie[100]
float chuck[13]
long double dipsea[64]
4.2.2使用模板类array而不是数组来完成问题1
array<char ,30> actor
array<short,100> betsie
array<float,13>chuck
array<long double ,64> dipsea
4.2.5编写一个语句来显示float数组ideas中第二个元素的值
cout<<ideas[1];
cout<<*(ideas+1)
4.2.8 设计一个结构
4.2.11假设ted是一个double变量,请声明一个指向ted的指针,并用该指针来显示ted的值
double* teddy=&ted;
cout<<*teddy;
4.2.14(int*)"hone sojdoa "s是否有效,如果有效打印出结果
4.2.15根据8的结构动态分配内存
4.2.17 vector and array
4.3编程练习
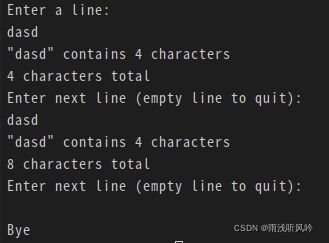
4.3.1 读取一行输入
#include4.3.2使用string类进行输入输出
#include4.3.6
4.3.10 new struct
#include4.8.4
总结
5循环和关系表达式
5.1 content
5.2复习题
5.2.1入口条件循环和出口用条件循环区别是上面?
5.2.3 for循环
0369
12
5.2.5 do while
k=8
5.2.6
#include5.2.7如何在循环体中包括多条语句
5.2.8 int =(1,024)是否有效
5.11表达式和语句
5.3编程练习
5.3.1 习题一 求两个整数之间所有整数的和
#include5.3.2 求阶乘 array
5.3.3
5.3.8 strcmp

参考内容5.1.14C语言风格字符比较

4.2.4getline 和get


#include5.3.9 在8的基础上用string
7函数
7.1content
#include
函数将字符串输入为char类型,这里之所以要用const char
等号两边的变量类型不一样,那么编译器会进行一种叫做 implicit conversion 的操作来使得变量可以被赋值。
在上面的表达式中等号右边的"abc"是一个不变常量,在c++中叫做string literal,type是const char *,而p则是一个char指针。如果强行赋值会发生什么呢?没错,就是将右边的常量强制类型转换成一个指针,结果就是我们在修改一个const常量。编译运行的结果会因编译器和操作系统共同决定,有的编译器会通过,有的会抛异常,就算过了也可能因为操作系统的敏感性而被杀掉。
7.2复习题
7.2.1函数使用的三个步骤
1定义函数
2提供原型
3调用函数
7.2.2定义函数
7.2.4 函数编写
void set_array(int begin ,int end ,int value){
for(int *pt=begin;pt!=end;pt++)
pt*=value;
}
7.2.6为什么不对类型为基础类型的函数使用const限定符
7.2.13
9内存模型和名称控件
9.1content
9.1.1定义赋值不会重复赋值
#include9.2复习题
9.2.1变量存储方式
9.2.2using申明和using编译指令
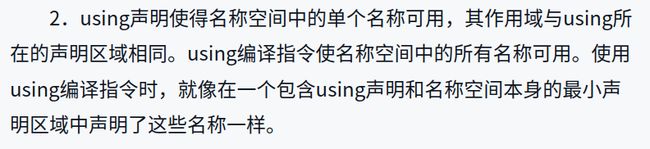 最小申明区域只有有局部变量不管在前在后都会被覆盖
最小申明区域只有有局部变量不管在前在后都会被覆盖
具体内容再9-3中
#include即使后使用using namespacee fetch依然是局部变量
![]()
9.2.3 不用using申明和编译指令
9.2.4 using申明
9.2.7
1
4,1,2
2
2
4,1,2
2
9.3 编程练习
9.3.1含有多文件的编译
// filename 9-1.cpp
#includegolf.cpp
// filename golf.cpp
#includegolf.h
// filename golf.h
const int Len=40;
struct golf
{
char fullname[Len];
int handicap;
};
void setgolf(golf&g,const char*name,int hc);
int setgolf(golf&g);
void handicap(golf&g,int hc);
void showgolf(const golf&g);
知识点
6.7中有知识点
#includecin 要有一个回车结束,这里面如果出现非整数,会直接全部清空,到换行符’\n’
 ### 9.3.2 string 和char的区别
### 9.3.2 string 和char的区别
知识点在4-10

// static.cpp -- using a static local variable
#include 编码
#include9.2.4名称空间
9-4.cpp
// filename 9-4.cpp
#includesales.h
namespace SALES
{
const int QUARTERS=4;
struct Sales
{
double sales[QUARTERS];
double average;
double max;
double min;
};
//copiesthelesserof4ornitemsfromthearrayar
//tothesalesmemberofsandcomputesandstoresthe
//average,maximum,andminimumvaluesoftheentereditems;
//remainingelementsofsales,ifany,setto0
void setSales(Sales&s,const double ar[],int n);
//gatherssalesfor4quartersinteractively,storesthem
//inthesalesmemberofsandcomputesandstoresthe
//average,maximum,andminimumvalues
void setSales(Sales&s);
//displayallinformationinstructures
void showSales(const Sales&s);
}
sales.cpp
// filename sales.cpp
#include10对象和类
10.1 content
10.2复习题
10.2.1什么是类

类是现实中物体的抽象,类声明定义了数据如何储存,同时指定了用来访问和操作这些数据的方法。
10.2.2类是如何实现抽象、封装和数据隐藏的
10.2.5
10.2.6类的构造函数何时被调用?类析构函数呢?
10.2.10 this和 *this
this指针是类方向可以使用的指针,它指向类调用方法的对象。*this是对象本身