13 # promise 的状态更改问题
下面需要实现两个功能,一个是下面这种 resolve 了一个 promise,还能等待这个 promise 的状态去返回。
另外一个就是如果同时调用了 resolvePromise 和 rejectPromise,或者对同一参数进行了多次调用,则第一次调用优先,任何进一步的调用都将被忽略。
没有实现前,我们目前返回的是一个promise:
下面实现:
// promise 就是一个类
// 1. promise 有三个状态:成功态(resolve) 失败态(reject) 等待态(pending)(又不成功又不失败)
// 2. 用户自己决定失败的原因和成功的原因,成功和失败也是用户定义的
// 3. promise 默认执行器立即执行
// 4. promise 的实例都拥有一个 then 方法,一个参数是成功的回调,另一个是失败的回调
// 5. 如果执行函数时发生了异常也会执行失败的逻辑
// 6. 如果 promise 一旦成功就不能失败,反之亦然,只有等待态的时候才能去更新状态
const RESOLVE = "RESOLVE"; // 成功态
const REJECT = "REJECT"; // 失败态
const PENDING = "PENDING"; // 等待态
// 解析 promise:所有的promise需要兼容,比如 bluebird q es6-promise
const resolvePromise = (promise2, x, resolve, reject) => {
// 处理一下循环引用(自己等待自己的错误实现),这个时候我们用一个类型错误结束掉 promise。
if (promise2 === x) {
reject(new TypeError("Chaining cycle detected for promise #" ));
}
// 用于防止走成功又走失败
let called;
// 后续的条件要严格判断 保证代码能和别的库一起使用
if ((typeof x === "object" && x !== null) || typeof x === "function") {
// 要继续判断是否是一个promise
try {
// x.then 取值时可能会报错,需要捕获异常
let then = x.then;
// then 是个函数我们就认为是promise
if (typeof then === "function") {
// 下面为什么不写成 x.then 的原因,可能第二次取出报错,直接写成 then.call(x)
// 根据 promise 的状态决定是成功还是失败
then.call(
x,
(y) => {
if (called) return;
called = true;
// 递归解析
resolvePromise(promise2, y, resolve, reject);
},
(e) => {
if (called) return;
called = true;
reject(e);
}
);
} else {
resolve(x);
}
} catch (e) {
// 防止失败了再次进入成功
if (called) return;
called = true;
reject(e);
}
} else {
resolve(x);
}
};
class KaimoPromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = PENDING;
// value 是任意合法的 Javascript 值,(包括 undefined,thenable, promise)。
this.value = undefined;
// reason 是表示 promise 为什么被 rejected 的值
this.reason = undefined;
// 存放成功回调
this.onResolveCallbacks = [];
// 存放失败回调
this.onRejectCallbacks = [];
let resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.value = value;
this.status = RESOLVE;
this.onResolveCallbacks.forEach((fn) => fn());
}
};
let reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.reason = reason;
this.status = REJECT;
this.onRejectCallbacks.forEach((fn) => fn());
}
};
try {
// 立即执行
executor(resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
// 处理错误异常
console.log("inner---->", error);
reject(error);
}
}
// 1. promise 成功和失败的回调的返回值可以传递到外层的下一个 then
// 2. promise 返回值情况
// 2.1. 如果返回的是普通的值的话:传递到下一次的成功中(不是错误也不是 promise 就是普通值)
// 2.2. 如果返回的是错误的情况:一定会走到下一次的失败中
// 2.3. 如果返回的是 promise 的情况:会采用 promise 的状态,决定下一步是走成功还是失败
// 3. 错误处理:如果离自己最近的 then 没有错误处理(没有写错误函数)会向下找
// 4. 每次执行完 `promise.then` 方法后返回的都是一个新的 promise (promise 一旦成功或者失败都不能去修改状态)
// promise 必须提供 then 方法来存取它当前或最终的值或者原因。
// then 接收两个参数:onFulfilled 和 onRejected
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 实现链式调用
let promise2 = new KaimoPromise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === RESOLVE) {
// setTimeout 处理 promise2 没有初始化的问题, 需要等 executor 执行完
setTimeout(() => {
// try catch 无法捕获异步代码,所以需要在 promise2 里面也加 try catch
try {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
// x 可能是一个 promise
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}, 0);
}
if (this.status === REJECT) {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}, 0);
}
// 下面是异步的,可以不加setTimeout,统一一下加了一下
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.onResolveCallbacks.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}, 0);
});
this.onRejectCallbacks.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}, 0);
});
}
});
return promise2;
}
}
module.exports = KaimoPromise;
测试:
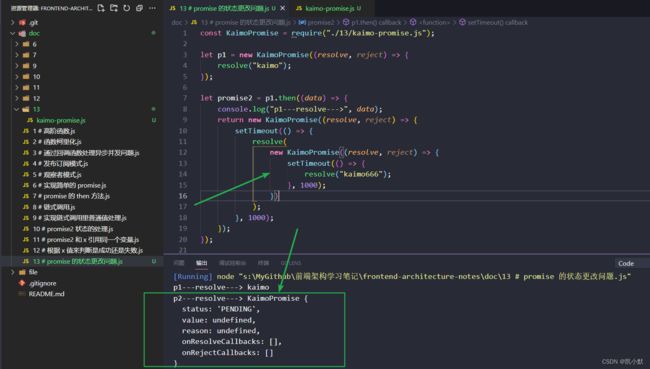
const KaimoPromise = require("./13/kaimo-promise.js");
let p1 = new KaimoPromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("kaimo");
});
let promise2 = p1.then((data) => {
console.log("p1---resolve--->", data);
return new KaimoPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(
new KaimoPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("kaimo666");
}, 1000);
})
);
}, 1000);
});
});
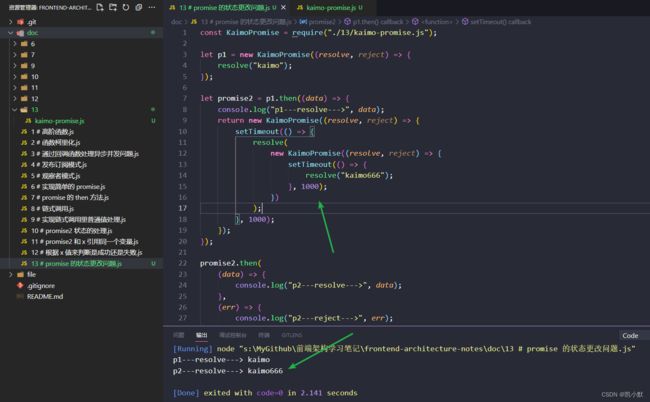
promise2.then(
(data) => {
console.log("p2---resolve--->", data);
},
(err) => {
console.log("p2---reject--->", err);
}
);
这样我们就实现了: