86 # express 基本实现
koa 和 express 的区别
- koa 内部原理使用 es6 来编写的(promise async + await),express 是使用 es5 来编写的,内部是基于回调函数来实现
- express 内置了很多中间件(功能会比 koa 强大一些,内部集成了路由,静态服务,模板引擎)
- express 本身会大一些,koa 主要关注的是核心(use)
- koa(基于 promise) 和 express(基于回调) 中间件有一些差异,错误处理也不一样
- webpack-dev-server 内部使用的是 express
- 开发人员是同一波,应用层面来说基本一致
- koa 的 ctx 上下文有 (req,res,request,response),而 express 直接对 res 和 req 进行了拓展
安装 express
npm init -y
npm i express
编写一个 express demo
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
// 调用回调时 会将原生的 req 和 res 传入(req,res 在内部也被扩展了)
// 内部不会将回调函数包装成 promise
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.end("ok");
});
app.get("/add", (req, res) => {
res.end("add");
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log(`server start 3000`);
console.log(`在线访问地址:http://localhost:3000/`);
});
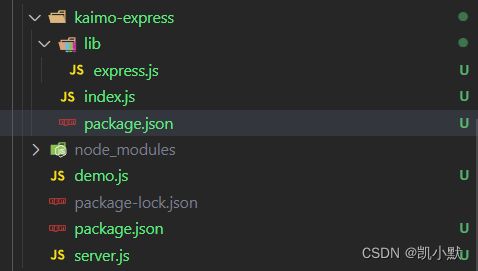
express 源码目录结构
├── index.js:入口文件,没有 main 入口,默认通过 index.js 入口找到 `lib/express`
├── lib
│ ├── middleware:中间件 内置了中间件
│ ├── router:路由系统
│ ├── application.js:应用
│ ├── request.js:用来拓展 req
│ ├── response.js:用来拓展 res
│ ├── utils.js:工具方法
│ └── view.js:模板引擎
express 基本实现
下面完成这个功能,有一个默认的路由,默认找不到时会执行 404 功能,配置的路由会默认从上到下来进行匹配
先新建 kaimo-express 文件夹,添加对应的文件
// 找到 express 的入口
console.log("使用的是 kaimo-express");
module.exports = require("./lib/express");
express.js
const http = require("http");
const url = require("url");
const routers = [
{
path: "*",
method: "all",
handler: (req, res) => {
res.end(`kaimo-express Cannot ${req.method} ${req.url}`);
}
} // 默认路由
];
function createApplication() {
return {
get(path, handler) {
routers.push({
path,
method: "get",
handler
});
},
listen() {
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
const { pathname } = url.parse(req.url);
const requestMethod = req.method.toLowerCase();
for (let i = 1; i < routers.length; i++) {
let { path, method, handler } = routers[i];
if (path === pathname && method === requestMethod) {
return handler(req, res);
}
}
return routers[0].handler(req, res);
});
server.listen(...arguments);
}
};
}
module.exports = createApplication;
下面引用自己的 kaimo-express 测试
const express = require("./kaimo-express");
const app = express();
// 调用回调时 会将原生的 req 和 res 传入(req,res 在内部也被扩展了)
// 内部不会将回调函数包装成 promise
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.end("ok");
});
app.get("/add", (req, res) => {
res.end("add");
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log(`server start 3000`);
console.log(`在线访问地址:http://localhost:3000/`);
});
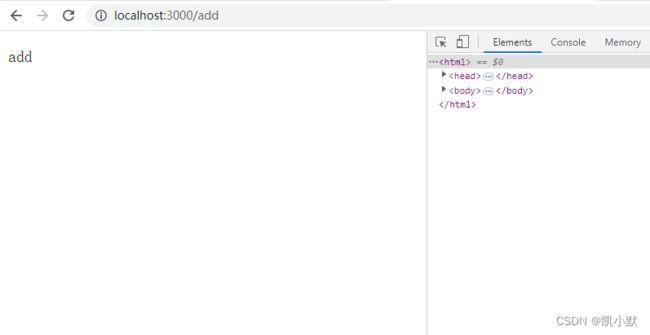
访问 http://localhost:3000/add
访问 http://localhost:3000/kaimo313