【Hydro】水文模型比较框架MARRMoT - 包含47个概念水文模型的Matlab代码
目录
- 说明
- 源代码
- 运行实例
-
- workflow_example_1.m
- workflow_example_2.m
- workflow_example_3.m
- workflow_example_4.m
- 测试
-
- 1、 结构体兼容性问题
- 2、append的兼容性问题
- 3、参数优化时间过长的问题
- 4、修改后的MARRMoT_model.m
说明
MARRMoT是一个新的水文模型比较框架,允许不同概念水文模型结构之间的客观比较。该框架为47个独特的模型结构提供了Matlab代码,所有模型结构的标准化参数范围以及每个模型的强大数值实现。该框架提供了大量的文档,用户手册和几个工作流脚本,给予如何使用该框架的例子。包括以下模型:
- FLEX-Topo
- IHACRES
- GR4J
- TOPMODEL
- SIMHYD
- VIC
- LASCAM
- TCM
- TANK
- XINANJIANG
- HYMOD
- SACRAMENTO
- MODHYDROLOG
- HBV-96
- MCRM
- SMAR
- NAM
- HYCYMODEL
- GSM-SOCONT
- ECHO
- PRMS
- CLASSIC
- IHM19
MARRMoT框架中的模型期望接近它们所基于的原始模型,但差异是不可避免的。在许多情况下,一个模型存在多个版本,但这些版本并不总是很容易区分的。存在一定程度的模型名称相等性,其中单个名称用来指代同一基模型的各种不同版本。一个很好的例子是TOPMODEL,其中许多变体存在于基于地形指数的最初概念之上。MARRMoT模型往往基于任何给定模型的旧出版物,而不是新出版物(以接近原作者的“预期”模型),但我们的选择是务实的,以实现MARRMoT中可用通量和模型结构的更大多样性。每个模型的描述列出了构成该模型MARRMoT版本基础的论文。
MARRMoT框架以模块化的方式设置,并以单个的通量文件作为基本的构建块。模型文件通过指定每个模型的内部工作方式来为其定义一类对象,而超类文件则定义了所有模型通用的所有过程。图1显示了工具箱结构的示意图概述。

源代码
降雨径流模型的模块化评估
运行实例
workflow_example_1.m
这个示例工作流程包含一个单一模型对单一集水区的应用示例。它包括5个步骤:
workflow_example_2.m
这个示例工作流程包含一个单一模型对单一集水区的应用示例。它包括5个步骤:
workflow_example_3.m
这个示例工作流程包含多个模型对单一集水区的应用示例。它包括6个步骤:
workflow_example_4.m
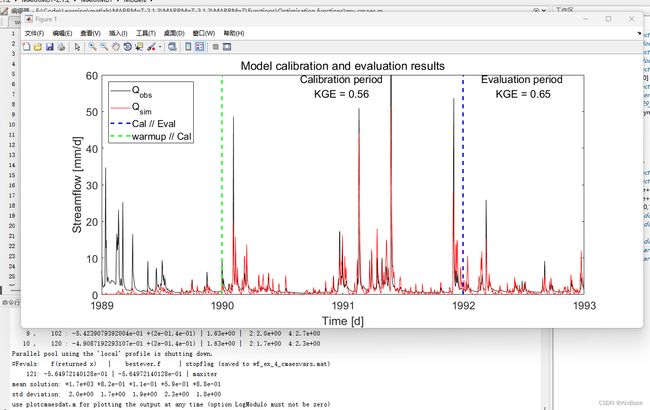
这个示例工作流程包含了一个单一模型对单一集水区的校准应用示例。它包括7个步骤:
- 数据准备
- 模型选择和设置
- 模型求解器设置和时间步进方案
- 校准设置
- 模型校准
- 校准结果评估
- 输出可视化
测试
原始代码根据作者描述,在MATLAB版本9.11.0.1873467(R2021b)上开发的,并使用Octave 6.4.0进行了测试。笔者使用R2017a时,出现了几个可能是兼容性的问题。
1、 结构体兼容性问题
动态字段或属性名称必须为字符矢量。

将string转换为char,即可使用结构体动态赋值。
2、append的兼容性问题
错误使用 append (line 38)
Wrong number of input arguments for obsolete matrix-based syntax.

在MATLAB中,append函数是用来将矩阵或数组的元素添加到另一个矩阵或数组的末尾。如果你想将字符串连接到另一个字符串,可以使用cat函数或者简单的加号+。
3、参数优化时间过长的问题
CMA-ES算法终止的参数,可以根据需要修改示例中的条件,比如调小MaxIter。

还修改优化文件my_cmaes.m,显示更多迭代过程

4、修改后的MARRMoT_model.m
classdef MARRMoT_model < handle
% Superclass for all MARRMoT models
% Copyright (C) 2019, 2021 Wouter J.M. Knoben, Luca Trotter
% This file is part of the Modular Assessment of Rainfall-Runoff Models
% Toolbox (MARRMoT).
% MARRMoT is a free software (GNU GPL v3) and distributed WITHOUT ANY
% WARRANTY. See