NodeMCU ESP8266 基于Arduino IDE的串口使用详解(图文并茂)
NodeMCU ESP8266 的UART使用
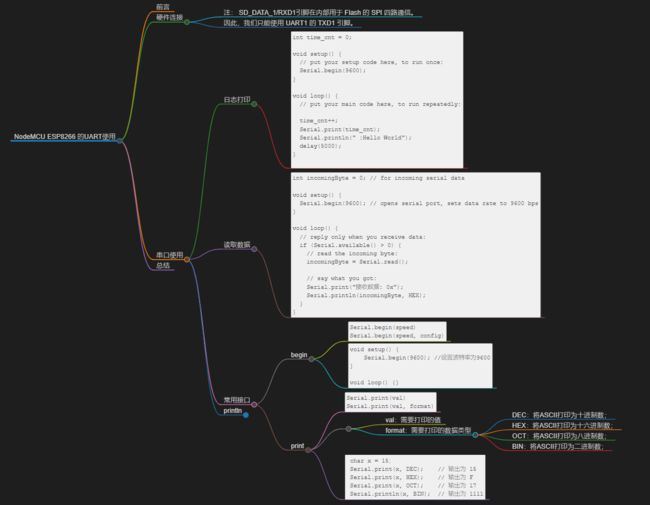
文章目录
- NodeMCU ESP8266 的UART使用
- 前言
- 硬件连接
- 串口使用
-
- 日志打印
- 读取数据
- 常用接口
-
- begin
- println
- 总结
前言
UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter),串口通讯在嵌入式开发中至关重要,我们可以通过串口打印程序里的数据,也可以通过串口将数据发送到PC上并进行可视化的图形显示。
注意:相关的串口通讯的知识可以参考这篇文章
UART串口协议快速扫盲(图文并茂+超详细)
NodeMCU ESP8266开发板可以直接通过MicroUSB线和PC进行连接,在Arduino IDE内置的串口工具进行数据显示,下面我们进一步介绍。
硬件连接
基于 NodeMCU 的 ESP8266 有两个 UART 接口:UART0 和 UART1。
ESP8266通过UART接口的数据传输速度可以达到115200的40倍,即4.5Mbps。
默认情况下,对于 40MHz 振荡器,UART0 波特率为 115200。
可以根据应用的需要将其更改为用户定义的值。具体的引脚定义如下所示;
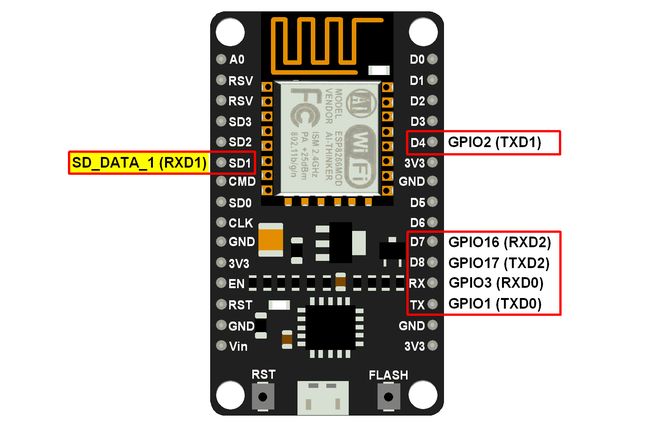
TXD(数据发送引脚)
该引脚用于串行传输数据。
RXD(数据接收引脚)
该引脚用于串行接收数据。
注: SD_DATA_1/RXD1引脚在内部用于 Flash 的 SPI 四路通信。
因此,我们只能使用 UART1 的 TXD1 引脚。
串口使用
日志打印
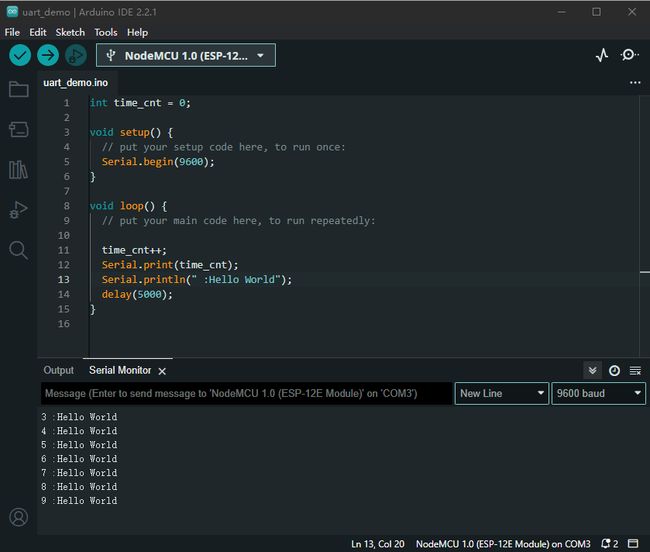
具体的示例代码如下所示;
int time_cnt = 0;
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
time_cnt++;
Serial.print(time_cnt);
Serial.println(" :Hello World");
delay(5000);
}
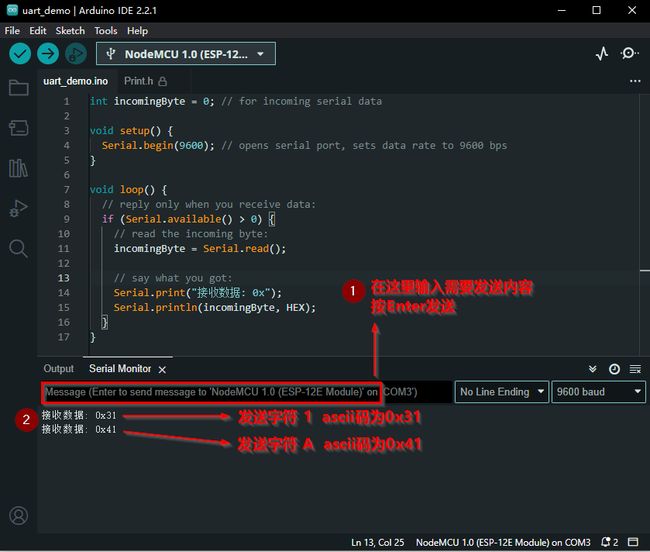
读取数据
int incomingByte = 0; // for incoming serial data
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // opens serial port, sets data rate to 9600 bps
}
void loop() {
// reply only when you receive data:
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
// read the incoming byte:
incomingByte = Serial.read();
// say what you got:
Serial.print("接收数据: 0x");
Serial.println(incomingByte, HEX);
}
}
常用接口
begin
设置串行数据传输的数据速率(波特率)。
为了与串行监视器通信,请确保使用屏幕右下角菜单中列出的波特率之一。
但是,您可以指定其他速率 - 例如,通过引脚 0 和 1 与需要特定波特率的组件进行通信。
可选的第二个参数配置数据、奇偶校验和停止位。默认为 8 个数据位,无奇偶校验,1 个停止位。
语法
Serial.begin(speed)
Serial.begin(speed, config)
示例
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); //设置波特率为9600
}
void loop() {}
将数据作为可读性比较好的 ASCII码 文本打印到串口,这个函数打印的效果不带换行。
语法
Serial.print(val)
Serial.print(val, format)
- val:需要打印的值
- format:需要打印的数据类型
- DEC:将ASCII打印为十进制数;
- HEX:将ASCII打印为十六进制数;
- OCT:将ASCII打印为八进制数;
- BIN:将ASCII打印为二进制数;
下面详细介绍
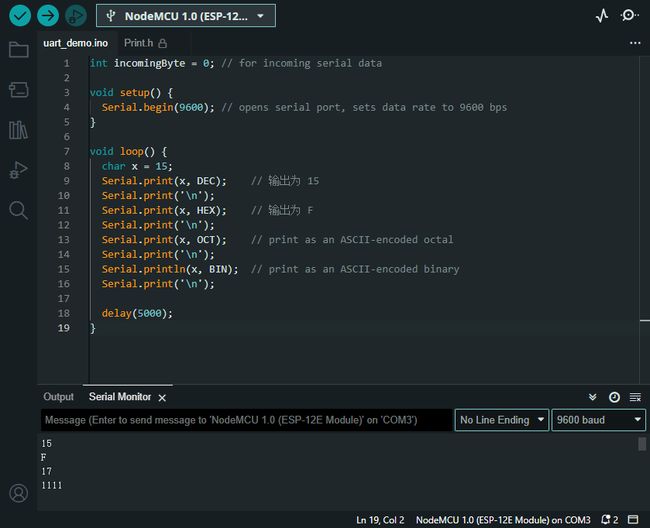
示例
char x = 15;
Serial.print(x, DEC); // 输出为 15
Serial.print(x, HEX); // 输出为 F
Serial.print(x, OCT); // 输出为 17
Serial.println(x, BIN); // 输出为 1111
println
将数据作为可读性比较好的 ASCII码 文本打印到串口,在每一行后跟回车符(ASCII码 13 或\r)和换行符(ASCII码 10 或\n”)
在每次打印的内容后面自动追加
\r\n,打印的内容会自动换行。
示例
读取DO端口的模拟值,即ADC数值(将模拟信号转化为数字信号,模数转换器),然后打印到串口,下面是示例代码;
/*
Analog input reads an analog input on analog in 0, prints the value out.
created 24 March 2006
by Tom Igoe
*/
int analogValue = 0; // variable to hold the analog value
void setup() {
// open the serial port at 9600 bps:
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// read the analog input on pin 0:
analogValue = analogRead(0);
// print it out in many formats:
Serial.println(analogValue); // print as an ASCII-encoded decimal
Serial.println(analogValue, DEC); // print as an ASCII-encoded decimal
Serial.println(analogValue, HEX); // print as an ASCII-encoded hexadecimal
Serial.println(analogValue, OCT); // print as an ASCII-encoded octal
Serial.println(analogValue, BIN); // print as an ASCII-encoded binary
// delay 10 milliseconds before the next reading:
delay(10);
}
总结
本文简单介绍了NodeMCU ESP8266 基于Arduino IDE的串口使用详解,以及Serial类的常用接口。
由于作者能力有限,文章中难免存在错误和纰漏,请大胆指正,如果对于文章中存在疑惑或者问题,欢迎在评论区进行留言。
如果文章帮到了你,请帮忙点赞,三连支持。