2021-04-10
计算机视觉(三)
直接线性变换
算法原理
单应性矩阵可以有两幅图像(或者平面)中对应点对计算出来。前面已经提到过,一个完全射影变换具有8个自由度。根据对应点约束,每个对应点对可以写出两个方程,分别对应于x和y坐标。因此,计算单应性矩阵H需要4个对应点对。
代码
def H_from_points(fp, tp):
"""使用线性DLT方法,计算单应性矩阵H,使fp映射到tp。点自动进行归一化"""
if fp.shape != tp.shape:
raise RuntimeError('number of points do not match')
# 对点进行归一化(对数值计算很重要)
# --- 映射起始点 ---
m = mean(fp[:2], axis=1)
maxstd = max(std(fp[:2], axis=1)) + 1e-9
C1 = diag([1/maxstd, 1/maxstd, 1])
C1[0][2] = -m[0]/maxstd
C1[1][2] = -m[1]/maxstd
fp = dot(C1,fp)
# --- 映射对应点 ---
m = mean(tp[:2], axis=1)
maxstd = max(std(tp[:2], axis=1)) + 1e-9
C2 = diag([1 / maxstd, 1 / maxstd, 1])
C2[0][2] = -m[0] / maxstd
C2[1][2] = -m[1] / maxstd
tp = dot(C2, tp)
# 创建用于线性方法的矩阵,对于每个对应对,在矩阵中会出现两行数值
nbr_correspondences = fp.shape[1]
A = zeros((2 * nbr_correspondences, 9))
for i in range(nbr_correspondences):
A[2*i] = [-fp[0][i], -fp[1][i],-1,0,0,0,
tp[0][i]*fp[0][i],tp[0][i]*fp[1][i],tp[0][i]]
A[2*i+1] = [0,0,0,-fp[0][i],-fp[1][i],-1,
tp[1][i]*fp[0][i],tp[1][i]*fp[1][i],tp[1][i]]
U,S,V = linalg.svd(A)
H = V[8].reshape((3,3))
#反归一化
H = dot(linalg.inv(C2),dot(H,C1))
#归一化,然后返回
return H / H[2,2]
仿射变换
算法原理
由于仿射变换具有6个自由度,因此我们需要三个对应点来估计矩阵H。通过将最后两个元素设置为0,即h7=h8=0,仿射变换可以用上面的DLT算法估计得出。
代码
def Haffine_from_points(fp, tp):
"""计算H仿射变换,使得tp是fp经过仿射变换H得到的"""
if fp.shape != tp.shape:
raise RuntimeError('number of points do not match')
# 对点进行归一化(对数值计算很重要)
# --- 映射起始点 ---
m = mean(fp[:2], axis=1)
maxstd = max(std(fp[:2], axis=1)) + 1e-9
C1 = diag([1/maxstd, 1/maxstd, 1])
C1[0][2] = -m[0]/maxstd
C1[1][2] = -m[1]/maxstd
fp_cond = dot(C1,fp)
# --- 映射对应点 ---
m = mean(tp[:2], axis=1)
C2 = C1.copy() # 两个点集,必须都进行相同的缩放
C2[0][2] = -m[0]/maxstd
C2[1][2] = -m[1]/maxstd
tp_cond = dot(C2,tp)
# 因为归一化后点的均值为0,所以平移量为0
A = concatenate((fp_cond[:2],tp_cond[:2]), axis=0)
U,S,V = linalg.svd(A.T)
# 如Hartley和Zisserman著的Multiplr View Geometry In Computer,Scond Edition所示,
# 创建矩阵B和C
tmp = V[:2].T
B = tmp[:2]
C = tmp[2:4]
tmp2 = concatenate((dot(C,linalg.pinv(B)),zeros((2,1))), axis=1)
H = vstack((tmp2,[0,0,1]))
# 反归一化
H = dot(linalg.inv(C2),dot(H,C1))
return H / H[2,2]
图像中的图像
算法原理
对图像块应用仿射变换,称为图像扭曲(或仿射扭曲)。该操作不仅经常应用在计算机图形学中。扭曲操作可以使用SciPy工具包中的ndimage包来简单完成。
代码
from matplotlib.pyplot import *
from numpy import array
from scipy import ndimage
from PIL import Image
im = array(Image.open('jmu.jfif').convert('L'))
H = array([[1.4,0.05,-100],[0.05,1.5,-100],[0,0,1]])
im2 = ndimage.affine_transform(im, H[:2,:2],(H[0,2],H[1,2]))
gray()
subplot(121)
imshow(im)
axis('off')
subplot(122)
imshow(im2)
axis('off')
show()
实验结果及分析
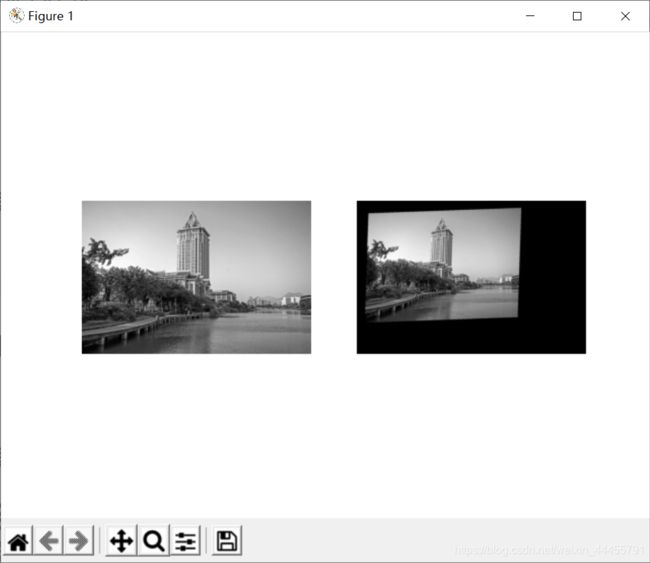
输出图像如右图所示,输出图像结果中丢失的像素用零来填充。用仿射变换来扭曲图像
图像映射
算法原理
仿射扭曲的一个简单例子是,将图像或者图像的一部分放置在另一幅图像中,是的他们能够和指定的区域或者标记物对齐。
代码
from PIL import Image
from matplotlib.pyplot import gray, subplot, imshow, axis, show
from scipy import linalg, ndimage
def Haffine_from_points(fp, tp):
"""计算H仿射变换,使得tp是fp经过仿射变换H得到的"""
if fp.shape != tp.shape:
raise RuntimeError('number of points do not match')
# 对点进行归一化(对数值计算很重要)
# --- 映射起始点 ---
m = mean(fp[:2], axis=1)
maxstd = max(std(fp[:2], axis=1)) + 1e-9
C1 = diag([1 / maxstd, 1 / maxstd, 1])
C1[0][2] = -m[0] / maxstd
C1[1][2] = -m[1] / maxstd
fp_cond = dot(C1, fp)
# --- 映射对应点 ---
m = mean(tp[:2], axis=1)
C2 = C1.copy() # 两个点集,必须都进行相同的缩放
C2[0][2] = -m[0] / maxstd
C2[1][2] = -m[1] / maxstd
tp_cond = dot(C2, tp)
# 因为归一化后点的均值为0,所以平移量为0
A = concatenate((fp_cond[:2], tp_cond[:2]), axis=0)
U, S, V = linalg.svd(A.T)
# 如Hartley和Zisserman著的Multiplr View Geometry In Computer,Scond Edition所示,
# 创建矩阵B和C
tmp = V[:2].T
B = tmp[:2]
C = tmp[2:4]
tmp2 = concatenate((dot(C, linalg.pinv(B)), zeros((2, 1))), axis=1)
H = vstack((tmp2, [0, 0, 1]))
# 反归一化
H = dot(linalg.inv(C2), dot(H, C1))
return H / H[2, 2]
from numpy import array, mean, std, diag, dot, concatenate, vstack, zeros
def image_in_image(im1, im2, tp):
"""使用仿射变换将im1放置在im2上,使im1图像的角和tp尽可能的靠近
tp是齐次表示的,并且是按照从左上角逆时针计算的"""
# 扭曲的点
m, n = im1.shape[:2]
fp = array([[0, m, m, 0], [0, 0, n, n], [1, 1, 1, 1]])
# 计算仿射变换,并且将其应用于图像im1中
H = Haffine_from_points(tp, fp)
im1_t = ndimage.affine_transform(im1, H[:2, :2],
(H[0, 2], H[1, 2]), im2.shape[:2])
alpha = (im1_t > 0)
return (1 - alpha) * im2 + alpha * im1_t
im1 = array(Image.open('jimei.jfif').convert('L'))
im2 = array(Image.open('jmu.jfif').convert('L'))
gray()
subplot(131)
imshow(im1)
axis('equal')
axis('off')
subplot(132)
imshow(im2)
axis('equal')
axis('off')
# 选定一些目标点
tp = array([[264, 538, 540, 264], [40, 36, 605, 605], [1, 1, 1, 1]])
im3 = image_in_image(im1, im2, tp)
subplot(133)
imshow(im3)
axis('equal')
axis('off')
show()
