Megatron-LM源码系列(二):Tensor模型并行和Sequence模型并行训练
代码库地址: https://github.com/NVIDIA/Megatron-LM/tree/23.05
1. 整体介绍
模型并行训练实现的核心代码在megatron/core/目录下,按README.md介绍来说,Megatron Core是一个专门针对transformer类模型、效率高、可扩展的计算库。
megatron/core
├── README.md
├── __init__.py
├── enums.py
├── package_info.py
├── parallel_state.py
├── pipeline_parallel
├── requirements.txt
├── tensor_parallel
└── utils.py
- enums.py: 定义了常见的几种transformer类模型,分别是
- encoder_or_decoder: 只包含encoder的模型有BERT、只包含有decoder的模型有GPT-2
- encoder_and_decoder: 既有encoder又有decoder的模型有标准的Transformer
- retro_encoder: 这里
retro这个词是从Retrieval-Enhanced TRansfOrmer (RETRO)中来的,出自Deepmind RETRO论文】,也就是RETRO中的encoder - retro_decoder: RETRO中的decoder
class ModelType(enum.Enum): encoder_or_decoder = 1 encoder_and_decoder = 2 retro_encoder = 3 retro_decoder = 4 - package_info.py: 包含一些python打包的必要信息。
- parallel_state.py: 包含并行训练状态相关操作,比如通信组的建立、模型并行初始化的相关操作。其中的
initialize_model_parallel在[系列一]中已经讲过。 - pipeline_parallel: 是pipeline并行实现
- tensor_parallel: 包含tensor并行和pipeline并行实现
- utils.py: 保存相关工具实现
2. parallel_state.py
除了initialize_model_parallel前面【Megatron-LM源码系列(一): 模型并行初始化】已经提过,这里其他函数主要是进行通信组rank号相关操作,比如获取一个通信组的上游或下游的rank号、从通信组的local_rank转为global_rank等。部分函数说明如下:
- is_pipeline_first_stage: 判断当前rank是否为pipeline模型并行的第一个stage。通过判断在pipeline并行组中当前local_rank是否为0。以
2机16卡,TP=2, PP=4, DP=2为例, 对应pipeline通信组为 [ g 0 , g 4 , g 8 , g 12 ] , [ g 1 , g 5 , g 9 , g 13 ] , [ g 2 , g 6 , g 10 , g 14 ] , [ g 3 , g 7 , g 11 , g 15 ] [g0, g4, g8, g12], [g1, g5, g9, g13], [g2, g6, g10, g14], [g3, g7, g11, g15] [g0,g4,g8,g12],[g1,g5,g9,g13],[g2,g6,g10,g14],[g3,g7,g11,g15] ,这里的 g 0 , g 1 , g 2 , g 3 g0, g1, g2, g3 g0,g1,g2,g3 对应的local_rank都是0,也就是会处理pipeline模型并行的第一阶段。
def is_pipeline_first_stage(ignore_virtual=False):
"""Return True if in the first pipeline model-parallel stage, False otherwise."""
......
return get_pipeline_model_parallel_rank() == 0
- is_pipeline_last_stage: 判断当前rank是否为pipeline模型并行的最后一个stage。通过判断在pipeline并行组中当前的local_rank是否为最后一个。对应是 g 12 , g 13 , g 14 , g 15 g12, g13, g14, g15 g12,g13,g14,g15
def is_pipeline_last_stage(ignore_virtual=False):
"""Return True if in the last pipeline model-parallel stage, False otherwise."""
......
return get_pipeline_model_parallel_rank() == (
get_pipeline_model_parallel_world_size() - 1)
- get_tensor_model_parallel_src_rank:根据当前结点的global_rank来获取所在tensor模型并行组中的第一个rank。比如以Tensor并行TP=4为例,假设
rank_2所在的tensor模型并行组为 [ g 0 , g 1 , g 2 , g 3 ] [g0, g1, g2, g3] [g0,g1,g2,g3],那么对应的src_rank即为g0。
def get_tensor_model_parallel_src_rank():
"""Calculate the global rank corresponding to the first local rank
in the tensor model parallel group."""
global_rank = torch.distributed.get_rank()
local_world_size = get_tensor_model_parallel_world_size()
return (global_rank // local_world_size) * local_world_size
- get_tensor_model_parallel_rank: 获取当前结点所在tensor并行组中的rank号。
def get_tensor_model_parallel_rank():
"""Return my rank for the tensor model parallel group."""
......
return torch.distributed.get_rank(group=get_tensor_model_parallel_group())
3. tensor_parallel目录
tensor_parallel目录中包含了tensor并行和pipeline并行的实现,目录结构如下:
megatron/core/tensor_parallel
├── __init__.py
├── cross_entropy.py
├── data.py
├── layers.py
├── mappings.py
├── random.py
└── utils.py
3.1 data.py
- data.py中的重点函数是
broadcast_data,用于把每一个tensor模型并行组中rank0的数据广播到该组其他rank结点。函数定义为broadcast_data(keys, data, datatype),data是dict字典类型,用来存放待broadcast的数据,字典中的key是字符串类型,value是cpu tensor数据;keys是保存data中所用key的集合列表;datatype是用于torch tensor中的数据类型。 broadcast_data中处理分为四步:- 对输入
keys和data进行处理,得到每个key对应的tensor的shape大小(key_size为dict类型)、每个key对应tensor中元素的个数(key_numel为dict类型)、所有总的元素个数(total_numel为int类型)。
key_size, key_numel, total_numel = _build_key_size_numel_dictionaries(keys, data)- 在rank0上对所有要broadcast的tensor数据进行打包操作,合并成一维的tensor;在其余的rank上初始化空的tensor,准备接收数据。
# Pack on rank zero. if get_tensor_model_parallel_rank() == 0: # Check that all keys have the same data type. _check_data_types(keys, data, datatype) # Flatten the data associated with the keys flatten_data = torch.cat( [data[key].contiguous().view(-1) for key in keys], dim=0).cuda() else: flatten_data = torch.empty(total_numel, device=torch.cuda.current_device(), dtype=datatype)- 调用
torch.distributed.broadcast函数发送数据,每个rank结点上都有一份完整的pack过后的数据
# Broadcast torch.distributed.broadcast(flatten_data, get_tensor_model_parallel_src_rank(), group=get_tensor_model_parallel_group())- unpack收到的数据,根据之前的
key_size恢复还原之前每个key对应的tensor
# Unpack output = {} offset = 0 for key in keys: size = key_size[key] numel = key_numel[key] output[key] = flatten_data.narrow(0, offset, numel).view(size) offset += numel- 对输入
3.2 mapping.py
mapping.py中包含了如何对tensor进行拆分和聚合的逻辑。
- _reduce: 对输入input进行
all_reduce操作。对torch.distributed.all_reduce做了封装,如果world_size为1,则直接返回。
# Bypass the function if we are using only 1 GPU.
if get_tensor_model_parallel_world_size()==1:
return input_
# All-reduce.
torch.distributed.all_reduce(input_, group=get_tensor_model_parallel_group())
- _split_along_last_dim: 在输入矩阵的最后一维,对矩阵进行切分为
world_size个子矩阵,并按照当前的结点的rank编号返回对应切分后的子矩阵。切分的具体实现是通过torch.split进行,切分后进行张量内存连续化。比如一个大小为 4 × 5 × 6 4 \times 5 \times 6 4×5×6 的矩阵拆为两个大小为 4 × 5 × 3 4 \times 5 \times 3 4×5×3 的矩阵。
# Get the size and dimension.
last_dim = tensor.dim() - 1
last_dim_size = divide(tensor.size()[last_dim], num_partitions)
# Split.
tensor_list = torch.split(tensor, last_dim_size, dim=last_dim)
# Note: torch.split does not create contiguous tensors by default.
if contiguous_split_chunks:
return tuple(chunk.contiguous() for chunk in tensor_list)
- _split_along_first_dim:在输入矩阵的第一维,对矩阵进行切分为
world_size个子矩阵,并按照当前的结点的rank编号返回对应切分后的子矩阵。由于矩阵是顺序存储的,先按rank号计算每个子矩阵的偏移,然后基于偏移计算输出。比如一个大小为 4 × 5 × 6 4 \times 5 \times 6 4×5×6 的矩阵拆为两个大小为 2 × 5 × 6 2 \times 5 \times 6 2×5×6 的矩阵。
# Split along first dimension.
dim_size = input_.size()[0]
assert dim_size % world_size == 0, \
"First dimension of the tensor should be divisible by tensor parallel size"
local_dim_size = dim_size // world_size
rank = get_tensor_model_parallel_rank()
dim_offset = rank * local_dim_size
output = input_[dim_offset:dim_offset+local_dim_size].contiguous()
- _gather_along_last_dim:一个tensor并行通信组内,在最后一个维度上进行矩阵拼接操作, 先通过
torch.distributed.all_gather获取所有的tensor, 得到一个tensor列表,然后在通过torch.cat在最后一维上进行拼接操作。比如rank为2的时候,两个大小为 4 × 5 × 3 4 \times 5 \times 3 4×5×3 的矩阵拼接为一个大小为 4 × 5 × 6 4 \times 5 \times 6 4×5×6 的矩阵。
torch.distributed.all_gather(tensor_list, input_, group=get_tensor_model_parallel_group())
# Note: torch.cat already creates a contiguous tensor.
output = torch.cat(tensor_list, dim=last_dim).contiguous()
- _gather_along_first_dim:一个tensor并行通信组内,在第一个维度上进行矩阵拼接操作,先初始化一个全量大小的空tensor,然后通过
torch.distributed._all_gather_base获取所有的tensor,直接得到一个tensor。比如两个大小为 2 × 5 × 3 2 \times 5 \times 3 2×5×3 的矩阵拼接为一个大小为 4 × 5 × 6 4 \times 5 \times 6 4×5×6 的矩阵。
output = torch.empty(dim_size, dtype=input_.dtype,
device=torch.cuda.current_device())
torch.distributed._all_gather_base(output, input_.contiguous(),
group=get_tensor_model_parallel_group())
- _reduce_scatter_along_first_dim:一个tensor并行通信组内,在第一个维度上进行
reduce_scatter操作。reduce_scatter返回的结果是当前rank上的结果。比如rank为2的时候,大小为 4 × 5 × 6 4 \times 5 \times 6 4×5×6 的矩阵经过reduce_scatter后,结果返回为一个大小为 2 × 5 × 6 2 \times 5 \times 6 2×5×6 的矩阵。
dim_size[0] = dim_size[0] // world_size
output = torch.empty(dim_size, dtype=input_.dtype,
device=torch.cuda.current_device())
torch.distributed._reduce_scatter_base(output, input_.contiguous(),
group=get_tensor_model_parallel_group())
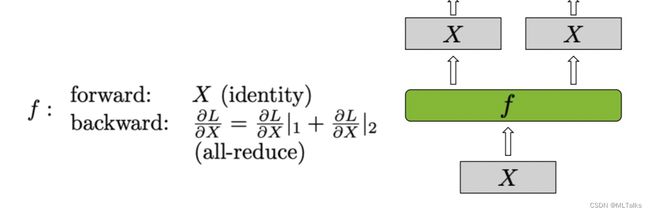
- copy_to_tensor_model_parallel_region:是对_CopyToModelParallelRegion类使用的封装,
_CopyToModelParallelRegion继承自torch.autograd.Function的自定义Function,在tensor并行中前向是复制输入,反向是all_reduce操作。对应Column Parallel Linear Layer中的 f f f 函数。
class _CopyToModelParallelRegion(torch.autograd.Function):
"""Pass the input to the model parallel region."""
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input_):
return input_
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
return _reduce(grad_output)
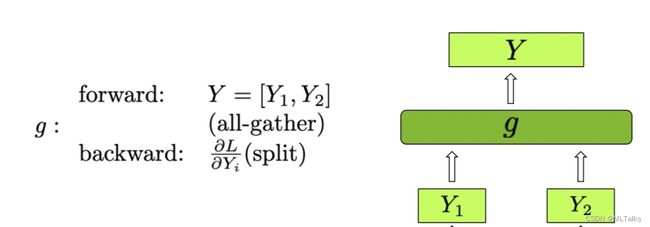
- gather_from_tensor_model_parallel_region:是对_GatherFromModelParallelRegion类使用的封装,
_GatherFromModelParallelRegion继承自torch.autograd.Function的自定义Function,在tensor并行中前向是all_gather,反向是split梯度操作。对应Column Parallel Linear Layer中的 g g g 函数。
class _GatherFromModelParallelRegion(torch.autograd.Function):
"""Gather the input from model parallel region and concatinate."""
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input_):
return _gather_along_last_dim(input_)
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
return _split_along_last_dim(grad_output)
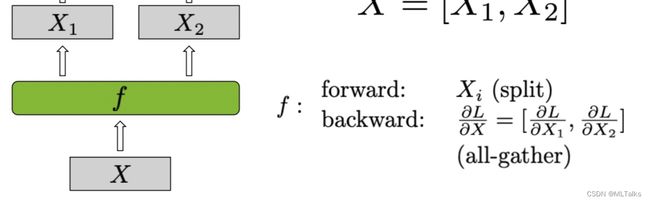
- scatter_to_tensor_model_parallel_region:是对_ScatterToModelParallelRegion类使用的封装,
_ScatterToModelParallelRegion继承自torch.autograd.Function的自定义Function,在tensor并行前向split操作,反向是all_gather所有梯度。对应Row Parallel Linear Layer中的 f f f 函数。
class _ScatterToModelParallelRegion(torch.autograd.Function):
"""Split the input and keep only the corresponding chuck to the rank."""
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input_):
return _split_along_last_dim(input_)
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
return _gather_along_last_dim(grad_output)
- reduce_from_tensor_model_parallel_region:是对_ReduceFromModelParallelRegion类使用的封装,
_ReduceFromModelParallelRegion继承自torch.autograd.Function的自定义Function,在tensor并行前向all_reduce操作,反向是复制梯度输出。对应Row Parallel Linear Layer中的 g g g 函数。
class _ReduceFromModelParallelRegion(torch.autograd.Function):
"""All-reduce the input from the model parallel region."""
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input_):
return _reduce(input_)
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
return grad_output
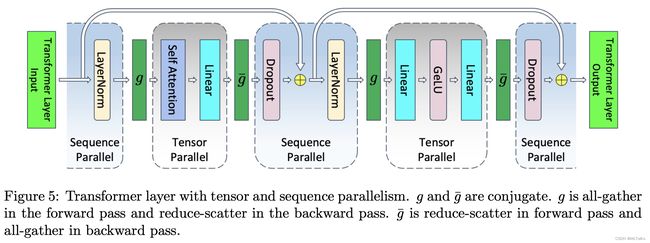
- gather_from_sequence_parallel_region:是对_GatherFromSequenceParallelRegion类使用的封装,
_GatherFromSequenceParallelRegion继承自torch.autograd.Function的自定义Function,在parallel并行前向进行all_gather操作,反向是梯度reduce_scatter输出。对应Pipeline Parallel Linear Layer中的 g g g 函数。
class _GatherFromSequenceParallelRegion(torch.autograd.Function):
"""Gather the input from sequence parallel region and concatinate."""
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input_, tensor_parallel_output_grad=True):
ctx.tensor_parallel_output_grad = tensor_parallel_output_grad
return _gather_along_first_dim(input_)
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
tensor_parallel_output_grad = ctx.tensor_parallel_output_grad
if tensor_parallel_output_grad:
return _reduce_scatter_along_first_dim(grad_output), None
else:
return _split_along_first_dim(grad_output), None
- reduce_scatter_to_sequence_parallel_region:是对_ReduceScatterToSequenceParallelRegion类使用的封装,
_ReduceScatterToSequenceParallelRegion继承自torch.autograd.Function的自定义Function,在parallel并行前向进行reduce_scatter操作,反向是梯度all_gather操作。对应Pipeline Parallel Linear Layer中的 g ‾ \overline{g} g 函数。
class _ReduceScatterToSequenceParallelRegion(torch.autograd.Function):
"""Reduce scatter the input from the model parallel region."""
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input_):
return _reduce_scatter_along_first_dim(input_)
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
return _gather_along_first_dim(grad_output)
- scatter_to_sequence_parallel_region:是对_ScatterToSequenceParallelRegion类使用的封装,
_ScatterToSequenceParallelRegion继承自torch.autograd.Function的自定义Function,用于embedding层的parallel并行,前向会进行split操作,反向是梯度all_gather操作。
class _ScatterToSequenceParallelRegion(torch.autograd.Function):
"""Split the input and keep only the corresponding chuck to the rank."""
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input_):
return _split_along_first_dim(input_)
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
return _gather_along_first_dim(grad_output)
3.3 layers.py
layers.py中实现了Tensor并行对外开放的自定义Module,主要有按列切分参数的ColumnParallelLinear和按行切为参数的RowParallelLinear。
3.3.1 ColumnParallelLinear
对于一个线性变换 Y = X A + b Y=XA+b Y=XA+b 来说, X X X 是输入, Y Y Y 是输出, A A A 是参数, b b b是bias,按列切分的时候把参数 A A A 切分为 [ A 1 , A 2 , . . . , A p ] [A_1, A_2, ..., A_p] [A1,A2,...,Ap],定义如下。
class ColumnParallelLinear(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, output_size, *,
bias=True, gather_output=True,
init_method=init.xavier_normal_, stride=1,
keep_master_weight_for_test=False,
skip_bias_add=False,
async_tensor_model_parallel_allreduce=True,
params_dtype=torch.float32,
use_cpu_initialization=False,
perform_initialization=True,
gradient_accumulation_fusion=False,
sequence_parallel_enabled: bool = False,
):
...
其中参数说明如下:
- input_size: 矩阵输入大小, 比如 X X X 的shape是 a × b a \times b a×b, A A A 的shape是 b × c b \times c b×c, 对应这里input_size是 b b b
- output_size: 矩阵输出大小, 比如 X X X 的shape是 a × b a \times b a×b, A A A 的shape是 b × c b \times c b×c, 对应这里output_size是 c c c
- bias:是否要增加使用bias偏差
- gather_output: 是否对output做all_gather操作,在多个MLP串联执行时候中间结果的output可以省略中间的gather操作,提高执行的效率
- init_method:参数初始化方法,默认使用
init.xavier_normal_ - stride: 用于strided linear layer, 用的情况很少
- return_master_weight: 返回权重用于测试
- skip_bias_add: 在为了使用fusion提升性能的情况下,可以选择跳过bias的累加,让bias的累加和后续其他算子进行fusion融合操作
- async_tensor_model_parallel_allreduce:在
linear_with_grad_accumulation_and_async_allreduce使用异步的allreduce提升速度,跟sequence_parallel_enabled二选一,因为在sequence并行中没有allreduce操作 - params_dtype:参数类型,默认为
torch.float32 - use_cpu_initialization:基于cpu进行参数初始化
- gradient_accumulation_fusion:使用fusion版的梯度累加,这个需要编译CUDA扩展
fused_weight_gradient_mlp_cuda模块 - sequence_parallel_enabled:使用sequence并行
在 forward(self, input_) 函数实现中,如果是tensor并行那么使用copy_to_tensor_model_parallel_region进行输入矩阵input_的复制(这样可求导),如果是sequence并行和parallel_allreduce则直接使用输入的input_。
if self.async_tensor_model_parallel_allreduce or \
self.sequence_parallel_enabled:
input_parallel = input_
else:
input_parallel = copy_to_tensor_model_parallel_region(input_)
在对输入处理完后,接下来就开始矩阵和权重相乘操作了,这里默认会使用gradient_accumulation_fusion和async_grad_allreduce。注意sequence并行中没有allreduce操作,所以sequence_parallel_enabled的使用和async_grad_allreduce二选一。
# Matrix multiply.
output_parallel = linear_with_grad_accumulation_and_async_allreduce(
input=input_parallel,
weight=self.weight,
bias=bias,
gradient_accumulation_fusion=self.gradient_accumulation_fusion,
async_grad_allreduce=self.async_tensor_model_parallel_allreduce,
sequence_parallel_enabled=self.sequence_parallel_enabled,
)
linear_with_grad_accumulation_and_async_allreduce的实际实现是在LinearWithGradAccumulationAndAsyncCommunication类中,在前向中判断如果是sequence并行刚进行allgather操作,如果没用的话则直接进行输入和权重的相乘。
class LinearWithGradAccumulationAndAsyncCommunication(torch.autograd.Function):
...
def forward(ctx, input, weight, bias, gradient_accumulation_fusion,
if sequence_parallel:
world_size = get_tensor_model_parallel_world_size()
dim_size = list(input.size())
dim_size[0] = dim_size[0] * world_size
all_gather_buffer = \
get_global_memory_buffer().get_tensor(dim_size, input.dtype, "mpu")
torch.distributed._all_gather_base(
all_gather_buffer,
input,
group=get_tensor_model_parallel_group())
total_input = all_gather_buffer
else:
total_input = input
output = torch.matmul(total_input, weight.t())
...
在矩阵计算 Y = X W Y=XW Y=XW 的反向中, 对输入 X X X的梯度计算等于 X ′ = Y ′ W T X'=Y'W^{T} X′=Y′WT。LinearWithGradAccumulationAndAsyncCommunication类的反向中先计算当前输入的梯度grad_input = grad_output.matmul(weight),然后对所有rank结点的grad_input进行聚合操作。如果没用pipeline并行的话刚直接进行torch.distributed.all_reduce操作,如果用了pipeline并行则使用torch.distributed._reduce_scatter_base操作, 最后得到最终的输入的梯度grad_input。
class LinearWithGradAccumulationAndAsyncCommunication(torch.autograd.Function):
...
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
......
grad_input = grad_output.matmul(weight)
......
if ctx.async_grad_allreduce:
......
# Asynchronous all-reduce
handle = torch.distributed.all_reduce(
grad_input, group=get_tensor_model_parallel_group(), async_op=True)
if ctx.sequence_parallel:
......
# reduce_scatter
handle = torch.distributed._reduce_scatter_base(sub_grad_input, grad_input,
group=get_tensor_model_parallel_group(),
async_op=True)
在矩阵计算 Y = X W Y=XW Y=XW 的反向中, 对权重 W W W 的梯度计算等于 W ′ = X T Y ′ W'=X^{T}Y' W′=XTY′。LinearWithGradAccumulationAndAsyncCommunication类的反向中,使用grad_output.t()和total_input相乘得到最终的权重的梯度grad_weight,可以使用gradient_accumulation_fusion进行加速。
class LinearWithGradAccumulationAndAsyncCommunication(torch.autograd.Function):
...
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
......
if ctx.gradient_accumulation_fusion:
if weight.main_grad.dtype == torch.float32:
fused_weight_gradient_mlp_cuda.wgrad_gemm_accum_fp32(total_input, grad_output, weight.main_grad)
elif weight.main_grad.dtype in (torch.float16, torch.bfloat16):
fused_weight_gradient_mlp_cuda.wgrad_gemm_accum_fp16(total_input, grad_output, weight.main_grad)
else:
raise RuntimeError("Unsupported gradient type for gradient accumulation fusion")
grad_weight = None
else:
grad_weight = grad_output.t().matmul(total_input)
......
return grad_input, grad_weight, grad_bias, None, None, None
在计算完linear_with_grad_accumulation_and_async_allreduce后, 在ColumnParallelLinear输出前向的结果,如果需要进行输出的合并则打开self.gather_output进行结果的gather_from_tensor_model_parallel_region操作,不需要的话则直接返回结果;对于有bias的情况,如果需要进行bias相关fusion操作,则打开self.skip_bias_add在结果中将bias一起返回。
class ColumnParallelLinear(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, input_):
......
if self.gather_output:
# All-gather across the partitions.
assert not self.sequence_parallel_enabled
output = gather_from_tensor_model_parallel_region(output_parallel)
else:
output = output_parallel
output_bias = self.bias if self.skip_bias_add else None
return output, output_bias
3.3.2 RowParallelLinear
对于一个线性变换 Y = X A + b Y=XA+b Y=XA+b 来说, X X X 是输入, Y Y Y 是输出, A A A 是参数, b b b是bias,按列切分的时候会把参数 A A A 按行切分为 [ A 1 A 2 . . . A p ] \left[ \begin{matrix} A_1 \\ A_2 \\ ... \\ A_p \end{matrix} \right] A1A2...Ap 。函数定义如下:
class RowParallelLinear(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, output_size, *,
bias=True, input_is_parallel=False,
init_method=init.xavier_normal_, stride=1,
keep_master_weight_for_test=False,
skip_bias_add=False,
params_dtype=torch.float32,
use_cpu_initialization=False,
perform_initialization=True,
gradient_accumulation_fusion=False,
sequence_parallel_enabled: bool = False,
):
...
其中参数说明如下:
- input_size: 矩阵输入大小, 比如 X X X 的shape是 a × b a \times b a×b, A A A 的shape是 b × c b \times c b×c, 对应这里input_size是 b b b
- output_size: 矩阵输出大小, 比如 X X X 的shape是 a × b a \times b a×b, A A A 的shape是 b × c b \times c b×c, 对应这里output_size是 c c c
- bias:是否要增加使用bias偏差
- input_is_parallel: 是否是并行切分过的input,在
RowParallelLinear接到ColumnParallelLinear后面的时候,可以直接使用传过来的被切分好的输入,可以加速计算 - init_method:参数初始化方法,默认使用
init.xavier_normal_ - stride: 用于strided linear layer, 用的情况很少
- return_master_weight: 返回权重用于测试
- skip_bias_add: 在为了使用fusion提升性能的情况下,可以选择跳过bias的累加,让bias的累加和后续其他算子进行fusion融合操作
- async_tensor_model_parallel_allreduce:在
linear_with_grad_accumulation_and_async_allreduce使用异步的allreduce提升速度,跟sequence_parallel_enabled二选一,因为在sequence并行中没有allreduce操作 - params_dtype:参数类型,默认为
torch.float32 - use_cpu_initialization:基于cpu进行参数初始化
- gradient_accumulation_fusion:使用fusion版的梯度累加,这个需要编译CUDA扩展
fused_weight_gradient_mlp_cuda模块 - sequence_parallel_enabled:使用sequence并行
在 forward(self, input_) 函数实现中,input_的维度是3维,分别是[sequence, batch, hidden]。如果使用了input_is_parallel=True, 则直接使用输入;否则会通过scatter_to_tensor_model_parallel_region对输入进行scatter。
class RowParallelLinear(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, input_):
if self.input_is_parallel:
input_parallel = input_
else:
assert not self.sequence_parallel_enabled
input_parallel = scatter_to_tensor_model_parallel_region(input_)
...
输入准备好后,使用linear_with_grad_accumulation_and_async_allreduce进行矩阵相乘,这个跟ColumnParallelLinear一样。
# Matrix multiply.
output_parallel = linear_with_grad_accumulation_and_async_allreduce(
input=input_parallel,
weight=self.weight,
bias=None,
gradient_accumulation_fusion=self.gradient_accumulation_fusion,
async_grad_allreduce=False,
sequence_parallel_enabled=False,
)
在计算完矩阵乘后,如果是用的pipeline并行,则使用reduce_scatter进行结果汇总;如果还是tensor并行的话,则使用allreduce进行汇总。对应bias也是通过skip_bias_add看是否需要直接在结果中返回。
# All-reduce across all the partitions.
if self.sequence_parallel_enabled:
output_ = reduce_scatter_to_sequence_parallel_region(output_parallel)
else:
output_ = reduce_from_tensor_model_parallel_region(output_parallel)
if not self.skip_bias_add:
output = output_ + self.bias if self.bias is not None else output_
output_bias = None
else:
output = output_
output_bias = self.bias
return output, output_bias
4. 参考:
- The Illustrated Retrieval Transformer
- Improving language models by retrieving from trillions of tokens
- Megatron-LM源码系列(一): 模型并行初始化
- 详解MegatronLM Tensor模型并行训练(Tensor Parallel)
- 详解MegatronLM Sequence序列模型并行训练(Sequence Parallel)