实践:基于Softmax回归完成鸢尾花分类任务
文件内引用的nndl包内的文件代码可翻看以往博客有详细介绍,这么就不详细赘述啦基于Softmax回归的多分类任务_熬夜患者的博客-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/m0_70026215/article/details/133690588?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_70026215/article/details/133690588?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
1.数据处理
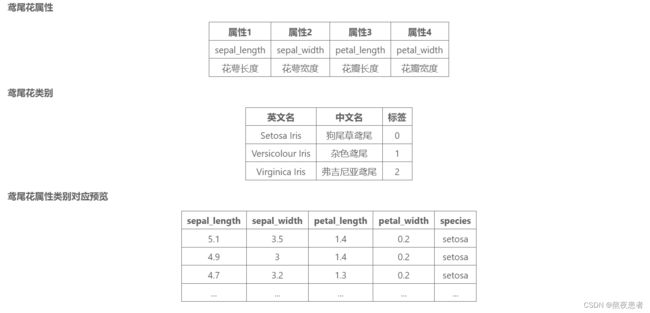
数据集介绍
缺失值分析
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
import pandas
import numpy as np
import torch
iris_features = np.array(load_iris().data, dtype=np.float32)
iris_labels = np.array(load_iris().target, dtype=np.int32)
print(pandas.isna(iris_features).sum())
print(pandas.isna(iris_labels).sum())运行结果:
异常值处理
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #可视化工具
# 箱线图查看异常值分布
def boxplot(features):
feature_names = ['sepal_length', 'sepal_width', 'petal_length', 'petal_width']
# 连续画几个图片
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5), dpi=200)
# 子图调整
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.6)
# 每个特征画一个箱线图
for i in range(4):
plt.subplot(2, 2, i+1)
# 画箱线图
plt.boxplot(features[:, i],
showmeans=True,
whiskerprops={"color":"#E20079", "linewidth":0.4, 'linestyle':"--"},
flierprops={"markersize":0.4},
meanprops={"markersize":1})
# 图名
plt.title(feature_names[i], fontdict={"size":5}, pad=2)
# y方向刻度
plt.yticks(fontsize=4, rotation=90)
plt.tick_params(pad=0.5)
# x方向刻度
plt.xticks([])
plt.savefig('ml-vis.pdf')
plt.show()
boxplot(iris_features)运行结果:
从输出结果看,数据中基本不存在异常值,所以不需要进行异常值处理。
数据读取
def load_data(shuffle=True):
'''
加载鸢尾花数据
输入:
- shuffle:是否打乱数据,数据类型为bool
输出:
- X:特征数据,shape=[150,4]
- y:标签数据, shape=[150]
'''
# 加载原始数据
X = np.array(load_iris().data, dtype=np.float32)
y = np.array(load_iris().target, dtype=np.float32)
X = torch.tensor(X)
y = torch.tensor(y)
# 数据归一化
X_min = torch.min(X, dim=0).values
X_max = torch.max(X, dim=0).values
X = (X-X_min) / (X_max-X_min)
# 如果shuffle为True,随机打乱数据
if shuffle:
idx = torch.randperm(X.shape[0])
X = X[idx]
y = y[idx]
return X, y
# 固定随机种子
torch.manual_seed(102)
num_train = 120
num_dev = 15
num_test = 15
X, y = load_data(shuffle=True)
print("X shape: ", X.shape, "y shape: ", y.shape)
X_train, y_train = X[:num_train], y[:num_train]
X_dev, y_dev = X[num_train:num_train + num_dev], y[num_train:num_train + num_dev]
X_test, y_test = X[num_train + num_dev:], y[num_train + num_dev:]
# 打印X_train和y_train的维度
print("X_train shape: ", X_train.shape, "y_train shape: ", y_train.shape)
# 打印前5个数据的标签
print(y_train[:5])运行结果:
2.模型构建
from nndl import op
# 输入维度
input_dim = 4
# 类别数
output_dim = 3
# 实例化模型
model = op.model_SR(input_dim=input_dim, output_dim=output_dim)3.模型训练
from nndl import op, metric, opitimizer, runner
lr = 0.2
# 梯度下降法
optimizer = opitimizer.SimpleBatchGD(init_lr=lr, model=model)
# 交叉熵损失
loss_fn = op.MultiCrossEntropyLoss()
# 准确率
metric = metric.accuracy
# 实例化RunnerV2
runner = runner.RunnerV2(model, optimizer, metric, loss_fn)
# 启动训练
runner.train([X_train, y_train], [X_dev, y_dev], num_epochs=200, log_epochs=10, save_path="best_model.pdparams")运行结果:
可视化观察训练集与验证集的准确率变化情况。
from nndl import tools
tools.plot(runner,fig_name='linear-acc3.pdf')运行结果:
4.模型评价
runner.load_model('best_model.pdparams')
# 模型评价
score, loss = runner.evaluate([X_test, y_test])
print("[Test] score/loss: {:.4f}/{:.4f}".format(score, loss))运行结果:
![]()
5.模型预测
# 预测测试集数据
logits = runner.predict(X_test)
# 观察其中一条样本的预测结果
pred = torch.argmax(logits[0]).numpy()
print("pred:",pred)
# 获取该样本概率最大的类别
label = y_test[0].numpy()
print("label:",label)
# 输出真实类别与预测类别
print("The true category is {0} and the predicted category is {1}".format(label, pred))运行结果:
小结
到这儿,三、四章的实验就写完了,但是这两天写的有点快,总感觉有些东西没弄的太透彻,但是说不上来是哪部分,总觉得不行,这两天事多,等我这两天忙完的,会把这几个文章全部过一遍,重新翻新一遍,弄透彻!!!!浅浅立个flag!!!加油