如何熟练的使用trtexec
目录
- 如何熟练的使用trtexec
-
- 注意事项
- 一、2023/5/9更新
- 前言
- 1. 参数解释
-
- 1.1 Model Options
- 1.2 Build Options
- 1.3 Inference Options
- 1.4 Reporting Options
- 1.5 System Options
- 1.6 完整的参数
- 2. ONNX模型的简单编译
-
- 2.1 静态onnx
- 2.2 动态onnx
如何熟练的使用trtexec
注意事项
一、2023/5/9更新
更新 onnx 模型的简单编译,即第 2 小结内容
前言
杜老师推出的 trtexec 工具的使用课程,链接。记录下个人学习笔记,仅供自己参考。
trtexec 工具是 tensorRT 安装包里面自带的一个命令行应用程序软件,能够极大的便利我们在 tensorRT 开发过程中的模型编译、精度设置、性能调优等工作
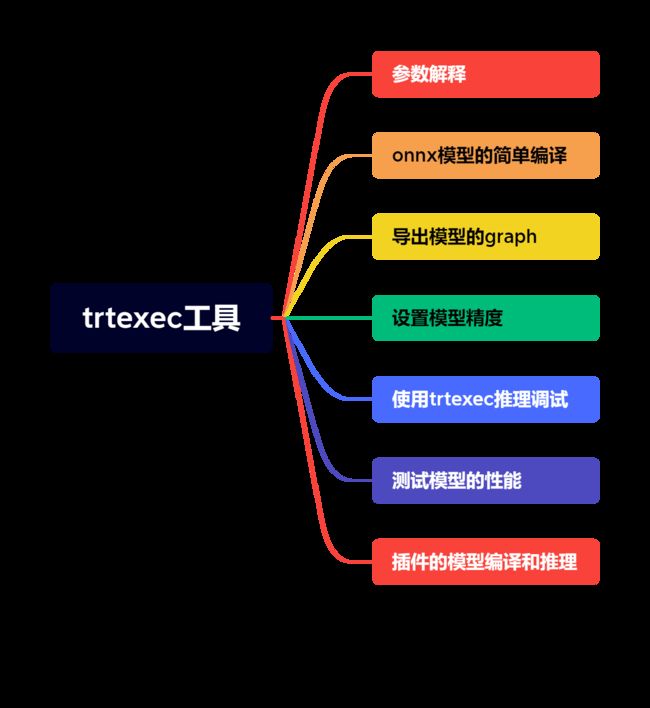
课程大纲可看下面的思维导图
1. 参数解释
trtexec 重点参数的相关介绍
1.1 Model Options
- –onnx=
ONNX model - 指定 onnx model 的路径
1.2 Build Options
- –minShapes=spec Build with dynamic shapes using a profile with the min shapes provided
- –optShapes=spec Build with dynamic shapes using a profile with the opt shapes provided
- –maxShapes=spec Build with dynamic shapes using a profile with the max shapes provided
- 上述三个参数用来做动态 Shape 的指定
Example input shapes spec: input0:1x3x256x256,input1:1x3x128x128
- –inputIOFormats=spec Type and format of each of the input tensors (default = all inputs in fp32:chw) Note: If this option is specified, please set comma-separated types and formats for all inputs.
- 输入类型和格式的指定 FP32、FP16、INT8
- –outputIOFormats=spec Type and format of each of the output tensors (default = all outputs in fp32:chw)
- 输出类型和格式的指定 FP32、FP16、INT8
- IO Formats:
- spec ::= IOfmt[","spec]
- IOfmt ::= type:fmt
- type ::= “fp32”|“fp16”|“int32”|“int8”
- fmt ::= (“chw”|“chw2”|“chw4”|“hwc8”|“chw16”|“chw32”|“dhwc8”| “cdhw32”|“hwc”|“dla_linear”|“dla_hwc4”)["+"fmt]
Example --inputIOFormats=fp32:chw,fp32:chw -outputIOFormats=fp16:chw,fp16:chw
- –memPoolSize=poolspec Specify the size constraints of the designated memory pool(s) in MiB.
- 替代以前的 workspace,当模型使用一些 shared memory 时,会去 workspace 中请求
Example: --memPoolSize=workspace:1024.5,dlaSRAM:256
- –profilingVerbosity=mode Specify profiling verbosity. mode ::= layer_names_only|detailed|none (default = layer_names_only)
- 打印信息的详细程度
Example: --profilingVerbosity=detailed
- –fp16 Enable fp16 precision, in addition to fp32 (default = disabled)
- 使能 FP16 精度
- –int8 Enable int8 precision, in addition to fp32 (default = disabled)
- 使能 INT8 量化精度
- –calib=
Read INT8 calibration cache file - INT8 的量化表,存储的是每个 tensor 的 scale 值,不常用
- 对于没有 calibration table 或者 QDQ 的,dynamic range 设置为 4,精度有较大影响,主要是为了测速
- –best Enable all precisions to achieve the best performance (default = disabled)
- 三个精度 FP32+FP16+INT8 同时使用,找一个速度最快的
- –saveEngine=
Save the serialized engine - 保存序列化后的引擎文件
- –loadEngine=
Load a serialized engine - 加载序列化后的引擎文件
- –tacticSources=tactics Specify the tactics to be used by adding (+) or removing (-) tactics from the default tactic sources (default = all available tactics). Note: Currently only cuDNN, cuBLAS, cuBLAS-LT, and edge mask convolutions are listed as optional tactics.
- 指定编译时优化策略的来源,比较冷门,使用较少
- Tactic Sources:
- tactics ::= [","tactic]
- tactic ::= (+|-)lib
- lib ::= “CUBLAS”|“CUBLAS_LT”|“CUDNN”|“EDGE_MASK_CONVOLUTIONS”
For example, to disable cudnn and enable cublas: --tacticSources=-CUDNN,+CUBLAS
1.3 Inference Options
- –shapes=spec Set input shapes for dynamic shapes inference inputs.
- 设置推理时输入的动态 shape
- –loadInputs=spec Load input values from files (default = generate random inputs). Input names can be wrapped with single quotes (ex: ‘Input:0’)
- 模型做 debug 看推理结果是否和 pytorch 一致时可以指定该参数
- 输入的 binary 通过 numyp 导出即可
For example: --loadInputs=input0:input0.binary,input1:input1.binary
- –iterations=N Run at least N inference iterations (default = 10)
- 运行最少 N 次推理
- –warmUp=N Run for N milliseconds to warmup before measuring performance (default = 200)
- 在性能测试时执行 N 毫秒的 warmup
- –duration=N Run performance measurements for at least N seconds wallclock time (default = 3)
- 最少运行 N 秒
- –sleepTime=N Delay inference start with a gap of N milliseconds between launch and compute (default = 0)
- 推理前延迟 N 毫秒
- –idleTime=N Sleep N milliseconds between two continuous iterations(default = 0)
- 两次连续推理之间空闲 N 毫秒
- –streams=N Instantiate N engines to use concurrently (default = 1)
- 启动 N 个实例,可以测试多流执行时是否提速
- –separateProfileRun Do not attach the profiler in the benchmark run; if profiling is enabled, a second profile run will be executed (default = disabled)
- profile 和 benchmark 分开
- –buildOnly Exit after the engine has been built and skip inference perf measurement (default = disabled)
- 只做编译不做 inference
1.4 Reporting Options
- –verbose Use verbose logging (default = false)
- 使用详细的日志输出信息
- –dumpOutput Print the output tensor(s) of the last inference iteration (default = disabled)
- 将推理结果直接打印出来
- –dumpProfile Print profile information per layer (default = disabled)
- 打印每一层的 profile 信息
- –dumpLayerInfo Print layer information of the engine to console (default = disabled)
- 打印 engine 的每层信息
- –exportOutput=
Write the output tensors to a json file (default = disabled) - 将 ouput 打印信息存储下来
- –exportProfile=
Write the profile information per layer in a json file (default = disabled) - 将 profile 打印信息存储下来
- –exportLayerInfo=
Write the layer information of the engine in a json file (default = disabled) - 将 engine 的 layer 打印信息存储下来
Example: --exportLayerInfo=layer.json --profilingVerbosity=detailed
1.5 System Options
- –device=N Select cuda device N (default = 0)
- device 设备的设置
- –useDLACore=N Select DLA core N for layers that support DLA (default = none)
- 使用较少
- –allowGPUFallback When DLA is enabled, allow GPU fallback for unsupported layers (default = disabled)
- 当 DLA 使能时,是否允许某些不支持的层在 GPU 上 fallback
- –plugins Plugin library (.so) to load (can be specified multiple times)
- 加载插件,实现自定义算子的编译工作
Example: --plugin=xxx.so --plugin=aaa.so --plugins=www.so
1.6 完整的参数
trtexec 的完整参数如下所示:
&&&& RUNNING TensorRT.trtexec [TensorRT v8401] # trtexec
=== Model Options ===
--uff=<file> UFF model
--onnx=<file> ONNX model
--model=<file> Caffe model (default = no model, random weights used)
--deploy=<file> Caffe prototxt file
--output=<name>[,<name>]* Output names (it can be specified multiple times); at least one output is required for UFF and Caffe
--uffInput=<name>,X,Y,Z Input blob name and its dimensions (X,Y,Z=C,H,W), it can be specified multiple times; at least one is required for UFF models
--uffNHWC Set if inputs are in the NHWC layout instead of NCHW (use X,Y,Z=H,W,C order in --uffInput)
=== Build Options ===
--maxBatch Set max batch size and build an implicit batch engine (default = same size as --batch)
This option should not be used when the input model is ONNX or when dynamic shapes are provided.
--minShapes=spec Build with dynamic shapes using a profile with the min shapes provided
--optShapes=spec Build with dynamic shapes using a profile with the opt shapes provided
--maxShapes=spec Build with dynamic shapes using a profile with the max shapes provided
--minShapesCalib=spec Calibrate with dynamic shapes using a profile with the min shapes provided
--optShapesCalib=spec Calibrate with dynamic shapes using a profile with the opt shapes provided
--maxShapesCalib=spec Calibrate with dynamic shapes using a profile with the max shapes provided
Note: All three of min, opt and max shapes must be supplied.
However, if only opt shapes is supplied then it will be expanded so
that min shapes and max shapes are set to the same values as opt shapes.
Input names can be wrapped with escaped single quotes (ex: \'Input:0\').
Example input shapes spec: input0:1x3x256x256,input1:1x3x128x128
Each input shape is supplied as a key-value pair where key is the input name and
value is the dimensions (including the batch dimension) to be used for that input.
Each key-value pair has the key and value separated using a colon (:).
Multiple input shapes can be provided via comma-separated key-value pairs.
--inputIOFormats=spec Type and format of each of the input tensors (default = all inputs in fp32:chw)
See --outputIOFormats help for the grammar of type and format list.
Note: If this option is specified, please set comma-separated types and formats for all
inputs following the same order as network inputs ID (even if only one input
needs specifying IO format) or set the type and format once for broadcasting.
--outputIOFormats=spec Type and format of each of the output tensors (default = all outputs in fp32:chw)
Note: If this option is specified, please set comma-separated types and formats for all
outputs following the same order as network outputs ID (even if only one output
needs specifying IO format) or set the type and format once for broadcasting.
IO Formats: spec ::= IOfmt[","spec]
IOfmt ::= type:fmt
type ::= "fp32"|"fp16"|"int32"|"int8"
fmt ::= ("chw"|"chw2"|"chw4"|"hwc8"|"chw16"|"chw32"|"dhwc8"|
"cdhw32"|"hwc"|"dla_linear"|"dla_hwc4")["+"fmt]
--workspace=N Set workspace size in MiB.
--memPoolSize=poolspec Specify the size constraints of the designated memory pool(s) in MiB.
Note: Also accepts decimal sizes, e.g. 0.25MiB. Will be rounded down to the nearest integer bytes.
Pool constraint: poolspec ::= poolfmt[","poolspec]
poolfmt ::= pool:sizeInMiB
pool ::= "workspace"|"dlaSRAM"|"dlaLocalDRAM"|"dlaGlobalDRAM"
--profilingVerbosity=mode Specify profiling verbosity. mode ::= layer_names_only|detailed|none (default = layer_names_only)
--minTiming=M Set the minimum number of iterations used in kernel selection (default = 1)
--avgTiming=M Set the number of times averaged in each iteration for kernel selection (default = 8)
--refit Mark the engine as refittable. This will allow the inspection of refittable layers
and weights within the engine.
--sparsity=spec Control sparsity (default = disabled).
Sparsity: spec ::= "disable", "enable", "force"
Note: Description about each of these options is as below
disable = do not enable sparse tactics in the builder (this is the default)
enable = enable sparse tactics in the builder (but these tactics will only be
considered if the weights have the right sparsity pattern)
force = enable sparse tactics in the builder and force-overwrite the weights to have
a sparsity pattern (even if you loaded a model yourself)
--noTF32 Disable tf32 precision (default is to enable tf32, in addition to fp32)
--fp16 Enable fp16 precision, in addition to fp32 (default = disabled)
--int8 Enable int8 precision, in addition to fp32 (default = disabled)
--best Enable all precisions to achieve the best performance (default = disabled)
--directIO Avoid reformatting at network boundaries. (default = disabled)
--precisionConstraints=spec Control precision constraint setting. (default = none)
Precision Constaints: spec ::= "none" | "obey" | "prefer"
none = no constraints
prefer = meet precision constraints set by --layerPrecisions/--layerOutputTypes if possible
obey = meet precision constraints set by --layerPrecisions/--layerOutputTypes or fail
otherwise
--layerPrecisions=spec Control per-layer precision constraints. Effective only when precisionConstraints is set to
"obey" or "prefer". (default = none)
The specs are read left-to-right, and later ones override earlier ones. "*" can be used as a
layerName to specify the default precision for all the unspecified layers.
Per-layer precision spec ::= layerPrecision[","spec]
layerPrecision ::= layerName":"precision
precision ::= "fp32"|"fp16"|"int32"|"int8"
--layerOutputTypes=spec Control per-layer output type constraints. Effective only when precisionConstraints is set to
"obey" or "prefer". (default = none)
The specs are read left-to-right, and later ones override earlier ones. "*" can be used as a
layerName to specify the default precision for all the unspecified layers. If a layer has more than
one output, then multiple types separated by "+" can be provided for this layer.
Per-layer output type spec ::= layerOutputTypes[","spec]
layerOutputTypes ::= layerName":"type
type ::= "fp32"|"fp16"|"int32"|"int8"["+"type]
--calib=<file> Read INT8 calibration cache file
--safe Enable build safety certified engine
--consistency Perform consistency checking on safety certified engine
--restricted Enable safety scope checking with kSAFETY_SCOPE build flag
--saveEngine=<file> Save the serialized engine
--loadEngine=<file> Load a serialized engine
--tacticSources=tactics Specify the tactics to be used by adding (+) or removing (-) tactics from the default
tactic sources (default = all available tactics).
Note: Currently only cuDNN, cuBLAS, cuBLAS-LT, and edge mask convolutions are listed as optional
tactics.
Tactic Sources: tactics ::= [","tactic]
tactic ::= (+|-)lib
lib ::= "CUBLAS"|"CUBLAS_LT"|"CUDNN"|"EDGE_MASK_CONVOLUTIONS"
For example, to disable cudnn and enable cublas: --tacticSources=-CUDNN,+CUBLAS
--noBuilderCache Disable timing cache in builder (default is to enable timing cache)
--timingCacheFile=<file> Save/load the serialized global timing cache
=== Inference Options ===
--batch=N Set batch size for implicit batch engines (default = 1)
This option should not be used when the engine is built from an ONNX model or when dynamic
shapes are provided when the engine is built.
--shapes=spec Set input shapes for dynamic shapes inference inputs.
Note: Input names can be wrapped with escaped single quotes (ex: \'Input:0\').
Example input shapes spec: input0:1x3x256x256, input1:1x3x128x128
Each input shape is supplied as a key-value pair where key is the input name and
value is the dimensions (including the batch dimension) to be used for that input.
Each key-value pair has the key and value separated using a colon (:).
Multiple input shapes can be provided via comma-separated key-value pairs.
--loadInputs=spec Load input values from files (default = generate random inputs). Input names can be wrapped with single quotes (ex: 'Input:0')
Input values spec ::= Ival[","spec]
Ival ::= name":"file
--iterations=N Run at least N inference iterations (default = 10)
--warmUp=N Run for N milliseconds to warmup before measuring performance (default = 200)
--duration=N Run performance measurements for at least N seconds wallclock time (default = 3)
--sleepTime=N Delay inference start with a gap of N milliseconds between launch and compute (default = 0)
--idleTime=N Sleep N milliseconds between two continuous iterations(default = 0)
--streams=N Instantiate N engines to use concurrently (default = 1)
--exposeDMA Serialize DMA transfers to and from device (default = disabled).
--noDataTransfers Disable DMA transfers to and from device (default = enabled).
--useManagedMemory Use managed memory instead of separate host and device allocations (default = disabled).
--useSpinWait Actively synchronize on GPU events. This option may decrease synchronization time but increase CPU usage and power (default = disabled)
--threads Enable multithreading to drive engines with independent threads or speed up refitting (default = disabled)
--useCudaGraph Use CUDA graph to capture engine execution and then launch inference (default = disabled).
This flag may be ignored if the graph capture fails.
--timeDeserialize Time the amount of time it takes to deserialize the network and exit.
--timeRefit Time the amount of time it takes to refit the engine before inference.
--separateProfileRun Do not attach the profiler in the benchmark run; if profiling is enabled, a second profile run will be executed (default = disabled)
--buildOnly Exit after the engine has been built and skip inference perf measurement (default = disabled)
=== Build and Inference Batch Options ===
When using implicit batch, the max batch size of the engine, if not given,
is set to the inference batch size;
when using explicit batch, if shapes are specified only for inference, they
will be used also as min/opt/max in the build profile; if shapes are
specified only for the build, the opt shapes will be used also for inference;
if both are specified, they must be compatible; and if explicit batch is
enabled but neither is specified, the model must provide complete static
dimensions, including batch size, for all inputs
Using ONNX models automatically forces explicit batch.
=== Reporting Options ===
--verbose Use verbose logging (default = false)
--avgRuns=N Report performance measurements averaged over N consecutive iterations (default = 10)
--percentile=P Report performance for the P percentage (0<=P<=100, 0 representing max perf, and 100 representing min perf; (default = 99%)
--dumpRefit Print the refittable layers and weights from a refittable engine
--dumpOutput Print the output tensor(s) of the last inference iteration (default = disabled)
--dumpProfile Print profile information per layer (default = disabled)
--dumpLayerInfo Print layer information of the engine to console (default = disabled)
--exportTimes=<file> Write the timing results in a json file (default = disabled)
--exportOutput=<file> Write the output tensors to a json file (default = disabled)
--exportProfile=<file> Write the profile information per layer in a json file (default = disabled)
--exportLayerInfo=<file> Write the layer information of the engine in a json file (default = disabled)
=== System Options ===
--device=N Select cuda device N (default = 0)
--useDLACore=N Select DLA core N for layers that support DLA (default = none)
--allowGPUFallback When DLA is enabled, allow GPU fallback for unsupported layers (default = disabled)
--plugins Plugin library (.so) to load (can be specified multiple times)
=== Help ===
--help, -h Print this message
&&&& PASSED TensorRT.trtexec [TensorRT v8401] # trtexec
2. ONNX模型的简单编译
使用 trtexec 工具对模型的编译工作,内容如下:
写一个静态的 onnx
- 基本的模型导出和编译
trtexec --onnx=static.onnx --saveEngine=static.enginetrtexec --loadEngine=static.engine- 让模型持续运行,并进行压测
trtexec --loadEngine=static.engine --duration=1000watch -n 0.1 nvidia-smi(Linux)nvidia-smi -l 1(Windows) 查看是否运行写一个动态的 onnx
- 基本的模型导出
- 编译模型,设置动态 shape 参数
trtexec --onnx=dynamic.onnx --minShapes=x:1x1x3x3 --optShapes=x:50x1x3x3 --maxShapes=x:100x1x3x3 --saveEngine=dynamic.enginetrtexec --loadEngine=dynamic.engine --shapes=x:100x1x3x3
2.1 静态onnx
示例代码如下:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.onnx as onnx
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(1, 3, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(27, 3)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = torch.relu(x)
x = x.view(-1, 27)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
torch.manual_seed(7)
dummy = torch.randn(1, 1, 3, 3)
model = Model().eval()
with torch.no_grad():
y = model(dummy)
print(f"y = {y}")
onnx.export(
model, dummy, "static.onnx", opset_version=14, input_names=["x"], output_names=["y"], verbose=True
)
在上面的示例代码中我们实现了一个简单的网络模型,并将其导出为 onnx,利用 Netron 软件可以查看其网络结构如下所示:
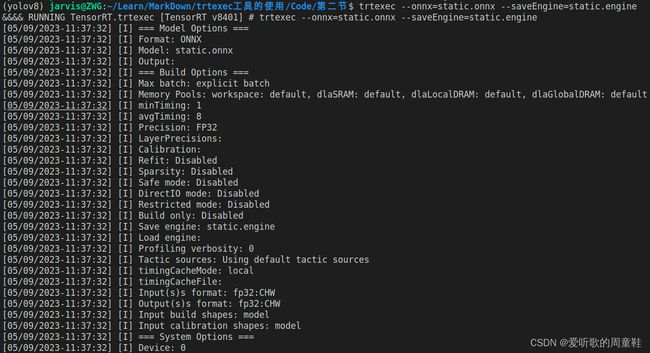
onnx 模型导出好后,我们就可以利用 trtexec 工具对其进行编译了,具体指令如下:
trtexec --onnx=static.onnx --saveEngine=static.engine
编译过程如下图所示:
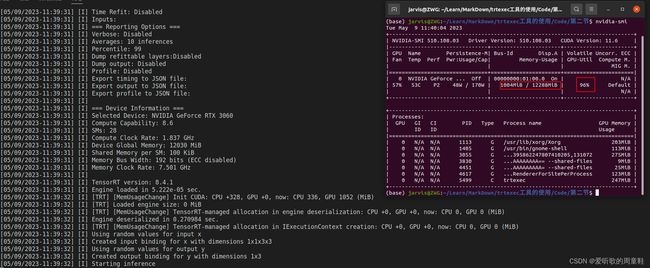
编译完成后,我们可以加载保存好的 engine 让其持续运行,进行压测,指令如下:
trtexec -loadEngine=static.engien --duration=1000
我们让 engine 持续运行 1000 秒,观察此时 GPU 的运行情况,如下图所示
2.2 动态onnx
示例代码如下:
from calendar import day_abbr
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.onnx as onnx
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(1, 3, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(27, 3)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = torch.relu(x)
x = x.view(-1, 27)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
torch.manual_seed(7)
dummy = torch.randn(1, 1, 3, 3)
model = Model().eval()
with torch.no_grad():
y = model(dummy)
print(f"y = {y}")
onnx.export(
model, dummy, "dynamic.onnx", opset_version=14, input_names=["x"], output_names=["y"], verbose=True,
dynamic_axes={"x": {0: "batch"}, "y":{0: "batch"}}
)
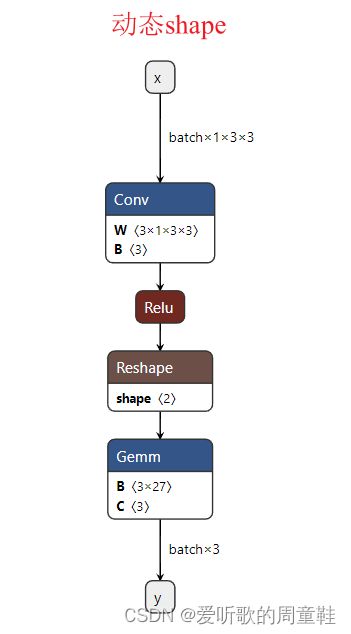
动态 shape 的 onnx 模型导出相比于静态就多了一个 dynamic_axes 参数的指定,指定输入和输出的第一个维度为动态,其它不指定,其 onnx 模型如下:
动态 onnx 模型的编译需要指定 Shapes 参数,编译指令如下:
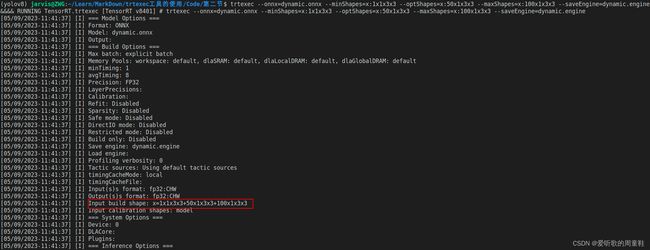
trtexec --onnx=dynamic.onnx --minShapes=x:1x1x3x3 --optShapes=x:50x1x3x3 --maxShapes=x:100x1x3x3 --saveEngine=dynamic.engine
我们指定了最小的 Shapes 为 1x1x3x3,最大的 Shapes 为 100x1x3x3,最优的 Shapes 为 50x1x3x3,编译过程如下:
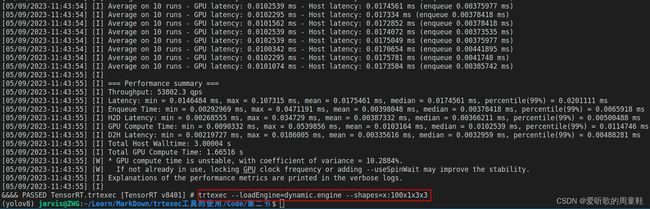
编译完成后我们可以加载动态的 engine,让它以特定的 shapes 去执行推理,指令如下:
trtexec --loadEngine=dynamic.engine --shapes=x:100x1x3x3