SpringBoot自动配置原理深入理解
SpringBoot自动配置原理深入理解
我的SpringBoot版本是2.4.3
main方法作为程序启动入口,拿到当前类的字节码对象,然后拿到@SpringBootApplication,扫描解析它,进入@SpringBootApplication
@SpringBootApplication用于启动SpringBoot,与@Configuration,@EnableAutoConfiguration,@Component等价。
@ComponentScan:扫描注解,默认是扫描当前类下的package。将@Controller/@Service/@Component/@Repository等注解加载到IOC容器中。
其中@SpringBootConfiguration:SpringBoot启动配置类,@Configuration:当前类是一个配置类,支持JavaConfig的方式来进行配置(使用Configuration配置类等同于XML文件)。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
我们知道SpringBoot可以帮我们减少很多的配置,也肯定听过“约定大于配置”这么一句话,那SpringBoot是怎么做的呢?其实靠的就是@EnableAutoConfiguration注解。
注解可以帮助我们自动载入应用程序所需要的所有默认配置。
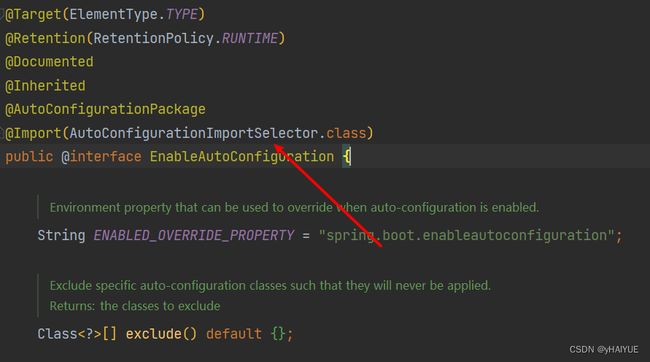
@EnableAutoConfiguration:启动自动化配置,自动配置我们需要的对象,是整个自动配置的核心
Web项目Springboot会根据@EnableAutoConfiguration自动去配置SPringMVC相关的对象
@AutoConfigurationPackage:自动扫描启动类所在的包以及注解
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class):导入SpringBoot自动配置的其他框架的实例
在@AutoConfigurationPackage自动配置包,为@Componentscan指明basepackages的路径。因为在组件扫描注解当中并没有指明basepackages只会扫描与主配置类包名相同的组件。所以自动配置包是为给组件扫描注解指明basepackages。本身并没有扫描组件的作用。
点进AutoConfigurationPackages:
在默认的情况下就是将:主配置类(@SpringBootApplication)的所在包及其子包里边的组件扫描到Spring容器中。
@Entity注解由@AutoConfigurationPackage扫描并加载
@Controller/@Service/@Component/@Repository这些注解是由@ComponentScan来扫描并加载的。
二者扫描的对象是不一样
回到之前的@Import
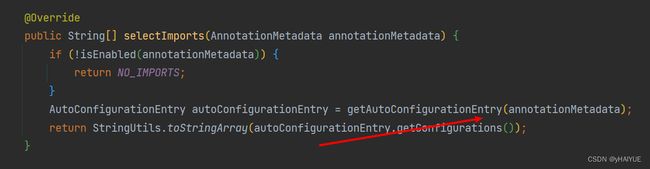
在AutoConfigurationImportSelector里面,会调用selectImports方法,做自动导入
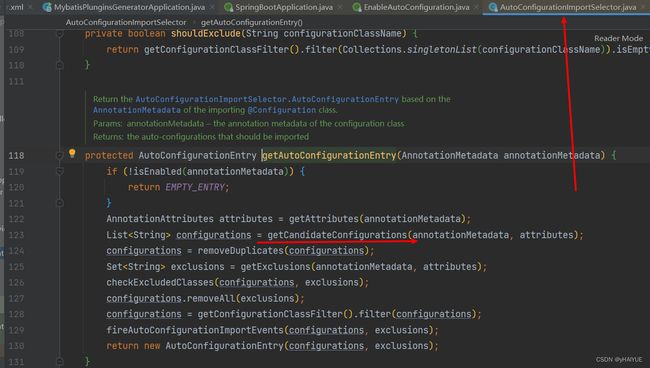
getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata) :获取SpringBoot自动配置的实体对象
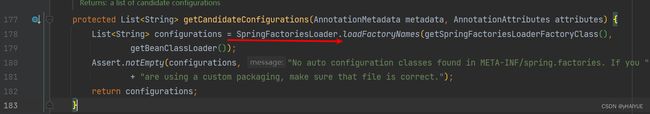
getCandidateConfigurations :获取候选配置,即默认配置
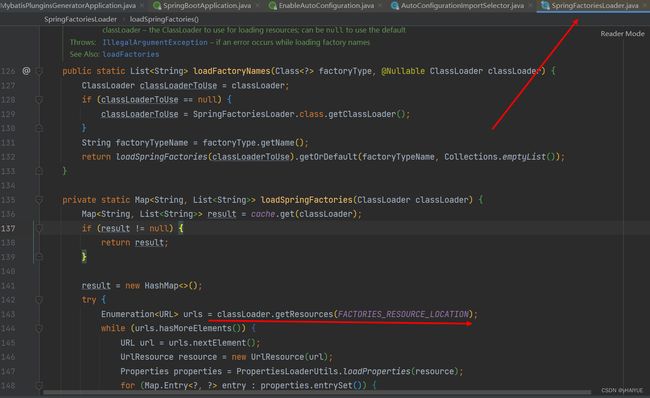
loadFactoryNames:加载工厂
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoaderToUse == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
Map<String, List<String>> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
result = new HashMap<>();
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION);
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] factoryImplementationNames =
StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue());
for (String factoryImplementationName : factoryImplementationNames) {
result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, key -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
// Replace all lists with unmodifiable lists containing unique elements
result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> implementations.stream().distinct()
.collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList)));
cache.put(classLoader, result);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
return result;
}
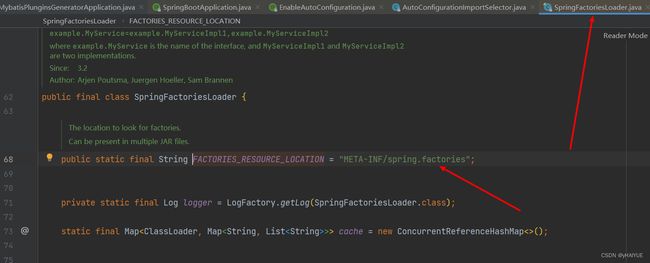
Enumeration urls = classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION),枚举类型,进入
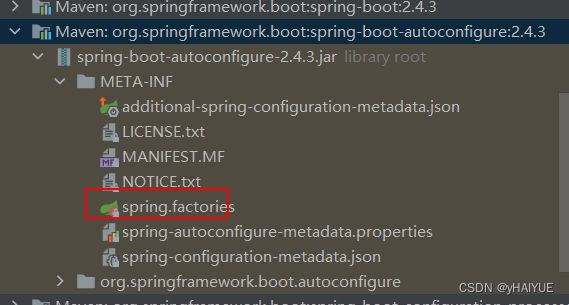
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = “META-INF/spring.factories”: SpringBoot要默认初始化的配置文件,SpringBoot在启动时,根据注解逐渐找到spring.factories,然后扫描它,拿到里面的默认配置。
这里面全是配置类,有三种配置方式:xml,注解,配置类(用注解的方式来替代xml的配置方式),存放了所有的自动配置类,SpringBoot启动后,会加载它们:
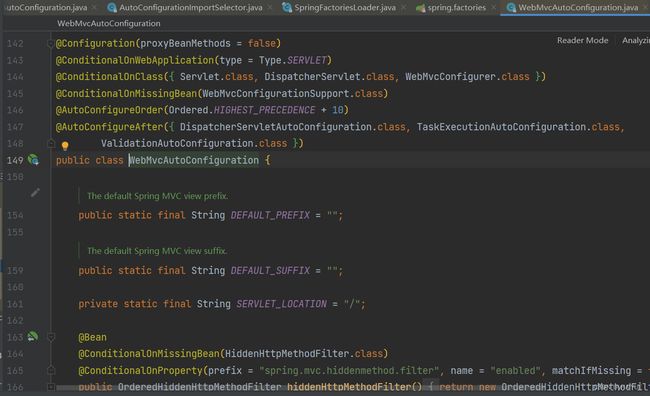
其中org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\是针对SpringMVC的自动配置类
来看看它WebMvcAutoConfiguration:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class,
ValidationAutoConfiguration.class })
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
解析:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false):当前类是一个配置类
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET):当前配置类仅仅使用在Web项目中,即servlet类型项目中,否则无效
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class }):配置好servlet实例,要有DispatcherServlet实例,WebMvcConfigurer对象
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class): 要让项目生效前提是没有WebMvcConfigurationSupport对象
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10):自动配置类的顺序
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class,
ValidationAutoConfiguration.class }):自动配置类必须要在哪些配置类解析之后再解析
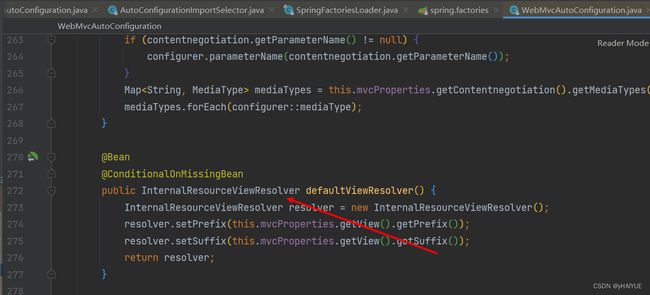
在这个类下,有很多方法,比如:造视图解析器的配置
进入mvcProperties:
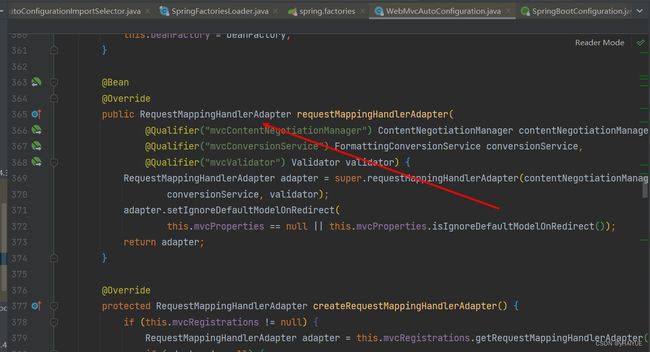
比如还有:
SpringBoot启动时把这些都配置好了
我们可以通过配置文件进行自定义对象属性初始值。
总结:@SpringBootApplication等同于三个注解:@SpringBootConfiguration,@EnableAutoConfiguration,@ComponentScan
中…(img-vmSz89Kv-1662650676241)]
SpringBoot启动时把这些都配置好了
我们可以通过配置文件进行自定义对象属性初始值。
总结:@SpringBootApplication等同于三个注解:@SpringBootConfiguration,@EnableAutoConfiguration,@ComponentScan
其中@EnableAutoConfiguration是关键(启用自动配置),内部实际上就去加载META-INF/spring.factories文件的信息,然后筛选出以EnableAutoConfiguration为key的数据,加载到IOC容器中,实现自动配置功能!