0基础学习PyFlink——时间滚动窗口(Tumbling Time Windows)
大纲
- map
- reduce
- 完整代码
- 参考资料
在《0基础学习PyFlink——个数滚动窗口(Tumbling Count Windows)》一文中,我们发现如果窗口内元素个数没有达到窗口大小时,计算个数的函数是不会被调用的。如下图中红色部分
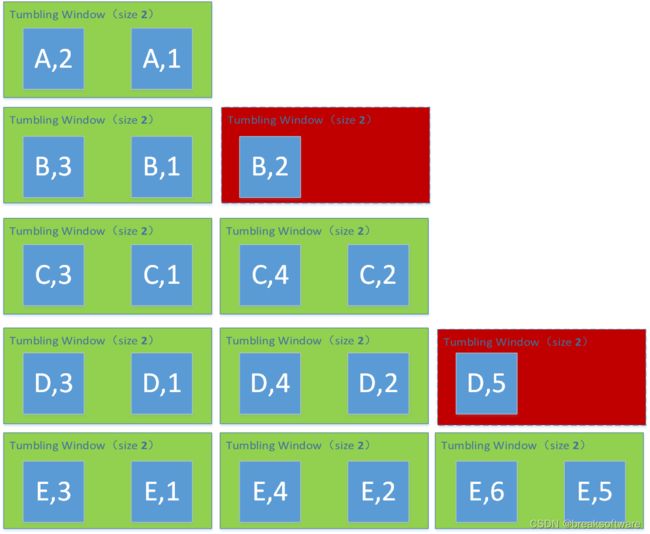
那么有没有办法让上图中(B,2)和(D,5)也会被计算呢?
这就可以使用本节介绍的时间滚动窗口。它不依赖于窗口中元素的个数,而是窗口的时间,即窗口时间到了,计算就会进行。
我们稍微修改下《0基础学习PyFlink——个数滚动窗口(Tumbling Count Windows)》的例子,让元素集中在“A”上。
map
class SumWindowFunction(WindowFunction[tuple, tuple, str, TimeWindow]):
def apply(self, key: str, window: TimeWindow, inputs: Iterable[tuple]):
print(*inputs, window)
return [(key, len([e for e in inputs]))]
word_count_data = [("A",2),("A",1),("A",4),("A",3),("A",6),("A",5),("A",7),("A",8),("A",9),("A",10),
("A",11),("A",12),("A",13),("A",14),("A",15),("A",16),("A",17),("A",18),("A",19),("A",20)]
def word_count():
env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.get_execution_environment()
env.set_runtime_mode(RuntimeExecutionMode.STREAMING)
# write all the data to one file
env.set_parallelism(1)
source_type_info = Types.TUPLE([Types.STRING(), Types.INT()])
# define the source
# mappging
source = env.from_collection(word_count_data, source_type_info)
# source.print()
# keying
keyed=source.key_by(lambda i: i[0])
reduce
# reducing
reduced=keyed.window(TumblingProcessingTimeWindows.of(Time.milliseconds(2))) \
.apply(SumWindowFunction(),
Types.TUPLE([Types.STRING(), Types.INT()]))
# # define the sink
reduced.print()
# submit for execution
env.execute()
这儿我们的Window使用的是滚动时间窗口,其中参数Time.milliseconds(2)是指窗口时长,即2毫秒一个窗口。
我们运行多次代码可以得到不同的结果
(‘A’, 2) (‘A’, 1) (‘A’, 4) (‘A’, 3) (‘A’, 6) (‘A’, 5) (‘A’, 7) (‘A’, 8) (‘A’, 9) (‘A’, 10) (‘A’, 11) (‘A’, 12) TimeWindow(start=1698771761164, end=1698771761166)
(A,12)
(‘A’, 13) (‘A’, 14) (‘A’, 15) (‘A’, 16) (‘A’, 17) (‘A’, 18) (‘A’, 19) (‘A’, 20) TimeWindow(start=1698771761166, end=1698771761168)
(A,8)
![]()
或者
(‘A’, 2) (‘A’, 1) (‘A’, 4) (‘A’, 3) (‘A’, 6) (‘A’, 5) (‘A’, 7) (‘A’, 8) (‘A’, 9) (‘A’, 10) (‘A’, 11) (‘A’, 12) (‘A’, 13) (‘A’, 14) (‘A’, 15) (‘A’, 16) TimeWindow(start=1698771731386, end=1698771731388)
(A,16)
(‘A’, 17) (‘A’, 18) (‘A’, 19) (‘A’, 20) TimeWindow(start=1698771731388, end=1698771731390)
(A,4)
![]()
或者
(‘A’, 2) (‘A’, 1) (‘A’, 4) (‘A’, 3) (‘A’, 6) (‘A’, 5) (‘A’, 7) (‘A’, 8) (‘A’, 9) (‘A’, 10) (‘A’, 11) (‘A’, 12) (‘A’, 13) (‘A’, 14) (‘A’, 15) (‘A’, 16) (‘A’, 17) (‘A’, 18) (‘A’, 19) (‘A’, 20) TimeWindow(start=1698771714992, end=1698771714994)
(A,20)
可以发现结果并不稳定。但是可以发现,每个元素都参与了计算,而不像个数滚动窗口那样部分数据没有被触发计算。
完整代码
from typing import Iterable
import time
from pyflink.common import Types, Time
from pyflink.datastream import StreamExecutionEnvironment, RuntimeExecutionMode, WindowFunction
from pyflink.datastream.window import TimeWindow, TumblingProcessingTimeWindows
class SumWindowFunction(WindowFunction[tuple, tuple, str, TimeWindow]):
def apply(self, key: str, window: TimeWindow, inputs: Iterable[tuple]):
print(*inputs, window)
return [(key, len([e for e in inputs]))]
word_count_data = [("A",2),("A",1),("A",4),("A",3),("A",6),("A",5),("A",7),("A",8),("A",9),("A",10),
("A",11),("A",12),("A",13),("A",14),("A",15),("A",16),("A",17),("A",18),("A",19),("A",20)]
def word_count():
env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.get_execution_environment()
env.set_runtime_mode(RuntimeExecutionMode.STREAMING)
# write all the data to one file
env.set_parallelism(1)
source_type_info = Types.TUPLE([Types.STRING(), Types.INT()])
# define the source
# mappging
source = env.from_collection(word_count_data, source_type_info)
# source.print()
# keying
keyed=source.key_by(lambda i: i[0])
# reducing
reduced=keyed.window(TumblingProcessingTimeWindows.of(Time.milliseconds(2))) \
.apply(SumWindowFunction(),
Types.TUPLE([Types.STRING(), Types.INT()]))
# # define the sink
reduced.print()
# submit for execution
env.execute()
if __name__ == '__main__':
word_count()
参考资料
- https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-master/api/python/reference/pyflink.datastream/api/pyflink.datastream.window.TumblingProcessingTimeWindows.html#pyflink.datastream.window.TumblingProcessingTimeWindows