C++ stack和queue模拟实现
目录
-
- stack
- 习题练习
-
- 逆波兰表达式求值
- 基本计算器
- stack模拟实现
- queue
- queue模拟实现
- deque了解
- priority_queue
- priority_queue模拟实现
- 仿函数
stack

stack是一种容器适配器,专门用在具有后进先出操作的上下文环境中,其删除只能从容器的一端进行元素的插入与提取操作。
习题练习
逆波兰表达式求值

思路:
遇到操作数就入栈
遇到操作符就取栈顶的两个操作数运算,结果再入栈
class Solution {
public:
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {
stack<int> st;
for(auto str:tokens)
{
if(str=="+"
|| str=="-"
|| str=="*"
|| str=="/")
{
//出栈中操作数进行运算
int right=st.top();
st.pop();
int left=st.top();
st.pop();
switch(str[0])
{
case '+':
st.push(left+right);
break;
case '-':
st.push(left-right);
break;
case '*':
st.push(left*right);
break;
case '/':
st.push(left/right);
break;
}
}
else
{
st.push(stoi(str));
}
}
return st.top();
}
};
基本计算器
class Solution {
public:
int pre(char ch)//优先级判断
{
if(ch=='+'
|| ch=='-')
return 1;
else if(ch=='(' || ch==')')
return 3;
else//如果有*/
return 2;
}
int calculate(string s) {
vector<int> v;
stack<char> st;
int i=0;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++)
{
if(isdigit(s[i]))//遇到操作数放到vector里
{
string s1;
while(isdigit(s[i]))
{
s1+=s[i++];
}
i--;
v.push_back(stoi(s1));
//如果遇到是-1
if(v.size()==st.size()==1)
{
v.pop_back();
st.pop();
v.push_back(-stoi(s1));
}
}
else if(s[i]!=' ')//遇到操作符
{
if(s[i]=='(')
{
//递归解决
string tmp(s,i+1);
v.push_back(calculate(tmp));
//找到)
i++;
int count=1;//代表1个(,对应着一个),如果在找的过程中发现了第二个(,count++
while(count!=0)
{
if(s[i]=='(')
{
count++;
}
else if(s[i]==')')
{
count--;
}
if(count!=0)
i++;
}
//递归解决完之后,面临和上面遇到-1一样的情况
if(v.size()==st.size()==1)
{
int a=v.back();
v.pop_back();
st.pop();
v.push_back(-a);
}
continue;
}
if(s[i]==')')
{
break;
}
while(!st.empty())
{
char top=st.top();
//ch运算符优先级比top高,入栈
if(pre(s[i])>pre(top))
{
st.push(s[i]);
}
else
{
_operator(st,v);
}
}
if(st.empty())
{
st.push(s[i]);
}
}
}
while(!st.empty())
{
_operator(st,v);
}
return v.back();
}
void _operator(stack<char>& st,vector<int>& v)//出栈顶操作符对两个操作数运算然后将结果放回vector
{
char top=st.top();
//出栈顶元素
st.pop();
int right=v.back();
v.pop_back();
int left=v.back();
v.pop_back();
//运算v中数据把结果放回去
switch(top)
{
case'+':
v.push_back(left+right);
break;
case'-':
v.push_back(left-right);
break;
}
}
};
stack模拟实现
namespace st
{
template<class T,class Container = deque<T>>
//不管Container这个底层容器是谁,都可以适配栈
class stack
{
public:
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
}
void pop()
{
_con.pop_back();
}
const T& top()
{
return _con.back();
}
bool empty()
{
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size()
{
return _con.size();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
};
void test_stack()
{
st::stack<int, vector<int>> v;
v.push(1);
v.push(3);
v.push(2);
v.push(7);
v.push(5);
while (!v.empty())
{
cout << v.top() << " ";
v.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test_stack();
return 0;
}
queue
队列是一种容器适配器,先进先出,其中从容器一端插入元素,另一端提取元素。
queue模拟实现
queue的接口中存在头删和尾插,因此使用vector来封装效率太低,可以借助list来模拟实现queue
namespace q
{
template<class T, class Container=deque<T>>
class queue
{
public:
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
}
void pop()
{
_con.pop_front();
}
const T& front()
{
return _con.front();
}
const T& back()
{
return _con.back();
}
size_t size()
{
return _con.size();
}
bool empty()
{
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
};
void test_queue()
{
q::queue<int, list<int>> q;
q.push(4);
q.push(3);
q.push(2);
q.push(9);
q.push(5);
while (!q.empty())
{
cout << q.front() << " ";
q.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test_queue();
return 0;
}
deque了解
deque(双端队列):是一种双开口的"连续"空间的数据结构,双开口的含义是:可以在头尾两端进行插入和删除操作,且时间复杂度为O(1),与vector比较,头插效率高,不需要搬移元素;与list比较,空间利用率比较高。
deque并不是真正连续的空间,而是由一段段连续的小空间拼接而成的,实际deque类似于一个动态的二维数组

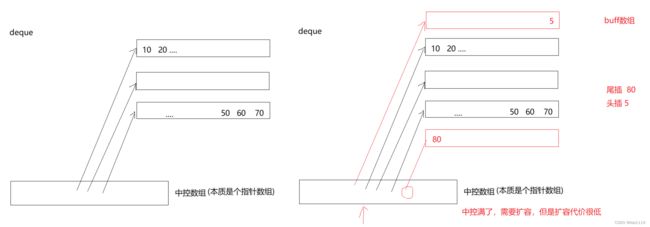

为什么选deque作为stack和queue的底层默认容器
stack是一种后进先出的特殊线性数据结构,因此只要具有push_back()和pop_back()操作的线性结构,都可以作为stack的底层容器,比如vector和list都可以;queue是先进先出的特殊线性数据结构,只要具有push_back和pop_front操作的线性结构,都可以作为queue的底层容器,比如list。
选deque是因为:
- stack和queue不需要遍历(因此stack和queue没有迭代器),只需要在固定的一端或者两端进行操作。
- 在stack中元素增长时,deque比vector的效率高(扩容时不需要搬移大量数据);queue中的元素增长时,deque不仅效率高,而且内存使用率高。
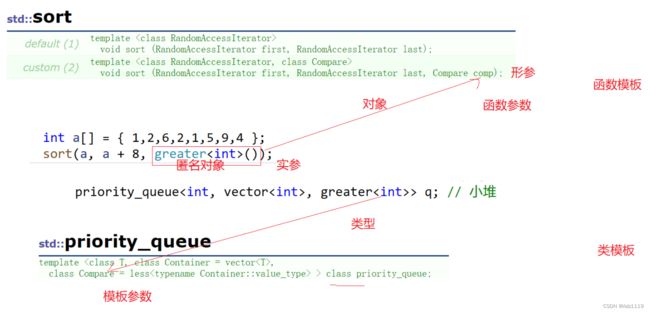
priority_queue

优先级队列默认使用vector作为其底层存储数据的容器,在vector上又使用了堆算法将vector中元素构造成
堆的结构,因此priority_queue就是堆
默认的Compare是less,也就是大堆
想创建的是小堆,可以用greater
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> q
priority_queue模拟实现
#include q;
my_pq::priority_queue<int,vector<int>,Greater<int>> q;
q.push(2);
q.push(1);
q.push(5);
q.push(3);
while (!q.empty())
{
cout << q.top() << " ";
q.pop();
}
return 0;
}
仿函数
在模拟实现优先级队列的时候,priority_queue是大堆还是小堆取决于比较方法,可以用函数指针,但函数指针可读性不是很好,为了替代函数指针,仿函数就是个好方法