异步获取多线程返回的数据
该问题涉及到四个接口:Callable、Runnable、Future、CompletionService,还有一个类:FutureTask。下面分别进行下简单介绍:
一、Future:

V get() :获取异步执行的结果,如果没有结果可用,此方法会阻塞直到异步计算完成。
V get(Long timeout , TimeUnit unit) :获取异步执行结果,如果没有结果可用,此方法会阻塞,但是会有时间限制,如果阻塞时间超过设定的timeout时间,该方法将抛出异常。
boolean isDone() :判断任务是否完成如果任务执行结束,无论是正常结束或是中途取消还是发生异常,都返回true。
boolean isCanceller() :如果任务完成前被取消,则返回true。
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptRunning) :如果任务还没开始,执行cancel(…)方法将返回false;如果任务已经启动,执行cancel(true)方法将以中断执行此任务线程的方式来试图停止任务,如果停止成功,返回true;当任务已经启动,执行cancel(false)方法将不会对正在执行的任务线程产生影响(让线程正常执行到完成),此时返回false;当任务已经完成,执行cancel(…)方法将返回false。mayInterruptRunning参数表示是否中断执行中的线程。
通过方法分析我们也知道实际上Future提供了3种功能:
(1)能够中断执行中的任务
(2)判断任务是否执行完成
(3)获取任务执行完成后的结果。
二、ExecutorService的submit方法

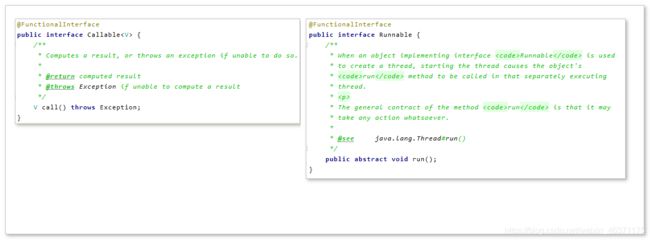
Callable接口的call方法有返回值,Runnable接口的run方法没有返回值。
submit(Runnable):Future ,返回的Future无法获取返回值。submit(Runnable, T):Future,返回的Future也无法获取返回值。
三、FutureTask
FutureTask定义
public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V> {
...
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING)
s = awaitDone(false, 0L);
return report(s);
}
...
}
看RunnableFuture定义
public interface RunnableFuture<V> extends Runnable, Future<V> {
/**
* Sets this Future to the result of its computation
* unless it has been cancelled.
*/
void run();
}
同时实现了Runnable、Future,所以,FutureTask
ExecutorService的submit方法接收Runnable和Callable,所以也可以接收FutureTask。
我们知道Thread只支持Runnable,所以也支持FutureTask。FutureTask让Thread也可以有返回值的效果。
四、实现异步获取多线程返回数据的三种方式:
- 通过Callable+Future,Callable负责执行返回,Future负责接收。Callable接口对象可以交给ExecutorService的submit方法去执行。
/**
* Callable接口配合ExecutorService的submit方法
*/
public static void asynTask1() {
try {
//使用Callable
Callable call = new Callable() {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(100l);
return "asynTask1 result";
}
};
//使用ExecutorService的submit
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
Future<String> future = executorService.submit(call);
//获取结果,get是阻塞方法
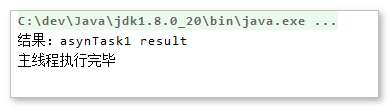
String result = future.get();
System.out.println("结果:" + result);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
结果:
2. 通过Callable+FutureTask,Callable负责执行返回,FutureTask负责接收。FutureTask同时实现了Runnable和Callable接口,可以给到ExecutorService的submit方法和Thread去执行。
Callable接口配合FutureTask,ExecutorService的submit方法去执行
public class AsynTask2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
asynTask2();
System.out.println("主线程执行完毕");
}
/**
* Callable接口配合FutureTask,ExecutorService的submit方法去执行
*/
private static void asynTask2() {
try {
//使用FutureTask
FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<String>(new Callable<String>() {
public String call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(100l);
//返回结果
return "asynTask2 result";
}
});
//使用ExecutorService
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
executorService.submit(futureTask);
//获取结果,get是阻塞方法
String result = futureTask.get();
System.out.println("结果:" + result);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
结果:

Callable接口配合FutureTask,给Thread类去执行
public class AsynTask3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
asynTask3();
System.out.println("主线程执行完毕");
}
/**
* Callable接口配合FutureTask,给Thread类去执行
*/
private static void asynTask3() {
try {
FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<String>(new Callable<String>() {
public String call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(100l);
//返回结果
return "asynTask3 result";
}
});
//使用Thread
Thread thread = new Thread(futureTask);
thread.start();
//获取结果,get是阻塞方法
String result = futureTask.get();
System.out.println("结果:" + result);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 通过CompletionService,jdk1.8之后提供了完成服务CompletionService,可以实现这样的需求。
CompletionService配合Callable
public class AsynTask4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
asynTask4();
System.out.println("主线程执行完毕");
}
/**
* CompletionService配合Callable
*/
private static void asynTask4() {
try {
//使用Callable
Callable call = new Callable() {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(100l);
return "asynTask4 result";
}
};
//使用ExecutorService
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
// 构建完成服务
CompletionService<String> completionService = new ExecutorCompletionService<String>(executorService);
completionService.submit(call);
//获取结果,get是阻塞方法
String result = completionService.take().get();
System.out.println("结果:" + result);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
注意,实现Runnable接口任务执行结束后无法获取执行结果,(Callable有返回值,Runnable没有返回值)。
CompletionService和Future的区别是什么?
- Future获取结果,一个一个的取,一个取完了,在取另外一个,就会等待
- CompletionService,任意一个线程有返回,就立马取出
public class AsynTask5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
asynCompletionService();
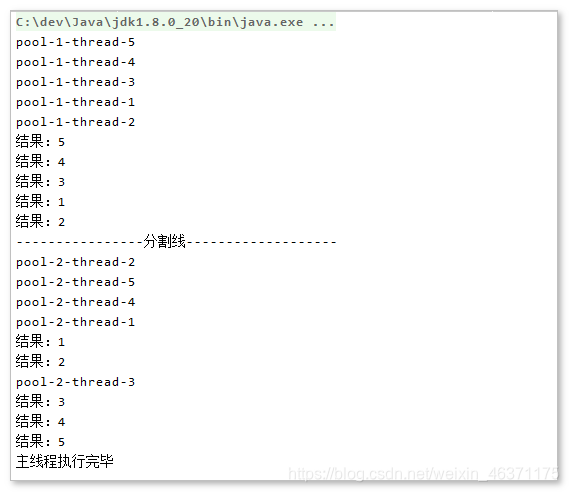
System.out.println("----------------分割线-------------------");
asynFuture();
System.out.println("主线程执行完毕");
}
private static void asynCompletionService() {
try {
//使用ExecutorService
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// 构建完成服务
CompletionService<Integer> completionService = new ExecutorCompletionService<Integer>(executorService);
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
//提交任务
completionService.submit(new HandleFuture<>(i));
}
//获取结果,一个一个阻塞的取出。这中间肯定会浪费一定的时间在等待上
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
Integer result = completionService.take().get();
System.out.println("结果:" + result);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void asynFuture() {
try {
//使用ExecutorService
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//Future列表
List<Future<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<Future<Integer>>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
//提交任务
Future<Integer> submit = executorService.submit(new HandleFuture<>(i));
result.add(submit);
}
//获取结果,输出和线程的放入顺序无关系。每一个线程执行成功后,立刻就输出
for (Future<Integer> integerFuture : result) {
Integer integer = integerFuture.get();
System.out.println("结果:" + integer);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class HandleFuture<Integer> implements Callable<Integer> {
private Integer num;
public HandleFuture(Integer num) {
this.num = num;
}
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(2 * 1000l);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
return num;
}
}