算法和数据结构(b站尚硅谷韩老师教程学习笔记)
教程学习地址:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1E4411H73v
一、数据结构和算法的关系
- 数据data结构(structure)是一门研究组织数据方式的学科,有了编程语言也就有了数据结构.学好数据结构可以编写出更加漂亮,更加有效率的代码。
- 要学习好数据结构就要多多考虑如何将生活中遇到的问题,用程序去实现解决.
- 程序 = 数据结构 + 算法
- 数据结构是算法的基础, 换言之,想要学好算法,需要把数据结构学到位。
总结:数据结构是基石,研究数据方式;算法是是数据处理更有效,更优雅
数据结构
一、线性结构和非线性结构
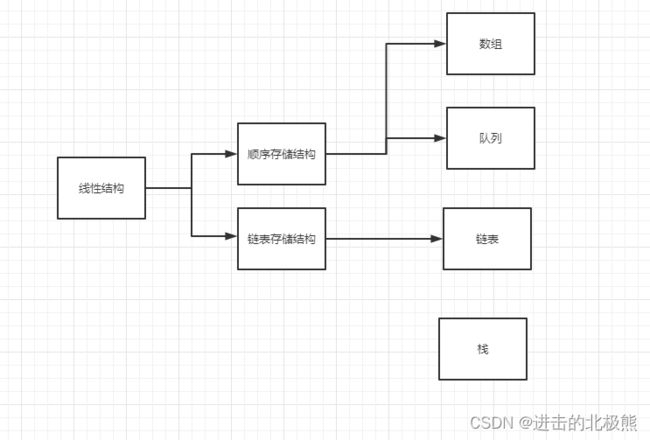
1、线性结构(常见结构:数组、队列、链表和栈)
- 线性结构作为最常用的数据结构,其特点是数据元素之间存在一对一的线性关系
- 线性结构有两种不同的存储结构,即顺序存储结构和链式存储结构。顺序存储的线性表称为顺序表,顺序表中的存储元素是连续的
- 链式存储的线性表称为链表,链表中的存储元素不一定是连续的,元素节点中存放数据元素以及相邻元素的地址信息
- 线性结构常见的有:数组、队列、链表和栈
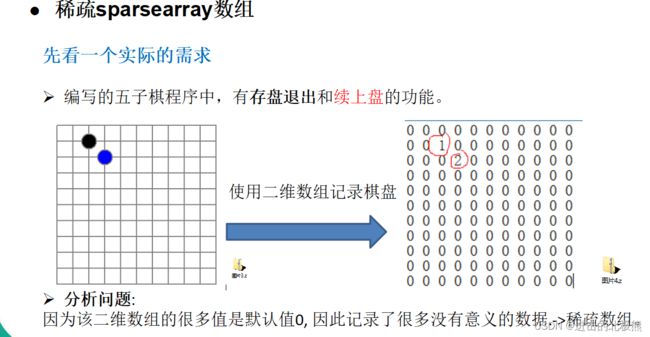
1.1、稀疏数组(sparsearray)
1.1.1 稀疏数组用于解决问题场景
1.1.2 解决方案:使用稀疏数组
稀疏数组的处理方法是:
记录数组一共有几行几列,有多少个不同的值
把具有不同值的元素的行列及值记录在一个小规模的数组中,从而缩小程序的规模

1.1.3 应用实例
1.1.4 数组转稀疏数组思路
1.1.4 代码实现
流程:正常的二维数组—>稀疏数组—>保存到磁盘中—>将磁盘中的数据还原成稀疏数组
package com.bear.稀疏数组;
import java.io.*;
/**
* <简述>
* <详细描述>
*
* @author LiuShanshan
* @version $Id$
*/
public class SparsearryTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
System.out.println("二维数组:");
// 生成二维数组 行 8 ,列7
int charArray[][] = new int[8][7];
// 1代表黑棋
charArray[1][2] = 1;
// 2代表蓝旗
// 没有赋值的为0
charArray[2][3] = 2;
charArray[4][3] = 3;
int sum = 0;
for (int[] hang : charArray) { // 2维数组变1维数组
for (int i : hang) {
if(i != 0){
sum ++;
}
System.out.printf("%d\t", i);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
}
System.out.println("=======================");
System.out.println("稀疏数组:");
// 生成散列数组 已知只会有3列,现在需要确实有几行
int sparseArray[][] = new int[sum + 1][3];
sparseArray[0][0] = 8;
sparseArray[0][1] = 7;
sparseArray[0][2] = sum;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 7; j++){
if(charArray[i][j] != 0){
count ++;
sparseArray[count][0] = i;
sparseArray[count][1] = j;
sparseArray[count][2] = charArray[i][j];
}
}
}
for (int[] ints : sparseArray) {
for (int anInt : ints) {
System.out.printf("%d\t", anInt);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
}
// 稀疏数组反推到二维数组
System.out.println("=======================");
System.out.println("散列数组反推到二维数组");
int thrustArray[][] = new int[sparseArray[0][0]][sparseArray[0][1]];
for (int i = 1; i < sparseArray.length; i++) {
thrustArray[sparseArray[i][0]][sparseArray[i][1]] = sparseArray[i][2];
}
for (int[] ints : thrustArray) {
for (int anInt : ints) {
System.out.printf("%d\t",anInt);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
}
// 将稀疏数组保存到磁盘上
// 将数据导入到磁盘中
stream(thrustArray);
// 将磁盘上的稀疏数组还原回来
System.out.println("==================");
System.out.println("磁盘中还原数据:");
stream();
}
// 保存数据到文件中
public static void stream(int[][] ob) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("c:\\javas\\map.data");//字节流
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);//对象输出流
oos.writeObject(ob);//存到磁盘上,序列化
// FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("c:\\javas\\map.data");
// ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);//对象输入流
// System.out.println(ois.readObject());//读的时候,反序列化
}
// 从文件中获取数据
public static void stream() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("c:\\javas\\map.data");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);//对象输入流
int[][] ints = (int[][]) ois.readObject(); //读的时候,反序列化
for (int[] anInt : ints) {
for (int i : anInt) {
System.out.printf("%d\t" , i);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
}
}
}
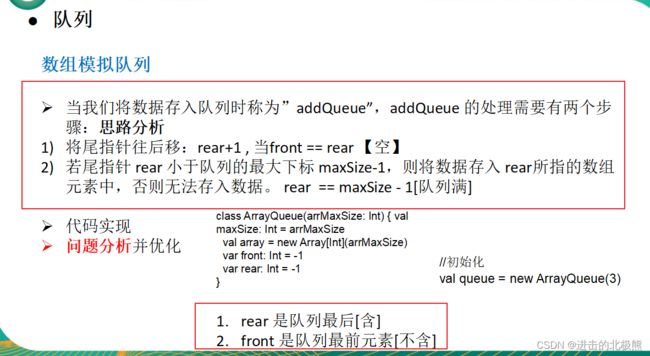
1.2、队列
1.2.1 数组模拟队列之— 队列图解
1.2.2 数组模拟队列之二:环形数组
1.2.2.1 环形数组实现原理
1.2.2.2 实现代码
package com.bear.队列;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* <简述> 环形数组模拟队列
* <详细描述>
*
* @author LiuShanshan
* @version $Id$
*/
public class QueueTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试
System.out.println("测试数组模拟环形队列的案例~~~");
//创建一个环形队列
CirciQueue queue=new CirciQueue(5);// 说明设置4,其队列的有效数据最大是3
char key ; //接收用户输入
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);//
boolean loop=true;
//输出一个菜单
while(loop){
System.out.println("s(show):显示队列");
System.out.println("e(exit):退出程序");
System.out.println("a(add):添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get):从队列取出数据");
System.out.println("h(head):查看队列头的数据");
key=scanner.next().charAt(0);//接收一个字符
switch(key){
case's':
queue.show();
break;
case'a':
System.out.println("输出一个数");
int value=scanner.nextInt();
queue.add(value);
break;
case'g'://取出数据
try{
int res=queue.get();
System.out.printf("取出的数据是%d\n",res);
}catch(Exception e){
//TODO:handleexception
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}break;
case'e':
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("程序退出");
}
}
// 环形队列
class CirciQueue{
// 最大容量
private int maxSize ;
// 最下面数据的下标(包含开始元素),从0开始
private int front;
// 最上面数据的上标 + 1(不包含结束元素), 从0开始
private int real;
// 环形数组
private int[] queueArray;
// 1、构造函数,赋值初始值
CirciQueue(int maxSize){
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.queueArray = new int[this.maxSize];
}
// 2、判断容器是否为空
private boolean notEmpty(){
return this.real == this.front;
}
// 3、容量是否已满
private boolean notFull(){
return (real + 1)% maxSize == front;
}
// 4、将数据放入环形数组中
public void add(int i){
if(notFull()){
System.out.println("容器已满,请先消费");
}else{
// 数据放入
this.queueArray[real] =i;
// real向后移动,这里需要考虑取模(余)(如果real正好在最上面,而front不等于0,并且可以放值,那么就需要将real放在最下面)
this.real = (real +1) % maxSize; // 取模
}
}
// 5、拿取数据 从下往上拿
public int get(){
// 是否容器为空
if(notEmpty()){
System.out.println("容器为空,请添加数据");
return -1;
}
int i = queueArray[front];
front = (front +1) % maxSize; // 取模
return i;
}
// 显示环形队列中的值
public void show(){
// 是否容器为空
if(notEmpty()){
System.out.println("容器为空,请添加数据");
}else{
// 循环次数为真实的有值的数据长度
for(int i = front; i < front + getRealLength(); i ++){
// 当前值,要取模
int i1 = queueArray[i % maxSize]; // 取模
System.out.printf("queueArray[%s]的值为:%s", queueArray[i % maxSize], i1);
}
}
}
// 获取真实的长度
private int getRealLength(){
// real在front上面 todo 这一部分重点看 取模
return (maxSize + real - front)% maxSize;
}
}
1.2.2.3 总结
环形数组组成队列,重要是观察3个值:maxSize(最大容量),real(尾部数据+1的索引),front(开头数据的索引),不管是算容器是否满,计算真实的数据长度,显示容器中的值,将数据放在容器中等都需要使用到取模,需要取模之后计算。
1.3 单项链表
1.3.1 链表实现原理讲解
1.3.2 链表实现代码(添加和显示所有—删除和更新简单没有写)
package com.bear.线性结构.单链表;
/**
* <简述>
* <详细描述>
*
* @author LiuShanshan
* @version $Id$
*/
public class SingleLinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试
SingleLinked singleLinked = new SingleLinked();
singleLinked.addByNo(new HeroNode(1, "宋江"));
singleLinked.addByNo(new HeroNode(4, "林冲"));
singleLinked.addByNo(new HeroNode(2, "卢俊义"));
singleLinked.addByNo(new HeroNode(3, "吴用"));
singleLinked.addByNo(new HeroNode(3, "吴用2"));
singleLinked.show();
}
}
// 单链表 处理类
class SingleLinked{
// head信息,在链表的第一个,不能变动
private HeroNode heroNodeHeard = new HeroNode(0, "");
// 添加
public void addByNo(HeroNode heroNode){
// 添加辅助节点
HeroNode temp = heroNodeHeard;
boolean isRep = false;
while (true){
// 当前节点next为null,退出
if(temp.next == null){
break;
}
// 当前节点next值的no值大于传入进来的heroNode中的no值(因为是从小到大排序),则退出
if(temp.next.no > heroNode.no){
break;
}else if (temp.next.no == heroNode.no){
isRep = true;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if(isRep){
System.out.println("有重复数据,报错.");
}else{
// 到了这里,temp中的next就应该放入参heroNode
heroNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = heroNode;
}
}
//显示
public void show(){
if(heroNodeHeard.next == null){
System.out.println("没有添加数据");
}else{
// 头信息不能动
HeroNode temp = heroNodeHeard.next;
while (true){
System.out.println(temp);
if(temp.next == null){
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}
}
// 类
class HeroNode{
// 编号
public int no;
// 名称
public String name;
// 指向下一个元素的对象
public HeroNode next;
HeroNode(int no, String name){
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
1.3.3 面试题
1.3.3.1 查找出有效个数
// 显示长度 heroNodeHeard 为头节点
public int getLength() {
// next没值返回0
if(heroNodeHeard.next == null){
return 0;
}
// next有值进行循环
int size = 0;
HeroNode temp = heroNodeHeard.next;
while (true){
size ++;
if(temp.next != null){
temp = temp.next;
}else{
break;
}
}
return size;
}
1.3.3.2 查找单链表中的倒数第k个结点
// 查找单链表中的倒数第k个结点
public HeroNode selectReciIndex(int index){
// index是否合理 // index不能比长度大
if(index <= 0 || index > getLength()){
return null;
}
// 用长度减去index,得到应该查询第几条数据
int shouldSelectLength = getLength() - index + 1;
// 进行循环,查找到数据
HeroNode temp = heroNodeHeard.next;
for (int i = 1; i < shouldSelectLength; i++){
temp = temp.next;
}
return temp;
}
1.3.3.3 单链表的反转(腾讯面试题)
思路:单项链表倒转,实现原理:创建一个单链表倒叙数据,将链表循环,每一次循环的数据作为倒转链表的next值,倒叙链表的next值作为传过来的数据的next值
// 倒转链表
public void reverse(){
// 定义一个辅助变量,帮助我们遍历原来的链表
HeroNode cur = heroNodeHeard.next;
HeroNode next = null; // 指向当前节点[cur]的下一个节点
// 倒转数组
HeroNode reverseHead = new HeroNode(0, "");
// 遍历原来的链表,每遍历一个节点,就将其取出,并放在新的链表reverseHead的最前端
while(cur != null){
next = cur.next;
// 将倒转数据下面的next给cur,因为cur将会成为倒转数组里面的第一个数据
cur.next = reverseHead.next;
reverseHead.next = cur;
cur = next;
}
// 赋值,将revers中的next放入head的next中, head.next = reverse.next
heroNodeHeard.next = reverseHead.next;
}
1.3.3.4 从头到尾打印单链表(百度面试题)
1、可以使用1.3.3.3的方式(不推荐)
2、使用stack(栈)的方式(先进后出)
// 链表倒叙输出 方法1:使用倒转链表的方法;方法2:使用栈的方式stack
public void stack(){
Stack<HeroNode> heroNodeStack = new Stack<HeroNode>();
HeroNode next = heroNodeHeard.next;
while(next != null){
heroNodeStack.push(next);
next = next.next;
}
while (heroNodeStack.size()>0){
System.out.println(heroNodeStack.pop());
}
}
1.4 双向链表(根据单项链表,增加pre)
1.4.1 思路讲解
1.4.2 代码实现
package com.bear.线性结构.单链表;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* <简述>
* <详细描述>
*
* @author LiuShanshan
* @version $Id$
*/
public class SingleLinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试
SingleLinked singleLinked = new SingleLinked();
singleLinked.addByNo(new HeroNode(1, "宋江"));
singleLinked.addByNo(new HeroNode(4, "林冲"));
singleLinked.addByNo(new HeroNode(2, "卢俊义"));
singleLinked.addByNo(new HeroNode(3, "吴用"));
singleLinked.addByNo(new HeroNode(3, "吴用2"));
singleLinked.show();
// 显示长度
int length = singleLinked.getLength();
System.out.println(length);
// 查询出倒数第2个元素的数据
HeroNode heroNode = singleLinked.selectReciIndex(4);
System.out.println(heroNode);
// ================================================将链表倒转===============
System.out.println("================================================将链表倒转===============");
// 单项链表倒转,实现原理:创建一个单链表倒叙数据,将链表循环,每一次循环的数据作为倒转链表的next值,
// 倒叙链表的next值作为传过来的数据的next值
singleLinked.reverse();
singleLinked.show();
//============================链表倒叙打印=================
System.out.println("============================链表倒叙打印=================");
singleLinked.stack();
}
}
// 单链表 处理类
class SingleLinked{
// head信息,在链表的第一个,不能变动
private HeroNode heroNodeHeard = new HeroNode(0, "");
// 添加
public void addByNo(HeroNode heroNode){
// 添加辅助节点
HeroNode temp = heroNodeHeard;
boolean isRep = false;
while (true){
// 当前节点next为null,退出
if(temp.next == null){
break;
}
// 当前节点next值的no值大于传入进来的heroNode中的no值(因为是从小到大排序),则退出
if(temp.next.no > heroNode.no){
break;
}else if (temp.next.no == heroNode.no){
isRep = true;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if(isRep){
System.out.println("有重复数据,报错.");
}else{
// 到了这里,temp中的next就应该放入参heroNode
heroNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = heroNode;
}
}
//显示
public void show(){
if(heroNodeHeard.next == null){
System.out.println("没有添加数据");
}else{
// 头信息不能动
HeroNode temp = heroNodeHeard.next;
while (true){
System.out.println(temp);
if(temp.next == null){
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}
// 显示长度 heroNodeHeard 为头节点
public int getLength() {
// next没值返回0
if(heroNodeHeard.next == null){
return 0;
}
// next有值进行循环
int size = 0;
HeroNode temp = heroNodeHeard.next;
while (true){
size ++;
if(temp.next != null){
temp = temp.next;
}else{
break;
}
}
return size;
}
// 查找单链表中的倒数第k个结点
public HeroNode selectReciIndex(int index){
// index是否合理 // index不能比长度大
if(index <= 0 || index > getLength()){
return null;
}
// 用长度减去index,得到应该查询第几条数据
int shouldSelectLength = getLength() - index + 1;
// 进行循环,查找到数据
HeroNode temp = heroNodeHeard.next;
for (int i = 1; i < shouldSelectLength; i++){
temp = temp.next;
}
return temp;
}
// 倒转链表
public void reverse(){
// 定义一个辅助变量,帮助我们遍历原来的链表
HeroNode cur = heroNodeHeard.next;
HeroNode next = null; // 指向当前节点[cur]的下一个节点
// 倒转数组
HeroNode reverseHead = new HeroNode(0, "");
// 遍历原来的链表,每遍历一个节点,就将其取出,并放在新的链表reverseHead的最前端
while(cur != null){
next = cur.next;
// 将倒转数据下面的next给cur,因为cur将会成为倒转数组里面的第一个数据
cur.next = reverseHead.next;
reverseHead.next = cur;
cur = next;
}
// 赋值,将revers中的next放入head的next中, head.next = reverse.next
heroNodeHeard.next = reverseHead.next;
}
// 链表倒叙输出 方法1:使用倒转链表的方法;方法2:使用栈的方式stack
public void stack(){
Stack<HeroNode> heroNodeStack = new Stack<HeroNode>();
HeroNode next = heroNodeHeard.next;
while(next != null){
heroNodeStack.push(next);
next = next.next;
}
while (heroNodeStack.size()>0){
System.out.println(heroNodeStack.pop());
}
}
}
// 类
class HeroNode{
// 编号
public int no;
// 名称
public String name;
// 指向下一个元素的对象
public HeroNode next;
// 指向上一个元素的对象
public HeroNode pre;
HeroNode(int no, String name){
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
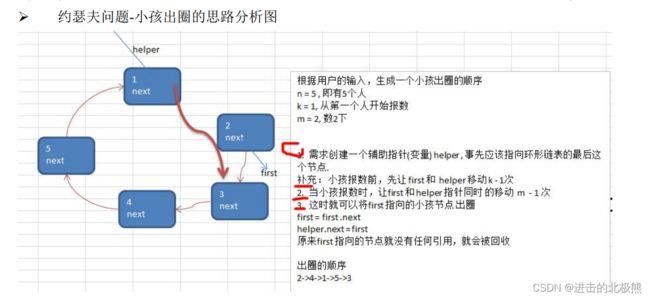
1.5 单项环形表----约瑟夫问题
1.5.1 原型思路图
1.5.2 代码实现
package com.bear.线性结构.单项环形表;
import java.beans.beancontext.BeanContext;
import java.lang.invoke.LambdaConversionException;
/** 单项环形表----约瑟夫问题
* <简述> 一个对象赋值给另一个对象,另一个对象可以改变自己的结构,但是如果改变自己的值,那么一个对象也会改变,这是因为
* 他们指向内存的值的内存地址是同一个
* <详细描述>
*
* @author LiuShanshan
* @version $Id$
*/
public class Josepfu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircleSingleLinkedList circleSingleLinkedList = new CircleSingleLinkedList();
// 添加a
for(int i = 1; i<=4; i++){
circleSingleLinkedList.add(new Boy(i));
}
// ==============查询=============
System.out.println(" ==============查询=============");
circleSingleLinkedList.show();
// =============取出数据===============
System.out.println("=============取出数据===============");
circleSingleLinkedList.delete(1,2);
}
}
class CircleSingleLinkedList{
private Boy first = null;
// 增
public void add(Boy needBoy){
if(first == null){
first = needBoy;
first.next = first;
}
// 给first后面增加数据
Boy cusboy = first.next;
while (true){
if(cusboy.next == first){
needBoy.next = first;
cusboy.next = needBoy;
break;
}
cusboy = cusboy.next;
}
System.out.println("添加成功");
}
// 出圈
/**
*<简述>
*<详细描述>
* @author Liushanshan
* @param startNo 从哪条数据开始
* @param nums 间隔几个数据进行取出
* @return void
*/
public void delete(int startNo, int nums){
// 判断当前first是否为空
// 开始取出,需要cub(当前辅助节点); later(cub只有的一个节点)
Boy later = first;
// 给later赋值为first的最后一个值
while(true){
if(later.next == first){
break;
}
later = later.next;
}
// 开始位置为nums-1 ,确认开始循环的位置
for (int i = 0; i < startNo - 1; i++){
first = first.next;
later = later.next;
}
// 开始循环,每次循环次数为nums-1
while (true){
// 退出
if(later == first){
break;
}
for(int j = 0; j < nums -1; j++){
first = first.next;
later = later.next;
}
// 要出圈的小孩
System.out.printf("\n要出去的数据:%s", first);
// 因为已经出圈了,所以将later里面的next设置为first.next
first = first.next;
later.next = first;
}
System.out.printf("\n最后一个数据为:%s", later);
}
// 改 改变里面的数据最简单,不实现
//查
public void show(){
// 判断first是否为空
if(first == null){
System.out.println("数据为空,请添加数据");
return;
}
// 循环查询,结束语句为cub.next = first
Boy cub = first;
while (true){
if(first.next == first){
System.out.printf("当前只有一个数据为:%s", first);
break;
}
if(cub.next == first){
break;
}
System.out.printf("\n开始打印数据:%s", cub);
cub = cub.next;
}
System.out.printf("\n最后一个数据为:%s", cub);
}
}
class Boy{
public int no;
public Boy next;
Boy(int no){
this.no = no;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Boy{" +
"no=" + no +
'}';
}
}
1.6 栈
1.6.1 栈的原理
栈的原理遵循先进后出的原理,所以可以用数组进行模拟
- 1)栈的英文为(stack)
- 2)栈是一个先入后出(FILO-FirstInLastOut)的有序列表。
- 3)栈(stack)是限制线性表中元素的插入和删除只能在线性表的同一端进行的一种特殊线性表。允许插入和删除的一端,为变化的一端,称为栈顶(Top),另一端为固定的一端,称为栈底(Bottom)。
- 4)根据栈的定义可知,最先放入栈中元素在栈底,最后放入的元素在栈顶,而删除元素刚好相反,最后放入的元素最先删除,最先放入的元素最后删除
- 5)图解方式说明出栈(pop)和入栈(push)的概念

1.6.2 代码
package com.bear.线性结构.栈;
/** 栈的实现使用数组的方式,遵循先进后出的原则
* <简述>
* <详细描述>
*
* @author LiuShanshan
* @version $Id$
*/
public class StackTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack stack = new Stack(3);
stack.show();
System.out.println("===============添加数据==================");
stack.add(1);
stack.add(2);
stack.add(3);
stack.show();
}
}
class Stack {
// 数组
private int[] arry ;
// top
private int top;
// 放入的值
private int value;
Stack(int length){
this.arry = new int[length];
this.top = -1;
}
//是否满
private boolean isFull(){
return arry.length == top + 1;
}
// 是否为空
private boolean isEntity(){
return top == -1;
}
// 添加
public void add (int value){
// 判断是否已满
if(isFull()){
System.out.println("容量已满");
return;
}
// 放入值,top+1
this.value = value;
top ++;
arry[top] = this.value;
}
// 查,显示
public void show(){
// 是否为空
if(isEntity()){
System.out.println("容器为空,请先添加数据");
return;
}
// 显示
for(int i = top; i>= 0; i--){
System.out.printf("\n输出数据:%s", arry[i]);
}
}
}
1.7 逆波兰表达式
1.7.1逆波兰表达式原理
1.7.2 逆波兰表达式写计算器()
package com.bear.线性结构.后缀表达式;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* <简述> 后缀表达式(逆波兰表达式)
* <详细描述>1、逆波兰表达式计算 2、中缀表达式转后缀表达式(逆波兰表达式)
*
* @author LiuShanshan
* @version $Id$
*/
public class PolandNotation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// (3+4)×5-6对应的后缀表达式就是3 4 + 5 × 6 -
// 2.逆波兰表达式计算
List<String> exp = new ArrayList<>();
exp.add("3");
exp.add("4");
exp.add("+");
exp.add("5");
exp.add("*");
exp.add("6");
exp.add("-");
System.out.printf("计算出来的值为:%s", calculate(exp));
// 1.中缀表达式转后缀表达式
}
// 逆波兰表达式,计算出值
public static int calculate(List<String> exp){
Stack<Integer> integerStack = new Stack<>();
if(exp.size() == 0){
System.out.println("没有需要计算的数据");
}
// 加入栈,并且计算,计算逻辑为:压入数据,遇到运算符的时候,取出最上面的2个数据,进行计算,将计算出来的值放回栈,直到运算到
// 栈中只剩下一个值为止
for (String s : exp) {
// 如果是数字,则直接放入栈
if(s.matches("\\d+")){
integerStack.push(Integer.valueOf(s));
}else{
// 如果是符号,则从栈中取出2个数据进行计算,然后再放回栈
Integer pop2 = integerStack.pop();
Integer pop1 = integerStack.pop();
//判断当前是 + - * / 哪一个
if("+".equals(s)){
integerStack.push(pop1 + pop2);
}else if ("-".equals(s)){
integerStack.push(pop1 - pop2);
}else if("*".equals(s)){
integerStack.push(pop1 * pop2);
}else if("/".equals(s)){
integerStack.push(pop1/pop2);
}
}
}
return integerStack.pop();
}
}
1.7.3 中缀转后缀表达式(逆波兰表达式)
todo 后面再写
1.8 递归
1.8.1 递归的原理和图解
总结:递归总的来说是将递归的方法,放在栈里面,每一个方法都是独立开来的,因为是栈,所以先放后拿,从最上面方法开始计算。
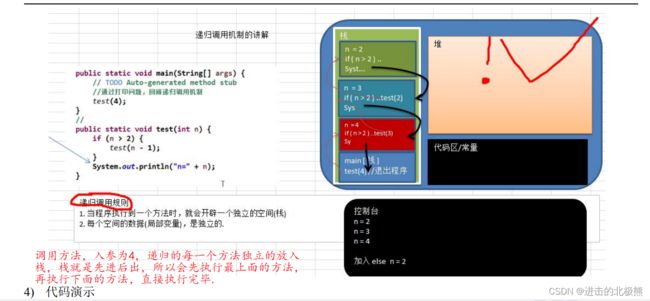
1.8.2 递归遵守的重要原则
- 1)执行一个方法时,就创建一个新的受保护的独立空间(栈空间)
- 2)方法的局部变量是独立的,不会相互影响,比如n变量
- 3)如果方法中使用的是引用类型变量(比如数组),就会共享该引用类型的数据.
- 4)递归必须向退出递归的条件逼近,否则就是无限递归,出现StackOverflowError,死龟了:)
- 5)当一个方法执行完毕,或者遇到return,就会返回,遵守谁调用,就将结果返回给谁,同时当方法执行完毕或者返回时,该方法也就执行完毕
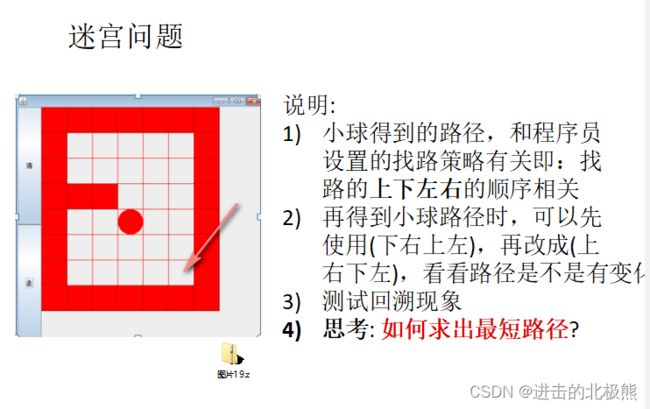
1.8.3 递归解决迷宫问题
package com.bear.线性结构.递归;
/** 迷宫问题(小球找路)
* <简述>
* <详细描述>
*
* @author LiuShanshan
* @version $Id$
*/
public class Maze {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义规则,定义一个二维数组,给里面的增加1代表墙
int[][] map = new int[8][7];
for(int i = 0; i<8; i++){
map[i][0] = 1;
map[i][6] = 1;
}
for(int j = 0; j< 7; j++){
map[0][j] = 1;
map[7][j] = 1;
}
// 第4行,第二列,第三列为1
map[3][1] = 1;
map[3][2] = 1;
// // 循环打印,看是不是组成了一个墙
// for(int i = 0; i< 8; i++){
// for(int j = 0; j<7; j++){
// System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
// }
// System.out.println();
// }
System.out.println("===========开始走迷宫===========");
Way way = new Way();
way.getOutLet(map, 1, 1);
System.out.println("============迷宫map图=========");
for(int i = 0; i< 8; i++){
for(int j = 0; j<7; j++){
System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
class Way{
/**
*<简述> 注意:1)需要指定规则,这个地图该如何走,这里指定 下->右->左->上 的规则;
* 2)1为墙,0为可以走,2为已经走过得地方,3为不能走
*<详细描述>
* @author Liushanshan
* @param map 地图 注意:不需要返回map,因为这里的数组是引入数据类型,用的地址是同一个
* @param i 行
* @param j 列
* @return void
*/
public boolean getOutLet(int[][] map, int i ,int j){
if(map[6][5] == 2){
return true;
}else if(map[i][j] == 0){ // 当为0时
map[i][j] = 2;
if(getOutLet(map, i+1, j)){
// 往下走可以走
return true;
}else if(getOutLet(map, i, j+1)){
// 往右走可以走
return true;
}else if(getOutLet(map,i, j-1)){
// 往左边走可以走
return true;
}else if(getOutLet(map, i-1, j)){
// 往上边走可以走
return true;
}else{
map[i][j] = 3;
return false;
}
}else {
return false;
}
}
}
1.8.4 八皇后问题解决—回溯算法
1.8.4.1 八皇后问题解析
1.8.4.2 代码
package com.bear.线性结构.递归;
import com.bear.线性结构.稀疏数组.SparsearryTest;
/**
* <简述> 8皇后问题
* <详细描述>
*
* @author LiuShanshan
* @version $Id$
*/
public class Queue8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
QueueTest queueTest = new QueueTest();
queueTest.check(0);
System.out.printf("一共有%d种解法:", QueueTest.count);
}
}
class QueueTest{
private int[] array;
private int max;
public static int count;
QueueTest(){
this.max = 8;
array = new int[max];
}
// 开始计算
public void check(int n){
// 当循环到第9行,索引为8的时候,直接放回true,并且打印出arry里面的值 (这是退出条件)
if(n == max){
print();
return;
}
// lien代表行,这里的循环代表把行里面的8个点都执行一次 todo 循环行
for(int i = 0; i<max; i++){
//先把当前这个皇后n,放到该行的第1列
array[n] = i;
// 判断是否冲突
if(judge(n)){
check(n +1);
}
}
}
// 判断是否满足8皇后的条件
private boolean judge(int n ){ //判断这一行数据跟之前的数据有没有冲突,不满足条件的
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){ // todo 循环行,保证行里面的列与8皇后满足条件保持一致
if(array[n] == array[i] /* 判断在不在一条竖线上**/|| Math.abs(array[n] - array[i]) == Math.abs(n - i) /* 判断在不在一条斜线上**/){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// 打印数组里面的值
private void print(){
count++;
for (int i : array) {
System.out.print(i +" ");
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
}
2、非线性结构
非线性结构包括:二维数组,多维数组,广义表,树结构,图结构
算法
1、排序算法
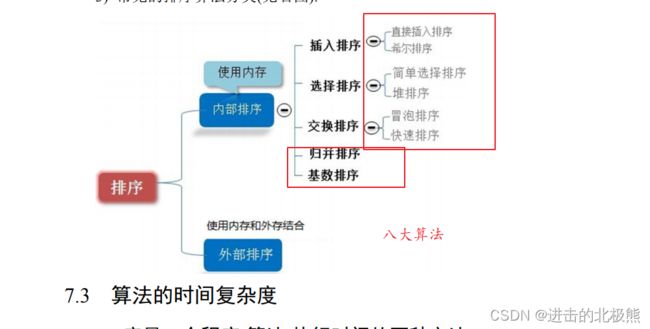
1.1 排序算法的种类
1.2 时间复杂度
时间复杂度是根据时间频度来的,如果时间频度是T(n) = 2n+20,则他的时间复杂度是O(n)
说明:去掉次项(去掉不重要的,留下关于n的东西),就是时间复杂度
如T(n)=n²+7n+6的时间复杂度是n²
时间复杂度的官方说明:一般情况下,算法中的基本操作语句的重复执行次数是问题规模n的某个函数,用T(n)表示,若有某个辅助函数f(n),使得当n趋近于无穷大时,T(n) / f(n) 的极限值为不等于零的常数,则称f(n)是T(n)的同数量级函数。记作 T(n)=O( f(n) ),称O( f(n) ) 为算法的渐进时间复杂度,简称时间复杂度。(说人话就是:时间频度去掉常数,去掉低次项,去掉系数,就是时间复杂度,表示为O( f(n) ) )
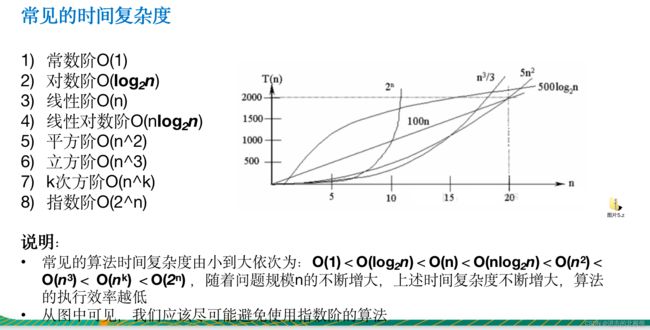
1.3 常见的时间复杂度
注释:1-8是推荐指数从高到底,最推荐的是1),最不推荐的是8)
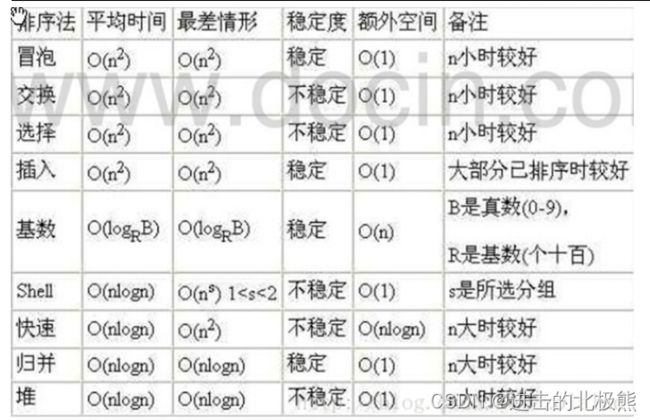
1.4 各个的排序算法和时间复杂度的具体关系图
1.5冒泡排序
1.5.1 冒泡排序思路网站
https://www.w3cschool.cn/article/49755893.html
1.5.2 代码
package com.bear.排序算法.冒泡排序;
import sun.plugin2.os.windows.FLASHWINFO;
/** 冒泡排序
* <简述>
* <详细描述>
*
* @author LiuShanshan
* @version $Id$
*/
public class BubblingDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arrayInt = {-1, 0 ,34, 23, 90, -5};
// 问题:将数组从小到大排序
int temp;
boolean flag = true;
// todo:解决思路:每次循环将最大/最小的数据找到,然后下一次循环-1次数
for(int i = 0; i< arrayInt.length -1; i++){ // todo 循环次数
for(int j = 0; j< arrayInt.length-1 - i; j++){ // todo 实际工作的循环次数
if(arrayInt[j] > arrayInt[j+1]){
flag = false;
temp = arrayInt[j];
arrayInt[j] = arrayInt[j+1];
arrayInt[j+1] = temp;
}
}
if(flag){
break;
}
}
for (int i : arrayInt) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
1.6 选择排序
1.6.1 思路
假设一个长度为4的数组,循环遍历 4次,设置每一次循环的索引为n,当n =0 时,根据循环排序的规则,需要遍历后面的n=1,2,3数据相比较,如果比n=0小,则调换2者位置;当n=1时,遍历后面的n=2,3数据相比较,如果比n=1小,则交换2者位置…,一直到循环排序完,实际上循环了n-1次,因为最后一次不用循环。
1.6.2代码
package com.bear.排序算法.选择排序;
import com.bear.线性结构.稀疏数组.SparsearryTest;
/**
* <简述> 选择排序
* <详细描述>
*
* @author LiuShanshan
* @version $Id$
*/
public class SelectSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ints = {12, 1, -1, 34, -89};
sort(ints);
}
// 选择排序
public static void sort(int[] array){
// 这里的for代表循环次数
for(int i = 0; i< array.length -1 ; i++){
int minIndex = i;
int min = array[i];
for(int j = 1 + i; j<array.length; j++){
// 查询到满足条件的数据
if(array[j] < min){
minIndex = j;
min = array[j];
}
}
// 如果发生变化,则将位置互换
if(minIndex != i){
array[minIndex] = array[i];
array[i] = min;
}
}
// 打印数据
for (int i : array) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
}
1.6.3 测试速度(比冒泡排序块)
80000条数据,使用选择排序只需要4s,冒泡排序则需要很长时。
1.7 插入排序
1.7.1、思路
17.2、代码
int insertVal = 0;
int insertIndex = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
insertVal = arr[i]; // 从第二个值开始循环往后,第一个值获取不到
insertIndex = i - 1; // 从第一个索引循环玩往后,最后一个索引获取不到;索引在值的前面,默认是在值的前面第一位
while (insertIndex >= 0 && insertVal < arr[insertIndex]) {
arr[insertIndex + 1] = arr[insertIndex];// arr[insertIndex]
insertIndex--;
}
if(insertIndex + 1 != i) {
arr[insertIndex + 1] = insertVal;
}
}
for (Integer integer : arr) {
System.out.println(integer);
}
2、查找算法
2.1、查找算法定义
2.2、顺序线性查找 (就是普通的for循环的去找有没有数据)
2.3、二分查找法
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需要 左索引,右索引,需要查找的值
int[] arr = {1,45,50,60,99,120};
int test = test(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, 99);
System.out.println("当前值的索引为:" + test);
}
public static int test(int[] arr, int leftIndex, int rightIndex, int valueof){
if(leftIndex > rightIndex){
return -1;
}
int midIndex = (leftIndex + rightIndex)/2;
if(arr[midIndex] < valueof){
// 往右找
return test(arr, midIndex, rightIndex, valueof);
}else if(arr[midIndex] > valueof){
// 往左找
return test(arr, leftIndex, midIndex, valueof);
}else {
return midIndex;
}
}
2.3.1、二分查找法查询多条重复数据
package com.bear.查找算法.二分查找法;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/** 二分查找法
* 二分查找法的前提就是列表需要先排好序
* @author LiuShanshan
* @version V1.0
* @Description
*/
public class BinaryTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需要 左索引,右索引,需要查找的值
int[] arr = {1,45,50,60,99,99,120};
List<Integer> objects = new ArrayList<>();
test(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, 99, objects);
System.out.println("当前值的索引为:" + objects);
}
public static void test(int[] arr, int leftIndex, int rightIndex, int valueof, List<Integer> valudofIndexArr){
if(leftIndex > rightIndex){
return ;
}
int midIndex = (leftIndex + rightIndex)/2;
if(arr[midIndex] < valueof){
// 往右找
test(arr, midIndex, rightIndex, valueof, valudofIndexArr);
}else if(arr[midIndex] > valueof){
// 往左找
test(arr, leftIndex, midIndex, valueof, valudofIndexArr);
}else {
valudofIndexArr.add(midIndex);
// 往左移动
int temp = midIndex -1;
while (true){
if(temp <0 || arr[temp] != arr[midIndex]){
break;
}
valudofIndexArr.add(temp);
temp = temp -1;
}
// 往右移动
int temp2 = midIndex + 1;
while (true){
if(temp2 > arr.length -1 || arr[temp2] != arr[midIndex]){
break;
}
valudofIndexArr.add(temp2);
temp2 = temp2 + 1;
}
}
}
}
2.4、插值查找算法 (与二分查找算法的区别在于midindex的算法不同)
package com.bear.查找算法.插入查找法;
import com.sun.org.glassfish.gmbal.Description;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/** 插值查找算法和二分查找法的区别在于 :midIndex 的算法不同
* @author LiuShanshan
* @version V1.0
* @Description
*/
public class CharRuBinaryTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需要 左索引,右索引,需要查找的值
int[] arr = {1,45,50,60,99,99,120};
List<Integer> objects = new ArrayList<>();
test(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, 99, objects);
System.out.println("当前值的索引为:" + objects);
}
public static void test(int[] arr, int leftIndex, int rightIndex, int valueof, List<Integer> valudofIndexArr){
if(leftIndex > rightIndex){
return ;
}
int midIndex = leftIndex + (rightIndex - leftIndex) * (valueof - arr[leftIndex]) / (arr[rightIndex] - arr[leftIndex]);
if(arr[midIndex] < valueof){
// 往右找
test(arr, midIndex, rightIndex, valueof, valudofIndexArr);
}else if(arr[midIndex] > valueof){
// 往左找
test(arr, leftIndex, midIndex, valueof, valudofIndexArr);
}else {
valudofIndexArr.add(midIndex);
// 往左移动
int temp = midIndex -1;
while (true){
if(temp <0 || arr[temp] != arr[midIndex]){
break;
}
valudofIndexArr.add(temp);
temp = temp -1;
}
// 往右移动
int temp2 = midIndex + 1;
while (true){
if(temp2 > arr.length -1 || arr[temp2] != arr[midIndex]){
break;
}
valudofIndexArr.add(temp2);
temp2 = temp2 + 1;
}
}
}
}
最后
码云代码地址:
在这里插入代码片