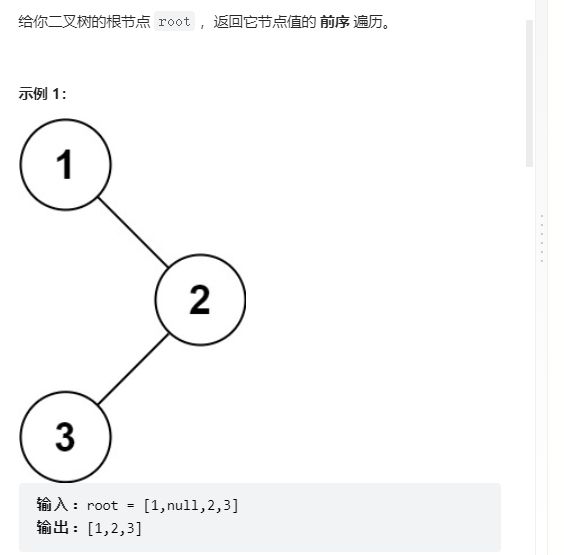
c++逆天改命进阶--二叉树练习题
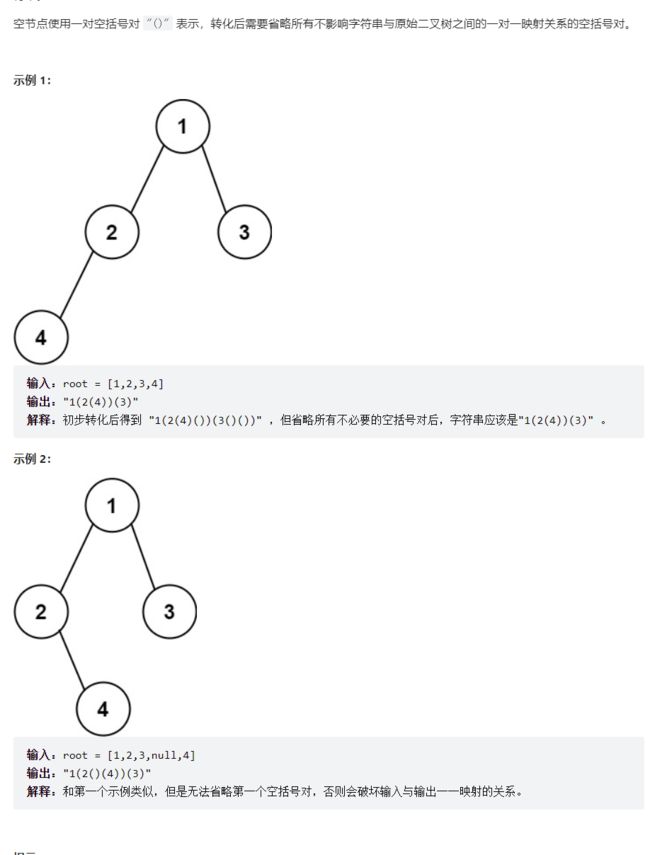
1.根据二叉树创建字符串
606. 根据二叉树创建字符串 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:
void _tree2str(TreeNode* root, string& str)
{
if(root==nullptr)//为空直接返回
{
return;
}
if(root->left&& root->right)//左右子树均不为空
{
str += to_string(root->val);
str += "(";
_tree2str(root->left, str);
str += ")";
str += "(";
_tree2str(root->right, str);
str += ")";
}
else if(root->left == nullptr)
{
if(root->right)//左子树为空,右子树不空
{
str += to_string(root->val);
str += "()";
str += "(";
_tree2str(root->right, str);
str += ")";
}
else//左右子树都空
{
str += to_string(root->val);
}
}
else//左子树不为空,右子树为空
{
str += to_string(root->val);
str += "(";
_tree2str(root->left, str);
str += ")";
}
}
string tree2str(TreeNode* root)
{
string s;
_tree2str(root, s);//调用子函数
return s;
}
};
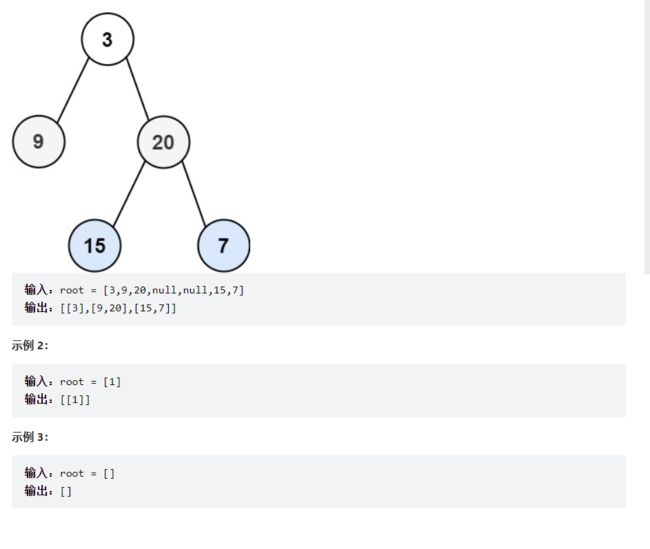
2.二叉树的层序遍历
102. 二叉树的层序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> vv;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
if(root == nullptr)//空树直接返回
{
return vv;
}
q.push(root);//不为空 队列q用来存放每一层的节点指针
int levelSize = 1;//每层的节点个数,最开始肯定是1
while(!q.empty())//队列不为空就继续
{
vector<int> v;
while(levelSize--)//节点个数是几,v就插入几次
{
TreeNode* front = q.front();//先把第一个节点指针保存下来,然后将该节点从队列删除
v.push_back(front->val);
q.pop();
//接下来判断刚刚删除的节点的左右孩子是否为空,不为空就插入到队列
if(front->left)
{
q.push(front->left);
}
if(front->right)
{
q.push(front->right);
}
}
levelSize = q.size();//更新下一层要插入的次数
vv.push_back(v);
}
return vv;
}
};
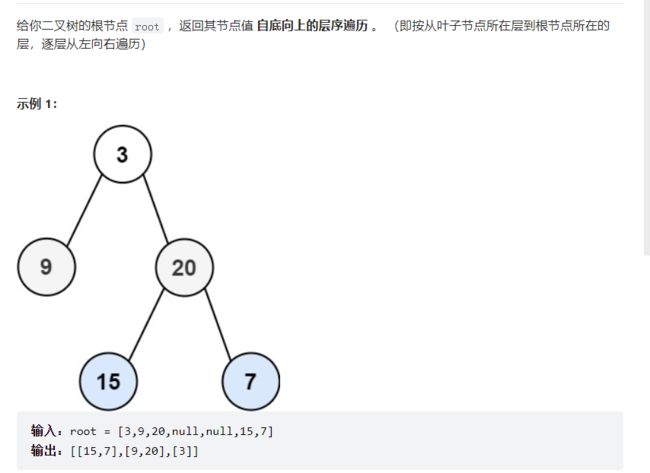
3.二叉树的层序遍历(自底向上)
107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
该题和上题类似,只需要逆置一下vv里面的vector v,我们直接上代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> vv;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
if(root == nullptr)
{
return vv;
}
q.push(root);
int levelSize = 1;
while(!q.empty())
{
vector<int> v;
while(levelSize--)
{
TreeNode* front = q.front();
v.push_back(front->val);
q.pop();
if(front->left)
{
q.push(front->left);
}
if(front->right)
{
q.push(front->right);
}
}
levelSize = q.size();
vv.push_back(v);
}
reverse(vv.begin(), vv.end());
return vv;
}
};
 4.二叉树的最近公共祖先
4.二叉树的最近公共祖先
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:
bool FindNode(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* x, stack<TreeNode*>& st)
{
if(root == nullptr)//root为空返回false
{
return false;
}
st.push(root);//不为空先把当前节点插入栈中,或许这个节点是目标节点的一个祖先,也有可能不是,那就需要我们在后面再将其pop掉
if(root == x)//找到了返回true
{
return true;
}
if(FindNode(root->left, x, st))//在左子树找到了返回true
{
return true;
}
if(FindNode(root->right, x, st))//在右子树找到了返回true
{
return true;
}
//到这里,说明我们插入的root不是目标节点的祖先,将其pop掉
st.pop();
return false;
}
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
stack<TreeNode*> st1, st2;//定义两个栈用于保存查找目标节点过程中所有祖先节点
//查找目标节点
FindNode(root, p, st1);
FindNode(root, q, st2);
//此时st1里面都是p的祖先,st2里面都是q的祖先。
//我们假定st1.size()更大,如果不是这样在将其长短交换
stack<TreeNode*> longSt = st1;
stack<TreeNode*> shortSt = st2;
if(longSt.size()<shortSt.size())
{
swap(longSt, shortSt);
}
//先让长的栈走差距步
while(longSt.size()>shortSt.size())
{
longSt.pop();
}
//此时两个栈一样长,从顶部开始依次比较,直到第一次相等,此时找到了最近的公共祖先
while(longSt.top() != shortSt.top())
{
longSt.pop();
shortSt.pop();
}
return longSt.top();
}
};
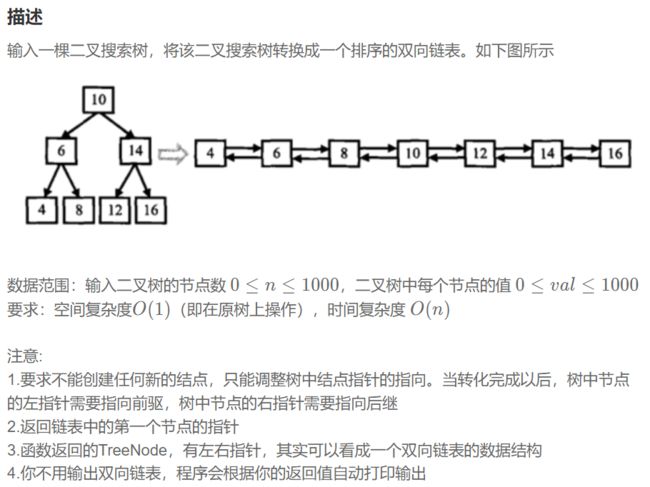
5.二插搜索树与双向链表
二叉搜索树与双向链表_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
class Solution {//该题显然是用到了中序遍历
public:
void InOrder(TreeNode* root, TreeNode*& prev)
{
if(root==nullptr)//root为空直接返回
{
return;
}
InOrder(root->left, prev);//不为空先对左子树遍历
root->left = prev;//左子树遍历之后,将prev赋给left
if(prev)//如果prev不为空,说明他是上一次的root,上面的那行代码只解决了前驱指针,而在这里我们解决了上一次的root的后继指针的问题。
{
prev->right = root;
}
prev = root;//更新prev
InOrder(root->right, prev);//中序遍历右子树
}
TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode* prev = nullptr;//前驱指针 初识为空,也就是图上4的left为空
InOrder(pRootOfTree, prev);//中序遍历
TreeNode* head = pRootOfTree;//找头,找到最左面的节点
while(head->left)
{
head = head->left;
}
return head;
}
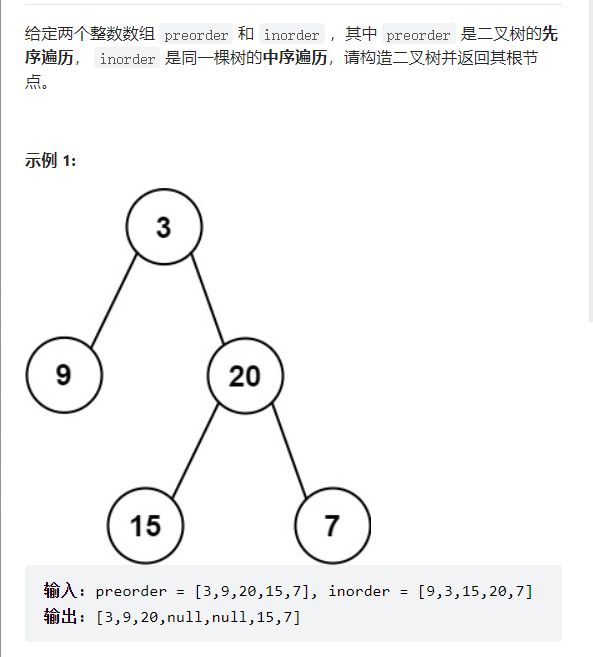
6.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder, int& pi, int inbegin, int inend)
{
if(inbegin>inend)//说明该树为空直接return
{
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[pi]);//不为空建树 ,通过前序建树,通过中序找区间
pi++;
int rooti = inbegin;
while(rooti<=inend)
{
if(root->val == inorder[rooti])//在中序找到值与root->val相等的下标
{
break;
}
else
{
rooti++;
}
}
//[inbegin, rooti-1][rooti][rooti+1, inend]
root->left = _buildTree(preorder, inorder, pi, inbegin, rooti-1);
root->right = _buildTree(preorder, inorder, pi, rooti+1, inend);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
int i = 0;
return _buildTree(preorder, inorder, i, 0, inorder.size()-1);
}
};
//注意pi必须用& 保证全局只有一个pi 否则会出错
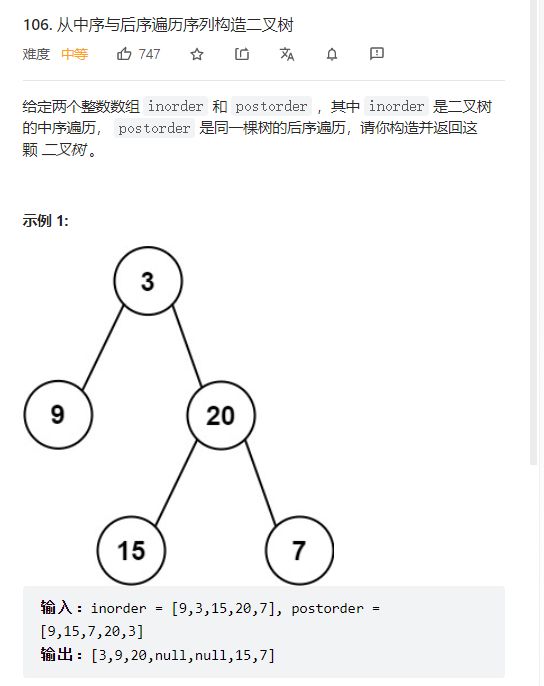
7.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
该题与上题类似,思路大体相同,不同之处在于这道题需要后序来确定根,因为后序是左右根, 所以我们从后序的最后一个值开始建树,并且建好根之后先建右子树,再建左子树。
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder, int& pi, int inBegin, int inEnd)
{
if(inBegin > inEnd)
{
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(postorder[pi]);
pi--;
int rooti = inBegin;
while(rooti <= inEnd)
{
if(root->val == inorder[rooti])
{
break;
}
else
{
rooti++;
}
}
//[inBegin,rooti-1][rooti][rooti+1, inEnd]
root->right = _buildTree(inorder, postorder, pi, rooti+1, inEnd);
root->left = _buildTree(inorder, postorder, pi, inBegin, rooti-1);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
int i = postorder.size()-1;
return _buildTree(inorder, postorder, i, 0, inorder.size()-1);
}
};
8.二叉树的前序遍历(非递归)
144. 二叉树的前序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
TreeNode* cur = root;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
vector<int> ret;
while(cur || !st.empty())//循环条件可以先空着我们之后在分析
{
while(cur)//先访问左路节点,并将左路节点入栈
{
ret.push_back(cur->val);
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
TreeNode* top = st.top();//top取栈顶元素,然后删除栈顶
st.pop();
cur = top->right;//此时左路节点已经访问晚了, 去访问他的右子树。cur指向谁,就表示开始前序遍历哪个树
//现在我们可以控制循环的条件 :1.cur不为空,说明此时cur指的树的左路节点没有访问完
// 2.st不为空,说明左路节点的右子树还没有访问完
}
return ret;
}
};
9.二叉树的中序遍历(非递归)
94. 二叉树的中序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
//该题和上题类似我们直接上代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
vector<int> ret;
TreeNode* cur = root;
while(cur || !st.empty())
{
while(cur)//cur不为空左路节点入栈
{
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
TreeNode* top = st.top();//取出栈顶,并pop掉
st.pop();
ret.push_back(top->val);
cur = top->right;//cur指向top节点的右子树
}
return ret;
}
};
10.二叉树的后序遍历(非递归)
145. 二叉树的后序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
//该题也和前面两题类似
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ret;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* cur = root;
TreeNode* prev = nullptr;//用来记录上一次插入的节点
while(cur || !st.empty())
{
while(cur)//左路节点入栈
{
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
TreeNode* top = st.top();//去栈顶元素
if(top->right == nullptr || top->right == prev)//如果top->right为空或者top->right为上一次插入的节点,就说明可以插入当前值
{
st.pop();
ret.push_back(top->val);
prev = top;
}
else//否则,访问右子树
{
cur = top->right;
}
}
return ret;
}
};
l