- 深度学习-笔记2
深度学习神经网络
paddlepaddle安装(使用cpu):dockerpullregistry.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddle:2.6.2查看下paddlepaddle的镜像层次和安装目录结构(没有看到dockerbuild文件,先感受一下目录结构吧):dockerinspectregistry.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddle:2.6.2|gr
- 软考高项笔记 数字化转型与元宇宙
人工智能
数字化转型与元宇宙随着众多信息通信新技术的迅速发展与普及应用,信息空间成长为第三空间,并与物理空间和社会空间共同构成人类社会的三元空间。数字化转型是建立在数字化转换、数字化升级基础上,进一步触及组织核心业务,以新建一种业务模式为目标的高层次转型。数字化转型是开发数字化技术及支持能力以新建一个富有活力的数字化商业模式。只有组织对其业务进行系统性、彻底的(或重大和完全的)重新定义,不仅是IT方面,而是
- 软考高项笔记 信息技术及其发展
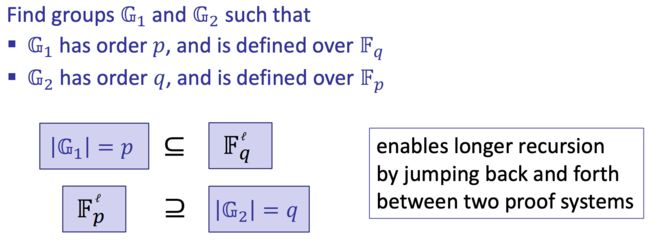
人工智能
信息技术及其发展信息系统项目管理师第二章第一节1.网络标准协议的定义网络协议是为计算机网络中进行数据交换而建立的规则、标准或约定的集合。网络协议由三个要素组成,分别是语义、语法和时序。语义:解释控制信息每个部分的含义,它规定了需要发出何种控制信息,完成的动作以及做出什么样的响应。语法:用户数据与控制信息的结构与格式,以及数据出现的顺序。时序:对事件发生顺序的详细说明。人们形象地将这三个要素描述为:
- 《Memory Barriers a Hardware View for Software Hackers》阅读笔记
落樱弥城
基础知识c++笔记
CPU设计者引入内存屏障(memorybarriers)是为了应对在多处理器系统(SMP)中,内存引用重排序可能导致的同步问题。尽管重排序可以提高性能,但在某些情况下(如同步原语),正确的操作依赖于有序的内存引用,因此需要使用内存屏障来强制执行顺序。 要深入理解这个问题,需要了解CPU缓存的工作原理,尤其是如何使缓存有效工作。以下是相关内容的概述:缓存结构:介绍缓存的基本结构和工作机制。缓存
- 【Spring Cloud 10】阿里巴巴分布式服务架构流量控件Sentinel,B站黑马程序员学习笔记
2501_90252715
springcloud架构sentinel
貌似还是他更强一些,不过没关系,加油!所以,今天开启为期一个月的博客疯狂之旅。一、百度百科Sentinel是面向分布式服务架构的高可用流量防护组件,主要以流量为切入点,从限流、流量整形、熔断降级、系统负载保护、热点防护等多个维度来帮助开发者保障微服务的稳定性。Sentinel具有以下特性:丰富的应用场景:Sentinel承接了阿里巴巴近10年的双十一大促流量的核心场景,例如秒杀(即突发流量控制在系
- C# 学习笔记
c#
pictureBox显示不出图片从网上找了一段代码,复制进visualstudio,显示本地的图片,结果始终显示不出来,查了好久,终于发现在Form1的构造函数中多了一个“InitializeComponent();”,删除就好了!消耗了太多时间。
- echarts样式设置笔记
weixin_45907672
vueecharts前端javascript
设置x轴的小标题xAxis:{type:'value',name:'DRGs组数',data:['2014','2015','2016','2017','2018','2019','2020']}设置y轴的小标题yAxis:[{type:'value',name:'预算总额',min:0,max:25,interval:5,//可以添加单位和后缀//axisLabel:{//formatter:'
- Python学习笔记 - 探索正则表达式对象和对象匹配
Mr数据杨
Python编程基础正则表达式python正则re
在文本处理和数据清洗任务中,正则表达式无疑是一把锋利的“瑞士军刀”。它不仅能够简洁地表达复杂的字符串匹配规则,还可以在各种编程语言中实现高效的文本处理。在Python中,re库提供了强大的正则表达式功能,允许开发者轻松进行模式匹配、数据提取、验证等操作。本教程将深入探讨Python中正则表达式的高级功能,尤其是如何使用正则表达式对象及其方法来高效处理文本。我们将详细讲解如何通过re.compile
- 使用 Docker 部署 pSQL 服务器 的教程
shelby_loo
docker服务器容器
如何使用Edu邮箱申请Azure订阅并开通免费VPS使用Edu邮箱不仅可以申请Azure的免费订阅来开通VPS,还可以免费使用Adobe和Notion等软件,极大地提高学习和工作的效率。如果您还没有Edu邮箱,可以参考在线笔记s3.tebi.io/notes-image/edu%E7%AC%94%E8%AE%B0.pdf获取相关信息和申请方法。新建一台UbuntuVPS并通过Docker部署pSQ
- python学习笔记——input()函数详解
blankcookie
学习笔记
1.input()函数概述功能:从标准输入中读取字符串,并且去掉末尾的换行符,最后返回数据数据类型:str-字符串2.input()函数的使用介绍方法1:直接使用input()函数print("Howoldareyou?")age=input()print(f"so,you're{age}old.")print(type(age))执行:2.方法2:带有提示词的使用input()函数print("
- WIFI模块中AP模式和STA模式是什么
LN花开富贵
硬件设计智能路由器网络单片机嵌入式硬件学习笔记物联网
1.AP模式(AccessPoint):AP模式即无线接入点模式,是一个无线网络的创建者,是网络的中心节点。一般家庭或办公室使用的无线路由器就是一个AP。功能:在AP模式下,设备充当无线网络的中心节点,负责管理无线网络,包括广播SSID(服务集标识符),管理连接的客户端设备,以及提供数据传输的中继点。客户端设备(如智能手机、笔记本电脑等)可以连接到AP模式的设备上,通过它访问互联网或其他网络资源。
- JVM运行时数据区常见知识点&面试题总结
栗子酱-
后端开发面试题#JVM面试题jvmjava开发语言面试springboot
目录运行时数据区前言面试题JVM内存区域/运行时数据区?说一下JDK1.6、1.7、1.8内存区域的变化?为什么使用元空间替代永久代作为方法区的实现?Java堆的内存分区了解吗?运行时常量池?字符串常量池了解吗?为什么将字符串常量池移动到堆中?运行时数据区前言已经找到工作了,分享秋招时的笔记。祝大家都能顺利找到自己心仪的工作。面试题JVM内存区域/运行时数据区?JVM运行时数据区包括程序计数器、虚
- JavaSE笔记总结
火车驶向云外.11
java开发语言
一、Java简介1、三大平台JavaSE:Java标准版,用于桌面应用开发,为今后从事JavaEE开发打基础(C语言和C++语言占有优势)。JavaME:小型版的Java语言,用于嵌入式电子设备或者小型移动设备。JavaEE:企业版,web方向的网站开发和服务器开发,这个领域Java第一。2、Java能做什么?桌面应用开发企业级应用开发移动应用开发科学计算大数据开发游戏开发3、Java的特性面向对
- 光纤通信系统架构
柠檬芭乐绿
网络信息与通信
#学习笔记系统架构光纤通信系统是一种利用光作为载波,通过光纤作为传输媒介来传输信息的通信系统。传输系统基本组成:信号发射端、传输光纤、光纤放大器、接收端信号解调一、信号发射端信号发射端是光纤通信系统的起点,主要负责将电信号转换为光信号,以便在光纤中传输。其主要组成部分包括:光源:光源是光纤通信系统的起点,负责产生光信号。常用的光源有激光器(如半导体激光器LD、垂直腔面发射激光器VCSELs、光纤激
- Web性能优化-详细讲解与实用方法-MDN文档学习笔记
LoveEmiliaForever
MDN前端入门文档前端性能优化学习笔记
Web性能优化查看更多学习笔记:GitHub:LoveEmiliaForeverMDN中文官网性能优良的网站能够提高访问者留存和用户满意度,减少客户端和服务器之间传输的数据量可降低各方的成本不同的业务目标和用户需求需要不同的性能度量,要提高网站性能,你需要了解用户体验、加载和渲染性能,以及如何将性能度量与业务指标结合起来什么是Web性能减少总体负载时间一般策略是使文件尽可能小,尽可能减少HTTP请
- 一文学会react+redux(模块化/同步/异步操作)
青山绿水的蓝
web前端react.js前端javascript
本文基于npxcreate-react-app创建太久没看react,闲来无事重新捡起做一点笔记,希望对部分vue的同行想学习redux起到一些帮助1.准备工作安装1.安装项目插件2.修改`package.json`中的scripts,将`react-scripts`替换为`craco`:3.craco.config.js根目录下创建或修改`craco.config.js`来配置Less以及@别名
- 《深入浅出HTTPS》读书笔记(7):安全的密码学Hash算法
earthzhang2021
httpshttp网络协议网络1024程序员节
密码学Hash算法除了常规Hash算法的特性,还应该具备下面三个特性。1)强抗碰撞性(CollisionResistance)如果两个不相同的值能够得到同样的摘要值,表示产生了Hash碰撞。密码学中,Hash算法必须具备强抗碰撞性,否则不应该使用。2)弱抗碰撞性(Secondpre-imageResistance)给定一个消息和这个消息对应的摘要值,很难找到一条不同的消息也具有相同的摘要值。如果某
- 《深入浅出HTTPS》读书笔记(5):随机数
earthzhang2021
https网络协议http
密码学中随机数的用途非常大,其他密码学算法内部都会用到随机数。1)效率在软件或者密码学应用中需要大量的随机数,必须在很短的时间内生成随机数。2)随机性生成的随机数只要不存在统计学偏差,那么这个随机数就具备随机性(randomness)。3)不可预测性密码学中的随机数必须具备不可预测性,否则就会存在安全问题,当然非密码学应用使用具备随机性的随机数就足够了。4)不可重现性所谓不可重现性(unrepea
- <深入浅出图神经网络> 读书笔记
数学工具构造器
GNN
文章目录笔记GNN代码chapter5|GCN分析TODO改代码得到的结论chapter6|GraphSage分析TODO去今年刚出就买了.一查豆瓣评分比我想的还低(我这种小白都能看出一些错误),有1说1对于入门还是可以的,至少能知道GNN大概的发展路线,如图卷积→\rightarrow→GCN→\rightarrow→GNN等.如果小白直接上手GNN啥的,连图滤波,空域频域等概念都不知道,也只能
- 《深入浅出HTTPS》读书笔记(31):HTTPS和TLS/SSL
earthzhang2021
python开发语言1024程序员节https网络
《深入浅出HTTPS》读书笔记(31):HTTPS和TLS/SSLTLS/SSL协议和应用层协议无关,它只是加密应用层协议(比如HTTP)并传递给下层的TCP。HTTP和TLS/SSL协议组合在一起就是HTTPS,HTTPS等同于HTTP+TLS/SSL。就是说HTTPS拥有HTTP所有的特征,并且HTTP消息由TLS/SSL协议进行安全保护。对于客户端(比如浏览器)来说,发送HTTPS请求就是连
- 【GAE】《High-Dimensional Continuous Control Using Generalized Advantage Estimation》译读笔记
songyuc
笔记
High-DimensionalContinuousControlUsingGeneralizedAdvantageEstimation摘要Policygradientmethods在reinforcementlearning中是一种具有吸引力的方法,因为它们直接优化累积奖励,并且可以很直接地与非线性functionapproximators如neuralnetworks一起使用。其两个主要挑战是
- spring cloud netflix笔记
精神病院丶吴院长
个人笔记springcloudspring
Ribbon可以通过配置文件制定负载均衡的规则默认使用轮训算法来实现负载均衡根据响应时间做权重两个自动装配类RibbonAutoConfiguration和LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration装配类会让加了LoadBalanced注解的RestTemplate加上一个拦截器LoadBalancerInterceptor关键类LoadBalancerInterceptorRib
- 《DirectX 12 3D游戏开发实战》读书笔记1:数学基础
tikris
3d游戏c++矩阵线性代数
文章目录学习内容内容关于浮点类型误差解决方案参数与D3D数据结构向量类型XMVECTOR与XMFLOATn:XMVECTOR与XMFLOATn的相互转化:取得某个分量或者将某个分量转换为XMVECTOR类型:参数向量特点:表示方法:运算求模:单位化(规范化、标准化等同义):正交化:加(减)法:乘法:其他函数杂项点常向量矩阵矩阵的传参矩阵的初始化XMMATRIX和XMFLOAT4X4的转换运算矩阵的
- directx12 3d+vs2022游戏开发第六章 笔记八 绘制几何体
云缘若仙
directx123d3d笔记算法directx123d
1.顶点与输入布局在DirectX123D中,顶点是构建几何体的基本单元,它不仅包含了空间位置信息,还可以存储颜色、法线、纹理坐标等其他属性数据。通过定义不同的顶点结构体,可以创建出满足各种需求的顶点格式。例如,以下结构体定义了一个包含位置和颜色信息的顶点:structVertex{ XMFLOAT3Pos; XMFLOAT4Color;};在这个结构体中,XMFLOAT3类型的Pos
- [C++]DirectX 12 3D游戏开发实战—第12章 学习笔记01 2019.5.7
卡酷酷
DirectX12C++
个人学习用,请勿转载第十二章几何着色器词汇曲面细分:tenssellation几何着色器:geometryshader三角形列表:trainglelist内容如果不启用曲面细分这一环节,几何着色器这个可选阶段会位于顶点着色器与像素着色器之间。顶点着色器以顶点作为输入数据,而几何着色器的输入数据则是完整的图元。如果要绘制三角形列表,那么几何着色器程序实际将对列表中的每个三角形T执行下列操作:for(
- [C++]DirectX 12 3D游戏开发实战—第12章 学习笔记02 2019.5.8
卡酷酷
C++DirectX12
个人学习使用,请勿转载12.3纹理数组12.3.1概述纹理数组即为存放纹理的数组。C++代码中纹理数组也由ID3D12Resource接口表示,创建ID3D12Resource对象时,可以通过设置DepthArraySize属性指定纹理数组所存储的元素个数。在d3dApp文件中创建深度/纹理模板时总是将该值设为1。CreateD3DResource12函数。Texture2DArraygTreeM
- [C++]DirectX 12 3D游戏开发实战—第9章 学习笔记03 2019.5.4
卡酷酷
DirectX12C++
@个人学习用,请勿转赞。DirectX123D游戏开发实战—第9章学习笔记03词汇内容9.11附有纹理的山川演示程序给陆地网格重复铺设草地纹理根据时间函数令流水纹理延波浪滚动起来9.11.1生成栅格纹理坐标上图是一个m*n的栅格,右侧是在归一化纹理坐标[0,1]2中与之相对应的栅格。纹理坐标中的第i行第j列顶点坐标为uij=j⋅δuu_{ij}=j·\deltauuij=
- 吴晓波 历代经济变革得失@简明“中国经济史” - 读书笔记
喝醉酒的小白
破万卷成长
目录《历代经济变革得失》读书笔记一、核心观点二、主要内容(一)导论(二)春秋战国时期(三)汉代(四)北宋(五)明清时期(六)近现代(七)结语三、金句书摘四、阅读感悟《历代经济变革得失》读书笔记一、核心观点本书以中国历史上重要的经济变革为脉络,深入探讨了从春秋战国到改革开放时期经济发展的得失,揭示了统一文化、分权均富、国有经济等因素在中国经济变革中的关键作用,以及对当下经济发展的启示。二、主要内容(
- MySQLDBA修炼之道-开发篇(一)
滔_GY
MySQLDBA修炼之道-读书笔记数据库oraclemysql
三、开发基础1.数据模型1.1关系数据模型介绍关于NULL如果某个字段的值是未知的或未定义的,数据库会提供一个特殊的值NULL来表示。NULL值很特殊,在关系数据库中应该小心处理。例如查询语句“select*fromemployeewhere绩效得分绩效得分>85;”就不能查询出绩效得分是未知的(NULL)的数据。关于key和索引key常指表中能唯一标识一笔记录的字段(属性)或多个字段的组合。现实
- 机器学习笔记——特征工程
好评笔记
补档机器学习人工智能论文阅读AIGCtransformer深度学习面试
大家好,这里是好评笔记,公主号:Goodnote,专栏文章私信限时Free。本笔记介绍机器学习中常见的特征工程方法、正则化方法和简要介绍强化学习。文章目录特征工程(FzeatureEngineering)1.特征提取(FeatureExtraction)手工特征提取(ManualFeatureExtraction):自动特征提取(AutomatedFeatureExtraction):2.特征选择
- jquery实现的jsonp掉java后台
知了ing
javajsonpjquery
什么是JSONP?
先说说JSONP是怎么产生的:
其实网上关于JSONP的讲解有很多,但却千篇一律,而且云里雾里,对于很多刚接触的人来讲理解起来有些困难,小可不才,试着用自己的方式来阐释一下这个问题,看看是否有帮助。
1、一个众所周知的问题,Ajax直接请求普通文件存在跨域无权限访问的问题,甭管你是静态页面、动态网页、web服务、WCF,只要是跨域请求,一律不准;
2、
- Struts2学习笔记
caoyong
struts2
SSH : Spring + Struts2 + Hibernate
三层架构(表示层,业务逻辑层,数据访问层) MVC模式 (Model View Controller)
分层原则:单向依赖,接口耦合
1、Struts2 = Struts + Webwork
2、搭建struts2开发环境
a>、到www.apac
- SpringMVC学习之后台往前台传值方法
满城风雨近重阳
springMVC
springMVC控制器往前台传值的方法有以下几种:
1.ModelAndView
通过往ModelAndView中存放viewName:目标地址和attribute参数来实现传参:
ModelAndView mv=new ModelAndView();
mv.setViewName="success
- WebService存在的必要性?
一炮送你回车库
webservice
做Java的经常在选择Webservice框架上徘徊很久,Axis Xfire Axis2 CXF ,他们只有一个功能,发布HTTP服务然后用XML做数据传输。
是的,他们就做了两个功能,发布一个http服务让客户端或者浏览器连接,接收xml参数并发送xml结果。
当在不同的平台间传输数据时,就需要一个都能解析的数据格式。
但是为什么要使用xml呢?不能使json或者其他通用数据
- js年份下拉框
3213213333332132
java web ee
<div id="divValue">test...</div>测试
//年份
<select id="year"></select>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload =
- 简单链式调用的实现技术
归来朝歌
方法调用链式反应编程思想
在编程中,我们可以经常遇到这样一种场景:一个实例不断调用它自身的方法,像一条链条一样进行调用
这样的调用你可能在Ajax中,在页面中添加标签:
$("<p>").append($("<span>").text(list[i].name)).appendTo("#result");
也可能在HQ
- JAVA调用.net 发布的webservice 接口
darkranger
webservice
/**
* @Title: callInvoke
* @Description: TODO(调用接口公共方法)
* @param @param url 地址
* @param @param method 方法
* @param @param pama 参数
* @param @return
* @param @throws BusinessException
- Javascript模糊查找 | 第一章 循环不能不重视。
aijuans
Way
最近受我的朋友委托用js+HTML做一个像手册一样的程序,里面要有可展开的大纲,模糊查找等功能。我这个人说实在的懒,本来是不愿意的,但想起了父亲以前教我要给朋友搞好关系,再加上这也可以巩固自己的js技术,于是就开始开发这个程序,没想到却出了点小问题,我做的查找只能绝对查找。具体的js代码如下:
function search(){
var arr=new Array("my
- 狼和羊,该怎么抉择
atongyeye
工作
狼和羊,该怎么抉择
在做一个链家的小项目,只有我和另外一个同事两个人负责,各负责一部分接口,我的接口写完,并全部测联调试通过。所以工作就剩下一下细枝末节的,工作就轻松很多。每天会帮另一个同事测试一些功能点,协助他完成一些业务型不强的工作。
今天早上到公司没多久,领导就在QQ上给我发信息,让我多协助同事测试,让我积极主动些,有点责任心等等,我听了这话,心里面立马凉半截,首先一个领导轻易说
- 读取android系统的联系人拨号
百合不是茶
androidsqlite数据库内容提供者系统服务的使用
联系人的姓名和号码是保存在不同的表中,不要一下子把号码查询来,我开始就是把姓名和电话同时查询出来的,导致系统非常的慢
关键代码:
1, 使用javabean操作存储读取到的数据
package com.example.bean;
/**
*
* @author Admini
- ORACLE自定义异常
bijian1013
数据库自定义异常
实例:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE test_Exception
(
ParameterA IN varchar2,
ParameterB IN varchar2,
ErrorCode OUT varchar2 --返回值,错误编码
)
AS
/*以下是一些变量的定义*/
V1 NUMBER;
V2 nvarc
- 查看端号使用情况
征客丶
windows
一、查看端口
在windows命令行窗口下执行:
>netstat -aon|findstr "8080"
显示结果:
TCP 127.0.0.1:80 0.0.0.0:0 &
- 【Spark二十】运行Spark Streaming的NetworkWordCount实例
bit1129
wordcount
Spark Streaming简介
NetworkWordCount代码
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
- Struts2 与 SpringMVC的比较
BlueSkator
struts2spring mvc
1. 机制:spring mvc的入口是servlet,而struts2是filter,这样就导致了二者的机制不同。 2. 性能:spring会稍微比struts快。spring mvc是基于方法的设计,而sturts是基于类,每次发一次请求都会实例一个action,每个action都会被注入属性,而spring基于方法,粒度更细,但要小心把握像在servlet控制数据一样。spring
- Hibernate在更新时,是可以不用session的update方法的(转帖)
BreakingBad
Hibernateupdate
地址:http://blog.csdn.net/plpblue/article/details/9304459
public void synDevNameWithItil()
{Session session = null;Transaction tr = null;try{session = HibernateUtil.getSession();tr = session.beginTran
- 读《研磨设计模式》-代码笔记-观察者模式
bylijinnan
java设计模式
声明: 本文只为方便我个人查阅和理解,详细的分析以及源代码请移步 原作者的博客http://chjavach.iteye.com/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Observable;
import java.util.Observer;
/**
* “观
- 重置MySQL密码
chenhbc
mysql重置密码忘记密码
如果你也像我这么健忘,把MySQL的密码搞忘记了,经过下面几个步骤就可以重置了(以Windows为例,Linux/Unix类似):
1、关闭MySQL服务
2、打开CMD,进入MySQL安装目录的bin目录下,以跳过权限检查的方式启动MySQL
mysqld --skip-grant-tables
3、新开一个CMD窗口,进入MySQL
mysql -uroot
- 再谈系统论,控制论和信息论
comsci
设计模式生物能源企业应用领域模型
再谈系统论,控制论和信息论
偶然看
- oracle moving window size与 AWR retention period关系
daizj
oracle
转自: http://tomszrp.itpub.net/post/11835/494147
晚上在做11gR1的一个awrrpt报告时,顺便想调整一下AWR snapshot的保留时间,结果遇到了ORA-13541这样的错误.下面是这个问题的发生和解决过程.
SQL> select * from v$version;
BANNER
-------------------
- Python版B树
dieslrae
python
话说以前的树都用java写的,最近发现python有点生疏了,于是用python写了个B树实现,B树在索引领域用得还是蛮多了,如果没记错mysql的默认索引好像就是B树...
首先是数据实体对象,很简单,只存放key,value
class Entity(object):
'''数据实体'''
def __init__(self,key,value)
- C语言冒泡排序
dcj3sjt126com
算法
代码示例:
# include <stdio.h>
//冒泡排序
void sort(int * a, int len)
{
int i, j, t;
for (i=0; i<len-1; i++)
{
for (j=0; j<len-1-i; j++)
{
if (a[j] > a[j+1]) // >表示升序
- 自定义导航栏样式
dcj3sjt126com
自定义
-(void)setupAppAppearance
{
[[UILabel appearance] setFont:[UIFont fontWithName:@"FZLTHK—GBK1-0" size:20]];
[UIButton appearance].titleLabel.font =[UIFont fontWithName:@"FZLTH
- 11.性能优化-优化-JVM参数总结
frank1234
jvm参数性能优化
1.堆
-Xms --初始堆大小
-Xmx --最大堆大小
-Xmn --新生代大小
-Xss --线程栈大小
-XX:PermSize --永久代初始大小
-XX:MaxPermSize --永久代最大值
-XX:SurvivorRatio --新生代和suvivor比例,默认为8
-XX:TargetSurvivorRatio --survivor可使用
- nginx日志分割 for linux
HarborChung
nginxlinux脚本
nginx日志分割 for linux 默认情况下,nginx是不分割访问日志的,久而久之,网站的日志文件将会越来越大,占用空间不说,如果有问题要查看网站的日志的话,庞大的文件也将很难打开,于是便有了下面的脚本 使用方法,先将以下脚本保存为 cutlog.sh,放在/root 目录下,然后给予此脚本执行的权限
复制代码代码如下:
chmo
- Spring4新特性——泛型限定式依赖注入
jinnianshilongnian
springspring4泛型式依赖注入
Spring4新特性——泛型限定式依赖注入
Spring4新特性——核心容器的其他改进
Spring4新特性——Web开发的增强
Spring4新特性——集成Bean Validation 1.1(JSR-349)到SpringMVC
Spring4新特性——Groovy Bean定义DSL
Spring4新特性——更好的Java泛型操作API
Spring4新
- centOS安装GCC和G++
liuxihope
centosgcc
Centos支持yum安装,安装软件一般格式为yum install .......,注意安装时要先成为root用户。
按照这个思路,我想安装过程如下:
安装gcc:yum install gcc
安装g++: yum install g++
实际操作过程发现,只能有gcc安装成功,而g++安装失败,提示g++ command not found。上网查了一下,正确安装应该
- 第13章 Ajax进阶(上)
onestopweb
Ajax
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/
- How to determine BusinessObjects service pack and fix pack
blueoxygen
BO
http://bukhantsov.org/2011/08/how-to-determine-businessobjects-service-pack-and-fix-pack/
The table below is helpful. Reference
BOE XI 3.x
12.0.0.
y BOE XI 3.0 12.0.
x.
y BO
- Oracle里的自增字段设置
tomcat_oracle
oracle
大家都知道吧,这很坑,尤其是用惯了mysql里的自增字段设置,结果oracle里面没有的。oh,no 我用的是12c版本的,它有一个新特性,可以这样设置自增序列,在创建表是,把id设置为自增序列
create table t
(
id number generated by default as identity (start with 1 increment b
- Spring Security(01)——初体验
yang_winnie
springSecurity
Spring Security(01)——初体验
博客分类: spring Security
Spring Security入门安全认证
首先我们为Spring Security专门建立一个Spring的配置文件,该文件就专门用来作为Spring Security的配置