redis 布隆过滤器理论及代码实现
理论知识
布隆过滤器
- 可以把布隆过滤器理解为一个不精确的set结构,官方的布隆过滤器在4.0之后才正式登场,不存储具体信息,只在内存中做一个是否存在的标记,节约了内存,可以用来判断数据是否存在一个大的集合中,bf.add 用来添加元素(bf.madd批量添加),bf.exists用于判断元素是否存在(bf.mexists批量判断)
- 布隆过滤器有两个重要参数;
- 错误率(error_rate),默认为0.01,错误率越小,需要的空间就越大
- 预计放入的元素数量(initial_size),默认为100,当实际数量超过这个数量,误判率就会上升,所以如果这个值过大就会浪费存储空间,过小又会影响准确率,使用之前要尽可能的估算元素数量
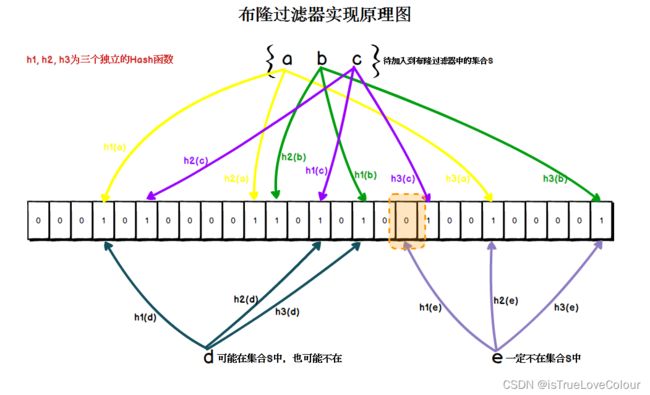
- 布隆过滤器底层是一个大的位数组(bitmap)和几个不一样的无偏hash函数,无偏指的是能把hash值算的比较均匀
- 向布隆过滤器添加元素的时候,会使用hash函数对key进行hash,取得一个整数索引值,然后根据索引值对位数组长度进行取模得到一个位置,每个hash函数都会得到一个位置,把这些位置都置为1
- 向布隆过滤器询问key是否存在时,和添加一样,也会把hash的几个位置都算出来,如果位数组中这几个位置有一个不为1,那么key一定不存在,如果都为1 ,并不能说明key一定存在,只是存在的概率很高
- 所以布隆过滤器判断对象是否存在时可能会误判:如果判断为不存在那么一定不存在,如果判断为存在有可能不存在
- 布隆过滤器最好不要删除元素,因为多个元素可能共享一位,删除元素有可能会删除其他元素的映射值,会导致误判率增加
- 如果实际元素数量远大于初始化量,错误率的上升会很快,此时就需要重建布隆过滤器,重新分配一个更大的容量,然后把历史数据添加进去
- 布隆过滤器用来做新闻推送时,能够精确的过滤用户已经看过的内容,对于一些没有看过的新内容也会过滤极小的一部分,能够保证用户不会看到重复内容,此外还可以做黑名单、白名单
- 还可以通过布隆过滤器降低数据库的IO请求,执行查询时,先访问布隆过滤器,过滤掉不存在的数据请求,然后再去查询数据库,解决了缓存穿透的问题(缓存穿透,数据库也不存在数据)
布隆过滤器的优缺点
- 因为不存储具体信息,只在内存中做一个是否存在的标记,可以很高效的插入和查询,而且内存占用少
- 但是最好不要删除元素,因为多个元素可能共享一位,删除元素有可能会删除其他元素的映射值,会导致误判率增加
- 如果实际元素数量远大于初始化量,错误率的上升会很快,此时就需要重建布隆过滤器,重新分配一个更大的容量,然后把历史数据添加进去
- 存在误判的可能,只有判断不存在是绝对准确的
代码实现
布隆过滤器使用步骤
- 初始化位数组
- 通过hash函数计算hash值,计算hash值对应bitmap的数组位置,把对应位置值改为1
- 用布隆过滤器判断元素是否存在
这里使用mybatis-plus和mysql
实体类
/**
* 测试表server实体类
*/
@Data
@ApiModel(value = "TestServer对象", description = "测试表server实体对象")
public class TestServer implements Serializable {
@TableId("id")
private Long id;
/**
* 金额
*/
@ApiModelProperty(value = "金额", name = "iNumber")
private String iNumber;
/**
* 描述
*/
@ApiModelProperty(value = "描述", name = "descd")
private String descd;
/**
* 删除标记
*/
@ApiModelProperty(value = "删除标记", name = "deleted")
@TableLogic
@TableField(value = "DELETED", fill = FieldFill.INSERT, jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR)
private String deleted;
}
初始化 布隆过滤器
/**
* 初始化 布隆过滤器
*/
@Component
public class BloomFilter {
@Autowired
private TestServerMapper mapper;
@Resource
private RedisTemplate<String, TestServer> redisTemplate;
public static final String BIT_KEY = "BloomFilter";
public static final String KEY = "test_Server:";
//Java5的时候引入的注解,在项目启动的时候执行这个方法
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
//获取数据库数据,这里应该用流式查询
QueryWrapper<TestServer> query = new QueryWrapper<>();
query.eq("deleted", "0");
List<TestServer> testServers = mapper.selectList(query);
long size = (long) Math.pow(2, 31);
for (TestServer testServer : testServers) {
//计算 hashCode
int hash = Math.abs((KEY+testServer.getId()).hashCode());
//计算 hashCode 再bitMap的位置
long index = (long) (hash % size);
//设置 bitmap 的值
redisTemplate.opsForValue().setBit(BIT_KEY, index, true);
}
}
}
判断布隆过滤器是否存在数据的工具类
@Component
public class BloomFilterUtils {
@Resource
private RedisTemplate<String, TestServer> redisTemplate;
public boolean check(String key) {
long size = (long) Math.pow(2, 31);
int hash = Math.abs(key.hashCode());
//计算 hashCode 再bitMap的位置
long index = (long) (hash % size);
//设置 bitmap 的值
Boolean bit = redisTemplate.opsForValue().getBit(BIT_KEY, index);
return bit;
}
}
查询和插入的逻辑
查询:
- 查询时,先去查询布隆过滤器,布隆过滤器不存在,就不在继续查询
- 布隆过滤器存在,才接着查询redis,
- redis存在就直接返回,redis不存在,再查询mysql
- mysql存在把数据写回redis,再返回
插入
- 先插入mysql,然后从mysql中再查出来
- 写入redis布隆过滤器
- 写入redis
@Service
public class TestServerServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<TestServerMapper, TestServer> implements TestServerService {
@Autowired
private TestServerMapper mapper;
@Autowired
private BloomFilterUtils bloomFilterUtils;
@Resource
private RedisTemplate<String, TestServer> redisTemplate;
public static final String KEY = "test_Server:";
/**
* 查询时,先去查询布隆过滤器,布隆过滤器不存在,就不在继续查询
* 布隆过滤器存在,才接着查询redis,
* redis存在就直接返回,redis不存在,再查询mysql
* mysql存在把数据写回redis,再返回
* 这里用了双检加锁策略,避免了缓存击穿
*/
@Override
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public BaseResultModel getOneById(Long id) {
String key = KEY + id;
if (!bloomFilterUtils.check(key)){
System.out.println("布隆过滤器中不存在,不在向下执行");
return BaseResultModel.success("记录不存在");
}
System.out.println("布隆过滤器中存在,去redis查询");
TestServer entity = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
//redis有就直接返回
if (entity != null) {
return BaseResultModel.success(entity);
}
//redis没有就需要去数据库查询,这里不能直接去查询redis,因为有可能造成缓存击穿问题,所以需要先获得锁
synchronized (this){
//拿到锁之后也不是直接查询数据库,而是在查询一遍redis,如果redis依然没有数据,才去查询数据库
entity = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (entity == null){
entity = baseMapper.selectById(id);
if (null == entity) {
throw new BaseException(ResultStatus.NO_RECORDS.getCode(), ResultStatus.NO_RECORDS.getMessage());
} else {
//redis没有,数据库有,需要把数据回些到redis
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, entity);
}
}
}
return BaseResultModel.success(entity);
}
@Override
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public BaseResultModel getOneById(Long id) {
String key = KEY + id;
if (!bloomFilterUtils.check(key)){
System.out.println("布隆过滤器中不存在,不在向下执行");
return BaseResultModel.success("记录不存在");
}
System.out.println("布隆过滤器中存在,去redis查询");
TestServer entity = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (entity != null) {
return BaseResultModel.success(entity);
}
entity = baseMapper.selectById(id);
if (null == entity) {
throw new BaseException(ResultStatus.NO_RECORDS.getCode(), ResultStatus.NO_RECORDS.getMessage());
} else {
//redis没有,数据库有,需要把数据回些到redis
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, entity);
}
return BaseResultModel.success(entity);
}
@Override
@Transactional
public BaseResultModel insert(ReqTestServerAdd req) {
TestServer entity = new TestServer();
BeanUtil.copyProperties(req, entity);
//雪花算法
IdWorker worker = new IdWorker(1, 1, 1);
Long id = worker.nextId();
entity.setId(id);
entity.setDeleted("0");
if (!this.save(entity)) {
throw new BaseException(ResultStatus.INSERT_FAIL.getCode(), ResultStatus.INSERT_FAIL.getMessage());
}
//插入成功,插入到布隆过滤器
//计算 hashCode
int hash = Math.abs((KEY+id).hashCode());
long size = (long) Math.pow(2, 31);
//计算 hashCode 再bitMap的位置
long index = (long) (hash % size);
//设置 bitmap 的值
redisTemplate.opsForValue().setBit(BIT_KEY, index, true);
//插入成功,同步把数据插入到redis
TestServer testServer = mapper.selectById(id);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(KEY + id, testServer);
return BaseResultModel.success();
}
雪花算法工具类
public class IdWorker {
//因为二进制里第一个 bit 为如果是 1,那么都是负数,但是我们生成的 id 都是正数,所以第一个 bit 统一都是 0。
//机器ID 2进制5位 32位减掉1位 31个
private long workerId;
//机房ID 2进制5位 32位减掉1位 31个
private long datacenterId;
//代表一毫秒内生成的多个id的最新序号 12位 4096 -1 = 4095 个
private long sequence;
//设置一个时间初始值 2^41 - 1 差不多可以用69年
private long twepoch = 1585644268888L;
//5位的机器id
private long workerIdBits = 5L;
//5位的机房id
private long datacenterIdBits = 5L;
//每毫秒内产生的id数 2 的 12次方
private long sequenceBits = 12L;
// 这个是二进制运算,就是5 bit最多只能有31个数字,也就是说机器id最多只能是32以内
private long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits);
// 这个是一个意思,就是5 bit最多只能有31个数字,机房id最多只能是32以内
private long maxDatacenterId = -1L ^ (-1L << datacenterIdBits);
private long workerIdShift = sequenceBits;
private long datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits;
private long timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits + datacenterIdBits;
private long sequenceMask = -1L ^ (-1L << sequenceBits);
//记录产生时间毫秒数,判断是否是同1毫秒
private long lastTimestamp = -1L;
public long getWorkerId(){
return workerId;
}
public long getDatacenterId() {
return datacenterId;
}
public long getTimestamp() {
return System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public IdWorker(long workerId, long datacenterId, long sequence) {
// 检查机房id和机器id是否超过31 不能小于0
if (workerId > maxWorkerId || workerId < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
String.format("worker Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0",maxWorkerId));
}
if (datacenterId > maxDatacenterId || datacenterId < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
String.format("datacenter Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0",maxDatacenterId));
}
this.workerId = workerId;
this.datacenterId = datacenterId;
this.sequence = sequence;
}
// 这个是核心方法,通过调用nextId()方法,让当前这台机器上的snowflake算法程序生成一个全局唯一的id
public synchronized long nextId() {
// 这儿就是获取当前时间戳,单位是毫秒
long timestamp = timeGen();
if (timestamp < lastTimestamp) {
System.err.printf(
"clock is moving backwards. Rejecting requests until %d.", lastTimestamp);
throw new RuntimeException(
String.format("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for %d milliseconds",
lastTimestamp - timestamp));
}
// 下面是说假设在同一个毫秒内,又发送了一个请求生成一个id
// 这个时候就得把seqence序号给递增1,最多就是4096
if (lastTimestamp == timestamp) {
// 这个意思是说一个毫秒内最多只能有4096个数字,无论你传递多少进来,
//这个位运算保证始终就是在4096这个范围内,避免你自己传递个sequence超过了4096这个范围
sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask;
//当某一毫秒的时间,产生的id数 超过4095,系统会进入等待,直到下一毫秒,系统继续产生ID
if (sequence == 0) {
timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp);
}
} else {
sequence = 0;
}
// 这儿记录一下最近一次生成id的时间戳,单位是毫秒
lastTimestamp = timestamp;
// 这儿就是最核心的二进制位运算操作,生成一个64bit的id
// 先将当前时间戳左移,放到41 bit那儿;将机房id左移放到5 bit那儿;将机器id左移放到5 bit那儿;将序号放最后12 bit
// 最后拼接起来成一个64 bit的二进制数字,转换成10进制就是个long型
return ((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) |
(datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) |
(workerId << workerIdShift) | sequence;
}
/**
* 当某一毫秒的时间,产生的id数 超过4095,系统会进入等待,直到下一毫秒,系统继续产生ID
* @param lastTimestamp
* @return
*/
private long tilNextMillis(long lastTimestamp) {
long timestamp = timeGen();
while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp) {
timestamp = timeGen();
}
return timestamp;
}
//获取当前时间戳
private long timeGen(){
return System.currentTimeMillis();
}
/**
* main 测试类
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdWorker worker = new IdWorker(1,1,1);
for (int i = 0; i < 22; i++) {
System.out.println(worker.nextId());
}
}
}
Controller
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/testServer")
@Api(value="测试表server接口管理,,维护人:psh",tags ={"测试表server接口管理"})
public class TestServerController {
@Autowired
private TestServerService testServerService;
/**
* 根据主键查询
*
* @param id 测试表server主键
* @return BaseResultModel对象
*/
@ApiOperation(value="根据主键获取测试表server信息")
@ApiImplicitParam(name="id",value="测试表server主键",dataType="Long", paramType = "query")
@GetMapping("/getById")
public BaseResultModel getById(@RequestParam("id") Long id) {
return testServerService.getOneById(id);
}
/**
* 新增
*
* @param req 实体类
* @return BaseResultModel对象
*/
@PostMapping(value = "/add")
@ApiOperation(value="新增测试表server")
public BaseResultModel insert(@RequestBody ReqTestServerAdd req) {
return testServerService.insert(req);
}
}
Guava布隆过滤器
@Component
public class GuavaBloomFilter {
@Autowired
private TestServerMapper mapper;
@Resource
private RedisTemplate<String, TestServer> redisTemplate;
public static final String BIT_KEY = "BloomFilter";
public static final String KEY = "test_Server:";
//初始化Guava布隆过滤器,第一个参数是数据类型,第二个是容量,第三个是误判率
public static BloomFilter<String> bloomFilter = BloomFilter.create(Funnels.stringFunnel(Charset.defaultCharset()),
10000, 0.03);
//Java5的时候引入的注解,在项目启动的时候执行这个方法
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("初始化GUAVA布隆过滤器------------------------>");
//获取数据库数据,这里应该用流式查询
QueryWrapper<TestServer> query = new QueryWrapper<>();
query.eq("deleted", "0");
List<TestServer> testServers = mapper.selectList(query);
for (TestServer testServer : testServers) {
String ss = KEY + testServer.getId();
bloomFilter.put(ss);
}
}
}
Guava 的使用和自己实现的布隆过滤器没有什么区别
@Override
public BaseResultModel getByIdGuava(Long id) {
String key = KEY + id;
if (! bloomFilter.mightContain(key)){
System.out.println("Guava布隆过滤器中不存在,不在向下执行");
return BaseResultModel.success("Guava布隆过滤器中不存在");
}
System.out.println("key:"+key+",Guava布隆过滤器中存在,去redis查询");
TestServer entity = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (entity != null) {
return BaseResultModel.success(entity);
}
//redis没有就需要去数据库查询,这里不能直接去查询redis,因为有可能造成缓存击穿问题,所以需要先获得锁
synchronized (this){
//拿到锁之后也不是直接查询数据库,而是在查询一遍redis,如果redis依然没有数据,才去查询数据库
entity = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (entity == null){
entity = baseMapper.selectById(id);
if (null == entity) {
throw new BaseException(ResultStatus.NO_RECORDS.getCode(), ResultStatus.NO_RECORDS.getMessage());
} else {
//redis没有,数据库有,需要把数据回些到redis
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, entity);
}
}
}
return BaseResultModel.success(entity);
}