Springboot之@Transactional事务注解原理详解
文章目录
-
- 注册事务切面逻辑
-
- 1、扫描spring-boot-autoconfigure依赖包下的META-INF/spring.factories,加载文件里的
TransactionAutoConfiguration类 - 2、解析
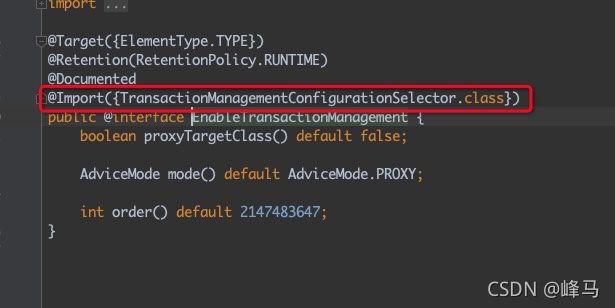
TransactionAutoConfiguration类里的@EnableTransactionManagement注解,根据该注解上的@Import加载TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector类 - 3、通过
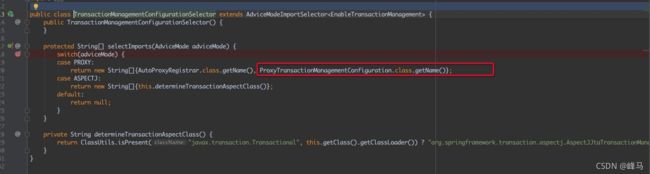
TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector类的selectImports方法加载ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration类 - 4、
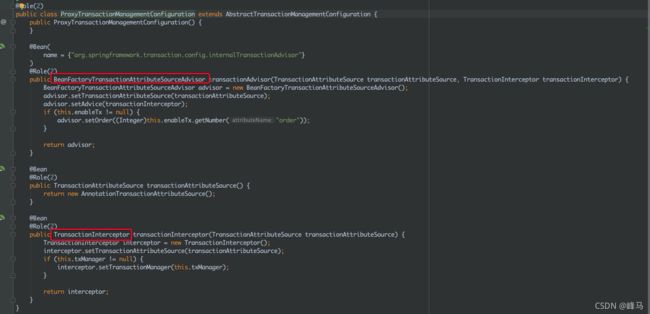
ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration类通过@Bean加载BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor类,该类实现了Pointcut,并且在该类里注入了实现了Advise接口的TransactionInterceptor类
- 1、扫描spring-boot-autoconfigure依赖包下的META-INF/spring.factories,加载文件里的
- 根据切面逻辑生成代理类
-
- 1、加载
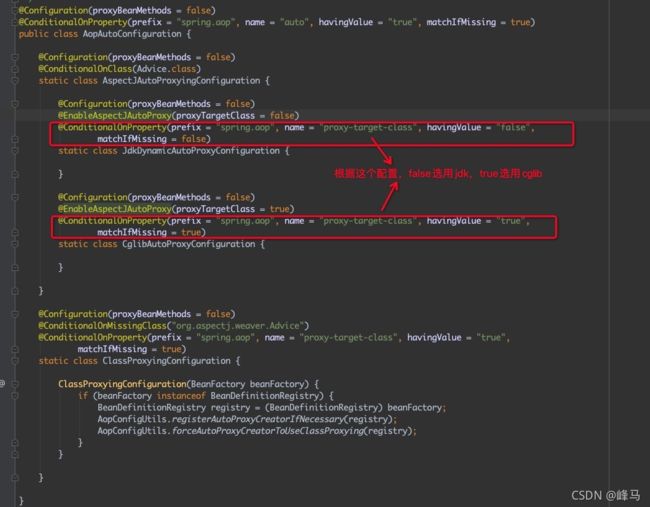
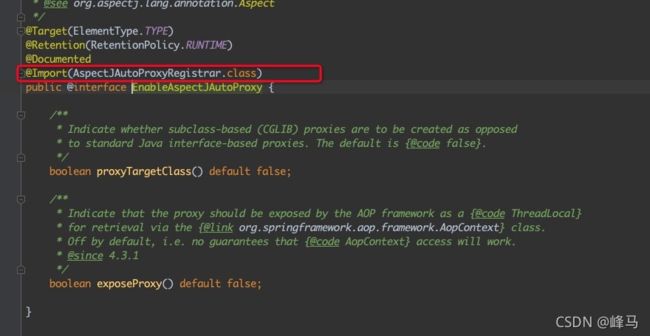
AopAutoConfiguration类,根据proxyTargetClass配置来选择是使用jdk的proxy还是cglib来生成动态代理类,截图如下: - 2、解析
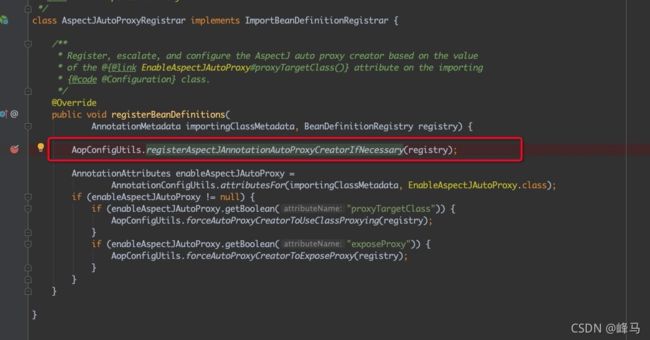
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解,通过该注解上的@Import加载AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar类 - 3、
AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar类会向Spring容器注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类,该类实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,所以这个aop逻辑是在Springbean生成过程中通过后置处理器逻辑来实现的。 - 4、生成动态代理类的核心逻辑在
AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar类的父类AbstractAutoProxyCreator类的postProcessAfterInitialization方法里,该方法实现的是后置处理器BeanPostProcessor类,用来生成动态代理类,这里看下具体逻辑:
- 1、加载
- 总结
@Transactional注解的逻辑是通过动态代理来实现的,而生成这个动态代理类分成了两步:
1、向spring容器注册事务相关的切面逻辑
2、根据切面逻辑生成动态代理
下面围绕这两点来看下Springboot里的实现原理
注册事务切面逻辑
切面逻辑里有三个概念:
Pointcut:负责告诉spring容器哪个类需要增强
Advise:具体的切面逻辑,这里就是根据异常进行commit或者回滚的相关逻辑
Advisor:封装了Advise和Pointcut的类
事务相关的这三个对象是由Springboot自动装载的(自动装载组件原理可以看这里),流程如下:
1、扫描spring-boot-autoconfigure依赖包下的META-INF/spring.factories,加载文件里的TransactionAutoConfiguration类
2、解析TransactionAutoConfiguration类里的@EnableTransactionManagement注解,根据该注解上的@Import加载TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector类
3、通过TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector类的selectImports方法加载ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration类
4、
ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration类通过@Bean加载BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor类,该类实现了Pointcut,并且在该类里注入了实现了Advise接口的TransactionInterceptor类
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor类图如下:
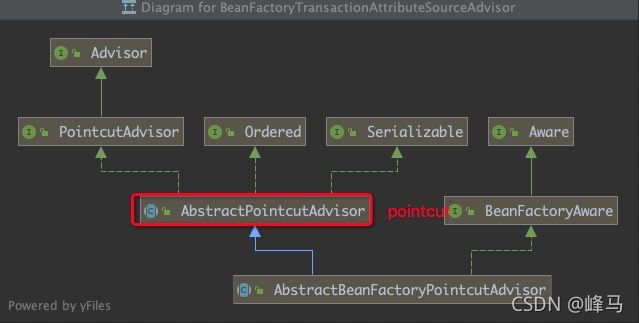
到这里,Spring容器加载了需要实现事务相关切面的关键的三个对象,其中Pointcut的匹配逻辑就是看这个方法有没有被@Transactional注解标注,最终会调用到SpringTransactionAnnotationParser类的parseTransactionAnnotation方法里,有兴趣的同学可以在这里打上断点看下调用链,debug图如下:
这里主要看下事务的核心逻辑,这个核心逻辑就在实现了Advise接口的TransactionInterceptor类的invoke方法里,这里看下这里的源码:
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Class<?> targetClass = invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null;
Method var10001 = invocation.getMethod();
invocation.getClass();
// 调用事务逻辑
return this.invokeWithinTransaction(var10001, targetClass, invocation::proceed);
}
@Nullable
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass, TransactionAspectSupport.InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
TransactionAttributeSource tas = this.getTransactionAttributeSource();
// 获取改方法上的事务配置,包括传播级别、异常信息等配置
TransactionAttribute txAttr = tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null;
// 事务管理器,负责生成事务上下文信息,比如开启事务、获取数据库链接等逻辑
TransactionManager tm = this.determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
...
PlatformTransactionManager ptm = this.asPlatformTransactionManager(tm);
String joinpointIdentification = this.methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
// 根据传播级别配置,看是否需要新建事务
TransactionAspectSupport.TransactionInfo txInfo = this.createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
// 通过try catch捕获异常来实现回滚逻辑
try {
// 调用真正的dao层逻辑
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
} catch (Throwable var18) {
// 根据@Transactional配置的异常来决定是否回滚
this.completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, var18);
throw var18;
} finally {
// 结束当前的事务,信息是保存在ThreadLocal里
this.cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && TransactionAspectSupport.VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
TransactionStatus status = txInfo.getTransactionStatus();
if (status != null && txAttr != null) {
retVal = TransactionAspectSupport.VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
}
// 没有异常时,执行commit操作
this.commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
...
}
总结下核心步骤如下:
通过动态代理为标注了@Transactional注解的方法增加切面逻辑,而事务的上下文包括数据库链接都是通过ThreadLocal来传递,在这个切面逻辑里主要做这几个事情:
- 获取方法上标注的注解的元数据,包括传播级别、异常配置等信息
- 通过
ThreadLocal获取事务上下文,检查是否已经激活事务 - 如果已经激活事务,则根据传播级别配置,看是否需要新建事务(如果新建事务,会生成一个新的事务上下文对象
TransactionInfo,并将上一个事务上下文赋值到新上下文的oldTransactionInfo属性上)代码位置在TransactionAspectSupport类的prepareTransactionInfo方法里的bindToThread方法里 - 开启事务,先通过数据库连接池获取链接,关闭链接的
autocommit,然后在try catch里反射执行真正的dao操作,通过异常情况来决定是commit还是rollback
下面看下Springboot怎么根据这三个对象来生成代理类的。
根据切面逻辑生成代理类
核心逻辑是Springboot会自动装载AopAutoConfiguration类(自动装载组件原理可以看这里),该类会根据加载到Spring容器里的Advisor对象来找到需要增强的类,并生成代理类,核心步骤如下:
1、加载AopAutoConfiguration类,根据proxyTargetClass配置来选择是使用jdk的proxy还是cglib来生成动态代理类,截图如下:
2、解析@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解,通过该注解上的@Import加载AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar类
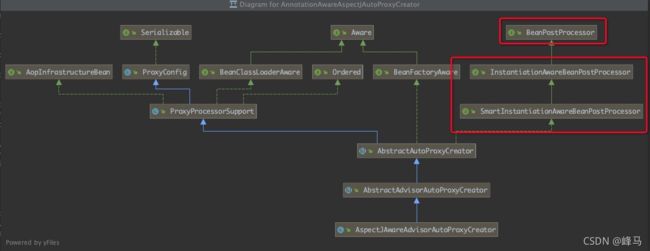
3、AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar类会向Spring容器注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类,该类实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,所以这个aop逻辑是在Springbean生成过程中通过后置处理器逻辑来实现的。
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类图如下:
4、生成动态代理类的核心逻辑在AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar类的父类AbstractAutoProxyCreator类的postProcessAfterInitialization方法里,该方法实现的是后置处理器BeanPostProcessor类,用来生成动态代理类,这里看下具体逻辑:
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = this.getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
// 生成动态代理类
return this.wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
...
// 遍历注册到spring容器内的advisor,根据class信息找到匹配到的advisor
Object[] specificInterceptors = this.getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, (TargetSource)null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// 生成动态代理类
Object proxy = this.createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
} else {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
...
}
通过bean找到匹配的advisor的debug图如下,可以看到这里的BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor就是上面注入的。
总结
可以看出Springboot里的@Transactional之所以能起作用,是由两个自动装载类配合的,一个就是负责生成动态代理类的AopAutoConfiguration类,一个就是TransactionAutoConfiguration类,负责向Spring容器注册事务相关的Advisor。这里也给我们提供了扩展,如果我们需要自定义自己的切面逻辑,只需要向spring容器注册自定义的Advisor,定义好Pointcut和Advise就行了。