信号灯集,消息队列
信号灯集
1、概念
信号灯(semaphore),也叫信号量。它是不同进程间或一个给定进程内部不同线程间同步的机制;System V的信号灯是一个或者多个信号灯的一个集合。其中的每一个都是单独的计数信号灯。而Posix信号灯指的是单个计数信号灯。
通过信号灯集实现共享内存的同步操作。
- 步骤
在不同的进程间,通过相同的key值,打开相同的信号灯集
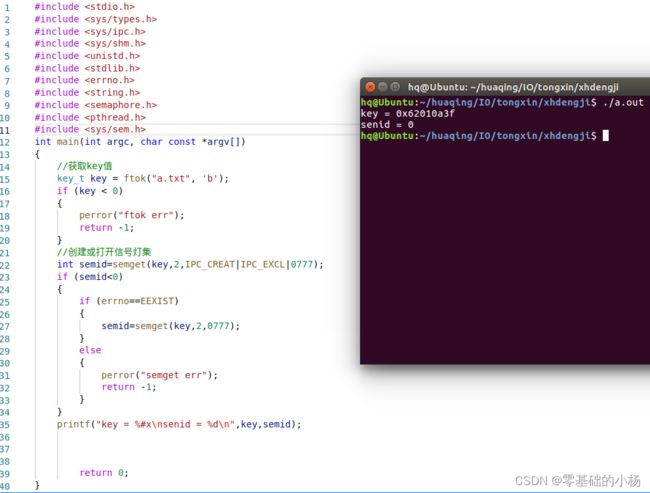
- 创建key值 ftok
- 创建或打开信号灯集semget
- 初始化信号灯 semctl
- PV操作 semop
- 删除信号灯集 semctl
- 函数
1)semget 创建\打开信号灯
int semget(key_t key, int nsems, int semflg);
功能:创建/打开信号灯
参数:key:ftok产生的key值
nsems:信号灯集中包含的信号灯数目
semflg:信号灯集的访问权限,通常为IPC_CREAT |IPC_EXCL |0666
返回值:成功:信号灯集ID
失败:-1
2)semctl 信号灯集合的控制(初始化/删除)
int semctl ( int semid, int semnum, int cmd…/*union semun arg*/);
功能:信号灯集合的控制(初始化/删除)
参数:semid:信号灯集ID
semnum: 要操作的集合中的信号灯编号
cmd:
GETVAL:获取信号灯的值,返回值是获得值
SETVAL:设置信号灯的值,需要用到第四个参数:共用体
IPC_RMID:从系统中删除信号灯集合
返回值:成功 0
失败 -1
用法:初始化:
union semun{
int val;
}mysemun;
mysemun.val = 10;
semctl(semid, 0, SETVAL, mysemun);
获取信号灯值:函数semctl(semid, 0, GETVAL)的返回值
删除信号灯集:semctl(semid, 0, IPC_RMID);
3)semop 对信号灯集合中的信号量进行PV操作
int semop ( int semid, struct sembuf *opsptr, size_t nops);
功能:对信号灯集合中的信号量进行PV操作
参数:semid:信号灯集ID
opsptr:操作方式
nops: 要操作的信号灯的个数 1个
返回值:成功 :0
失败:-1
struct sembuf {
short sem_num; // 要操作的信号灯的编号
short sem_op; // 0 : 等待,直到信号灯的值变成0
// 1 : 释放资源,V操作
// -1 : 申请资源,P操作
short sem_flg; // 0(阻塞),IPC_NOWAIT, SEM_UNDO
};
用法:
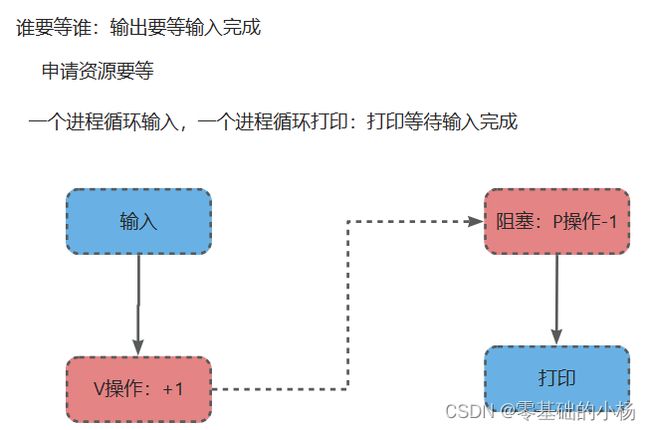
申请资源 P操作:
mysembuf.sem_num = 0;
mysembuf.sem_op = -1;
mysembuf.sem_flg = 0;
semop(semid, &mysembuf, 1);
释放资源 V操作:
mysembuf.sem_num = 0;
mysembuf.sem_op = 1;
mysembuf.sem_flg = 0;
semop(semid, &mysembuf, 1);
#include - 命令查看灯集
ipcs -s:查看信号灯集
ipcrm -s semid:删除信号灯集
- 练习
两个进程实现通信,一个进程循环从终端输入,另一个进程循环打印,当输入quit时结束
共享内存+信号灯集+封装函数(自主选择)
#include #include 消息队列
1、特点
消息队列是IPC对象的一种
消息队列由消息队列ID来唯一标识
消息队列就是一个消息的列表。用户可以在消息队列中添加消息、读取消息等。
消息队列可以按照类型来发送(添加)/接收(读取)消息
2.步骤
在不同的进程中,通过相同的key值,拿到相同的消息队列
- 创建key值 ftok
- 创建或打开消息队列 msgget
- 添加消息:按照类型将消息添加到已经打开的消息队列末尾 msgsnd
- 读取消息:按照类型把消息从消息队列中读走 msgrcv
- 删除消息队列 msgctl
3.函数
1)msgget创建或打开一个消息队列
#include 2)msgsnd添加消息
#include 3)msgrcv读取消息
#include - msgctl对消息队列的操作,删除消息队列
#include 
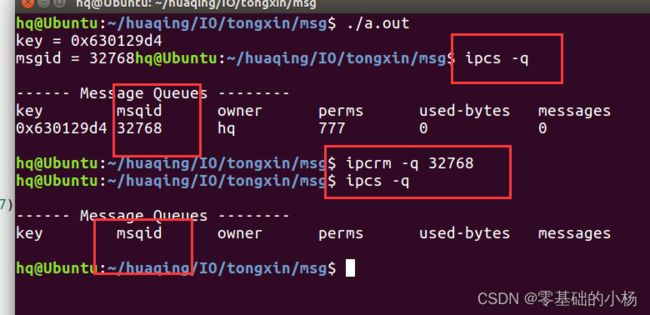
#include 4.命令
ipcs -q :查看消息队列
ipcrm -q msgid :删除消息队列