Leetcode刷题笔记--Hot81--90
目录
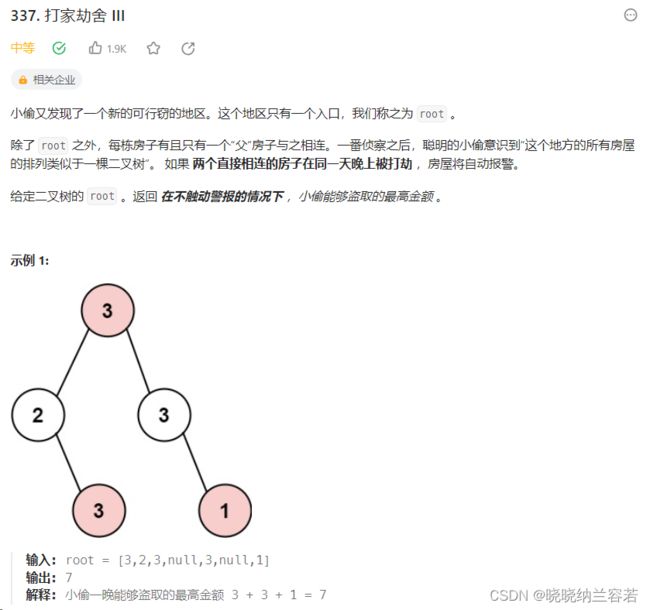
1--打家劫舍III(337)
2--比特位计数(338)
3--前K个高频元素(347)
4--字符串解码(394)
5--除法求值(399)
6--根据身高重建队列(406)
7--分割等和子集(416)
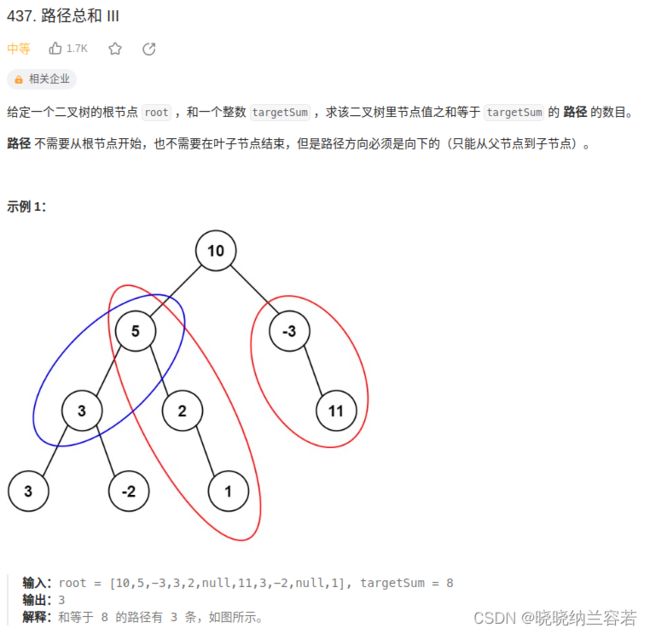
8--路径总和III(437)
9--找到字符串中所有字母异位词(438)
10--找到所有数组中消失的数字(448)
1--打家劫舍III(337)
主要思路:
基于从下到上的 dp 回溯法,每一个节点只有两种状态,dp[0]表示被打劫,dp[1]表示不被打劫;
当前节点被打劫时,其孩子只能都不被打劫;dp[0] = left[1] + right[1] + cur->val;
当前节点不被打劫时,其孩子可以都被打劫,也可以都不被打劫,或者一个被打劫另一个不被打劫。
dp[1] = max(left[0] + right[0], left[1] + right[1], left[0] + right[1], left[1] + right[0]);
#include
#include
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
int rob(TreeNode* root) {
// 对于每一间房屋,有被打劫和不被打劫两种状态
std::vector res = dfs(root);
return std::max(res[0], res[1]);
}
std::vector dfs(TreeNode* cur){
if(cur == nullptr) return {0, 0};
std::vector left = dfs(cur->left);
std::vector right = dfs(cur->right);
std::vector dp(2, 0); // dp[0]表示被打劫 dp[1]表示不被打劫
dp[0] = left[1] + right[1] + cur->val; // 当前房屋被打劫,其孩子只能不被打劫
// 当前房屋不被打劫,其孩子可以同时被打劫,也可以同时不被打劫
// 当前房屋不被打劫,其孩子可以一个被打劫,另一个不被打劫
dp[1] = std::max(std::max(std::max(left[0] + right[0], left[1] + right[1]), left[0] + right[1]), left[1] + right[0]);
return dp;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
// root = [3, 2, 3, null, 3, null, 1]
TreeNode *Node1 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode *Node2 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode *Node3 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode *Node4 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode *Node5 = new TreeNode(1);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node3;
Node2->right = Node4;
Node3->right = Node5;
Solution S1;
int res = S1.rob(Node1);
std::cout << res << std::endl;
return 0;
} 2--比特位计数(338)
主要思路:
#include
#include
class Solution {
public:
std::vector countBits(int n) {
std::vector dp(n + 1, 0);
int high_valid = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if((i & (i - 1)) == 0){ // i是2的指数幂,更新最高有效位
high_valid = i;
}
dp[i] = dp[i - high_valid] + 1;
}
return dp;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
// n = 5
int n = 5;
Solution S1;
std::vector res = S1.countBits(n);
for(auto num : res)
std::cout << num << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
} 3--前K个高频元素(347)
主要思路:
维护一个小根堆,存储k个高频元素;
#include
#include
#include
#include
class Solution{
public:
std::vector topKFrequent(std::vector& nums, int k){
std::unordered_map hash_map;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){
hash_map[nums[i]] += 1;
}
// 小顶堆
std::priority_queue, std::vector>, mycompare> pri_q;
for(auto i = hash_map.begin(); i != hash_map.end(); i++){
if(pri_q.size() >= k){
if(i->second > pri_q.top().second){
pri_q.pop();
pri_q.emplace(i->first, i->second);
}
}
else{
pri_q.emplace(i->first, i->second);
}
}
std::vector res;
while(!pri_q.empty()){
res.push_back(pri_q.top().first);
pri_q.pop();
}
return res;
}
class mycompare{
public:
bool operator()(std::pair& item1, std::pair& item2){
return item1.second > item2.second;
}
};
};
int main(int argc, char argv[]){
// nums = [1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3], k = 2
std::vector test = {1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3};
int k = 2;
Solution S1;
std::vector res = S1.topKFrequent(test, k);
for(int num : res) std::cout << num << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
} 4--字符串解码(394)
主要思路:
从后开始遍历,用一个栈存储访问的字符,遇到左括号就处理字符串和重复次数;
#include
#include
#include
class Solution {
public:
std::string decodeString(std::string s) {
std::stack stk;
int i = s.length() - 1; // 从后开始遍历
while(i >= 0){
if(s[i] == ']' || ('a' <= s[i] && s[i] <= 'z')){
stk.push(s.substr(i, 1));
i--; // 移到下一个字符
}
else{ // 遇到 '['
// 取出栈中的所有字符串(除']')
std::string tmp;
while(!stk.empty() && stk.top() != "]"){
tmp += stk.top();
stk.pop();
}
if(!stk.empty()) stk.pop(); // 弹出 "]"
i--; // 移到数字位
// 处理数字
int val = 0, base = 1;
while(i >= 0 && s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9'){
val += (s[i] - '0') * base;
base = base * 10;
i--;
}
// 存储字符串到栈中
while(val > 0){
stk.push(tmp);
val--;
}
}
}
std::string res;
// 将栈中的字符串取出
while(!stk.empty()){
res += stk.top();
stk.pop();
}
return res;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
// s = "3[a]2[bc]"
std::string test = "3[a]2[bc]";
Solution S1;
std::string res = S1.decodeString(test);
std::cout << res << std::endl;
return 0;
} 5--除法求值(399)
主要思路:
基于带权重的并查集。I think this is a hard question....
#include
#include
#include
#include
class Solution {
public:
int findf(std::vector& f, std::vector& w, int x) { // 引用传递,方便递归更新
if (f[x] != x) { // 递归查找父亲节点
int father = findf(f, w, f[x]);
w[x] = w[x] * w[f[x]]; // 更新权重
f[x] = father; // 更新父亲节点
}
return f[x];
}
void merge(std::vector& f, std::vector& w, int x, int y, double val) {
int fx = findf(f, w, x); // 查找父亲节点
int fy = findf(f, w, y); // 查找父亲节点
f[fx] = fy; // 对于x节点的父亲节点,其父亲节点设置为y的父亲节点
w[fx] = val * w[y] / w[x]; // 同时更新权重, x / y = val, 而 y/f[y] = w[y], x / f[x] = w[x] 则 f[x] / f[y] = val * w[y] / w[x]
} // x / f[y] = val*w[y], x = f[x]*w[x] -> f[x]*w[x] / f[y] = val * w[y] -> f[x] / f[y] = val * w[y] / w[x]
std::vector calcEquation(std::vector>& equations, std::vector& values, std::vector>& queries) {
// 为每个字符节点记录其对应的id
int nvars = 0;
std::unordered_map variables;
int n = equations.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (variables.find(equations[i][0]) == variables.end()) {
variables[equations[i][0]] = nvars++;
}
if (variables.find(equations[i][1]) == variables.end()) {
variables[equations[i][1]] = nvars++;
}
}
std::vector f(nvars);
std::vector w(nvars, 1.0);
for (int i = 0; i < nvars; i++){ // 初始化字符节点的父亲节点
f[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int va = variables[equations[i][0]], vb = variables[equations[i][1]];
merge(f, w, va, vb, values[i]); // 合并
}
std::vector ret;
for (const auto& q: queries) { // 遍历queries
double result = -1.0;
if (variables.find(q[0]) != variables.end() && variables.find(q[1]) != variables.end()) { // 同时存在
int ia = variables[q[0]], ib = variables[q[1]]; // 取出对应的id
int fa = findf(f, w, ia), fb = findf(f, w, ib); // 计算对应的父亲
if (fa == fb) { // 具有相同的父亲,表明联通
result = w[ia] / w[ib];
}
}
ret.push_back(result);
}
return ret;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
// equations = [["a","b"],["b","c"]], values = [2.0,3.0], queries = [["a","c"],["b","a"],["a","e"],["a","a"],["x","x"]]
std::vector> equations = {{"a", "b"}, {"b", "c"}};
std::vector values = {2.0, 3.0};
std::vector> queries = {{"a", "c"}, {"b", "a"}, {"a", "e"}, {"a", "a"}, {"x", "x"}};
Solution S1;
std::vector res = S1.calcEquation(equations, values, queries);
for(double num : res) std::cout << num << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
} 6--根据身高重建队列(406)
主要思路:
对数组按身高从大到小排序,身高相同按k从小到大排序;
遍历数组,根据k来插入到结果数组中。
#include
#include
#include
class Solution {
public:
std::vector> reconstructQueue(std::vector>& people) {
std::sort(people.begin(), people.end(), [](std::vector a, std::vector b){
if(a[0] == b[0]) return a[1] < b[1];
return a[0] > b[0];
});
std::vector> res;
for(int i = 0; i < people.size(); i++){
int pos = people[i][1];
res.insert(res.begin() + pos, people[i]);
}
return res;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
// people = [[7,0],[4,4],[7,1],[5,0],[6,1],[5,2]]
std::vector> test = {{7, 0}, {4, 4}, {7, 1}, {5, 0}, {6, 1}, {5, 2}};
Solution S1;
std::vector> res = S1.reconstructQueue(test);
for(auto vec : res){
for(int num : vec) std::cout << num << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
}
return 0;
} 7--分割等和子集(416)
主要思路:
转化成0 - 1背包问题,一半的子集和vec作为背包容量,另一半的子集和作为物品,只需判断最后 dp[vec] 是否等于 vec 即可;
这道题使用 0-1 背包问题的 1 维解法时,需要先正序遍历物品,再倒序遍历背包,防止物品被多次选择(回看背包问题的笔记)。
#include
#include
#include
class Solution {
public:
bool canPartition(std::vector& nums) {
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){
sum += nums[i];
}
if(sum % 2 != 0) return false;
// 转化为背包问题
int vec = int(sum / 2); // 背包容量
std::vector dp(vec+1, 0); // dp[i] 背包容量为i时装的物品价值
dp[0] = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < nums.size(); j++){ // 遍历物品
for(int i = vec; i >= 0; i--){ // 遍历背包
if(i >= nums[j]){
dp[i] = std::max(dp[i - nums[j]] + nums[j], dp[i]);
}
}
}
if(dp[vec] == vec) return true;
else return false;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
// nums = [1, 5, 11, 5]
std::vector test = {1, 5, 11, 5};
Solution S1;
bool res = S1.canPartition(test);
if(res) std::cout << "true" << std::endl;
else std::cout << "false" << std::endl;
return 0;
} 8--路径总和III(437)
主要思路:
经典二叉树深搜,本题需要向下传递每一个节点的加和值(因为每一个节点都可以作为起始节点)。
#include
#include
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
int pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
int res = 0, num = 0; // 结果
dfs(root, targetSum, {}, res);
return res;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int targetSum, std::vector sum, int& res){
if(root == nullptr) return;
for(long long& num : sum) {
if(num + root->val == targetSum){ // 上面的节点作为起始节点,以当前节点作为终点,匹配成功
res++; // 结果+1
}
num += root->val; // 更新路径和:加上当前节点
}
if(root->val == targetSum) res++; // 判断单个当前节点是否匹配
sum.push_back(root->val); // 更新路径和(当前节点可以作为新的起始节点)
dfs(root->left, targetSum, sum, res); // 深搜
dfs(root->right, targetSum, sum, res);
return;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
// root = [10, 5, -3, 3, 2, null, 11, 3, -2, null, 1], targetSum = 8
TreeNode *Node1 = new TreeNode(10);
TreeNode *Node2 = new TreeNode(5);
TreeNode *Node3 = new TreeNode(-3);
TreeNode *Node4 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode *Node5 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode *Node6 = new TreeNode(11);
TreeNode *Node7 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode *Node8 = new TreeNode(-2);
TreeNode *Node9 = new TreeNode(1);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node3;
Node2->left = Node4;
Node2->right = Node5;
Node3->right = Node6;
Node4->left = Node7;
Node4->right = Node8;
Node5->right = Node9;
int targetSum = 8;
Solution S1;
int res = S1.pathSum(Node1, targetSum);
std::cout << res << std::endl;
return 0;
} 9--找到字符串中所有字母异位词(438)
主要思路:
基于滑动窗口,判断s串滑动窗口的元素是否与p串匹配;
#include
#include
class Solution {
public:
bool check(std::vector cnts, std::vector cntp){
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++){
if(cnts[i] != cntp[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
std::vector findAnagrams(std::string s, std::string p) {
// 基于滑动窗口
// 先统计p串各字符出现的次数
std::vector cntp(26);
for(int i = 0; i < p.length(); i++){
cntp[p[i] - 'a']++;
}
// 初始化s串第一个滑动窗口各字符出现的次数
std::vector cnts(26);
for(int i = 0; i < std::min(p.length(), s.length()); i++){ // s串可能会小于p串
cnts[s[i] - 'a']++;
}
std::vector res;
if(check(cnts, cntp)) res.push_back(0); // 判断第一个窗口是否合法
for(int r = p.length(); r < s.length(); r++){ // 枚举右边界
int l = r - p.length() + 1; // 当前窗口左边界
cnts[s[l-1] - 'a']--; // 移除上一个窗口左边界元素
cnts[s[r] - 'a']++; // 移入右边界元素
if(check(cnts, cntp)) res.push_back(l); // 匹配,记录当前窗口的左边界索引
}
return res;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
// s = "cbaebabacd", p = "abc"
std::string s = "cbaebabacd";
std::string p = "abc";
Solution S1;
std::vector res = S1.findAnagrams(s, p);
for(int num : res) std::cout << num << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
} 10--找到所有数组中消失的数字(448)
主要思路:
原地修改数组,遍历数组,根据数组的值修改对应原数组索引的值,具体对应关系是 1对应坐标0,2对应坐标1;修改数组时,将对应坐标的值加上 nums.size(),最后只需判断哪个坐标的值 <= nums.size(),就可以知道哪些值没有出现过。
#include
#include
class Solution {
public:
std::vector findDisappearedNumbers(std::vector& nums) {
std::vector res;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){
int pos = (nums[i] - 1) % nums.size();
nums[pos] += nums.size();
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){
if (nums[i] <= nums.size()) res.push_back(i+1);
}
return res;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
// nums = [4, 3, 2, 7, 8, 2, 3, 1]
std::vector test = {4, 3, 2, 7, 8, 2, 3, 1};
Solution S1;
std::vector res = S1.findDisappearedNumbers(test);
for(int num : res) std::cout << num << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}