链表练习题1
目录
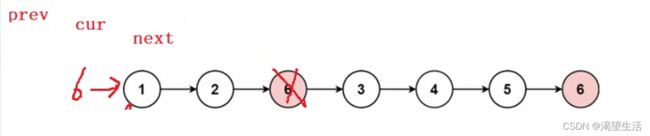
1. 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
扩展:链表有头结点的情况
2. 反转一个单链表。
2.1思路1:直接使用三个指针反转(迭代)
2.2思路2:头插法(迭代)(此处的头不创建新结点)
2.3思路3:递归法
3. 给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。
4. 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
5. 将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
6. 编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前 。
*7. 链表的回文结构。
8. 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点 。
1. 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
struct ListNode*cur = head;
struct ListNode*prev = NULL;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val == val)
{
struct ListNode*next = cur->next;
prev->next = next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur ->next;
}
}
return head;
}出现如下错误
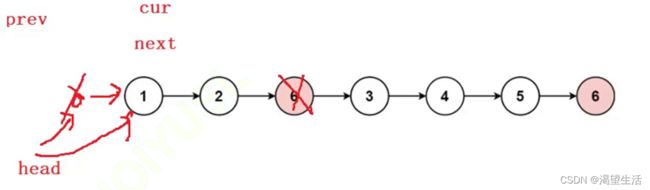
原因在于出现下面情况时prev为空指针。改动如下
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
struct ListNode*cur = head;
struct ListNode*prev = NULL;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val == val)
{
struct ListNode*next = cur->next;
if(prev == NULL)//cur是头
{
free(cur);
head = next;
cur = next;
}
else
{
struct ListNode*next = cur->next;
prev->next = next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur ->next;
}
}
return head;
}扩展:链表有头结点的情况
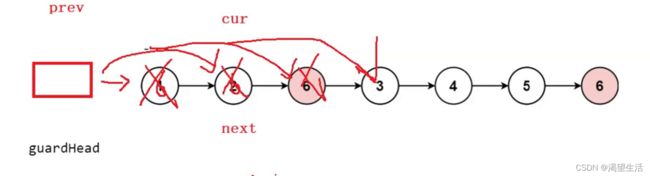
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {
struct ListNode* guardHead = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
guardHead->next = head;
struct ListNode* prev = guardHead;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->val == val)
{
struct ListNode* next = cur->next;
prev->next = next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
//防止内存泄露
head = guardHead->next;
free(guardHead);
return head;
}2. 反转一个单链表。
2.1思路1:直接使用三个指针反转(迭代)
n1指向n2,n2指向n3,然后n3指向n3next。当n2为空的时候结束
代码如下的时候,出现错误:n3可能为空
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
if(head = NULL||head->next == NULL)
{
return head;
}
struct ListNode*n1 = NULL,*n2 = head,*n3 = head->next;
while(n2)
{
//反转
n2->next = n1;
//迭代
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
n3 = n3->next;
}
return n1;
}
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
if(head == NULL||head->next == NULL)
return head;
struct ListNode* n1 = NULL,*n2 = head,*n3 = head->next;
while(n2)
{
//反转
n2->next = n1;
//迭代
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if(n3)
n3 = n3->next;
}
return n1;
}2.2思路2:头插法(迭代)(此处的头不创建新结点)
取原链表中的结点头插到新结点。(next用来保存cur的下一个)
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
struct ListNode*cur = head;
struct ListNode*newhead = NULL;
while(cur)
{
struct ListNode*next = cur->next;//先保存下一个
cur->next = newhead;
newhead = cur;
cur = next;
}
return newhead;
}若链表为空,程序不进入while循坏,返回的newhead也为空。故不考虑为空的情况
若链表只有一个结点,直接头插一个结点
2.3思路3:递归法
3. 给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。
要求:只能遍历一遍链表->快慢指针法
慢指针一次走一步,快指针一次走两步,当快指针移动到最后一个结点的位置时候慢指针的位置即为链表中间位置
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){
struct ListNode*fast = head, *slow = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}4. 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
如果fast走K步,则判断结束的标志为fast等于空
如果fast走K-1步,则判断结束的标志为fast等于尾
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail( struct ListNode* pListHead,int k) {
struct ListNode*fast = pListHead,*slow = pListHead;
while(k--)//注意是k--
//k--走k次,--k走k次
{
fast = fast->next;
}
while(fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead,int k) {
struct ListNode*fast = pListHead,*slow = pListHead;
while(k--)//注意是k--
//k--走k次,--k走k次
{
fast = fast->next;
//说明k比链表长度要长,那么倒数第k个就是空
if(fast == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
}
while(fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}5. 将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
取小的结点,尾插法
其中一个链表结束则标志结束,然后拷贝剩余的链表部分即可
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2){
if(list1 == NULL)
return list2;
if(list2 == NULL)
return list1;
struct ListNode*head = NULL,*tail = NULL;
//先取一个小的去做第一个结点,方便后面尾插
if(list1->valval)
{
head = tail = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
}
else
{
head = tail = list2;
list2 = list2 ->next;
}
while(list1&&list2)
{
//取小的尾插的新链表
if(list1->val < list2->val)
{
tail ->next = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
}
else
{
tail->next = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
//tail还要指向新的尾
tail = tail->next;
}
if(list1)
{
tail->next = list1;//不为空则连接到tail的后面
}
if(list2)
{
tail->next = list2;
}
return head;//返回新的头
} 采用带哨兵位指针的链表
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2){
struct ListNode*head = NULL,*tail = NULL;
//创建一个哨位位的头结点
head = tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
tail->next = NULL;
while(list1&&list2)
{
//取小的尾插的新链表
if(list1->val < list2->val)
{
tail ->next = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
}
else
{
tail->next = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
//tail还要指向新的尾
tail = tail->next;
}
if(list1)
{
tail->next = list1;//不为空则连接到tail的后面
}
if(list2)
{
tail->next = list2;
}
struct LsitNode*node = head;
head = head->next;
free(node);
return head;//返回新的头
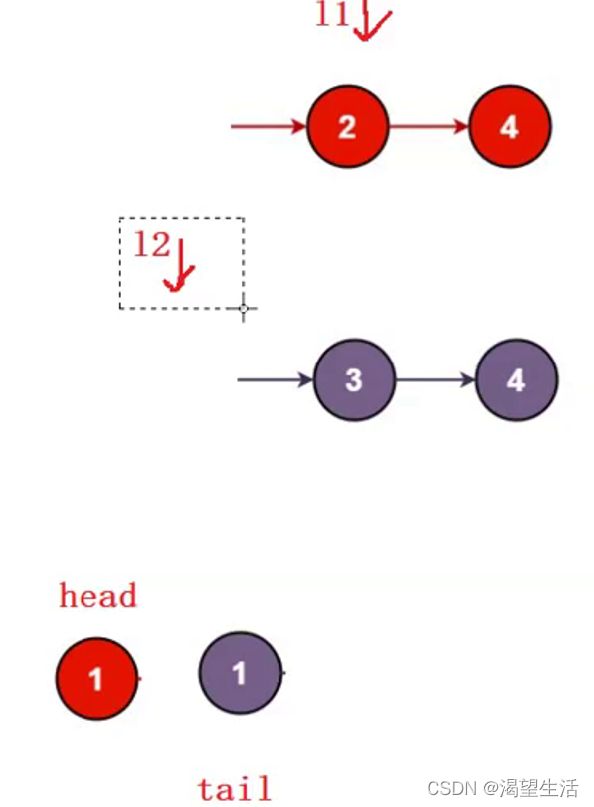
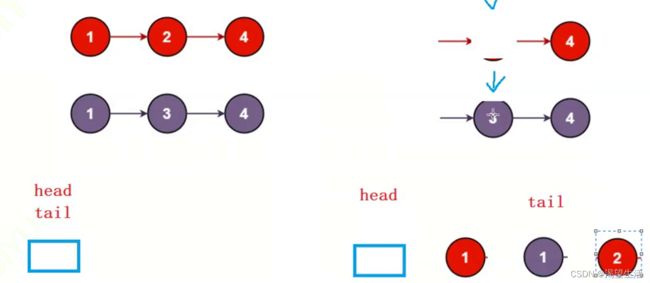
}6. 编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前 。
现有一链表的头指针 ListNode* pHead,给一定值x,编写一段代码将所有小于x的结点排在其余结点之前,且不能改变原来的数据顺序,返回重新排列后的链表的头指针。
思路:把小于x的尾插到一个链表,把大于x的尾插到一个链表,把两个链表链接在一起
class Partition {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {
// write code here
ListNode* lessHead,*lessTail,*greaterHead,*greaterTail;
lessHead = lessTail =(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
greaterHead = greaterTail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
lessTail->next = NULL;
greaterTail->next = NULL;
struct ListNode*cur =pHead;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val next = cur;
lessTail = lessTail->next;
}
else
{
greaterTail->next = cur;
greaterTail = lessTail->next;
}
cur = cur -> next;
}
//链接两个链表
lessTail->next = greaterTail->next;
pHead = lessHead->next;
free(lessHead);
free(greaterHead);
return pHead;
}
}; 代码如上,出现问题:
*7. 链表的回文结构。
思路1:开一个int a[900],链表的数据放到数组,用数组判断->不符合空间复杂度
思路2:先找到中间结点(用快慢指针),后半部分逆置,再比较
class PalindromeList {
public:
struct ListNode*middleNode(struct ListNode*head){
struct ListNode*fast = head,*slow = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
struct ListNode*reverseList(struct ListNode*head){
struct ListNode*cur = head;
struct ListNode*newHead = NULL;
while(cur)
{
struct ListNode*next = cur->next;
cur->next = newHead;
newHead = cur;
cur = next;
}
return newHead;
}
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {
// write code
//先找中间结点
struct ListNode*mid = middleNode(A);
struct ListNode*rHead = reverseList(mid);
while(A && rHead)
{
if(A->val != rHead->val)
return false;
else
{
A = A ->next;
rHead = rHead->next;
}
}
return true;
}
};8. 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点 。
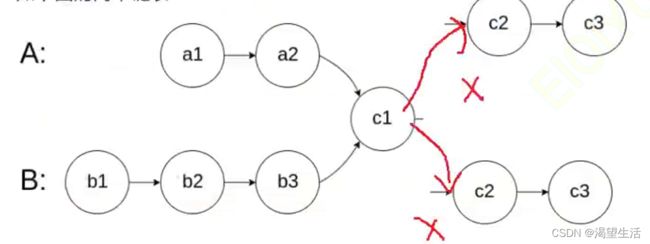
单链表中一个结点不存在两个指针
1.判断两个链表是否相交?->判断尾指针是否相同,注意比较结点的指针,不要比较结点的值
2.若相交,求交点?
思路:计算出两个链表的长度,然后让长的链表先走差距步,再同时走,第一个相同的结点就是交点
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
if(headA == NULL || headB == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode*curA = headA,*curB = headB;
int lenA = 0,lenB = 0;
while(curA->next)
{
curA = curA->next;
lenA++;
}
while(curB->next)
{
curB = curB->next;
lenB++;
}
//不相交
if(curA != curB)
return NULL;
//长的先走差距步,再同时走
struct ListNode*longList = headA,*shortList = headB;
if(lenB>lenA)
{
longList = headB;
shortList = headA;
}
int gap = abs(lenB - lenA);//二者之间的差距
while(gap--)
{
longList = longList->next;
}
while(longList != shortList)
{
longList = longList->next;
shortList = shortList->next;
}
return longList;
}