【Python报错合集】Python元组tuple、张量tensor(IndexError、TypeError、RuntimeError……)~持续更新
文章目录
- IndexError
-
- 1. tuple index out of range
-
- a. 示例代码
- b.报错原因
- c.解决方案
- TypeError
-
- 1. len() of a 0-d tensor
-
- a. 示例代码
- b.报错原因
- c.解决方案
- RuntimeError
-
- 1. output with shape … doesn't match the broadcast shape …
-
- a. 示例代码
- b.报错原因
- c.解决方案
- 2. Can't call numpy() on Tensor that requires grad. Use tensor.detach().numpy() instead.
-
- a. 示例代码
- b.报错原因
- c.解决方案
- 3. The size of tensor a (3) must match the size of tensor b (4) at non-singleton dimension 0
-
- a.报错原因
- b.解决方案
- c. 示例代码
- 4. Only Tensors of floating point and complex dtype can require gradients
-
- a. 示例代码
- b.报错原因
- c.解决方案
IndexError
1. tuple index out of range
a. 示例代码
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3)
# 尝试访问索引超出范围的元组
value = my_tuple[3] # 这里会抛出 "IndexError: tuple index out of range" 错误
b.报错原因
IndexError: tuple index out of range
在尝试访问元组中的索引超出了范围,即你尝试访问的索引超过了元组的长度。
c.解决方案
要解决这个问题,你需要检查你的代码,确认在访问元组时使用的索引是否正确,并确保索引值在元组的有效范围内。
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3)
# 尝试访问索引超出范围的元组
# value = my_tuple[3] # 这里会抛出 "IndexError: tuple index out of range" 错误
# 确保索引值在元组的有效范围内
value = my_tuple[2] # 现在可以成功访问索引为2的元素
# 输出结果
print(value)
TypeError
1. len() of a 0-d tensor
a. 示例代码
import torch
tensor = torch.tensor(5) # 创建一个0维张量
print(len(tensor))
b.报错原因
TypeError: len() of a 0-d tensor
这个错误提示表明你正在尝试对一个零维张量执行len()操作,但是len()函数无法应用于零维张量。在Python中,len()函数用于获取对象的长度或大小。然而,对于零维张量,它没有定义长度的概念,因此无法使用len()函数。
c.解决方案
要解决这个问题,你需要检查代码中对零维张量使用len()函数的部分,并确保该操作适用于张量的形状。如果你需要获取零维张量的值,可以使用其他适当的方法,例如item()函数。
import torch
tensor = torch.tensor(5) # 创建一个0维张量
value = tensor.item() # 获取0维张量的值
print(value) # 输出:5
RuntimeError
1. output with shape … doesn’t match the broadcast shape …
a. 示例代码
RuntimeError: output with shape [1, 64, 64] doesn't match the broadcast shape [3, 64, 64]
b.报错原因
这个错误提示表明在进行广播操作时,形状不匹配。它指出你正在尝试将形状为[1, 64, 64]的输出广播到形状为[3, 64, 64]的目标形状,但两者的形状不匹配。
广播是一种在不同形状的数组之间进行运算的机制,它能够自动地扩展数组的维度以匹配操作所需的形状。然而,为了进行广播,数组的形状必须满足一定的条件,例如在每个维度上的长度要么相等,要么其中一个数组的长度为1。
c.解决方案
要解决这个错误,你需要确保输出数组和目标数组在进行广播操作时具有兼容的形状。可能的解决方案包括:
- 检查代码中广播操作的部分,确保输入和输出数组的形状符合广播规则。
- 在进行广播之前,使用适当的方法来改变输出数组的形状,使其与目标数组的形状匹配。你可以使用NumPy库的reshape()函数或其他相关函数来实现这一点。
- 检查输入数据的维度和形状,确保其与期望的形状一致。有时候,错误可能是由于输入数据的形状不正确引起的。
2. Can’t call numpy() on Tensor that requires grad. Use tensor.detach().numpy() instead.
a. 示例代码
import torch
# 假设你有一个需要梯度计算的张量
tensor = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3], dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
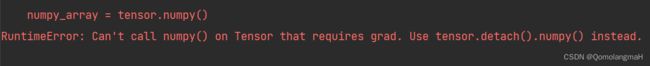
numpy_array = tensor.numpy()
b.报错原因
RuntimeError: Can't call numpy() on Tensor that requires grad. Use tensor.detach().numpy() instead.
这个错误提示表明你正在尝试在需要梯度计算的张量上直接调用numpy()函数,但是这是不允许的。在PyTorch中,如果一个张量需要梯度计算,就不能直接使用numpy()函数转换为NumPy数组。
c.解决方案
要解决这个问题,你可以使用tensor.detach().numpy()函数来获取不需要梯度计算的张量的NumPy数组表示。detach()函数用于创建一个新的张量,它与原始张量共享相同的数据,但不会进行梯度计算。然后,你可以在detach()函数之后使用numpy()函数将其转换为NumPy数组。
import torch
# 假设你有一个需要梯度计算的张量
tensor = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3], dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
# 使用detach().numpy()获取不需要梯度计算的NumPy数组
numpy_array = tensor.numpy()
# numpy_array = tensor.detach().numpy()
# 输出NumPy数组
print(numpy_array)
3. The size of tensor a (3) must match the size of tensor b (4) at non-singleton dimension 0
a.报错原因
RuntimeError: The size of tensor a (3) must match the size of tensor b (4) at non-singleton dimension 0
这个错误提示表明你在执行某个操作时遇到了张量大小不匹配的问题。具体来说,张量a的大小为3,张量b的大小为4,在非单例维度0上大小不匹配。
b.解决方案
要解决这个问题,你需要检查你的代码,找出导致张量大小不匹配的原因,并确保两个张量在执行操作时具有相同的形状或大小。
可能的原因包括:
- 你正在尝试对两个张量进行相加或相乘等操作,但它们的形状不兼容。在这种情况下,你需要调整其中一个张量的形状,使其与另一个张量具有相同的形状。
- 你可能在使用某个函数或操作时,错误地传递了不匹配大小的张量作为输入。你可以检查函数或操作的文档,确保传递的张量具有正确的形状和大小。
c. 示例代码
import torch
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])
b = torch.tensor([4, 5, 6, 7])
# 尝试对两个大小不匹配的张量进行相加
c = a + b # 这里会抛出 "The size of tensor a (3) must match the size of tensor b (4) at non-singleton dimension 0" 错误
# 需要调整张量的形状使其匹配
b_resized = b[:3] # 调整张量b的形状与张量a相匹配
c = a + b_resized # 现在可以成功执行相加操作
# 输出结果
print(c)
在这个示例中,我们通过使用切片操作将张量b的大小从4调整为3,使其与张量a的大小匹配,然后可以成功执行相加操作。
4. Only Tensors of floating point and complex dtype can require gradients
a. 示例代码
import torch
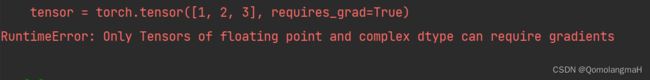
tensor = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3], requires_grad=True)
b.报错原因
RuntimeError: Only Tensors of floating point and complex dtype can require gradients
这个错误提示表明只有浮点数和复数类型的张量才能要求梯度。在你的代码中,你创建了一个整数类型的张量torch.tensor([1, 2, 3], requires_grad=True)并尝试要求梯度,这是不支持的操作。
c.解决方案
要解决这个问题,你可以将张量的数据类型更改为浮点数类型,以便能够要求梯度。你可以使用torch.float将整数张量转换为浮点数张量,然后再要求梯度。
import torch
tensor = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3], requires_grad=True)
# tensor = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3], dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
# 输出张量和梯度要求
print(tensor)
print(tensor.requires_grad)