springboot启动流程,手把手打断点一步步看运行步骤
目录
一、让我们从启动类打断点一点点剖析启动过程
二、创建 SpringApplication
1.new SpringApplication
2.初始化参数
(1)获取bootstrappers:初始启动引导器
(2)获取ApplicationContextInitializer初始化器
(3)获取ApplicationListener 应用监听器
三、运行 SpringApplication
1.进入run方法
(1)创建引导上下文(Context环境)
(2)bootstrapper其实是个接口
(3)获取所有 RunListener(运行监听器)
(4)准备运行时环境
(5)创建IOC容器
(6)准备ApplicationContext IOC容器的基本信息
(7)IOC容器的经典初始化过程
(8)调用所有runners
一、让我们从启动类打断点一点点剖析启动过程
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(WebApplicationCxf.class, args);
}二、创建 SpringApplication
1.new SpringApplication
// org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}2.初始化参数
// org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#SpringApplication(org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader, java.lang.Class...)
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;// 资源加载器
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");// 断言,判断是否有主配置类
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));// 主配置类信息保存起来(标注@SpringBootApplication的)
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();// 判断web应用的类型(判断是响应式还是原生的servlet工程)
// bootstrappers:初始启动引导器(List):去spring.factories文件中找 org.springframework.boot.Bootstrapper
this.bootstrappers = new ArrayList<>(getSpringFactoriesInstances(Bootstrapper.class));
// 找 ApplicationContextInitializer初始化器;去spring.factories找 ApplicationContextInitializer
// 存放在List> initializers中,总共7个
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 找 ApplicationListener ;应用监听器。去spring.factories找 ApplicationListener
// 存放在List> listeners中,总共9个
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
// 决定谁是主程序,有main方法的类就是主程序
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
} (1)获取bootstrappers:初始启动引导器
// org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#getSpringFactoriesInstances(java.lang.Class, java.lang.Class[], java.lang.Object...)
private Collection getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class type, Class[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
// 去spring.factories文件中找 org.springframework.boot.Bootstrapper
Set names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
List instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
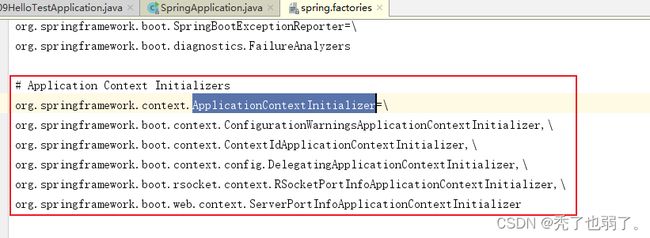
} (2)获取ApplicationContextInitializer初始化器
都是从spring.factories文件中查找 ApplicationContextInitializer,可能不仅局限于一个spring.factories文件
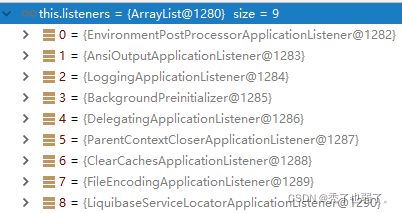
(3)获取ApplicationListener 应用监听器
都是从spring.factories文件中查找ApplicationListener ,可能不仅局限于一个spring.factories文件
三、运行 SpringApplication
1.进入run方法
// org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}// org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#run(java.lang.String...)
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 应用停止监听器
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start(); // 记录应用的启动时间
// 创建引导上下文(Context环境)createBootstrapContext()
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
// 设置headless属性方法(java.awt.headless),让当前应用进入headless模式(自力更生模式,详情自行百度)
configureHeadlessProperty();
//获取所有 RunListener(运行监听器)【为了方便所有Listener进行事件感知】
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// 遍历 SpringApplicationRunListener 调用 starting 方法,相当于通知所有对系统正在启动过程感兴趣的人,项目正在 starting。
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
// 保存命令行参数;ApplicationArguments
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 准备运行时环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 打印banner
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 创建IOC容器
// 根据项目类型(Servlet)创建容器,当前会创建 AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
// 准备ApplicationContext IOC容器的基本信息
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 刷新IOC容器,调用IOC容器的经典初始化过程,创建容器中的所有组件
refreshContext(context);
// 容器刷新完成后工作,方法是空的
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
// 监控花费的时间
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
// 所有监听器 调用 listeners.started(context); 通知所有的监听器 started
listeners.started(context);
// 调用所有runners
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
// 如果有异常,调用Listener 的 failed方法
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
// 调用所有监听器的 running 方法 listeners.running(context); 通知所有的监听器 running
listeners.running(context);
}
// running如果有问题。继续通知 failed 。调用所有 Listener 的 failed;通知所有的监听器 failed
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}(1)创建引导上下文(Context环境)
private DefaultBootstrapContext createBootstrapContext() {
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = new DefaultBootstrapContext(); // 创建默认的引导上下文
// 获取到所有之前的 bootstrappers 挨个执行 intitialize() 来完成对引导启动器上下文环境设置
this.bootstrappers.forEach((initializer) -> initializer.intitialize(bootstrapContext));
return bootstrapContext;
}(2)bootstrapper其实是个接口
public interface Bootstrapper {
/**
* Initialize the given {@link BootstrapRegistry} with any required registrations.
* @param registry the registry to initialize
*/
void intitialize(BootstrapRegistry registry);
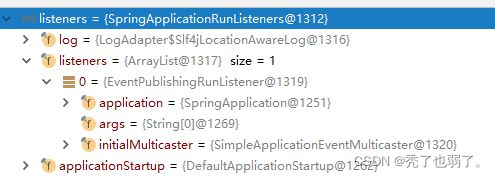
}(3)获取所有 RunListener(运行监听器)
还是去从spring.factories文件中查找SpringApplicationRunListener。
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
Class[] types = new Class[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger,
getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args),
this.applicationStartup);
}找到一个listener:
Listener实际是个接口,有如下方法:
(4)准备运行时环境
// org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#prepareEnvironment
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
// 返回或者创建基础环境信息对象。StandardServletEnvironment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 配置环境信息,通过命令行参数或者配置文件获取配置属性值
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// 绑定环境信息
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 所有监听器遍历调用 listener.environmentPrepared();通知所有的监听器当前环境准备完成
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);
// 激活额外的环境
configureAdditionalProfiles(environment);
// 绑定一些值
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}(5)创建IOC容器
// org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#createApplicationContext
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
// 根据项目类型(Servlet)创建容器,当前会创建 AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
return this.applicationContextFactory.create(this.webApplicationType);
}(6)准备ApplicationContext IOC容器的基本信息
// org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#prepareContext
private void prepareContext(DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
// 保存基础环境信息
context.setEnvironment(environment);
// IOC容器的后置处理流程(注册一些组件、读取配置文件资源、注册资源加载器、准备类型转换器等等)
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
// 应用初始化器:applyInitializers
// 遍历所有的 ApplicationContextInitializer 。调用 initialize方法。来对ioc容器进行初始化扩展功能
applyInitializers(context);
// 遍历所有的 listener 调用 contextPrepared方法。
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
bootstrapContext.close(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
// Load the sources
Set(7)IOC容器的经典初始化过程
spring容器创建流程参考博文
spring系列-注解驱动原理及源码-spring容器创建流程-CSDN博客
注意:
spring默认的onRefresh()方法是空的,springboot将onRefresh()方法重写,加入了tomcat的启动。
// org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext#onRefresh
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
// 创建一个web应用
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}springboot嵌入式tomcat启动原理参考博文:
https://blog.csdn.net/A_art_xiang/article/details/122435665
(8)调用所有runners
默认是没有runner。
// org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#callRunners
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
Listrunner是一个接口:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationRunner {
/**
* Callback used to run the bean.
* @param args incoming application arguments
* @throws Exception on error
*/
void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception;
}