mybatis缓存源码解析
为什么使用缓存
- 减少和数据库交互次数,提高执行效率
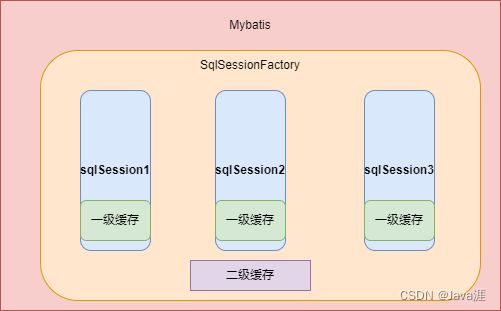
mybatis的缓存
mybatis一级缓存,也就是局部的sqlSession级别的缓存,默认是开启的- 每一个
session会话都会有各自的缓存,这缓存是局部的,也就是所谓的一级缓存 mybatis二级缓存,是sqlSessionFactory级别的缓存,不同的sqlSession可以获取到同样SQL的缓存结果,在mybatis3中也是默认开启的,但是需要配置指定的接口或方法进行缓存
关闭一级缓存
xml配置:
<settings>
<setting name="localCacheScope" value="STATEMENT"/>
settings>
yml配置:
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
local-cache-scope: STATEMENT
@Test
@Transactional
public void test_cache_one() {
userService.getUserCacheOne(1);
userService.getUserCacheOne(1);
userService.getUserCacheOne(1);
}
开启一级缓存(默认就是session)
xml配置:
<settings>
<setting name="localCacheScope" value="session"/>
settings>
yml配置:
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
local-cache-scope: session
@Test
@Transactional
public void test_cache_one() {
userService.getUserCacheOne(1);
userService.getUserCacheOne(1);
userService.getUserCacheOne(1);
}
- 从以上截图中可明显看到,默认开启一级缓存,
myabits只跟数据库交互了一次
源码分析均在myabtis整合spring中
1. 创建SqlSessionTemplate对象
com.baomidou.mybatisplus.autoconfigure.MybatisPlusAutoConfiguration
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
ExecutorType executorType = this.properties.getExecutorType();
if (executorType != null) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory, executorType);
} else {
// 创建sqlSession
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory)创建sqlSession代理对象- 默认使用
protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
2. 创建sqlSessionProxy代理对象
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sqlSessionFactory, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' is required");
notNull(executorType, "Property 'executorType' is required");
this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
this.executorType = executorType;
this.exceptionTranslator = exceptionTranslator;
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession)
// 创建sqlsession的动态代理,代理对象是SqlSessionInterceptor方法
newProxyInstance(SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { SqlSession.class }, new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// getSqlSession是个关键方法,决定是重新拿个新sqlSession还是复用
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType, SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
...
getSqlSession()方法是个关键方法,决定是创建一个新的sqlSession还是复用旧的sqlSession
3. 创建或复用sqlSession对象
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sessionFactory, NO_SQL_SESSION_FACTORY_SPECIFIED);
notNull(executorType, NO_EXECUTOR_TYPE_SPECIFIED);
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
// 判断是否在事务中,如果在事务中,就共同同一个session
SqlSession session = sessionHolder(executorType, holder);
if (session != null) {
return session;
}
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Creating a new SqlSession");
// 如果不是同一个事务中,则创建一个新的sqlsession,打印的日志很明显
session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);
registerSessionHolder(sessionFactory, executorType, exceptionTranslator, session);
return session;
}
- 如果在同一个事务中,则使用旧的
sqlSession对象 - 如果不在同一个事务中,则重新通过
session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);创建新的sqlSession对象 - 如果不在同一个事务下,那么每次查询都会创建一个新的
sqlSession,那就看不到一级缓存的效果了,所以想要看效果,需要开启事务,保证几次查询用的是同一个sqlSession LOGGER.debug(() -> "Creating a new SqlSession");创建新的sqlSession对象这个日志很明显
4. 创建sqlSession()对象
session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
// 配置数据库环境
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
// 配置事务管理器
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
// 选择执行器,默认使用的是simple
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
// 返回使用DefaultSqlSession实现类
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
// 默认使用的就是executorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
-
这里的
cacheEnabled就是二级缓存的开关,myabtis3默认是开启的protected boolean cacheEnabled = true; -
从
newExecutor()方法中不难看出,executor使用SimpleExecutor处理器,然后放入到CachingExecutor,二级缓存被称为SqlSessionFactory级别的缓存,它是可以缓存不同sqlSession会话中相同的sql语句 -
创建
sqlSession对象就此结束,myabtis的初始化也就到这里,接下来就是使用mapper层接口代理对象了
5. 创建MapperFactoryBean对象
MapperFactoryBean是一个Bean对象,继承了FactoryBean,在spring中通过getObject()获取对应接口方法的代理对象
public class MapperFactoryBean<T> extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean<T> {
@Override
public T getObject() throws Exception {
// 这个的getSession方法返回的就是上面产生的那个sqlSession
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
...
}
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
// 创建mapperProxyFactory动态代理,这里的产生的代理对象主要是用来执行sql的
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
- 生成代理对象,代理对象为
MapperProxy
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
// 生成代理对象,代理对象为MapperProxy
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
6. 执行代理方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
// 执行代理方法
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
private static class PlainMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {
private final MapperMethod mapperMethod;
public PlainMethodInvoker(MapperMethod mapperMethod) {
super();
this.mapperMethod = mapperMethod;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
// 这里就是执行sql地方了
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
}
然后随便找个select语句一直往下,找到sqlSession提供的select方法
private <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
7. 二级缓存判断
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
// 判断这个sqlStatement是否开启了二级缓存
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
// 如果发现没有使用到二级缓存,则才会使用simple处理器去执行sql
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
- 判断这个
sql是否开启了二级缓存,这个缓存是可以在不同的sqlSession共享数据的,按照这个顺序应该是先走的二级缓存,然后再走到一级缓存,二级缓存的优先级更高 - 如果有二级缓存,则使用缓存数据,缓存的
key跟一级缓存的key一致 - 如果没有二级缓存,则会使用默认的
simpleExecutor处理器去执行sql语句
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
// 找个key就是一级缓存的key
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
MyBatis 的一级缓存的key是由以下三个部分组成的:
- 执行的
SQL语句(包括语句的类型、命名空间以及具体的SQL语句内容)。 SQL语句中的参数(参数的值)。- 数据库连接的标识(
Connection Id)。
key的生成策略:id + offset + limit + sql + param value + environment id,这些值都相同,生成的key就相同。
这三个部分共同构成了一级缓存的 key,用于唯一标识一个查询操作。只有当这三个部分完全匹配时,才会从缓存中获取相应的结果。如果其中任何一个部分不匹配,就会重新执行 SQL 查询,并将结果存入缓存。
8. 一级缓存
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
// ms.isFlushCacheRequired() 如果不是select语句,则会清空缓存
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
// 清空一级缓存
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
// 根据key去查询缓存
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
// 用于缓存存储过程输出参数的缓存对象
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
// 如果不存在缓存,则去数据库查询
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
deferredLoads.clear();
// 这里就是配置是否启动一级缓存的地方
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// 清空一级缓存
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
ms.isFlushCacheRequired()判断是否为select语句,如果不是则会清理一级缓存的内容clearLocalCache();清空一级缓存localCache.getObject(key)根据组装的key去查询缓存是否存在queryFromDatabase()如果缓存不存在,则去查询数据configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT这里也是配置一级缓存的开关,默认是LocalCacheScope.SESSION开启的,如果设置成LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT则会关闭一级缓存
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
// 添加一级缓存,添加占位符,标记该查询一级在执行中,避免在并发环境下多个线程执行相同的查询语句,导致数据库重复查询
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
// 与数据库交互,组装sql参数
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
// 删除缓存
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
// 添加一级缓存,list就是返回的数据
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
// 用于缓存存储过程输出参数的缓存对象
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}