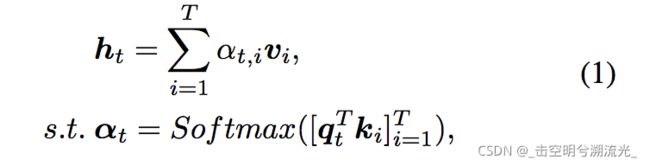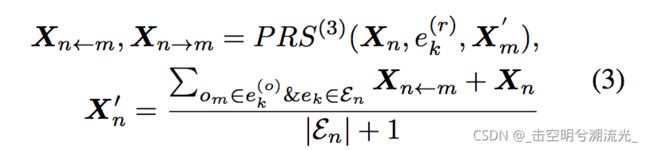论文笔记:CVPR2021 Bottom-Up Shift and Reasoning for Referring Image Segmentation
任务名字:Referring Image Segmentation (RIS)
keywords:one-stage RIS、graph、relation reasoning
背景:方法比较
vision-and-language approaches based on their designing principles,
(1)multimodal fusion and representation learning
(2)language-conditioned visual rea- soning
two-stage RIS:
优:explicit object instances and their relation-ships to conduct visual reasoning
缺:slow inference speed 、has poor generalization、the relational and spatial priors in images are lost when conducting reasoning over feature vectors of those object instances.
one-stage RIS:
优:fast inference speed、contextual representations
缺:no ex-plicit object-level information、inferior in handling complex visual scenes and expressions because they lack sufficient visual reasoning capability
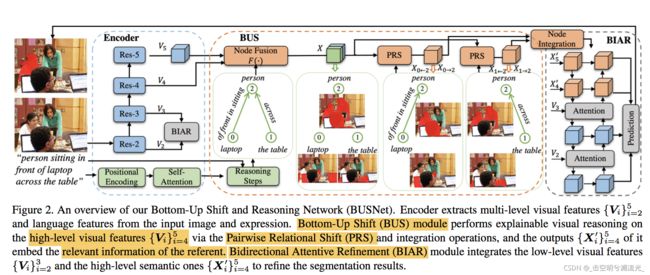
Method:
图像encoder:DeepLab ResNet101
language encoder: GloVe word embedding wt of each word l_t + position encoding
为了进一步增加词间相互关系的表达,引入了自注意力机制
Bottom-Up Shift:
(1)Analysis of Reasoning Steps
利用图表达,将复杂的推理抽象成简单的节点和边
使用language graph(directed acyclic graph):A node and a directed edge of the graph respectively correspond to a noun phrase and the linguistic relationship
(2)Stepwise Inference逐步推理:
the reasoning from bottom to up
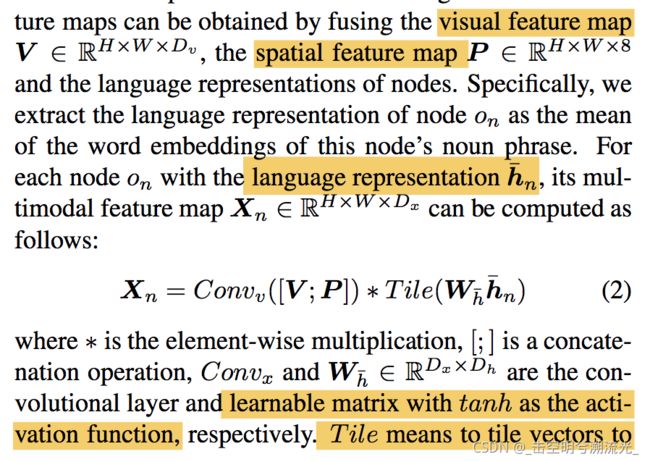
首先节点和图融合得到X
接下来,通过对节点之间的关系(即边)按照遍历的顺序进行逐步推理,将节点在图像中的初始空间位置转移到正确的位置。
同样,我们假设上的节点在当前步骤中作为节点处理。首先通过PRS对图的每条边单独执行关系推理,然后通过平均池操作集成所有连接边中节点o_n结果。
edges的集成,对于具有初始特征映射Xn和连接边En的节点,其更新的特征映射Xn′计算如下:
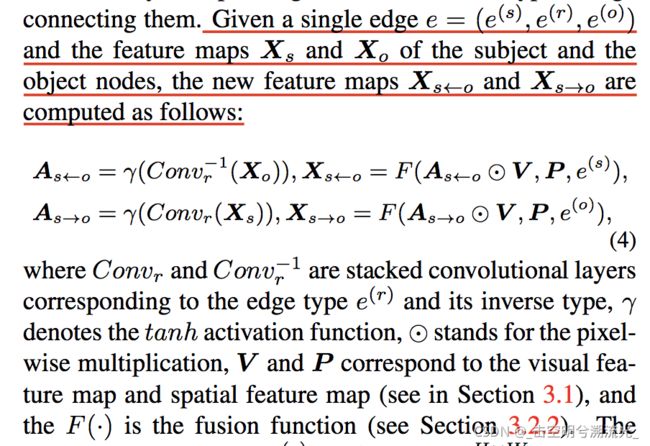
(3)Pairwise Relational Shift
Bidirectional Attentive Refinement:
将上个模块输出的x4、x5,与前文encoder的浅层特征v2、v3、v4通过自上而下的策略合并
因为浅层包含全图的详细信息,可能引起不相关的噪声,因此使用自注意力机制
最后上采样相加