一篇超详细的pytorch基础语法讲解及理论推导(一)
张量 - 线性回归 - 自动求导 - 逻辑回归
来源:投稿 来源:阿克西
编辑:学姐
1 pytorch简介
PyTorch是2017年1月FAIR(Facebook AI Research)发布的一款深度学习框架。从名称可以看出,PyTorch是由Py和Torch构成的。其中,Torch是纽约大学在2012年发布的一款机器学习框架,采用Lua语言为接口,但因Lua语言较为小众,导致Torch知名度不高。PyTorch是在Torch基础上用 python语言进行封装和重构打造而成的。
1.1 pytorch优点及适合人群
pytorch优点:
● 上手快:掌握Numpy和基本深度学习概念即可上手
● 代码简洁灵活:用nn.module封装使网络搭建更方便;基于动态图机制,更灵活
● Debug方便:调试pytorch就像调试python代码一样简单
● 文档规范:https://pytorch.org/docs/可查各版本文档
● 资源多:arXiv中的新算法大多有PyTorch实现
● 开发者多:GitHub上贡献者(Contributors)已超过1350+
● 背靠大树:FaceBook维护开发
● 。。。
pytorch适合人群:
● 深度学习初学者:模型算法实现容易,加深深度学习概念认识
● 机器学习爱好者:数十行代码便可实现人脸识别,目标检测,图像生成等有趣实验
● 算法研究员:最新arXiⅳv论文算法快速复现
1.2 pytorch发展
PyTorch发展:
● 2017年1月正式发布PyTorch
● 2018年4月更新0.4.0版,支持Windows系统,caffe2正式并入PyTorch
● 2018年11月更新1.0稳定版,已GitHub 增长第二快的开源项目
● 2019年5月更新1.1.0版,支持TensorBoard,增强可视化功能
● 2019年8月更新1.2.0版,更新torchvision,torchaudio 和torchtext,增加更多功能
arXiv是学术界风向标,Github是工业界风向标,可观察GitHub上的Start, Forks,Watchers和Contributors数量。
1.3 pytorch模型训练步骤
pytorch定位:
深度学习框架,实现深度学习模型算法。
● 人工智能:多领域交叉科学技术
● 机器学习:计算机智能决策算法
● 深度学习:高效的机器学习算法
pytorch模型训练步骤:
1.4 pytorch学习路径
学pytorch的困境:
● 学哪些?网上资料一箩筐哪些适合你?
● 代码难理解:代码复杂,难取精华;函数复杂,无人解答;百度搜索,效率低下
● 难形成系统:自学的知识点散乱,无系统性,学了就忘
● 难以坚持,效率低:世上无难事,只要肯放弃
2 张量(Tensor)的概念
张量:即Tensor,是PyTorch的基本数据结构。张量是一个多维数组,它是标量、向量、矩阵的高维拓展。类似于NumPy的ndarray,但还可以在GPU上使用来加速计算。
Tensor与Variable:torch.autograd.Variable,Variable是torch.autograd中的数据类型,主要用于封装Tensor,进行自动求导。PyTorch0.4.0版开始,Variable并入Tensor。
torch.Tensor中的属性:
与数据有关:
● data:被包装的Tensor
● dtype:张量的数据类型,如torch.FloatTensor,torch.cuda.FloatTensor
● shape:张量的形状,如(64, 3, 224, 224)
● device:张量所在设备,GPU/CPU,只有在GPU上才可以使用GPU进行加速运算
与求导有关:
● grad:data的梯度
● grad_fn:创建Tensor的Function,是自动求导的关键
● requires_grad:指示是否需要梯度
● is_leaf:指示是否是叶子结点(张量)
说明:
● GPU tensor表示数据放在GPU上。
● torch.float32用得最多,卷积层的权值,以及图像预处理之后,都默认为float32。torch.Tensor 默认类型torch.FloatTensor的别名。
● 其次是torch.long,图像类别标签通常就是用64位长整型表示。
3 张量的创建
3.1 直接创建
torch.tensor()
torch.tensor(data,
dtype=None,
device=None,
requires_grad=False,
pin_memory=False)
功能:从data创建tensor。
● data:数据,可以是list,numpy
● dtype:数据类型,默认与data的一致
● device:所在设备,cuda/cpu
● requires_grad:是否需要计算梯度,False可节省内存
● pin_memory:是否存于锁页内存,与转换效率有关,通常为False
import torch
import numpy as np
arr = np.ones((3, 3))
print("ndarray的数据类型: ", arr.dtype)
t1 = torch.tensor(arr)
print(t1)
t2 = torch.tensor(arr, device='cuda')
print(t2)
print(t2.dtype)
t3 = torch.Tensor(arr) # 为32位浮点型
print(t3.dtype)
ndarray的数据类型: float64
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float64)
torch.float64
torch.float32
torch.from_numpy()
torch.from_numpy(ndarray)
功能:从numpy创建tensor。
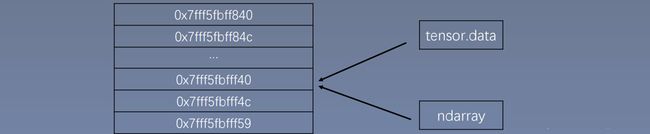
注意事项:从torch.from_numpy创建的tensor与原ndarray共享内存,当修改其中一个的数据,另外一个也将会被改动。
import torch
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
print("原始的arr:\n", arr)
t1 = torch.from_numpy(arr)
print("转变为tensor的t1:\n", t1)
print("t1的类型: ", t1.dtype)
arr[0][2] = 0
print("修改后的arr:\n", arr)
print("修改后的t1:\n", t1)
print(id(arr), id(t1))
注意地址是不同的,是tensor.data与ndarray共享内存,不是tensor。
原始的arr:
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
转变为tensor的t1:
tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
t1的类型: torch.int64
修改后的arr:
[[1 2 0]
[4 5 6]]
修改后的t1:
tensor([[1, 2, 0],
[4, 5, 6]])
140426912546288 140423314894352
3.2 依据数值创建
torch.zeros()与torch.ones()
torch.zeros(size,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:依size创建全0张量。
● size:张量的形状,如(3, 3)、(3, 224,224)
● out:输出的张量,将创建的tensor赋值给out,共享内存
● dtype:数据类型
● layout:内存中布局形式,有 strided(默认),sparse_coo(稀疏张量使用)等
● device:所在设备,cuda/cpu
● requires_grad:是否需要计算梯度
示例:
import torch
import numpy as np
out_t = torch.tensor([1])
print(out_t)
t = torch.zeros((3, 3), out = out_t)
print(t, '\n', out_t)
print(id(t), id(out_t), id(t)==id(out_t))
tensor([1])
tensor([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]])
tensor([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]])
139873122569584 139873122569584 True
torch.zeros_like()与torch.ones_like()
torch.zeros_like(input,
dtype=None,
layout=None,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:依input形状创建全0张量。
● intput:创建与input同形状的全0张量
示例:
t1 = torch.tensor([1, 1, 1])
t2 = torch.zeros_like(t1)
print(t1)
print(t2)
tensor([1, 1, 1])
tensor([0, 0, 0])
torch.ones_like()与torch.ones()功能:创建全1张量,用法与zero相同。
torch.full() 和 torch.full_like()
torch.full(size,
fill_value,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
torch.full_like(input,
fill_value,
dtype=None,
layout=None,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:创建自定义数值的张量,用法与zero相同。
● size:张量的形状,如(3, 3)
● input:依input形状创建指定数据的张量
● fill_value:填充张量的值
示例:
t1 = torch.full((3, 3), 9)
print(t1)
t2 = torch.full_like(t1, 8)
print(t2)
tensor([[9., 9., 9.],
[9., 9., 9.],
[9., 9., 9.]])
tensor([[8., 8., 8.],
[8., 8., 8.],
[8., 8., 8.]])
torch.arange()
torch.arange(start=0,
end,
step=1,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:创建等差的1维张量。
注意事项:数值区间为[start, end) ,end取不到。
● start:数列起始值
● end:数列结束值
● step:数列公差,默认为1
示例:
t = torch.arange(2, 10, 2)
print(t)
tensor([2, 4, 6, 8])
torch.linspace()
torch.linspace(start,
end,
steps=100,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:创建均分的1维张量。
注意事项:数值区间为[start, end],包含end。
● start:数列起始值
● end:数列结束值
● steps:数列长度
示例:
t1 = torch.linspace(2, 10, 5)
t2 = torch.linspace(2, 10, 6)
print(t1)
print(t2)
# 步长计算
print((10-2)/(6-1))
tensor([ 2., 4., 6., 8., 10.])
tensor([ 2.0000, 3.6000, 5.2000, 6.8000, 8.4000, 10.0000])
1.6
torch.logspace()
torch.logspace(start,
end,
steps=100,
base=10.0,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:创建对数均分的1维张量,从到 的等比1维张量。
注意事项:长度为steps,底为base。
● start:数列起始值
● end:数列结束值
● steps:数列长度
● base:对数函数的底,默认为10
示例:
t = torch.logspace(0, 3, 4, 10)
print(t)
tensor([ 1., 10., 100., 1000.])
torch.eye()
torch.eye(n,
m=None,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:创建单位对角矩阵(2维张量)。
注意事项:默认为方阵。
● n:矩阵行数
● m:矩阵列数
t1 = torch.eye(3)
t2 = torch.eye(3, 5)
print(t1)
print(t2)
tensor([[1., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 1.]])
tensor([[1., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0.]])
3.3 依据概率创建
torch.normal()
torch.normal(mean,
std,
out=None)
torch.normal(mean,
std,
size,
out=None)
功能:生成正态分布(高斯分布),从给定参数(均值和标准差)的正态分布(高斯分布)中抽取随机数创建张量。
● mean:均值
● std:标准差
● size:仅在mean和std均为标量时使用,表示创建张量的形状
四种模式:
● mean为标量,std为标量
● mean为标量,std为张量
● mean为张量,std为标量
● mean为张量,std为张量
示例1:mean为标量,std为标量
# 均值为0,标准差为1的一维数组
t1 = torch.normal(0, 1, size=(4,))
print(t1, "\n")
tensor([ 0.0404, -2.2129, -0.5106, 1.3788])
示例2:mean为张量,std为张量
mean = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float)
std = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float)
print("mean: ", mean)
print("std: ", std)
t = torch.normal(mean, std)
print("生成的高斯分布:", t)
1.7841是通过均值为1,标准差为1生成;-0.9183通过均值为2,标准差为2生成....,即对应取mean和std中的值作为均值和标准差构成正态分布,从每个正太分布中随机抽取一个数字。
mean: tensor([1., 2., 3., 4.])
std: tensor([1., 2., 3., 4.])
生成的高斯分布: tensor([ 1.7841, -0.9183, 2.5703, 6.8318])
示例3:mean为张量,std为标量
mean = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float)
print("mean: ", mean)
std = 1
print("std: ", std)
t_normal = torch.normal(mean, std)
print("生成的高斯分布:", t_normal)
2.3503是通过均值为1,标准差为1生成;2.1444通过均值为2,标准差为1生成....,即对应取mean中的值作为均值,所有标准差均为1构成正态分布,从每个正太分布中随机抽取一个数字。
mean: tensor([1., 2., 3., 4.])
std: 1
生成的高斯分布: tensor([2.3503, 2.1444, 1.1052, 6.2726])
torch.randn() 和 torch.randn_like()
torch.randn(size,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
torch.randn_like(input,
dtype=None,
layout=None,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:生成标准正态分布,从标准正态分布(均值为0,标准差为1)中抽取随机数创建张量。
● size:张量的形状
● input:依input形状创建指定数据的张量
torch.rand() 和 torch.rand_like()
torch.rand(size,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
torch.rand_like(input,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:从[0, 1)上的均匀分布中抽取随机数创建张量。
示例:
t = torch.rand((4, ))
print(t)
tensor([0.0038, 0.2467, 0.4185, 0.0038])
torch.randint() 和 torch.randint_like()
torch.randint(low=0,
high,
size,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
torch.randint_like(input,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:区间[low, high)生成整数均匀分布。
示例:
t = torch.randint(2, 8, size=(4, ))
print(t)
tensor([6, 2, 4, 5])
torch.randperm()
torch.randperm(n,
out=None,
dtype=torch.int64,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:生成生成从0到n-1的随机排列,可以用来生成乱序的索引。
● n:张量的长度
torch.bernoulli()
torch.bernoulli(input,
*,
generator=None,
out=None)
功能:从伯努利分布中抽取二元随机数(0或者1),输入中所有值必须在[0, 1]区间,输出张量的第 个元素值,将依输入张量的第 个概率值等于1。
● input:概率值
示例:
t1 = torch.rand((4,))
t = torch.bernoulli(t1)
print(t1)
print(t)
tensor([0.5793, 0.7866, 0.6888, 0.2221])
tensor([0., 1., 0., 0.])
3.4 创建未初始化的张量
torch.empty()
torch.empty(size,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:创建一个未被初始化数值的tensor,tensor的大小由size确定。
示例:
t1 = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])
print(t1)
t2 = torch.empty(size=[2, 3], out=t1)
print(t2)
tensor([1, 2, 3])
tensor([[ 1, 2, 3],
[30962681235898419, 31525592536121462, 32088624093986937]])
说明:t2与t1共享内存地址,由于t2未初始化,所以显示的前3个元素是t1的值,后面的元素是乱码;如果t2初始化了,那么打印t1和t2将显示t2的值。
点击下方卡片《学姐带你玩AI》
关注回复“500”领取300+经典论文合集&讲解视频
码字不易,欢迎大家点赞评论收藏!