2023面试笔记四
1、gc导致的cpu冲高
排查是否为gc导致,看如下两点:
-
gc频率和耗时
-
内存占用率
(1)gc频率和耗时有两种手段看:
第一种:根据gc日志的打印时间,可确定每次gc间隔的时间和耗时:
使用这种方式的前提是配置了gc日志的打印,参考jvm参数如下:
-XX:+PrintGCDetails -XX:+PrintGCDateStamps -XX:+PrintHeapAtGC -Xloggc:../../logs/gc.log
第二种:使用如下命令,可每隔5s打印一次gc情况,从打印结果可以判断gc频率,在通过YGCT/YGC和FGCT/FGC可以计算出每次gc的耗时。
jstat -gc 5000
Jstat是JDK自带的一个轻量级小工具。它位于java的bin目录下,主要利用JVM内建的指令对Java应用程序的资源和性能进行实时的命令行的监控,包括了对Heap size和垃圾回收状况的监控。
命令用法:jstat [-命令选项] [pid] [间隔时间/毫秒] [查询次数]
若gc频率低,且耗时短,则基本可以排除是gc导致的cpu冲高问题。
- S0C:年轻代中 To Survivor 的容量(单位 KB);
- S1C:年轻代中 From Survivor 的容量(单位 KB);
- S0U:年轻代中 To Survivor 目前已使用空间(单位 KB);
- S1U:年轻代中 From Survivor 目前已使用空间(单位 KB);
- EC:年轻代中 Eden 的容量(单位 KB);
- EU:年轻代中 Eden 目前已使用空间(单位 KB);
- OC:老年代的容量(单位 KB);
- OU:老年代目前已使用空间(单位 KB);
- MC:Metaspace 的容量(单位 KB);
- MU:Metaspace 目前已使用空间(单位 KB);
- CCSC:压缩类空间大小
- CCSU:压缩类空间使用大小
- YGC:从应用程序启动到采样时年轻代中 gc 次数;
- YGCT:从应用程序启动到采样时年轻代中 gc 所用时间 (s);
- FGC:从应用程序启动到采样时 old 代(全 gc)gc 次数;
- FGCT:从应用程序启动到采样时 old 代(全 gc)gc 所用时间 (s);
- GCT:从应用程序启动到采样时 gc 用的总时间 (s)
(2)jvm内存占用
使用jmap命令导出dump文件
jmap -dump:format=b,file=/tmp/1/dump.hprof 3618
也可以通过arthas工具,导出dump文件
heapdump /tmp/1/dump.hprof
通过堆栈信息分析占用内存的对象是哪些代码。
2、aqs
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 抽象队列同步器。
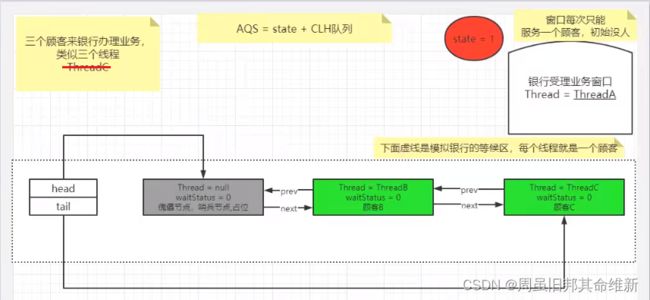
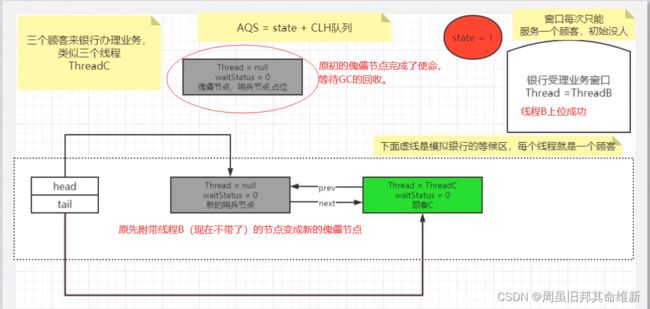
抢到资源的线程直接使用处理业务逻辑,抢不到资源的必然涉及一种排队等候机制。抢占资源失败的线程继续去等待(类似银行业务办理窗口都满了,暂时没有受理窗口的顾客只能去候客区排队等候),但等候线程仍然保留获取锁的可能且获取锁流程仍在继续(候客区的顾客也在等着叫号,轮到了再去受理窗口办理业务)。
既然说到了排队等候机制,那么就一定会有某种队列形成,这样的队列是什么数据结构呢?
如果共享资源被占用,就需要一定的阻塞等待唤醒机制来保证锁分配。这个机制主要用的是CLH队列的变体实现的,将暂时获取不到锁的线程加入到队列中,这个队列就是AQS的抽象表现。它将请求共享资源的线程封装成队列的结点(Node),通过CAS、自旋以及LockSupportpark)的方式,维护state变量的状态,使并发达到同步的控制效果。
总结:state变量+CLH变种的双端队列(FIFO)
2.1、aqs是什么
AQS同步器是Java并发编程的基础,从资源共享的角度分成独占和共享两种模式,像ReentrantLock、ThreadPoolExecutor、CountDownLatch等都是基于AQS来实现的,如图:
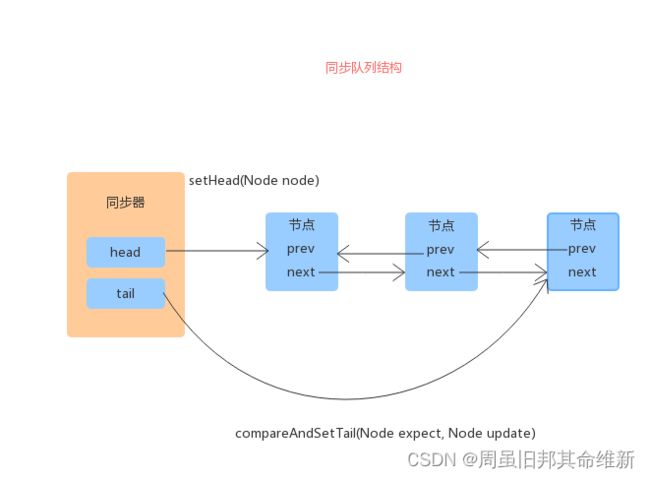
2.2、AQS同步队列的基本结构
AQS维护了一个头节点(head)和一个尾节点(tail)结构的双向链表,当一个线程获取锁失败时,会将该线程打包成一个Node节点,挂到同步队列尾节点
private transient volatile Node head;//同步队列头结点
private transient volatile Node tail;//同步队列尾结点
private volatile int state;//同步状态
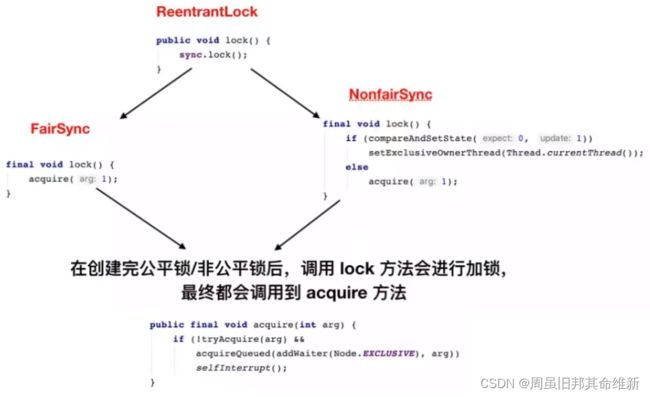
2.3、从ReentrantLock开始
* A reentrant mutual exclusion {@link Lock} with the same basic
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7373984872572414699L;
/** Synchronizer providing all implementation mechanics */
private final Sync sync;
* Base of synchronization control for this lock. Subclassed
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
* Sync object for non-fair locks
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
* Sync object for fair locks
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
* Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock}.
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();
}
* Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock} with the
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}
* Acquires the lock.
public void lock() {
sync.lock();//<------------------------注意,我们从这里入手
}
* Attempts to release this lock.
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
...
}
从最简单的lock方法开始看看公平和非公平,先浏览下AbstractQueuedSynchronizer,FairSync,NonfairSync类的源码。
public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
extends AbstractOwnableSynchronizer
implements java.io.Serializable {
...
* Acquires in exclusive mode, ignoring interrupts. Implemented
public final void acquire(int arg) {//公平锁或非公平锁都会调用这方法
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&//0.
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))//1. 2.
selfInterrupt();//3.
}
//0.
* Attempts to acquire in exclusive mode. This method should query
protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) {//取决于公平锁或非公平锁的实现
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//1.
* Acquires in exclusive uninterruptible mode for thread already in
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
//2.
* Creates and enqueues node for current thread and given mode.
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}
//3.
static void selfInterrupt() {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
//这个方法将会被公平锁的tryAcquire()调用
* Queries whether any threads have been waiting to acquire longer
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
// The correctness of this depends on head being initialized
// before tail and on head.next being accurate if the current
// thread is first in queue.
Node t = tail; // Read fields in reverse initialization order
Node h = head;
Node s;
return h != t &&
((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());
}
...
}
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
...
//非公平锁与公平锁的公共父类
* Base of synchronization control for this lock. Subclassed
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
...
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
...
}
//非公平锁
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;
/**
* Performs lock. Try immediate barge, backing up to normal
* acquire on failure.
*/
final void lock() {//<---ReentrantLock初始化为非公平锁时,ReentrantLock.lock()将会调用这
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);//调用父类AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的acquire()
}
//acquire()将会间接调用该方法
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);//调用父类Sync的nonfairTryAcquire()
}
}
* Sync object for fair locks
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L;
final void lock() {//<---ReentrantLock初始化为非公平锁时,ReentrantLock.lock()将会调用这
acquire(1);调用父类AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的acquire()
}
//acquire()将会间接调用该方法
* Fair version of tryAcquire. Don't grant access unless
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&//<---公平锁与非公平锁的唯一区别,公平锁调用hasQueuedPredecessors(),而非公平锁没有调用
//hasQueuedPredecessors()在父类AbstractQueuedSynchronizer定义
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
...
}
可以明显看出公平锁与非公平锁的lock()方法唯一的区别就在于公平锁在获取同步状态时多了一个限制条件:hasQueuedPredecessors()
hasQueuedPredecessors是公平锁加锁时判断等待队列中是否存在有效节点的方法
hasQueuedPredecessors()中判断了是否需要排队,导致公平锁和非公平锁的差异如下:
公平锁:公平锁讲究先来先到,线程在获取锁时,如果这个锁的等待队列中已经有线程在等待,那么当前线程就会进入等待队列中;
非公平锁:不管是否有等待队列,如果可以获取锁,则立刻占有锁对象。也就是说队列的第一个排队线程在unpark(),之后还是需要竞争锁(存在线程竞争的情况下)
接下来讲述非公平锁的lock()
整个ReentrantLock 的加锁过程,可以分为三个阶段:
- 尝试加锁;
- 加锁失败,线程入队列;
- 线程入队列后,进入阻赛状态。
ReentrantLock默认是选用非公平锁。
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
...
* Acquires the lock.
public void lock() {
sync.lock();//<------------------------注意,我们从这里入手,线程A
}
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
...
//被NonfairSync的tryAcquire()调用
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
...
}
//非公平锁
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;
/**
* Performs lock. Try immediate barge, backing up to normal
* acquire on failure.
*/
final void lock() {//<----线程A的lock.lock()调用该方法
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))//AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的方法,刚开始这方法返回true
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());//设置独占的所有者线程,显然一开始是线程A
else
acquire(1);//稍后紧接着的线程B将会调用该方法。
}
//acquire()将会间接调用该方法
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);//调用父类Sync的nonfairTryAcquire()
}
}
...
}
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
...
* Acquires the lock.
public void lock() {
sync.lock();//<------------------------注意,我们从这里入手,线程B
}
//非公平锁
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;
/**
* Performs lock. Try immediate barge, backing up to normal
* acquire on failure.
*/
final void lock() {//<-------------------------线程B的lock.lock()调用该方法
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))//这是预定线程A还在工作,这里返回false
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());//
else
acquire(1);//线程B将会调用该方法,该方法在AbstractQueuedSynchronizer,
//它会调用本类的tryAcquire()方法
}
//acquire()将会间接调用该方法
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);//调用父类Sync的nonfairTryAcquire()
}
}
//非公平锁与公平锁的公共父类
* Base of synchronization control for this lock. Subclassed
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
//acquire()将会间接调用该方法
...
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();//这里是线程B
int c = getState();//线程A还在工作,c=>1
if (c == 0) {//false
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {//(线程B == 线程A) => false
int nextc = c + acquires;//+1
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;//最终返回false
}
...
}
...
}
public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
extends AbstractOwnableSynchronizer
implements java.io.Serializable {
...
* Acquires in exclusive mode, ignoring interrupts. Implemented
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&//线程B调用非公平锁的tryAcquire(), 最终返回false,加上!,也就是true,也就是还要执行下面两行语句
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))//下一节论述
selfInterrupt();
}
...
}
public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
extends AbstractOwnableSynchronizer
implements java.io.Serializable {
...
* Acquires in exclusive mode, ignoring interrupts. Implemented
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&//线程B调用非公平锁的tryAcquire(), 最终返回false,加上!,也就是true,也就是还要执行下面两行语句
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))//线程B加入等待队列
selfInterrupt();//下一节论述
}
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {//根据上面一句注释,本语句块的意义是将新节点快速添加至队尾
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);//快速添加至队尾失败,则用这方法调用(可能链表为空,才调用该方法)
return node;
}
//Inserts node into queue, initializing if necessary.
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))//插入一个哨兵节点(或称傀儡节点)
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {//真正插入我们需要的节点,也就是包含线程B引用的节点
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
//CAS head field. Used only by enq.
private final boolean compareAndSetHead(Node update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, headOffset, null, update);
}
//CAS tail field. Used only by enq.
private final boolean compareAndSetTail(Node expect, Node update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, tailOffset, expect, update);
}
...
}
另外
假设线程B,C还没启动,正在工作线程A重新尝试获得锁,也就是调用lock.lock()多一次
//非公平锁与公平锁的公共父类fa
* Base of synchronization control for this lock. Subclassed
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
...
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();//这里是线程A
int c = getState();//线程A还在工作,c=>1;如果线程A恰好运行到在这工作完了,c=>0,这时它又要申请锁的话
if (c == 0) {//线程A正在工作为false;如果线程A恰好工作完,c=>0,这时它又要申请锁的话,则为true
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {//线程A重新获得锁
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);//这里相当于NonfairSync.lock()另一重设置吧!
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {//(线程A == 线程A) => true
int nextc = c + acquires;//1+1=>nextc=2
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);//state=2,说明要unlock多两次吧(现在盲猜)
return true;//返回true
}
return false;
}
...
}
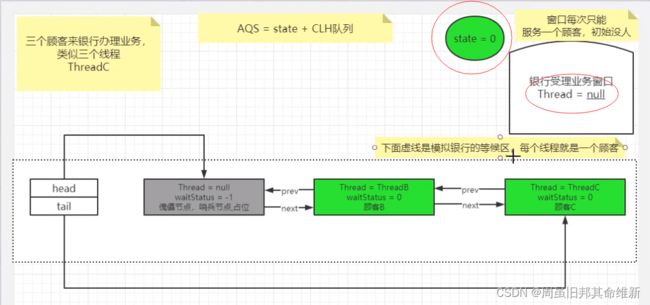
双向链表中,第一个节点为虚节点(也叫哨兵节点),其实并不存储任何信息,只是占位。真正的第一个有数据的节点,是从第二个节点开始的。
接下来讨论ReentrantLock.unLock()方法。假设线程A工作结束,调用unLock(),释放锁占用。
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
private final Sync sync;
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
...
// unlock()间接调用本方法,releases传入1
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;//c为0
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {//c为0,条件为ture,执行if语句块
free = true;
// 设置当前占用锁线程为null
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;//最后返回true
}
...
}
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {...}
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();//我们使用的非公平锁
}
//注意!注意!注意!
public void unlock() {//<----------从这开始,假设线程A工作结束,调用unLock(),释放锁占用
sync.release(1);//在AbstractQueuedSynchronizer类定义
}
...
}
public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
extends AbstractOwnableSynchronizer
implements java.io.Serializable {
...
//1.
public final boolean release(int arg) {
//2.
if (tryRelease(arg)) {//该方法看子类NonfairSync实现,最后返回true
Node h = head;//返回傀儡节点
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)//傀儡节点非空,且状态为-1,条件为true,执行if语句
//7.
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;//返回true,false都无所谓了,unlock方法只是简单调用release方法,对返回结果没要求
}
/**
* The synchronization state.
*/
private volatile int state;
//3.
protected final int getState() {
return state;
}
//6.
protected final void setState(int newState) {
state = newState;
}
//7. Wakes up node's successor, if one exists.
//传入傀儡节点
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int ws = node.waitStatus;//傀儡节点waitStatus为-1
if (ws < 0)//ws为-1,条件成立,执行if语块
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);//8.将傀儡节点waitStatus由-1变为0
/*
* Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally
* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,
* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual
* non-cancelled successor.
*/
Node s = node.next;//傀儡节点的下一节点,也就是带有线程B的节点
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {//s非空,s.waitStatus非0,条件为false,不执行if语块
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)//s非空,条件为true,不执行if语块
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);//唤醒线程B。运行到这里,线程A的工作基本告一段落了。
}
//8.
private static final boolean compareAndSetWaitStatus(Node node,
int expect,
int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(node, waitStatusOffset,
expect, update);
}
}
线程A结束工作,调用unlock()的tryRelease()后的状态,state由1变为0,exclusiveOwnerThread由线程A变为null。
线程B被唤醒,即从原先park()的方法继续运行
public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
extends AbstractOwnableSynchronizer
implements java.io.Serializable {
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);//线程B从阻塞到非阻塞,继续执行
return Thread.interrupted();//线程B没有被中断,返回false
}
...
//Acquires in exclusive uninterruptible mode for thread already inqueue.
//Used by condition wait methods as well as acquire.
//
//return true if interrupted while waiting
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();//线程B所在的节点的前一节点是傀儡节点
//傀儡节点是头节点,tryAcquire()的说明请移步至#21_AQS源码深度解读03
//tryAcquire()返回true,线程B成功上位
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);//1.将附带线程B的节点的变成新的傀儡节点
p.next = null; // help GC//置空原傀儡指针与新的傀儡节点之间的前后驱指针,方便GC回收
failed = false;
return interrupted;//返回false,跳到2.acquire()
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
//唤醒线程B继续工作,parkAndCheckInterrupt()返回false
//if语块不执行,跳到下一循环
parkAndCheckInterrupt())//<---------------------------------唤醒线程在这里继续运行
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
//1.
private void setHead(Node node) {
head = node;
node.thread = null;
node.prev = null;
}
//2.
* Acquires in exclusive mode, ignoring interrupts. Implemented
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
//acquireQueued()返回fasle,条件为false,if语块不执行,acquire()返回
//也就是说,线程B成功获得锁,可以展开线程B自己的工作了。
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();//
}
}
3、spring AOP
springboot1和springboot分别使用了spring4、spring5,对比不同版本aop执行的顺序
3.1、spring4下的aop测试案例
pom文件
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
1.5.9.RELEASE
com.example
aoptest
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
aoptest
Demo project for Spring Boot
8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.aspectj
aspectjrt
org.aspectj
aspectjweaver
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
切面类
package com.example.aoptest.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class MyAspect {
@Before("execution(* com.example.aoptest..*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void beforeNotify() {
System.out.println("********@Before我是前置通知");
}
@After("execution(* com.example.aoptest..*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void afterNotify() {
System.out.println("********@After我是后置通知");
}
@AfterReturning("execution(* com.example.aoptest..*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void afterReturningNotify() {
System.out.println("********@AfterReturning我是返回后通知");
}
@AfterThrowing(" execution(* com.example.aoptest..*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void afterThrowingNotify() {
System.out.println("********@AfterThrowing我是异常通知");
}
@Around(" execution(* com.example.aoptest..*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
Object retvalue = null;
System.out.println("我是环绕通知之前AAA");
retvalue = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("我是环绕通知之后BBB");
return retvalue ;
}
}
业务service
package com.example.aoptest.service.impl;
import com.example.aoptest.service.HelloService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@Override
public void helloWorld() {
System.out.println("=========hello world");
}
}
测试类
package com.example.aoptest;
import com.example.aoptest.service.HelloService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class AopTest {
@Resource
private HelloService helloService;
@Test
public void testAop4() {
helloService.helloWorld();
}
}
aop执行顺序
我是环绕通知之前AAA
********@Before我是前置通知
=========hello world
我是环绕通知之后BBB
********@After我是后置通知
********@AfterReturning我是返回后通知
业务service发生异常的情况下aop执行顺序
我是环绕通知之前AAA
********@Before我是前置通知
********@After我是后置通知
********@AfterThrowing我是异常通知
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
3.2、spring5下的aop测试案例
修改pom文件中springboot版本为2.4.4
修改单元测试类
package com.example.aoptest;
import com.example.aoptest.service.HelloService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@SpringBootTest
public class AopTest {
@Resource
private HelloService helloService;
@Test
public void testAop4() {
helloService.helloWorld();
}
}
aop执行顺序
我是环绕通知之前AAA
********@Before我是前置通知
=========hello world
********@AfterReturning我是返回后通知
********@After我是后置通知
我是环绕通知之后BBB
业务service发生异常的情况下aop执行顺序
我是环绕通知之前AAA
********@Before我是前置通知
********@AfterThrowing我是异常通知
********@After我是后置通知
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
4、spring循环依赖
spring默认的单例(Singleton)的场景是支持循环依赖
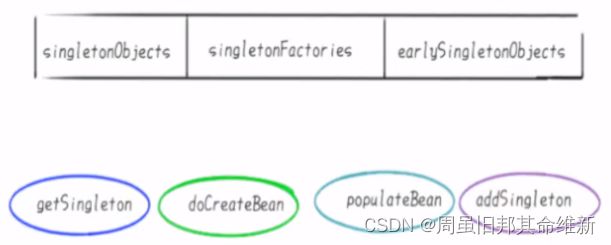
spring内部通过3级缓存来解决循环依赖 - DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
只有单例的bean会通过三级缓存提前暴露来解决循环依赖的问题,而非单例的bean,每次从容器中获取都是一个新的对象,都会重新创建,所以非单例的bean是没有缓存的,不会将其放到三级缓存中。
第一级缓存(也叫单例池)singletonObjects:存放已经经历了完整生命周期的Bean对象。
第二级缓存:earlySingletonObjects,存放早期暴露出来的Bean对象,Bean的生命周期未结束(属性还未填充完。
第三级缓存:Map
4.1、哪些循环依赖Spring无法解决
- prototype 类型的循环依赖
- constructor 注入的循环依赖
- @Async 标记的类产生的代理 bean 发生循环依赖(@Async 标记产生的循环依赖本地可能正常,打包启动报错)
4.2、spring循环依赖debug前置知识
实例化 - 内存中申请一块内存空间,如同租赁好房子,自己的家当还未搬来。
初始化属性填充 - 完成属性的各种赋值,如同装修,家具,家电进场。
3个Map和四大方法,总体相关对象
package org.springframework.beans.factory.support;
...
public class DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry extends SimpleAliasRegistry implements SingletonBeanRegistry {
...
/**
单例对象的缓存:bean名称—bean实例,即:所谓的单例池。
表示已经经历了完整生命周期的Bean对象
第一级缓存
*/
private final Map singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
/**
早期的单例对象的高速缓存: bean名称—bean实例。
表示 Bean的生命周期还没走完(Bean的属性还未填充)就把这个 Bean存入该缓存中也就是实例化但未初始化的 bean放入该缓存里
第二级缓存
*/
private final Map earlySingletonObjects = new HashMap<>(16);
/**
单例工厂的高速缓存:bean名称—ObjectFactory
表示存放生成 bean的工厂
第三级缓存
*/
private final Map> singletonFactories = new HashMap<>(16);
...
}
A / B两对象在三级缓存中的迁移说明
- A创建过程中需要B,于是A将自己放到三级缓里面,去实例化B。
- B实例化的时候发现需要A,于是B先查一级缓存,没有,再查二级缓存,还是没有,再查三级缓存,找到了A然后把三级缓存里面的这个A放到二级缓存里面,并删除三级缓存里面的A。
- B顺利初始化完毕,将自己放到一级缓存里面(此时B里面的A依然是创建中状态),然后回来接着创建A,此时B已经创建结束,直接从一级缓存里面拿到B,然后完成创建,并将A自己放到一级缓存里面。
Spring为了解决单例的循坏依赖问题,使用了三级缓存:
其中一级缓存为单例池(singletonObjects)。
二级缓存为提前曝光对象(earlySingletonObjects)。
三级级存为提前曝光对象工厂(singletonFactories) 。
假设A、B循环引用,实例化A的时候就将其放入三级缓存中,接着填充属性的时候,发现依赖了B,同样的流程也是实例化后放入三级缓存,接着去填充属性时又发现自己依赖A,这时候从缓存中查找到早期暴露的A,没有AOP代理的话,直接将A的原始对象注入B,完成B的初始化后,进行属性填充和初始化,这时候B完成后,就去完成剩下的A的步骤,如果有AOP代理,就进行AOP处理获取代理后的对象A,注入B,走剩下的流程。
4.3 debug循环依赖源码(注解)
4.3.1 源码跟踪
进入SpringApplication.run,源码一
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context); // 这一步创建了循环依赖对象
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
进入refreshContext(context),经过几次断点,最终进入refresh()方法,源码二
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// 重点关注点是这里
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // 这一步创建了循环依赖对象
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory),源码三
/**
* Finish the initialization of this context's bean factory,
* initializing all remaining singleton beans.
*/
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Initialize conversion service for this context.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// Register a default embedded value resolver if no BeanFactoryPostProcessor
// (such as a PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:
// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal));
}
// Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(); // 这一步创建了循环依赖对象
}
进入beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(),源码四
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// 这里要注意beanNames有很多,找到创建a、b实例的循环,再继续向下debug
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
// 对象类型是不是FactoryBean
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
FactoryBean factory = (FactoryBean) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedAction) ((SmartFactoryBean) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
StartupStep smartInitialize = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.beans.smart-initialize")
.tag("beanName", beanName);
SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction a的类型不是FactoryBean,走else进入getBean(beanName),源码五
protected T doGetBean(
String name, @Nullable Class requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object beanInstance;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName); // 第一个getSingleton
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
......
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
StartupStep beanCreation = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.beans.instantiate")
.tag("beanName", name);
try {
if (requiredType != null) {
beanCreation.tag("beanType", requiredType::toString);
}
RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 第二个getSingleton,注意和第一个getSingleton不相同,是重载方法
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
.......
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
......
}
finally {
beanCreation.end();
}
}
return adaptBeanInstance(name, beanInstance, requiredType);
}
第一个getSingleton,源码六
@Override
@Nullable
public Object getSingleton(String beanName) {
return getSingleton(beanName, true);
}
继续进入getSingleton,源码七
/**
* Return the (raw) singleton object registered under the given name.
* Checks already instantiated singletons and also allows for an early
* reference to a currently created singleton (resolving a circular reference).
* @param beanName the name of the bean to look for
* @param allowEarlyReference whether early references should be created or not
* @return the registered singleton object, or {@code null} if none found
*/
@Nullable
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// 1级缓存
// Quick check for existing instance without full singleton lock
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
// 1级缓存拿不到,则去2级缓存拿
// 不要忽略isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation这个方法,得益于这个方法,我们才能终止循环,下文会详解
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
// 2级缓存
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
// 注意,如果allowEarlyReference是false,则不会进入
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// Consistent creation of early reference within full singleton lock
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
// 则从3级缓存加载,最后移动到2级缓存
ObjectFactory singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
// 调用3级缓存,getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean)
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
// 放入2级缓存
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
// 从3级缓存移除
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
第二个getSingleton,源码八
/**
* Return the (raw) singleton object registered under the given name,
* creating and registering a new one if none registered yet.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param singletonFactory the ObjectFactory to lazily create the singleton
* with, if necessary
* @return the registered singleton object
*/
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
if (this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction) {
throw new BeanCreationNotAllowedException(beanName,
"Singleton bean creation not allowed while singletons of this factory are in destruction " +
"(Do not request a bean from a BeanFactory in a destroy method implementation!)");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating shared instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
// beforeSingletonCreation设置第一个getSingleton方法中的isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation数据(4.3.2)
beforeSingletonCreation(beanName);
boolean newSingleton = false;
boolean recordSuppressedExceptions = (this.suppressedExceptions == null);
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
try {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
newSingleton = true;
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// Has the singleton object implicitly appeared in the meantime ->
// if yes, proceed with it since the exception indicates that state.
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
throw ex;
}
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
for (Exception suppressedException : this.suppressedExceptions) {
ex.addRelatedCause(suppressedException);
}
}
throw ex;
}
finally {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = null;
}
// 没看懂这一步作用是什么
afterSingletonCreation(beanName);
}
if (newSingleton) {
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
}
第二个getSingleton调用createBean,在createBean中调用doCreateBean,实际创建bean,源码九
/**
* Actually create the specified bean. Pre-creation processing has already happened
* at this point, e.g. checking {@code postProcessBeforeInstantiation} callbacks.
* Differentiates between default bean instantiation, use of a
* factory method, and autowiring a constructor.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param args explicit arguments to use for constructor or factory method invocation
* @return a new instance of the bean
* @throws BeanCreationException if the bean could not be created
* @see #instantiateBean
* @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod
* @see #autowireConstructor
*/
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
......
// 如果是循环引用,在为bean填充属性前,先走addSingletonFactory放入三级缓存
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
// 放入三级缓存
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 填充bean的属性
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
......
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
创建bean的时候先放入三级缓存addSingletonFactory,源码十
/**
* Add the given singleton factory for building the specified singleton
* if necessary.
* To be called for eager registration of singletons, e.g. to be able to
* resolve circular references.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param singletonFactory the factory for the singleton object
*/
protected void addSingletonFactory(String beanName, ObjectFactory singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(singletonFactory, "Singleton factory must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) {
// 放入三级缓存
this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory);
// 从二级缓存移除
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
// 放入registeredSingletons中
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
}
然后填充bean的属性populateBean,源码十一
/**
* Populate the bean instance in the given BeanWrapper with the property values
* from the bean definition.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @param bw the BeanWrapper with bean instance
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation") // for postProcessPropertyValues
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
......
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
for (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware) {
// 在这里会对@Autowire标记的属性进行依赖注入
PropertyValues pvsToUse = bp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
// 对解析完但未设置的属性再进行处理
pvsToUse = bp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) {
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}
postProcessPropertyValues这个方法为一个默认的钩子方法,有默认的实现。直接返回null,源码十二
@Nullable
default PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
return null;
}
调用AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的postProcessProperties()方法,在方法中,首先获取类中@Autowired注解的元信息,再通过inject()方法从容器中获取对象利用反射进行注入,如果容器中不包含该Bean,则同样使用getBean()方法进行获取,源码十三
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
// 获取指定类中@Autowire相关注解的元信息
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
// 对bean的属性进行自动注入
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
源码八中的addSingleton也就是4.2中的图例的最后一步addSingleton,从二、三级缓存移动到一级缓存,源码十四
/**
* Add the given singleton object to the singleton cache of this factory.
* To be called for eager registration of singletons.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param singletonObject the singleton object
*/
protected void addSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// 放入一级缓存
this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
// 从三级缓存移除
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
// 从二级缓存移除
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
// 放入registeredSingletons中
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
4.3.2两个需要注意的点
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation循环终止条件判断
singletonsCurrentlyInCreation是一个Set集合,存放正在创建的bean,在Bean开始创建时放入
4.3.1第一个getSingleton中的singletonsCurrentlyInCreation源码如下,如果一个bean存在于该set中,则开始调用第3级缓存中的方法,产生bean。
/**
* Return whether the specified singleton bean is currently in creation
* (within the entire factory).
* @param beanName the name of the bean
*/
public boolean isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(String beanName) {
return this.singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.contains(beanName);
}
singletonsCurrentlyInCreation中的数据来自于第二个getSingleton中调用的beforeSingletonCreation
/**
* Callback before singleton creation.
* The default implementation register the singleton as currently in creation.
* @param beanName the name of the singleton about to be created
* @see #isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation
*/
protected void beforeSingletonCreation(String beanName) {
// 如果inCreationCheckExclusions中不包含就添加
if (!this.inCreationCheckExclusions.contains(beanName) && !this.singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.add(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
}
第二个getSingleton中调用的afterSingletonCreation(beanName),如果不包含没必要remove,如果包含beanName,取反为false,后面的移除也不会走,没看懂作用是什么
/**
* Callback after singleton creation.
* The default implementation marks the singleton as not in creation anymore.
* @param beanName the name of the singleton that has been created
* @see #isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation
*/
protected void afterSingletonCreation(String beanName) {
if (!this.inCreationCheckExclusions.contains(beanName) && !this.singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.remove(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Singleton '" + beanName + "' isn't currently in creation");
}
}
allowEarlyReference
boolean类型的变量,
注意,根据上面的代码,只有allowEarlyReference为true,才能调用第3级缓存!
而调用完第3级缓存,马上会移动到第2级缓存!
而只有一个地方该参数是true:
而这唯一传参true的地方就在4.3.1源码六。
所以这就说明了,当递归创建bean的时候,如果发现成环了,那么就开始调用第三级缓存。
所以并不是所有的bean都会用到第3级缓存,甚至只是少数bean才会用到。
5、redis分布式锁
5.1 第一版
Redis具有极高的性能,且其命令对分布式锁支持友好,借助SET命令即可实现加锁处理。
EX seconds – Set the specified expire time, in seconds.
PX milliseconds – Set the specified expire time, in milliseconds.
NX – Only set the key if it does not already exist.
XX – Only set the key if it already exist.
在Java层面
public static final String REDIS_LOCK = "redis_lock";
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
public void m(){
String value = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + Thread.currentThread().getName();
Boolean flag = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(REDIS_LOCK, value);
if(!flag) {
return "抢锁失败";
}
...//业务逻辑
stringRedisTemplate.delete(REDIS_LOCK);
}
5.2 第二版
上面Java源码分布式锁问题:出现异常的话,可能无法释放锁,必须要在代码层面finally释放锁。
解决方法:try…finally…
public static final String REDIS_LOCK = "redis_lock";
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
public void m(){
String value = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + Thread.currentThread().getName();
try{
Boolean flag = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(REDIS_LOCK, value);
if(!flag) {
return "抢锁失败";
}
...//业务逻辑
}finally{
stringRedisTemplate.delete(REDIS_LOCK);
}
}
5.3 第三版
另一个问题:部署了微服务jar包的机器挂了,代码层面根本没有走到finally这块,没办法保证解锁,这个key没有被删除,需要加入一个过期时间限定key。
public static final String REDIS_LOCK = "redis_lock";
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
public void m(){
String value = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + Thread.currentThread().getName();
try{
Boolean flag = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue()//使用另一个带有设置超时操作的方法
.setIfAbsent(REDIS_LOCK, value, 10L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
//设定时间
//stringRedisTemplate.expire(REDIS_LOCK, 10L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if(!flag) {
return "抢锁失败";
}
...//业务逻辑
}finally{
stringRedisTemplate.delete(REDIS_LOCK);
}
}
5.4 第四版
另一个新问题:张冠李戴,删除了别人的锁
解决方法:只能自己删除自己的,不许动别人的。
public static final String REDIS_LOCK = "redis_lock";
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
public void m(){
String value = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + Thread.currentThread().getName();
try{
Boolean flag = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue()//使用另一个带有设置超时操作的方法
.setIfAbsent(REDIS_LOCK, value, 10L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
//设定时间
//stringRedisTemplate.expire(REDIS_LOCK, 10L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if(!flag) {
return "抢锁失败";
}
...//业务逻辑
}finally{
if(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(REDIS_LOCK).equals(value)) {
stringRedisTemplate.delete(REDIS_LOCK);
}
}
}
新的问题,finally块的判断 + del删除操作不是原子性的
用lua脚本或者用redis自身的事务
事务介绍
可以一次执行多个命令,本质是一组命令的集合。一个事务中的所有命令都会序列化,按顺序地串行化执行而不会被其它命令插入,不许加塞。
一个队列中,一次性、顺序性、排他性的执行一系列命令。
| 命令 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| DISCARD | 取消事务,放弃执行事务块内的所有命令。 |
| EXEC | 执行所有事务块内的命令。 |
| MULTI | 标记一个事务块的开始。 |
| UNWATCH | 取消 WATCH 命令对所有 key 的监视。 |
| WATCH key [key …] | 监视一个(或多个) key ,如果在事务执行之前这个(或这些) key 被其他命令所改动,那么事务将被打断。 |
官网文档http://www.redis.cn/topics/transactions.html
5.5 第五版
用redis自身的事务解决第四版的问题
public static final String REDIS_LOCK = "redis_lock";
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
public void m(){
String value = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + Thread.currentThread().getName();
try{
Boolean flag = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue()//使用另一个带有设置超时操作的方法
.setIfAbsent(REDIS_LOCK, value, 10L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
//设定时间
//stringRedisTemplate.expire(REDIS_LOCK, 10L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if(!flag) {
return "抢锁失败";
}
...//业务逻辑
}finally{
while(true){
stringRedisTemplate.watch(REDIS_LOCK);
if(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(REDIS_LOCK).equalsIgnoreCase(value)){
stringRedisTemplate.setEnableTransactionSupport(true);
stringRedisTemplate.multi();
stringRedisTemplate.delete(REDIS_LOCK);
List5.6 第六版
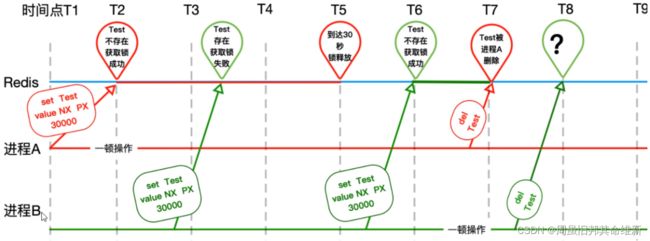
第五版任然有两个问题
1、如何确保RedisLock过期时间大于业务执行时间
2、redis集群模式下master设置锁成功会立即返回,如果在这个信息同步下发给其他slave之前,master宕机,master降级为slave,这个锁信息就会丢失。
Redis分布式锁如何续期?
集群 + CAP对比ZooKeeper 对比ZooKeeper,重点,CAP
Redis - AP -redis异步复制造成的锁丢失,比如:主节点没来的及把刚刚set进来这条数据给从节点,就挂了。
ZooKeeper - CP
CAP
C:Consistency(强一致性)
A:Availability(可用性)
P:Partition tolerance(分区容错性)
综上所述
Redis集群环境下,我们自己写的也不OK,直接上RedLock之Redisson落地实现。
public static final String REDIS_LOCK = "REDIS_LOCK";
@Autowired
private Redisson redisson;
@GetMapping("/doSomething")
public String doSomething(){
RLock redissonLock = redisson.getLock(REDIS_LOCK);
redissonLock.lock();
try {
//doSomething
}finally {
//添加后,更保险
if(redissonLock.isLocked() && redissonLock.isHeldByCurrentThread()) {
redissonLock.unlock();
}
}
}
可避免如下异常:
IllegalMonitorStateException: attempt to unlock lock,not loked by current thread by node id:da6385f-81a5-4e6c-b8c0
6、redis内存设置
redis默认内存多少可以用?
如果不设置最大内存大小或者设置最大内存大小为0,在64位操作系统下不限制内存大小,在32位操作系统下最多使用3GB内存
一般生产上你如何配置?
一般推荐Redis设置内存为最大物理内存的四分之三。
如何修改redis内存设置
修改配置文件redis.conf的maxmemory参数,如:
maxmemory 104857600
通过命令修改
config set maxmemory 1024
config get maxmemory
什么命令查看redis内存使用情况?
info memory
真要打满了会怎么样?如果Redis内存使用超出了设置的最大值会怎样?
(error) OOM command not allowed when used memory > 'maxmemory'.
如果一个键是过期的,那它到了过期时间之后是不是马上就从内存中被被删除呢?
三种不同的删除策略
- 定时删除 - 总结:对CPU不友好,用处理器性能换取存储空间(拿时间换空间)
- 惰性删除 - 总结:对memory不友好,用存储空间换取处理器性能(拿空间换时间)
- 定期删除 - 定期抽样key,判断是否过期(存在漏网之鱼)
定时删除
Redis不可能时时刻刻遍历所有被设置了生存时间的key,来检测数据是否已经到达过期时间,然后对它进行删除。
立即删除能保证内存中数据的最大新鲜度,因为它保证过期键值会在过期后马上被删除,其所占用的内存也会随之释放。但是立即删除对cpu是最不友好的。因为删除操作会占用cpu的时间,如果刚好碰上了cpu很忙的时候,比如正在做交集或排序等计算的时候,就会给cpu造成额外的压力,让CPU心累,时时需要删除,忙死。
这会产生大量的性能消耗,同时也会影响数据的读取操作。
惰性删除
数据到达过期时间,不做处理。等下次访问该数据时,
如果未过期,返回数据;
发现已过期,删除,返回不存在。
惰性删除策略的缺点是,它对内存是最不友好的。
如果一个键已经过期,而这个键又仍然保留在数据库中,那么只要这个过期键不被删除,它所占用的内存就不会释放。
在使用惰性删除策略时,如果数据库中有非常多的过期键,而这些过期键又恰好没有被访问到的话,那么它们也许永远也不会被删除(除非用户手动执行FLUSHDB),我们甚至可以将这种情况看作是一种内存泄漏 – 无用的垃圾数据占用了大量的内存,而服务器却不会自己去释放它们,这对于运行状态非常依赖于内存的Redis服务器来说,肯定不是一个好消息。
定期删除
定期删除策略是前两种策略的折中:
定期删除策略每隔一段时间执行一次删除过期键操作,并通过限制删除操作执行的时长和频率来减少删除操作对CPU时间的影响。
周期性轮询Redis库中的时效性数据,来用随机抽取的策略,利用过期数据占比的方式控制删除频度
特点1:CPU性能占用设置有峰值,检测频度可自定义设置
特点2:内存压力不是很大,长期占用内存的冷数据会被持续清理
总结:周期性抽查存储空间(随机抽查,重点抽查)
看起来使用惰性删除+定期删除会比较好,但是仍然存在问题;
定期删除时,从来没有被抽查到
惰性删除时,也从来没有被点中使用过
上述2步骤====>大量过期的key堆积在内存中,导致redis内存空间紧张或者很快耗尽
7、redis内存淘汰策略
volatile-lru:当内存不足以容纳新写入数据时,在设置了过期时间的键空间中,移除最近最少使用的key。
allkeys-lru:当内存不足以容纳新写入数据时,在键空间中,移除最近最少使用的key(这个是最常用的)。
volatile-lfu:当内存不足以容纳新写入数据时,在过期密集的键中,使用LFU算法进行删除key。
allkeys-lfu:当内存不足以容纳新写入数据时,使用LFU算法移除所有的key。
volatile-random:当内存不足以容纳新写入数据时,在设置了过期的键中,随机删除一个key。
allkeys-random:当内存不足以容纳新写入数据时,随机删除一个或者多个key。
volatile-ttl:当内存不足以容纳新写入数据时,在设置了过期时间的键空间中,有更早过期时间的key优先移除。
noeviction:当内存不足以容纳新写入数据时,新写入操作会报错。
如何配置,修改
- 命令
- config set maxmemory-policy noeviction
- config get maxmemory
- 配置文件 - 配置文件redis.conf的maxmemory-policy参数
8、lru算法
LRU是Least Recently Used的缩写,即最近最少使用,是一种常用的页面置换算法,选择最近最久未使用的数据予以淘汰。
查找快、插入快、删除快,且还需要先后排序---------->什么样的数据结构可以满足这个问题?
你是否可以在O(1)时间复杂度内完成这两种操作?
如果一次就可以找到,你觉得什么数据结构最合适?
答案:LRU的算法核心是哈希链表
编码手写如何实现LRU
本质就是HashMap + DoubleLinkedList
时间复杂度是O(1),哈希表+双向链表的结合体
借用LinkedHashMap完成lru算法
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class LRUCache {
private LinkedHashMap cache;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
cache = new LinkedHashMap(capacity, 0.75f, true){
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry eldest) {
return super.size() > capacity;
}
};
}
public int get(int key) {
return cache.get(key);
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
cache.put(key, value);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return cache.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LRUCache lru = new LRUCache(3);
lru.put(1,4);
lru.put(2,4);
lru.put(3,4);
System.out.println(lru);
lru.put(4,4);
System.out.println(lru);
lru.put(3,4);
lru.put(3,4);
lru.put(3,4);
lru.put(5,4);
System.out.println(lru);
}
}
手写lru算法
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class LRUCacheNoLinkedHashMap {
class Node{
K key;
V value;
Node prev;
Node next;
public Node() {
this.prev = this.next = null;
}
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.prev = this.next = null;
}
}
class DoubleLinkedList{
Node head;
Node tail;
public DoubleLinkedList() {
this.head = new Node<>();
this.tail = new Node<>();
this.head.next = this.tail;
this.tail.prev = this.head;
}
public void addHead(Node node){
node.next = this.head.next;
node.prev = this.head;
this.head.next.prev = node;
this.head.next = node;
}
public void removeNode(Node node){
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
node.next = null;
node.prev = null;
}
public Node getLast(){
if (this.tail.prev == this.head){
return null;
}
return this.tail.prev;
}
}
private Integer cacheSize;
private Map> map;
private DoubleLinkedList linkedList;
public LRUCacheNoLinkedHashMap(int capacity) {
this.cacheSize = capacity;
map = new HashMap<>();
linkedList = new DoubleLinkedList();
}
public int get(int key) {
if (!map.containsKey(key)){
return -1;
}
Node node = map.get(key);
linkedList.removeNode(node);
linkedList.addHead(node);
return node.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if (map.containsKey(key)){
Node node = map.get(key);
linkedList.removeNode(node);
linkedList.addHead(node);
} else {
if (map.size() == cacheSize){
Node lastNode = linkedList.getLast();
map.remove(lastNode.key);
linkedList.removeNode(lastNode);
}
Node node = new Node<>(key, value);
linkedList.addHead(node);
map.put(key, node);
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return map.keySet().toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LRUCacheNoLinkedHashMap lru = new LRUCacheNoLinkedHashMap(3);
lru.put(1,4);
lru.put(2,4);
lru.put(3,4);
System.out.println(lru);
lru.put(4,4);
System.out.println(lru);
lru.put(3,4);
lru.put(3,4);
lru.put(3,4);
lru.put(5,4);
System.out.println(lru);
}
}
9、lfu算法
LFU是Least Frequently Used的缩写,即最不频繁使用
因为 LFU 算法是根据数据访问的频率来选择被淘汰数据的,所以 LFU 算法会记录每个数据的访问次数。当一个数据被再次访问时,就会增加该数据的访问次数。
不过,访问次数和访问频率还不能完全等同。访问频率是指在一定时间内的访问次数,也就是说,在计算访问频率时,我们不仅需要记录访问次数,还要记录这些访问是在多长时间内执行的。否则,如果只记录访问次数的话,就缺少了时间维度的信息,进而就无法按照频率来淘汰数据了。
我来给你举个例子,假设数据 A 在 15 分钟内访问了 15 次,数据 B 在 5 分钟内访问了 10 次。如果只是按访问次数来统计的话,数据 A 的访问次数大于数据 B,所以淘汰数据时会优先淘汰数据 B。不过,如果按照访问频率来统计的话,数据 A 的访问频率是 1 分钟访问 1 次,而数据 B 的访问频率是 1 分钟访问 2 次,所以按访问频率淘汰数据的话,数据 A 应该被淘汰掉。
所以说,当要实现 LFU 算法时,我们需要能统计到数据的访问频率,而不是简单地记录数据访问次数就行。
LFU 是在 Redis 4.0 新增的淘汰策略,它涉及的巧妙之处在于,其复用了 redisObject 结构的 lru 字段,把这个字段「一分为二」,保存最后访问时间和访问次数
key 的访问次数不能只增不减,它需要根据时间间隔来做衰减,才能达到 LFU 的目的
每次在访问一个 key 时,会「懒惰」更新这个 key 的访问次数:先衰减访问次数,再更新访问次数
衰减访问次数,会根据时间间隔计算,间隔时间越久,衰减越厉害
因为 redisObject lru 字段宽度限制,这个访问次数是有上限的(8 bit 最大值 255),所以递增访问次数时,会根据「当前」访问次数和「概率」的方式做递增,访问次数越大,递增因子越大,递增概率越低
Redis 实现的 LFU 算法也是「近似」LFU,是在性能和内存方面平衡的结果