Pytest自动化测试框架
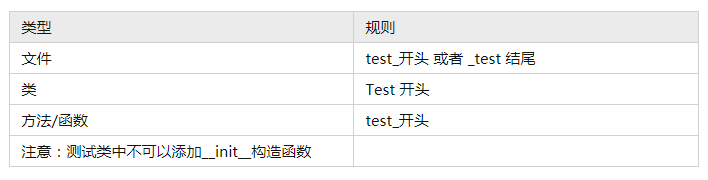
Pytest 命名规则
练习
- (多选)下面哪个测试方法,符合 pytest 命名规范
- A、测试类 TestDemo
- B、测试方法 test_demo
- C、测试文件 testdemo
- D、测试包 test_demo
答案是:ABD
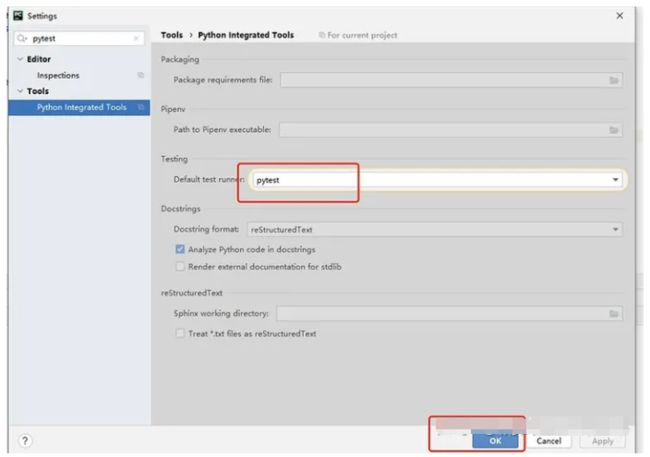
Pycharm 默认测试执行器为Pytest
pytest 用例结构
- 三部分构成
- 用例名称
- 用例步骤
- 用例断言
def test_XXX(self):
# 测试步骤1
# 测试步骤2
# 断言 实际结果 对比 预期结果
assert ActualResult == ExpectedResult类级别的用例示例
class TestXXX:
def setup(self):
# 资源准备
pass
def teardown(self):
# 资源销毁
pass
def test_XXX(self):
# 测试步骤1
# 测试步骤2
# 断言 实际结果 对比 预期结果
assert ActualResult == ExpectedResultpytest 用例断言
断言的用法
- 第一种:
assert <表达式> - 第二种:
assert <表达式>,<描述>
def test_a():
assert True
def test_b():
a = 1
b = 1
c = 2
assert a + b == c, f"{a}+{b}=={c}, 结果为真"- assert <表达式>
def test_c():
a = 1
b = 1
c = 2
assert 'abc' in "abcd"
import sys
def test_plat():
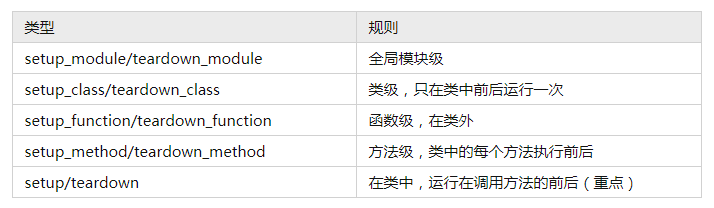
assert ('linux' in sys.platform), "该代码只能在 Linux 下执行"Pytest 测试框架结构(setup/teardown)
测试装置介绍
pytest 参数化用例
参数化
- 通过参数的方式传递数据,从而实现数据和脚本分离。
- 并且可以实现用例的重复生成与执行。
参数化应用场景
- 测试登录场景
- 测试登录成功,登录失败(账号错误,密码错误)
- 创建多种账号: 中⽂文账号,英⽂文账号
- 普通测试用例方法
- Copy 多份代码 or 读⼊入参数?
- 一次性执⾏多个输⼊入参数
def test_param_login_ok():
# 登录成功
username = "right"
password = "right"
login(username,password)
def test_param_login_fail():
# 登录失败
username = "wrong"
password = "wrong"
login(username,password)参数化实现方案
- pytest 参数化实现方法
- 装饰器:
@pytest.mark.parametrize
@pytest.mark.parametrize("username,password",[["right","right"], ["wrong","wrong"]])
def test_param(username,password):
login(username,password)Mark:参数化测试函数使用
参数化:单参数情况
- 单参数,可以将数据放在列表中
search_list = ['appium','selenium','pytest']
@pytest.mark.parametrize('name',search_list)
def test_search(name):
assert name in search_list参数化:多参数情况
- 将数据放在列表嵌套元组中
- 将数据放在列表嵌套列表中
import pytest
# 数据放在元组中
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_input,expected",[
("3+5",8),("2+5",7),("7+5",12)
])
def test_mark_more(test_input,expected):
assert eval(test_input) == expected
# 数据放在列表中
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_input,expected",[
["3+5",8],["2+5",7],["7+5",12]
])
def test_mark_more(test_input,expected):
assert eval(test_input) == expected参数化:用例重命名-添加 ids 参数
- 通过ids参数,将别名放在列表中
import pytest
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_input,expected",[
("3+5",8),("2+5",7),("7+5",12)
],ids=['add_3+5=8','add_2+5=7','add_3+5=12'])
def test_mark_more(test_input,expected):
assert eval(test_input) == expected参数化:用例重命名-添加 ids 参数(中文)
# 创建conftest.py 文件 ,将下面内容添加进去,运行脚本
def pytest_collection_modifyitems(items):
"""
测试用例收集完成时,将收集到的用例名name和用例标识nodeid的中文信息显示在控制台上
"""
for i in items:
i.name=i.name.encode("utf-8").decode("unicode_escape")
i._nodeid=i.nodeid.encode("utf-8").decode("unicode_escape")
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_input,expected",[
("3+5",8),("2+5",7),("7+5",12)
],ids=["3和5相加","2和5相加","7和5相加"])
def test_mark_more(test_input,expected):
assert eval(test_input) == expected参数化:笛卡尔积
两组数据
a=[1,2,3]
b=[a,b,c]
对应有几种组合形势 ?9
(1,a),(1,b),(1,c)
(2,a),(2,b),(2,c)
(3,a),(3,b),(3,c)
import pytest
@pytest.mark.parametrize("b",["a","b","c"])
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a",[1,2,3])
#如果有多个装饰器,由近到远,先a后b,一共有9条案例
def test_param1(a,b):
print(f"笛卡积形式的参数化中 a={a} , b={b}")使用 Mark 标记测试用例
- 场景:只执行符合要求的某一部分用例 可以把一个web项目划分多个模块,然后指定模块名称执行。
- 解决: 在测试用例方法上加 @pytest.mark.标签名
- 执行: -m 执行自定义标记的相关用例
pytest -s test_mark_zi_09.py -m=webtest
pytest -s test_mark_zi_09.py -m apptest
pytest -s test_mark_zi_09.py -m "not ios"pytest 设置跳过、预期失败
Mark:跳过(Skip)及预期失败(xFail)
- 这是 pytest 的内置标签,可以处理一些特殊的测试用例,不能成功的测试用例
- skip - 始终跳过该测试用例
- skipif - 遇到特定情况跳过该测试用例
- xfail - 遇到特定情况,产生一个“期望失败”输出
Skip 使用场景
- 调试时不想运行这个用例
- 标记无法在某些平台上运行的测试功能
- 在某些版本中执行,其他版本中跳过
- 比如:当前的外部资源不可用时跳过
- 如果测试数据是从数据库中取到的,
- 连接数据库的功能如果返回结果未成功就跳过,因为执行也都报错
- 解决 1:添加装饰器
@pytest.mark.skip@pytest.mark.skipif
- 解决 2:代码中添加跳过代码
pytest.skip(reason)
@pytest.skip(reason="这个有Bug")
def test_add_3(self):
#a的参数超出范围
expect = Calculator().add(-100,99)
assert expect == "参数大小超出范围"xfail 使用场景
- 与 skip 类似 ,预期结果为 fail ,标记用例为 fail
- 用法:添加装饰器
@pytest.mark.xfail
pytest 运行用例
运行多条用例
- 运行 某个/多个 用例包
- 运行 某个/多个 用例模块
- 运行 某个/多个 用例类
- 运行 某个/多个 用例方法
运行多条用例方式
- 执行包下所有的用例:
pytest/py.test [包名] - 执行单独一个 pytest 模块:
pytest 文件名.py - 运行某个模块里面某个类:
pytest 文件名.py::类名 - 运行某个模块里面某个类里面的方法:
pytest 文件名.py::类名::方法名
运行结果分析
- 常用的:fail/error/pass
- 特殊的结果:warning/deselect
pytest 测试用例调度与运行
命令行参数-使用缓存状态
--lf(--last-failed)只重新运行故障。--ff(--failed-first)先运行故障然后再运行其余的测试
pytest常用命令行参数
命令行参数 - 常用命令行参数
—help
-x 用例一旦失败(fail/error),就立刻停止执行
–maxfail=num 用例达到
-m 标记用例
-k 执行包含某个关键字的测试用例
-v 打印详细日志
-s 打印输出日志(一般-vs一块儿使用)
—collect-only(测试平台,pytest 自动导入功能 )
python 执行 pytest
- 使用 main 函数
- 使用 python -m pytest 调用 pytest(jenkins 持续集成用到)
Python 代码执行 pytest - main 函数
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 1、运行当前目录下所有符合规则的用例,包括子目录(test_*.py 和 *_test.py)
pytest.main()
# 2、运行test_mark1.py::test_dkej模块中的某一条用例
pytest.main(['test_mark1.py::test_dkej','-vs'])
# 3、运行某个 标签
pytest.main(['test_mark1.py','-vs','-m','dkej'])
运行方式
`python test_*.py `pytest 异常处理
常用的异常处理方法
- try…except
- pytest.raises()
异常处理方法 try …except
try:
可能产生异常的代码块
except [ (Error1, Error2, ... ) [as e] ]:
处理异常的代码块1
except [ (Error3, Error4, ... ) [as e] ]:
处理异常的代码块2
except [Exception]:
处理其它异常异常处理方法 pytest.raise()
- 可以捕获特定的异常
- 获取捕获的异常的细节(异常类型,异常信息)
- 发生异常,后面的代码将不会被执行
异常处理方法 pytest.raise()
def test_raise():
with pytest.raises(ValueError, match='must be 0 or None'):
raise ValueError("value must be 0 or None")
def test_raise1():
with pytest.raises(ValueError) as exc_info:
raise ValueError("value must be 42")
assert exc_info.type is ValueError
assert exc_info.value.args[0] == "value must be 42"Pytest 结合数据驱动 YAML
数据驱动
- 什么是数据驱动?
- 数据驱动就是数据的改变从而驱动自动化测试的执行,最终引起测试结果的改变。简单来说,就是参数化的应用。数据量小的测试用例可以使用代码的参数化来实现数据驱动,数据量大的情况下建议大家使用一种结构化的文件(例如 yaml,json 等)来对数据进行存储,然后在测试用例中读取这些数据。
- 应用:
- App、Web、接口自动化测试
- 测试步骤的数据驱动
- 测试数据的数据驱动
- 配置的数据驱动
yaml 文件介绍
- 对象:键值对的集合,用冒号 “:” 表示
- 数组:一组按次序排列的值,前加 “-”
- 纯量:单个的、不可再分的值
- 字符串
- 布尔值
- 整数
- 浮点数
- Null
- 时间
- 日期
# 编程语言
languages:
- PHP
- Java
- Python
book:
Python入门: # 书籍名称
price: 55.5
author: Lily
available: True
repertory: 20
date: 2018-02-17
Java入门:
price: 60
author: Lily
available: False
repertory: Null
date: 2018-05-11yaml 文件使用
- 查看 yaml 文件
- pycharm
- txt 记事本
- 读取 yaml 文件
- 安装:
pip install pyyaml - 方法:
yaml.safe_load(f)读取yaml文件内容 - 方法:
yaml.safe_dump(f)
- 安装:
import yaml
file_path = './my.yaml'
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
data = yaml.safe_load(f)工程目录结构
- data 目录:存放 yaml 数据文件
- func 目录:存放被测函数文件
- testcase 目录:存放测试用例文件
# 工程目录结构
├── data
│ └── data.yaml
├── func
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── operation.py
└── testcase
├── __init__.py
└── test_add.py
测试准备
- 被测对象:
operation.py - 测试用例:
test_add.py - 测试数据:
data.yaml
# operation.py 文件内容
def my_add(x, y):
result = x + y
return result
# test_add.py 文件内容
class TestWithYAML:
@pytest.mark.parametrize('x,y,expected', [[1, 1, 2]])
def test_add(self, x, y, expected):
assert my_add(int(x), int(y)) == int(expected)
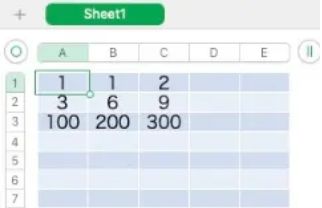
# data.yaml 文件内容
-
- 1
- 1
- 2
-
- 3
- 6
- 9
-
- 100
- 200
- 300Pytest 数据驱动结合 yaml 文件
# 读取yaml文件
def get_yaml():
"""
获取json数据
:return: 返回数据的结构:[[1, 1, 2], [3, 6, 9], [100, 200, 300]]
"""
with open('../datas/data.yaml', 'r') as f:
data = yaml.safe_load(f)
return dataPytest 结合数据驱动 Excel
读取 Excel 文件
- 第三方库
xlrdxlwingspandas
- openpyxl
- 官方文档: openpyxl - A Python library to read/write Excel 2010 xlsx/xlsm files — openpyxl 3.1.2 documentation
openpyxl 库的安装
- 安装:
pip install openpyxl - 导入:
import openpyxl
openpyxl 库的操作
import openpyxl
# 获取工作簿
book = openpyxl.load_workbook('../data/params.xlsx')
# 读取工作表
sheet = book.active
# 读取单个单元格
cell_a1 = sheet['A1']
cell_a3 = sheet.cell(column=1, row=3) # A3
# 读取多个连续单元格
cells = sheet["A1":"C3"]
# 获取单元格的值
cell_a1.value工程目录结构
- data 目录:存放 excel 数据文件
- func 目录:存放被测函数文件
- testcase 目录:存放测试用例文件
# 工程目录结构
.
├── data
│ └── params.excel
├── func
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── operation.py
└── testcase
├── __init__.py
└── test_add.py
测试准备
- 被测对象:
operation.py - 测试用例:
test_add.py
# operation.py 文件内容
def my_add(x, y):
result = x + y
return result
# test_add.py 文件内容
class TestWithEXCEL:
@pytest.mark.parametrize('x,y,expected', get_excel())
def test_add(self, x, y, expected):
assert my_add(int(x), int(y)) == int(expected)测试准备
- 测试数据:
params.xlsx
Pytest 数据驱动结合 Excel 文件
# 读取Excel文件
import openpyxl
import pytest
def get_excel():
# 获取工作簿
book = openpyxl.load_workbook('../data/params.xlsx')
# 获取活动行(非空白的)
sheet = book.active
# 提取数据,格式:[[1, 2, 3], [3, 6, 9], [100, 200, 300]]
values = []
for row in sheet:
line = []
for cell in row:
line.append(cell.value)
values.append(line)
return valuesPytest 结合数据驱动 csv
csv 文件介绍
- csv:逗号分隔值
- 是 Comma-Separated Values 的缩写
- 以纯文本形式存储数字和文本
- 文件由任意数目的记录组成
- 每行记录由多个字段组成
csv 文件内容为:
- Linux从入门到高级,linux,¥5000
- web自动化测试进阶,python,¥3000
- app自动化测试进阶,python,¥6000
- Docker容器化技术,linux,¥5000
- 测试平台开发与实战,python,¥8000
csv 文件使用
- 读取数据
- 内置函数:
open() - 内置模块:
csv
- 内置函数:
- 方法:
csv.reader(iterable)- 参数:iterable ,文件或列表对象
- 返回:迭代器,每次迭代会返回一行数据。
# 读取csv文件内容
import csv
def get_csv():
with open('demo.csv', 'r',encoding='utf_8') as file:
raw = csv.reader(file)
for line in raw:
print(line)
get_csv()
#结果为:
# ['Linux从入门到高级', 'linux', '¥5000']
# ['web自动化测试进阶', 'python', '¥3000']
# ['app自动化测试进阶', 'python', '¥6000']
# ['Docker容器化技术', 'linux', '¥5000']
# ['测试平台开发与实战', 'python', '¥8000']工程目录结构
- data 目录:存放 csv 数据文件
- func 目录:存放被测函数文件
- testcase 目录:存放测试用例文件
# 工程目录结构
.
├── data
│ └── params.csv
├── func
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── operation.py
└── testcase
├── __init__.py
└── test_add.py
测试准备
- 被测对象:
operation.py - 测试用例:
test_add.py - 测试数据:
params.csv
# operation.py 文件内容
def my_add(x, y):
result = x + y
return result
# test_add.py 文件内容
class TestWithCSV:
@pytest.mark.parametrize('x,y,expected', [[1, 1, 2]])
def test_add(self, x, y, expected):
assert my_add(int(x), int(y)) == int(expected)
# params.csv 文件内容
1,1,2
3,6,9
100,200,300Pytest 数据驱动结合 csv 文件
# 读取 data目录下的 params.csv 文件
import csv
def get_csv():
"""
获取csv数据
:return: 返回数据的结构:[[1, 1, 2], [3, 6, 9], [100, 200, 300]]
"""
with open('../data/params.csv', 'r') as file:
raw = csv.reader(file)
data = []
for line in raw:
data.append(line)
return data
#返回值为:[['1', '1', '2'], ['3', '6', '9'], ['100', '200', '300']]Pytest 结合数据驱动 json
json 文件介绍
- json 是 JS 对象
- 全称是 JavaScript Object Notation
- 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式
- json 结构
- 对象
{"key": value} - 数组
[value1, value2 ...]
- 对象
{
"name:": "hogwarts ",
"detail": {
"course": "python",
"city": "北京"
},
"remark": [1000, 666, 888]
}json 文件使用
- 查看 json 文件
- pycharm
- txt 记事本
- 读取 json 文件
- 内置函数 open()
- 内置库 json
- 方法:
json.loads()将json转为字典 - 方法:
json.dumps()
# 读取json文件内容
def get_json():
with open('demo.json', 'r') as f:
data = json.loads(f.read())
print(data)工程目录结构
- data 目录:存放 json 数据文件
- func 目录:存放被测函数文件
- testcase 目录:存放测试用例文件
# 工程目录结构
.
├── data
│ └── params.json
├── func
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── operation.py
└── testcase
├── __init__.py
└── test_add.py
测试准备
- 被测对象:
operation.py - 测试用例:
test_add.py - 测试数据:
params.json
import pytest
# operation.py 文件内容
def my_add(x, y):
result = x + y
return result
# test_add.py 文件内容
class TestWithJSON:
@pytest.mark.parametrize('x,y,expected', [[1, 1, 2]])
def test_add(self, x, y, expected):
assert my_add(int(x), int(y)) == int(expected)
# params.json 文件内容
{
"case1": [1, 1, 2],
"case2": [3, 6, 9],
"case3": [100, 200, 300]
}Pytest 数据驱动结合 json 文件
# 读取json文件
import json
def get_json():
"""
获取json数据
:return: 返回数据的结构:[[1, 1, 2], [3, 6, 9], [100, 200, 300]]
"""
with open('demo.json', 'r') as f:
data = json.loads(f.read())
#打印结果:{'case1': [1, 1, 2], 'case2': [3, 6, 9], 'case3': [100, 200, 300]}
print(data)
#打印结果为:dict_values([[1, 1, 2], [3, 6, 9], [100, 200, 300]])
print(data.values())
#返回结果为:[[1, 1, 2], [3, 6, 9], [100, 200, 300]]
return list(data.values())Fixture 用法
Fixture 特点及优势
- 1、命令灵活:对于 setup,teardown,可以不起这两个名字
- 2、数据共享:在 conftest.py 配置⾥写⽅法可以实现数据共享,不需要 import 导⼊。可以跨⽂件共享
- 3、scope 的层次及神奇的 yield 组合相当于各种 setup 和 teardown
- 4、实现参数化
Fixture 在自动化中的应用- 基本用法
- 场景:
测试⽤例执⾏时,有的⽤例需要登陆才能执⾏,有些⽤例不需要登陆。
setup 和 teardown ⽆法满⾜。fixture 可以。默认 scope(范围)function
- 步骤:
- 1.导⼊ pytest
- 2.在登陆的函数上⾯加@pytest.fixture()
- 3.在要使⽤的测试⽅法中传⼊(登陆函数名称),就先登陆
- 4.不传⼊的就不登陆直接执⾏测试⽅法。
Fixture 用法
Fixture 在自动化中的应用 - 作用域
Fixture 用法
Fixture 在自动化中的应用 - yield 关键字
- 场景:
你已经可以将测试⽅法【前要执⾏的或依赖的】解决了,
测试⽅法后销毁清除数据的要如何进⾏呢?
- 解决:
通过在 fixture 函数中加⼊ yield 关键字,yield 是调⽤第⼀次返回结果,
第⼆次执⾏它下⾯的语句返回。
- 步骤:
在@pytest.fixture(scope=module)。
在登陆的⽅法中加 yield,之后加销毁清除的步骤
Fixture 在自动化中的应用 - 数据共享
- 场景:
你与其他测试⼯程师合作⼀起开发时,公共的模块要在不同⽂件中,要在⼤家都访问到的地⽅。
- 解决:
使⽤ conftest.py 这个⽂件进⾏数据共享,并且他可以放在不同位置起着不同的范围共享作⽤。
- 前提:
- conftest ⽂件名是不能换的
- 放在项⽬下是全局的数据共享的地⽅
- 执⾏:
- 系统执⾏到参数 login 时先从本模块中查找是否有这个名字的变量什么的,
- 之后在 conftest.py 中找是否有。
- 步骤:
将登陆模块带@pytest.fixture 写在 conftest.py
Fixture 在自动化中的应用 - 自动应用
场景:
不想原测试⽅法有任何改动,或全部都⾃动实现⾃动应⽤,
没特例,也都不需要返回值时可以选择⾃动应⽤
解决:
使⽤ fixture 中参数 autouse=True 实现
步骤:
在⽅法上⾯加 @pytest.fixture(autouse=True)
Fixture 在自动化中的应用 -参数化
场景:
测试离不开数据,为了数据灵活,⼀般数据都是通过参数传的
解决:
fixture 通过固定参数 request 传递
步骤:
在 fixture 中增加@pytest.fixture(params=[1, 2, 3, ‘linda’])
在⽅法参数写 request,方法体里面使用 request.param 接收参数
Fixture 的用法总结
- 模拟 setup,teardown(一个用例可以引用多个 fixture)
- yield 的用法
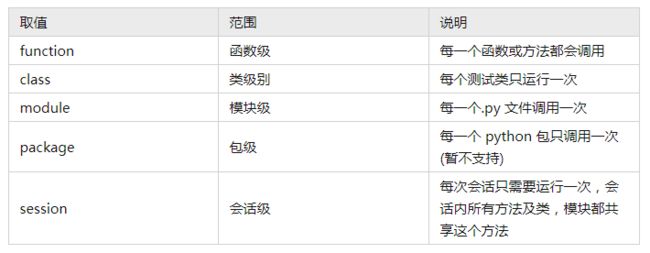
- 作用域( session,module, 类级别,方法级别 )
- 自动执行 (autouse 参数)
- conftest.py 用法,一般会把 fixture 写在 conftest.py 文件中(这个文件名字是固定的,不能改)
- 实现参数化
pytest.ini 配置
pytest.ini 是什么
- pytest.ini 是 pytest 的配置文件
- 可以修改 pytest 的默认行为
- 不能使用任何中文符号,包括汉字、空格、引号、冒号等等
pytest.ini
- 修改用例的命名规则
- 配置日志格式,比代码配置更方便
- 添加标签,防止运行过程报警告错误
- 指定执行目录
- 排除搜索目录
pytest 配置- 改变运行规则
;执行check_开头和 test_开头的所有的文件,后面一定要加*
python_files = check_* test_*
;执行所有的以Test和Check开头的类
python_classes = Test* Check*
;执行所有以test_和check_开头的方法
python_functions= test_* check_*pytest 配置- 添加默认参数
addopts = -v -s --alluredir=./resultspytest 配置- 指定/忽略执行目录
;设置执行的路径
;testpaths = bilibili baidu
;忽略某些文件夹/目录
norecursedirs = result logs datas test_demo*pytest 配置- 日志
配置参考链接:pytest logging 收集日志
总结 pytest.ini
- 修改用例的命名规则
- 配置日志格式,比代码配置更方便
- 指定执行目录
- 排除搜索目录
- 添加标签,防止运行过程报警告错误
- 添加默认参数
Pytest 插件开发
pytest 插件分类
- 外部插件:pip install 安装的插件
- 本地插件:pytest 自动模块发现机制(conftest.py 存放的就是本地插件)
- 内置插件:代码内部的_pytest 目录加载
Pytest 实用的插件介绍
pytest 常用的插件
pip install pytest-ordering 控制用例的执行顺序(重点)
pip install pytest-xdist 分布式并发执行测试用例(重点)
pip install pytest-dependency 控制用例的依赖关系 (了解)
pip install pytest-rerunfailures 失败重跑(了解)
pip install pytest-assume 多重较验(了解)
pip install pytest-random-order 用例随机执行(了解)
pip install pytest-html 测试报告(了解)pytest 执行顺序控制
场景:
对于集成测试,经常会有上下文依赖关系的测试用例。
比如 10 个步骤,拆成 10 条 case,这时候能知道到底执行到哪步报错。
用例默认执行顺序:自上而下执行
解决:
可以通过 setup,teardown 和 fixture 来解决。也可以使用对应的插件。
安装:pip install pytest-ordering
用法:@pytest.mark.run(order=2)
注意:多个插件装饰器(>2)的时候,有可能会发生冲突
pytest测试用例并行运行与分布式
Pytest 并行与分布式执行
场景 1:
测试用例 1000 条,一个用例执行 1 分钟,一个测试人员执行需要 1000 分钟。
通常我们会用人力成本换取时间成本,加几个人一起执行,时间就会 缩短。
如果 10 人一起执行只需要 100 分钟,这就是一种分布式场景。
场景 2:
假设有个报名系统,对报名总数统计,数据同时进行修改操作的时候有可能出现问题,
需要模拟这个场景,需要多用户并发请求数据。
解决:
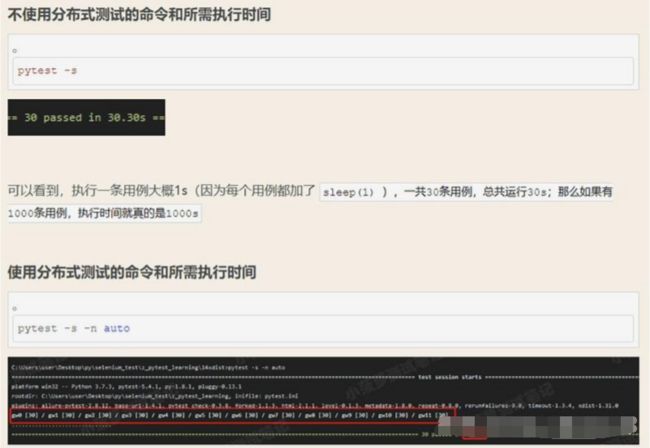
使用分布式并发执行测试用例。分布式插件:pytest-xdist
安装及运行:pip install pytest-xdist
注意: 用例多的时候效果明显,多进程并发执行,同时支持 allure
可以看到,最终运行时间只需要6s,我的电脑是真6核,假12核
-n auto:可以自动检测到系统的CPU核数;从测试结果来看,检测到的是逻辑处理器的数量,即假12核
使用auto等于利用了所有CPU来跑用例,此时CPU占用率会特别高
分布式执行测试用例原则
- 用例之间是独立的,不要有依赖关系
- 用例执行没有顺序,随机顺序都能正常执行
- 每个用例都能重复运行,运行结果不会影响其他用例
pytest 内置插件 hook 体系
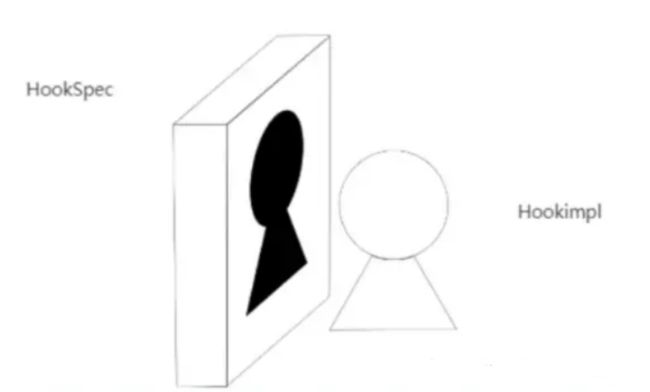
pytest hook 介绍
pytest hook 介绍
- 是个函数,在系统消息触时被系统调用
- 自动触发机制
- Hook 函数的名称是确定的
- pytest 有非常多的勾子函数
- 使用时直接编写函数体
pytest 执行顺序
pytest_addoption : 添加命令行参数,运时会先读取命令行参数
pytest_collection_modifyitems : 收集测试用例,收集之后(改编码,改执行顺序)
pytest_collection_finish:收集之后的操作
pytest_runtest_setup:在调用 pytest_runtest_call 之前调用
pytest_runtest_call:调用执行测试的用例
pytest_runtest_makereport:运行测试用例,返回setup,call,teardown的执行结果简单的例子
def pytest_runtest_setup(item):
# 执行测试用例前执行的setup方法
print("setting up", item)
def pytest_runtest_call(item):
# 调用执行测试的用例
print("pytest_runtest_call")
def pytest_runtest_teardown(item):
# 执行测试用例后执行的teardown
print("pytest runtest teardown",item)总结
- 1、hook 函数名字固定
- 2、hook 函数会被自动执行
- 3、执行是有先后顺序的
- 4、pytest 定义了很多 hook 函数,可以在不同阶段实现不同的功能
pytest 编写自己的插件
Pytest 编写插件 1 - 修改默认编码
pytest_collection_modifyitems 收集上来的测试用例实现定制化功能
解决问题:
- 自定义用例的执行顺序
- 解决编码问题 (中文的测试用例名称)
- 自动添加标签
Pytest 编写插件 1 - 修改默认编码
在conftest.py文件中加入以下代码:
含有中文的测试用例名称,改写编码格式:
def pytest_collection_modifyitems(session, config, items):
for item in items:
item.name = item.name.encode('utf-8').decode('unicode-escape')
item._nodeid = item.nodeid.encode('utf-8').decode('unicode-escape')Pytest 编写插件 2 - 添加命令行参数
def pytest_addoption(parser):
mygroup = parser.getgroup("hogwarts") #group 将下面所有的 option都展示在这个group下。
mygroup.addoption("--env", #注册一个命令行选项
default='test', # 参数的默认值
dest='env', # 存储的变量,为属性命令,可以使用Option对象访问到这个值,暂用不到
help='set your run env' # 帮助提示 参数的描述信息
)
@pytest.fixture(scope='session')
def cmdoption(request):
return request.config.getoption("--env")打包发布
打包发布到 pypi
- 发布到:www.pypi.org
- 代码上传到:github
打包项目构成
- 源码包
- setup.py
- 测试包
setup.py 配置
构建文件 setup.py 代码路径:
https://ceshiren.com/t/topic/14156
from setuptools import setup,find_packages
setup(
name='pytest_encode',
url='https://github.com/xxx/pytest-encode',
version='1.0',
author="xixi",
author_email='[email protected]',
description='set your encoding and logger',
long_description='Show Chinese for your mark.parametrize(). Define logger variable for getting your log',
classifiers=[# 分类索引 ,pip 对所属包的分类
'Framework :: Pytest',
'Programming Language :: Python',
'Topic :: Software Development :: Testing',
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.8',
],
license='proprietary',
packages = find_packages(), #['pytest_encode'],
keywords=[
'pytest', 'py.test', 'pytest_encode',
],
# 需要安装的依赖
install_requires=[
'pytest'
],
# 入口模块 或者入口函数
entry_points={
'pytest11': [
'pytest_encode = pytest_encode.main',
]
},
zip_safe=False
)打包命令
依赖包安装:
pip install setuptools python 的包管理工具,负责 安装和发布,尤其是安装拥有信赖关系的包。
pip install wheel 生成 *.whl 格式的安装包,本质上也是一个压缩包
打包命令:
python setup.py sdist bdist_wheel发布命令
python3 -m pip install --user --upgrade twine ## 安装 twine 工具
python3 -m twine upload --repository testpypi dist/* ## 上传代码最后:下面是配套学习资料,对于做【软件测试】的朋友来说应该是最全面最完整的备战仓库,这个仓库也陪伴我走过了最艰难的路程,希望也能帮助到你!【100%无套路免费领取】
![]()
软件测试面试小程序
被百万人刷爆的软件测试题库!!!谁用谁知道!!!全网最全面试刷题小程序,手机就可以刷题,地铁上公交上,卷起来!
涵盖以下这些面试题板块:
1、软件测试基础理论 ,2、web,app,接口功能测试 ,3、网络 ,4、数据库 ,5、linux
6、web,app,接口自动化 ,7、性能测试 ,8、编程基础,9、hr面试题 ,10、开放性测试题,11、安全测试,12、计算机基础
![]()