【云备份项目两万字总结】服务端篇 -----附源码
项目总结
- 整体回顾
- 逐步实现
-
- utill.hpp
- config.hpp
- data.hpp
- hot.hpp
- service.hpp
- 代码
整体回顾
服务端的目标是:
- 对客户端的请求进行处理
- 管理客户端上传的文件
于客户端进行数据交换,我们需要引入网络,所以我们引入第三方库----httplib.h库,搭建服务端。在进行网络通讯时,数据需要被系列化和反序列化,否则有数据丢失的风险,还需引入json库
在管理文件时,需要进行热点管理,把非热点文件进行压缩也需要引入第三方库 ----bundle.h,对文件进行压缩。
因此我们可以给服务端的各种功能实现划分模块,逐步实现服务端的整体功能。
要对上传的文件的文件进行管理,我们需要---- 文件管理模块,
同时,在将文件管理后,我们需要对其进行更一步的热带管理模块,热点管理的实现是在文件管理模块的实现之上的。
在本地测试好了上述两个模块后,我们可以进行网络通讯了。
需要一个网络通讯模块,通过其搭建我们的服务端,
能进行网络通讯后,还需要一个业务处理模块,处理客户端发送过来的请求,并予以响应。
逐步实现
先创建一个库,util.hpp工具库文件
里面有我们自己实现的几个util工具类。
工欲善其事,必先利其器。
utill.hpp
class FileUtil{}
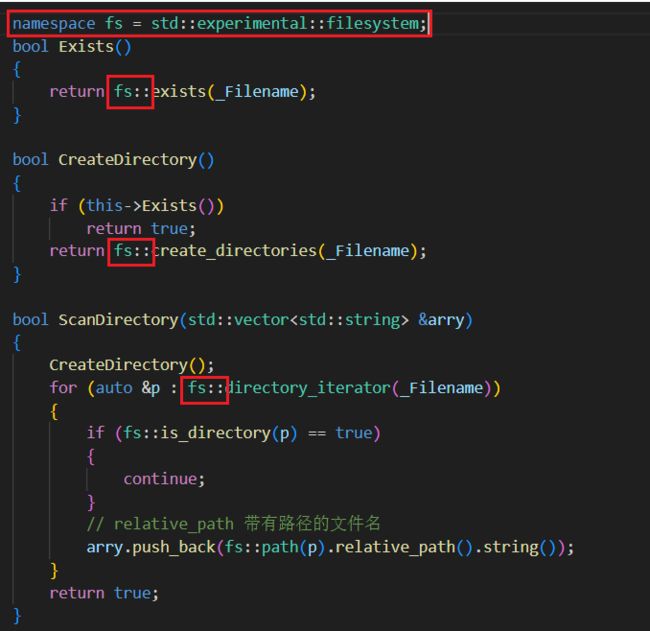
创建一个FileUtil 类,文件工具类,对系统的文件接口进行封装,便于我们对文件快捷操作,提供对文件的增删查改
class FileUtil{
private:
std::string _name;
public:
FileUtil(const std::string &name);
size_t FileSize();// 文件大小
time_t LastATime(); // 最后一次查看文件时间
time_t LastMTime(); // 最后一次修改文件的时间
std::string FileName(); //文件名字
bool GetPosLen(std::string *content, size_t pos, size_t len); //获取文件流pos 后len个长度的数据
bool GetContent(std::string *content); //获取文件内容
bool SetContent(std::strint *content); //写入文件
bool Compress(const std::string &packname); //压缩文件
bool UnCompress(const std::string &filename); //解压文件
bool Exists(); //判断文件是否存在
bool CreateDirectory(); //创建一个目录
bool ScanDirectory(std::vector<std::string> *arry); //查看目录下的文件内容
}
- FileUtile 工具提供了对文件的增删查改的功能,
- 也提供了对目录的查看功能,和创建目录的功能
其中,对文件压缩解压缩时,我们需要借用bundle.h库的函数,如何使用bundle库里的函数,在GitHub上有完整的教程。

同时,我们在查看目录时,需要借助filesystem库的使用,但是只有在c++17以上的版本才支持filesystem:
注意:
- 在Windows下,我们要选择了vs2017以上的版本
- 在Linux下,我们需要将gcc进行升级,7.3版本
class jsonutil
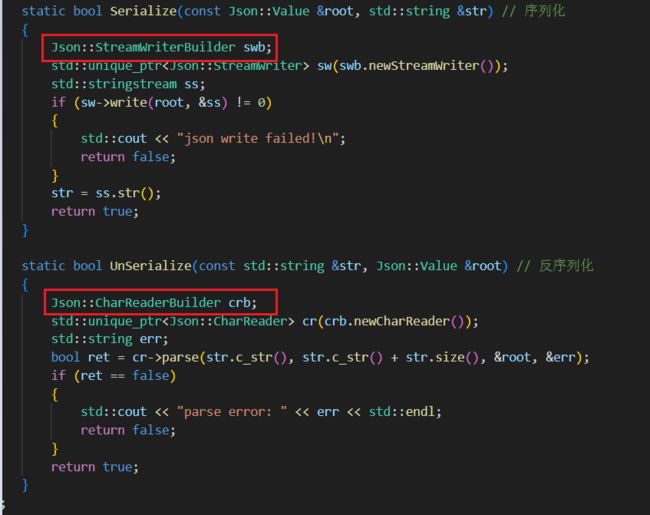
jsonutil类为网络通讯时的数据提供系列化和反序列化的功能,当然需要引入json库
至此,我们的基础工具已经完善,可以以此为基础,更一步完善服务端的功能。
config.hpp
项目配置信息的管理,启动项目时,会自动从 .conf文件加载项目的配置信息。需要修改部分内容时,不需要在代码上修改,只需要修改配置文件,然后重启服务器即可。
采用json 格式将配置信息存放在Cloud.conf中,当启动服务器时,由服务器从.conf文件中读取关键数据。
Cloud.conf 文件
{
“hot_time” : 30,
“server_port” : 9090,
“server_ip” : “1.1.1.1”,
“url_prefix” : “/download/”,
“arc_suffix” : “.lz”,
“pack_dir” : “./packdir/”,
“back_dir” : “./backdir/”,
“manager_file” : “./back.dat”
}
#define CONFIG_FILE "./cloud.conf"
class Config{
private:
time_t _hot_time;
int _server_port;
std::string _server_ip;
std::string _url_prefix;
std::string _arc_suffix;
std::string _pack_dir;
std::string _back_dir;
std::string _manager_file;//备份信息的配置管理
private:
static std::mutex _mutex;
static Config *_instance;
Config();
public:
bool ReadConfig(const std::string &filename);
int GetHotTime();
int GetServerPort();
std::string GetServerIp();
std::string GetURLPrefix();
std::string GetArcSuffix();
std::string GetPackDir();
std::string GetBackDir();
std::string GetManagerFile();
public:
static Config *GetInstance();
};
且,在实现配置信息类时,我们采取单例模式。
data.hpp
data.hpp是数据管理模块的主要部分。
要管理文件数据,就得先对文件的信息进行组织。
struct BackupInfo{}
typedef struct BackupInfo
{
bool pack_flag; // 文件是否被压缩的标识
time_t atime; // 最后一次查看时间
time_t mtime; // 最后一次修改时间
size_t fsize; //文件大小
std::string real_path; // 文件在服务器上的真实存储路径
std::string url; // 客户端访问文件时的请求url
std::string packpath; // 压缩包存储路径
bool FillBackupInfo(const std::string &realpath){}
}BackupInfo;
有了这些数据后,我们能准确的描述一个文件,并可以很好的进行管理。
上传的文件信息都以BackuoInfo的模式,以json的格式存储在backup_file中,当程序启动时,需要去文件加载数据到内存。同时,在新上传文件后,我们也需要将文件数据永久化存储到backup_file中。也需要支持对已经被管理的文件信息的增删查改(我们暂时不支持对信息的删除,现在只涉及最基础的功能实现,更多功能在已经构建好整个框架后会进一步实现)。
整个数据管理模块,也为让上层迅速查找文件的备份信息
class DateManager{}
class DataManager{
private:
FileUtil _backup_file;
pthread_rwlock_t _rwlock; // 读写锁
std::unordered_map<std::string, BackupInfo> _table;
public:
DataManager();
bool InitLoad();//初始化程序运行时从文件读取数据
bool Storage(); //每次有信息改变则需要持久化存储一次
bool Insert(const std::string &key, const BackupInfo &val);
bool Update(const std::string &key, const BackupInfo &val);
bool GetOneByURL(const std::string &key, BackupInfo *info);
bool GetOneByRealPath(const std::string &key, BackupInfo *info);
bool GetAll(std::vector<BackupInfo> *arry);
};
其具体实现内容在项目日志时已经说过,在此不再重复。
注意:
我们是对 _table 加上了rwlock 读写锁,因为这里的并发访问场景更多的是读读,读写场景,能提高服务器运行速度。
同时,加锁的原因是:
在httplib库中,使用了线程池的技术,当服务端accept一个客户端后,会另起一个线程在服务端处理请求,所以, _table属于临界资源,需要加锁保护。
我们的Storage()是覆盖式存储,是将 内存中 _table里的所有数据进行反序列,将 backup_file里的内容进行覆盖。
hot.hpp
热点管理模块就压要简单一点,很大一部分工作在数据管理模块已经完成。
循环遍历目录下的所有文件,然后通过文件最后一次修改时间来判断该文件是否为热点文件,然后压缩至指定目录即可。
extern cloud::DataManager *_data;
class HotManager{
private:
std::string _back_dir;
std::string _pack_dir;
std::string _pack_suffix;
time_t _hot_time;
public:
HotManager();
bool HotJudge(const std::string &file);
bool RunModule();
};
因为数据管理是要在多个模块中访问的,因此将其作为全局数据定义。
service.hpp
云备份项目中 ,业务处理模块是针对客户端的业务请求进行处理,并最终给与响应。而整个过程中包含以下要实现
的功能:
- 借助网络通信模块httplib库搭建http服务器与客户端进行网络通信
- 针对收到的请求进行对应的业务处理并进行响应(文件上传,列表查看,文件下载(包含断点续传))
响应给客户端的 rsp在之前的项目日志里也有描述。
class Service{
private:
int _server_port;
std::string _server_ip;
std::string _url_prefix;
httplib::Server _srv;
private:
static void Upload(const httplib::Request &req, httplib::Response &rsp);
static void List(const httplib::Request &req, httplib::Response &rsp);
static void Download(const httplib::Request &req,httplib::Response &rsp);
public:
Service();
bool RunModule();
}
注意:
业务处理的回调函数没有传入参数的地方(大概是因为,回调函数的模板被固定化了),因此无法直接访问外部的数据管理模块数据,因此将数据管理模块的对象定义为全局数据,在这里声明一下,就可以在任意位置访问了,且回调函数必须为静态函数,(类内函数成员变量会隐藏一个this指针)。
文件上传函数和文件列表查看函数都按照思路来写。
文件下载函数有部分事项需要注意:
1 . 服务端要判断是否需要进行断点重传,判断条件:
有If-Range字段且,这个字段的值与请求文件的最新etag一致则符合断点续传
也就是说需要在客户端请求里有If-Range字段,且在这段时间内,文件的数据内容没有被修改过。
这是Download 函数正常的响应rsp:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Length: 100000
ETags: "filename-size-mtime一个能够唯一标识文件的数据"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Accept-Ranges报头:
服务器使用 HTTP 响应头 Accept-Ranges 标识自身支持范围请求 (partial
requests)。字段的具体值用于定义范围请求的单位。
当浏览器发现Accept-Ranges头时,可以尝试继续中断了的下载,而不是重新开始。
这是Download执行断点续传的rsp:
HTTP/1.1 206 Partial Content
Content-Length:
Content-Range: bytes 89-999/100000
Content-Type: application/octet-stream
ETag: "inode-size-mtime一个能够唯一标识文件的数据"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
httplib内部实现了对于区间请求也就是断点续传请求的处理
只需要我们用户将文件所有数据读取到rsp.body中,它内部会自动根据请求
区间,从body中取出指定区间数据进行响应,并且会自动填充rsp内容。
代码
代码里边会有博主的一些思考和理解,各位大佬见笑了
util.hpp
#pragma once
#include data.hpp
#pragma once
#include
}
bool insert(const BackupInfo &bf)
{
// ? 我自己的思路 --------- 传入一个 filename ,然后在insert函数中,自己填充BackupInfo数据 ,在插入进_table中 ----》 可以减少上层的工作量 (我觉得)
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&_rwlock);
std::string url = bf.url;
_table[url] = bf;
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);
Storage();
return true;
}
bool update(const BackupInfo &bf)
{
// ? 问题同 insert函数
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&_rwlock);
std::string url = bf.url;
_table[url] = bf;
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);
Storage();
return true;
}
bool GetOneByURL(const std::string &url, BackupInfo *info)
{
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&_rwlock);
auto it = _table.find(url);
if (it != _table.end())
{
*info = it->second;
}
else
{
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);
return false;
}
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);
return true;
}
bool GetOneByRealpath(const std::string &realpath, BackupInfo *info)
{
// std::cout<<"准备拿锁"<
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&_rwlock);
// std::cout<<"拿到锁了"<
std::unordered_map<std::string, BackupInfo>::iterator it = _table.begin();
// std::cout<<"找到初始位置了"<
for (; it != _table.end(); ++it)
{
if (it->second.real_path == realpath)
{
*info = it->second;
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);
return true;
}
}
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);
return false;
}
void GetAll(std::vector<BackupInfo> *arry)
{
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&_rwlock);
for (auto it = _table.begin(); it != _table.end(); ++it)
{
arry->push_back(it->second);
}
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);
}
bool Storage() // 每次有信息改变则需要持久化存储一次
{
// 1. 获取所有数据
std::vector<BackupInfo> arry;
this->GetAll(&arry);
// 2. 添加到Json::Value
Json::Value root;
for (int i = 0; i < arry.size(); i++)
{
Json::Value item;
item["pack_flag"] = arry[i].pack_flag;
item["fsize"] = (Json::Int64)arry[i].fsize;
item["atime"] = (Json::Int64)arry[i].atime;
item["mtime"] = (Json::Int64)arry[i].mtime;
item["real_path"] = arry[i].real_path;
item["packpath"] = arry[i].packpath;
item["url"] = arry[i].url;
root.append(item); // 添加数组元素
}
// 3. 对Json::Value序列化
std::string body;
jsonutil::Serialize(root, body);
// 4. 写文件
FileUtil fu(_backup_file);
fu.SetContent(body);
return true;
}
bool initload() 初始化程序运行时从文件读取数据 -------> 为什么不从备份目录中提取数据? --- 备份目录下的文件会被压缩至压缩目录
{
// 1. 从文件中读取数据
// printf("准备读数据\n");
FileUtil ft(_backup_file);
// printf("读数据成功\n");
if (ft.Exists() == false) // 如果文件不存在,说明还没有数据存入数据文件,也就是还没有创建数据文件
{
// printf("文件不存在\n");
return true;
}
std::string str;
// printf("准备获得文\n");
ft.GetContent(str);
// printf("获得文成功\n");
// 2. 将数据反序列化
// printf("准备序列化\n");
Json::Value root;
jsonutil::UnSerialize(str, root);
// printf("反序列化成功\n");
// 3. 将数据插入_table
// printf("准备插入数据:%d\n",root.size());
for (int i = 0; i < root.size(); i++)
{
// std::cout<<"开始插入数据"<
BackupInfo info;
info.pack_flag = root[i]["pack_flag"].asBool();
info.fsize = root[i]["fsize"].asInt64();
info.atime = root[i]["atime"].asInt64();
info.mtime = root[i]["mtime"].asInt64();
info.packpath = root[i]["packpath"].asString();
info.real_path = root[i]["real_path"].asString();
info.url = root[i]["url"].asString();
// std::cout<<"插入:"<
insert(info);
}
return true;
}
~DateManager()
{
pthread_rwlock_destroy(&_rwlock);
}
};
}
hot.hpp
#pragma once
#include
// 2. 判断文件是否为热点文件
// std::cout<
for (const auto &it : arry)
{
// std::cout<<"开始遍历判断是否为热点文件"<
// std::cout<
if (HotJudge(it) == false)
{
// std::cout<<"不是热点文件"<
continue;
}
// 获取文件的备份信息
BackupInfo info;
// std::cout<<"准备执行HOT里的GetonebyRealpath"<
if (_data->GetOneByRealpath(it, &info) == false)
{
// std::cout<<"准备执行fillBackupInfo"<
info.FillBackupInfo(it);
}
// 3. 对非热点文件进行压缩
FileUtil tmp(it);
tmp.Compress(info.packpath);
// 4. 删除源文件,修改备份信息
tmp.Remove();
info.pack_flag = true;
_data->update(info);
}
// std::cout<<"准备进入睡眠"<
usleep(1000);
}
}
};
}
service.hpp
#pragma once
#include Download ";
ss << "Download
";
for (auto &a : arry)
{
ss << "";
std::string filename = FileUtil(a.real_path).Filename();
ss << "" << filename << " ";
ss << "" << totimestring(a.atime) << " ";
ss << "" << a.fsize / 1024 << "k"
<< " ";
ss << " ";
}
ss << "
";
//std::cout << "文件信息填充完毕,开始填写rsq" << std::endl;
// 3. 填充rsp响应
rsp.body = ss.str();
rsp.status = 200;
rsp.set_header("Content-Type", "text/html");
printf("showlist请求完毕\n");
return;
}
};
}