Android换肤框架原理解析,实现皮肤随心换
前言
首先须知道系统资源如何加载,怎么拦截并替换资源,以下都有讲解
xml的View怎么解析的
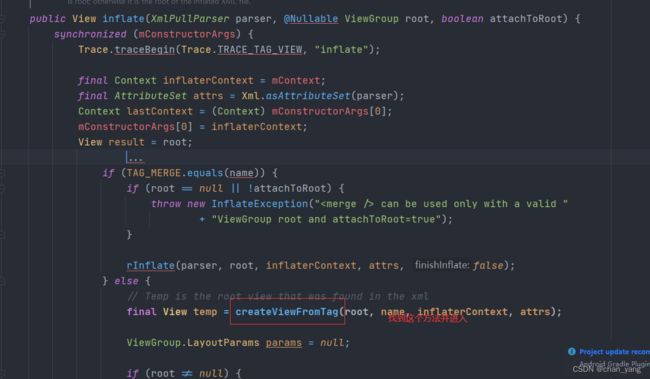
从setContentView进入
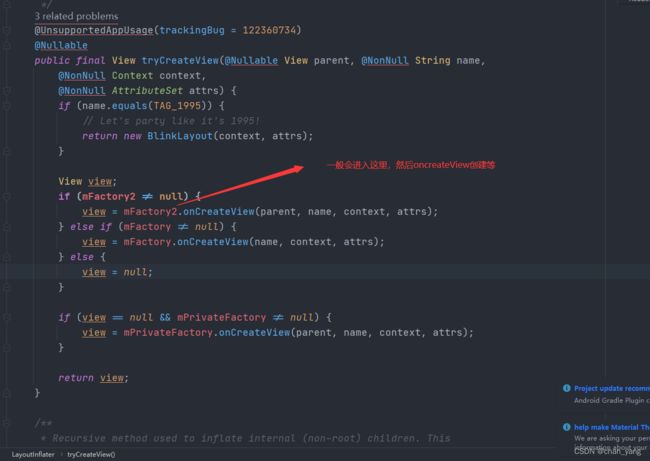
一路走到下图这里
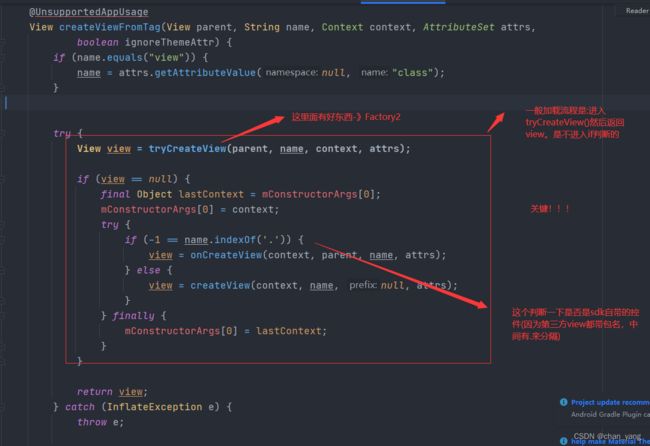
找到createViewFromTag
操作几乎都在这里
进入tryCreateView()看看
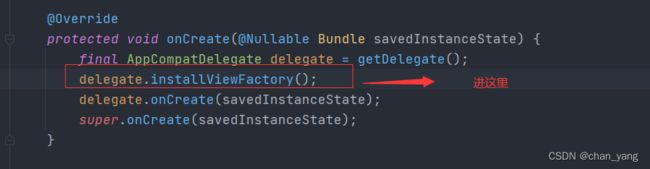
那么mFactory2在哪里初始化了?
让我们进入oncreate
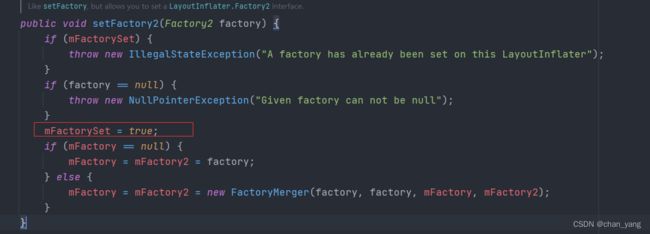
那么如何拦截系统的创建流程?
直接使用系统的setFactory2方法
public class Factory2Activity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// 必须在 super 之前调用
//name:view的名字 如 Textview,ListView
//attrs:view里面的参数 如 宽高等
LayoutInflater.from(this).setFactory2(new LayoutInflater.Factory2() {
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@Nullable View parent, @NonNull String name, @NonNull Context context,
@NonNull AttributeSet attrs) {
return null;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@NonNull String name, @NonNull Context context, @NonNull AttributeSet attrs) {
return null;
}
});
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 如果想在super之后调用,需要反射 设置mFactorySet = false;
setContentView(R.layout.activity_factory2);
}
}
这个方法必须在super之前调用,因为setFactory2只能执行一次
如果原来界面上只有一个Textview,经过我下面操作会变成一个Button
LayoutInflater.from(this).setFactory2(new LayoutInflater.Factory2() {
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@Nullable View parent, @NonNull String name, @NonNull Context context,
@NonNull AttributeSet attrs) {
if (TextUtils.equals(name, "TextView")) {
Button btn = new Button(Factory2Activity.this);
btn.setText("我是一个按钮");
return btn;
}
return null;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@NonNull String name, @NonNull Context context, @NonNull AttributeSet attrs) {
return null;
}
});
拦截后怎么做
因为这不能每一个activity里面都写一段,写在baseActivity里也比较low。况且如果把功能抽出来让别人使用也不方便。
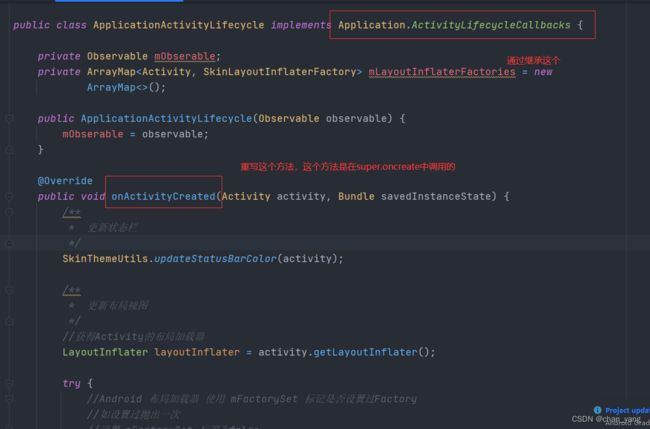
答案:使用lifecycle实现Aop切面编程,来重写系统的创建过程的代码(复制)
然后只要activity进入super.onCreate方法就会执行我们的onActivityCreated()。接下来看下onActivityCreated里的代码。
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(Activity activity, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
/**
* 更新状态栏
*/
SkinThemeUtils.updateStatusBarColor(activity);
/**
* 更新布局视图
*/
//获得Activity的布局加载器
LayoutInflater layoutInflater = activity.getLayoutInflater();
try {
//因为需在super之前调用,但现在在之后了,需要反射修改一下属性
//设置 mFactorySet 标签为false
Field field = LayoutInflater.class.getDeclaredField("mFactorySet");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.setBoolean(layoutInflater, false);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//使用factory2 设置布局加载工程
SkinLayoutInflaterFactory skinLayoutInflaterFactory = new SkinLayoutInflaterFactory
(activity);
LayoutInflaterCompat.setFactory2(layoutInflater, skinLayoutInflaterFactory);
mLayoutInflaterFactories.put(activity, skinLayoutInflaterFactory);
mObserable.addObserver(skinLayoutInflaterFactory);
}
然后进入SkinLayoutInflaterFactory。这下面的onCreateView方法就是系统tryCreateView()里mFactory2.onCreateview的onCreateview
public class SkinLayoutInflaterFactory implements LayoutInflater.Factory2, Observer {
private static final String[] mClassPrefixList = {
"android.widget.",
"android.webkit.",
"android.app.",
"android.view."
};
//记录对应VIEW的构造函数
private static final Class<?>[] mConstructorSignature = new Class[]{
Context.class, AttributeSet.class};
private static final HashMap<String, Constructor<? extends View>> mConstructorMap =
new HashMap<String, Constructor<? extends View>>();
// 当选择新皮肤后需要替换View与之对应的属性
// 页面属性管理器
private SkinAttribute skinAttribute;
// 用于获取窗口的状态框的信息
private Activity activity;
public SkinLayoutInflaterFactory(Activity activity) {
this.activity = activity;
skinAttribute = new SkinAttribute();
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(View parent, String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
//换肤就是在需要时候替换 View的属性(src、background等)
//所以这里创建 View,从而修改View属性
View view = createSDKView(name, context, attrs);
if (null == view) {
view = createView(name, context, attrs);
}
//这就是我们加入的逻辑
if (null != view) {
//加载属性
skinAttribute.look(view, attrs);
}
return view;
}
private View createSDKView(String name, Context context, AttributeSet
attrs) {
//如果包含 . 则不是SDK中的view 可能是自定义view包括support库中的View
if (-1 != name.indexOf('.')) {
return null;
}
//不包含就要在解析的 节点 name前,拼上: android.widget. 等尝试去反射
for (int i = 0; i < mClassPrefixList.length; i++) {
View view = createView(mClassPrefixList[i] + name, context, attrs);
if (view != null) {
return view;
}
}
return null;
}
private View createView(String name, Context context, AttributeSet
attrs) {
Constructor<? extends View> constructor = findConstructor(context, name);
try {
return constructor.newInstance(context, attrs);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
return null;
}
private Constructor<? extends View> findConstructor(Context context, String name) {
Constructor<? extends View> constructor = mConstructorMap.get(name);
if (constructor == null) {
try {
Class<? extends View> clazz = context.getClassLoader().loadClass
(name).asSubclass(View.class);
constructor = clazz.getConstructor(mConstructorSignature);
mConstructorMap.put(name, constructor);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
return constructor;
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
return null;
}
//如果有人发送通知,这里就会执行
@Override
public void update(Observable o, Object arg) {
SkinThemeUtils.updateStatusBarColor(activity);
skinAttribute.applySkin();
}
}
收集view以及属性
进入skinAttribute.look(view, attrs)来进行一个属性的收集
//记录下一个VIEW身上哪几个属性需要换肤textColor/src
public void look(View view, AttributeSet attrs) {
List<SkinPair> mSkinPars = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < attrs.getAttributeCount(); i++) {
//获得属性名 如 textColor background
String attributeName = attrs.getAttributeName(i);
if (mAttributes.contains(attributeName)) {
// 获取属性值
String attributeValue = attrs.getAttributeValue(i);
// 比如color 以#开头表示写死的颜色 不可用于换肤
if (attributeValue.startsWith("#")) {
continue;
}
int resId;
// 以 ?开头的表示使用 属性
if (attributeValue.startsWith("?")) {
int attrId = Integer.parseInt(attributeValue.substring(1));
resId = SkinThemeUtils.getResId(view.getContext(), new int[]{attrId})[0];
} else {
// 正常以 @ 开头
resId = Integer.parseInt(attributeValue.substring(1));
}
SkinPair skinPair = new SkinPair(attributeName, resId);
mSkinPars.add(skinPair);
}
}
if (!mSkinPars.isEmpty() || view instanceof SkinViewSupport) {
SkinView skinView = new SkinView(view, mSkinPars);
// 如果选择过皮肤 ,调用 一次 applySkin 加载皮肤的资源
skinView.applySkin();
mSkinViews.add(skinView);
}
}
创建皮肤包
皮肤包其实就是apk。
里面只放了一些资源
如何使用皮肤包(插件化)
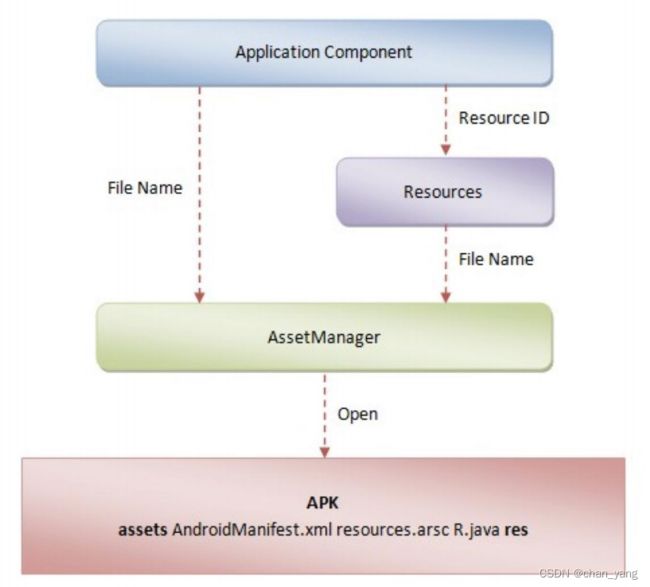
系统的资源如何加载
一般这样来拿资源(Resources)
还有AsserManager(加载最后走的都是AsserManager)
这里放上AsserManager创建流程(有需要了解可根据下方的方法来看)
performLaunchActivity @ActivityThread.java --> ContextImpl appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r); --> ContextImpl.createActivityContext --> context.setResources --> createResources --> ResourcesImpl resourcesImpl = findOrCreateResourcesImplForKeyLocked(key); --> impl = createResourcesImpl(key); --> final AssetManager assets = createAssetManager(key); --> builder.addApkAssets(loadApkAssets(key.mResDir, false /*sharedLib*/,false /*overlay*/));
AsserManager加载资源默认传入的资源路径是key.mResDir(app下面的res),当我们把这个资源路径改成皮肤包资源路径,那不就加载我们皮肤包的资源了(通过Hook实现)
使用自己创建的AsserManager来加载资源
/**
* 记载皮肤并应用
*
* @param skinPath 皮肤路径 如果为空则使用默认皮肤
*/
public void loadSkin(String skinPath) {
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(skinPath)) {
//还原默认皮肤
SkinPreference.getInstance().reset();
SkinResources.getInstance().reset();
} else {
try {
//反射创建AssetManager 与 Resource
AssetManager assetManager = AssetManager.class.newInstance();
//资源路径设置 目录或压缩包
Method addAssetPath = assetManager.getClass().getMethod("addAssetPath",
String.class);
addAssetPath.invoke(assetManager, skinPath);
//宿主app的 resources;
Resources appResource = mContext.getResources();
//根据当前的设备显示器信息 与 配置(横竖屏、语言等) 创建Resources
Resources skinResource = new Resources(assetManager, appResource.getDisplayMetrics(),
appResource.getConfiguration());
//获取外部Apk(皮肤包) 包名
PackageManager mPm = mContext.getPackageManager();
PackageInfo info = mPm.getPackageArchiveInfo(skinPath, PackageManager.GET_ACTIVITIES);
String packageName = info.packageName;
SkinResources.getInstance().applySkin(skinResource, packageName);
//记录路径
SkinPreference.getInstance().setSkin(skinPath);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//通知采集的View 更新皮肤
//被观察者改变 通知所有观察者
setChanged();
notifyObservers(null);
}
这里为什么使用自己创建的AsserManager?
因为防止资源冲突()⬇
当点击换肤按钮后,通过上方代码,然后通知观察者执行下方代码
/**
* 对一个View中的所有的属性进行修改
*/
public void applySkin() {
applySkinSupport();
for (SkinPair skinPair : skinPairs) {
Drawable left = null, top = null, right = null, bottom = null;
switch (skinPair.attributeName) {
case "background":
Object background = SkinResources.getInstance().getBackground(skinPair
.resId);
//背景可能是 @color 也可能是 @drawable
if (background instanceof Integer) {
view.setBackgroundColor((int) background);
} else {
ViewCompat.setBackground(view, (Drawable) background);
}
break;
case "src":
background = SkinResources.getInstance().getBackground(skinPair
.resId);
if (background instanceof Integer) {
((ImageView) view).setImageDrawable(new ColorDrawable((Integer)
background));
} else {
((ImageView) view).setImageDrawable((Drawable) background);
}
break;
case "textColor":
((TextView) view).setTextColor(SkinResources.getInstance().getColorStateList
(skinPair.resId));
break;
case "drawableLeft":
left = SkinResources.getInstance().getDrawable(skinPair.resId);
break;
case "drawableTop":
top = SkinResources.getInstance().getDrawable(skinPair.resId);
break;
case "drawableRight":
right = SkinResources.getInstance().getDrawable(skinPair.resId);
break;
case "drawableBottom":
bottom = SkinResources.getInstance().getDrawable(skinPair.resId);
break;
default:
break;
}
if (null != left || null != right || null != top || null != bottom) {
((TextView) view).setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds(left, top, right,
bottom);
}
}
}
//通过下方代码来获取资源ID来进行上方代码的设置资源ID
//思路:首先找到app的资源ID,然后拿到资源name ,再通过name拿到皮肤包资源ID
// app的resId
String resName=mAppResources.getResourceEntryName(resId); // 通过app的resId 找到 resName
String resType=mAppResources.getResourceTypeName(resId);// 通过app的resId 找到 类型,layout、drawable
// 获取对应皮肤包的资源Id
int skinId=mSkinResources.getIdentifier(resName,resType,mSkinPkgName)





![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-WA7fxfgp-1652971781548)(C:\Users\Admin\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20220519213851513.png)]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/7aa0aad068fd489ba3b6e86df0f6dffa.jpg)