算法训练营day14|二叉树层序遍历10题,226.翻转二叉树,101.对称二叉树
1.知识点
二叉树的层序遍历模板比较固定
递归模板
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/3
* @Description todo
*/
public class ErChaShuDeCengXuBianLi_MoBan_DiGui {
/**
* 层序遍历:方法1-递归
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public List> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList> result = new ArrayList<>();
int depth = 0;
order(root, result, depth);
return result;
}
private void order(TreeNode cur, ArrayList> result, int depth) {
if (cur == null) {
return;
}
if (result.size() == depth) {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
result.add(list);
}
result.get(depth).add(cur.val);
order(cur.left, result, depth + 1);
order(cur.right, result, depth + 1);
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
bfs+队列模板
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/3
* @Description todo
*/
public class ErChaShuDeCengXuBianLi_MoBan_DuiLie {
/**
* 方法1:层序遍历-bfs+队列
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public List> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return result;
}
LinkedList que = new LinkedList<>();
// 加入根节点
que.offerLast(root);
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
// 当前队列中的元素个数就是这一层的节点个数
int size = que.size();
// list保存这层所有的节点
ArrayList itmList = new ArrayList<>();
// 依次处理当前层的所有节点
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
// 将本节点加入到本层的list中
TreeNode tmpNode = que.removeFirst();
itmList.add(tmpNode.val);
// 将左右孩子加入到队列方便下一层处理
if (tmpNode.left != null) {
que.offerLast(tmpNode.left);
}
if (tmpNode.right != null) {
que.offerLast(tmpNode.right);
}
}
result.add(itmList);
}
return result;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
2.刷题
102.二叉树的层序遍历
LeetCode链接 102. 二叉树的层序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述
方法1:bfs+队列
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/4
* @Description todo
*/
public class ErChaShuDeCengXuBianLi102_2 {
/**
* 方法1:bfs-队列
* 1.队列中维护的是每层的所有节点
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public List> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return result;
}
ArrayDeque deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque.addLast(root);
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
//每层中有多少个节点就是size的大小
int size = deque.size();
ArrayList levelList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
//元素出队列,并加入到levelList中
TreeNode treeNode = deque.removeFirst();
levelList.add(treeNode.val);
if (treeNode.left != null) {
deque.addLast(treeNode.left);
}
if (treeNode.right != null) {
deque.addLast(treeNode.right);
}
}
result.add(levelList);
}
return result;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
107.二叉树的层序遍历II
LeetCode链接 107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述
方法1:bfs+队列
将102题目中得到的数组从后往前遍历就是本题的结果
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/4
* @Description todo
*/
public class ErChaShuDeCengXuBianLiII107_2 {
/**
* 方法1:bfs-队列
* 1.获取从上向下遍历的结果,保存在list中
* 2.翻转list的元素位置即可
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public static List> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
//1.创建一个队列用来存放二叉树节点
LinkedList que = new LinkedList<>();
if (root != null) {
que.push(root);
}
//2.创建一个list用来存放最后的结果
ArrayList> result = new ArrayList<>();
//3.动态处理que中的元素
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
//3.1获取当前que中的元素个数(二叉树这层的元素个数)
//因为que.size是动态变化的,要用固定大小size,不能用que.size
int size = que.size();
//3.2创建vec列表用来保存这层的元素
ArrayList leveList = new ArrayList<>();
//3.3通过for循环来遍历每一层中的所有元素
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
//3.3.1出队列
TreeNode node = que.removeFirst();
//3.3.2此元素加入到vec中
leveList.add(node.val);
//3.3.3左节点入队
if (node.left != null) {
que.addLast(node.left);
}
//3.3.4右节点入队
if (node.right != null) {
que.addLast(node.right);
}
}
//3.4将这层元素vec的list加入到结果中
result.add(leveList);
}
//4.翻转结果,并返回
Collections.reverse(result);
return result;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
199.二叉树的右视图
LeetCode链接 199. 二叉树的右视图 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述
方法1:bfs+队列
层序遍历的时候,判断是否遍历到单层的最后面的元素,如果是,就放进result数组中,随后返回result就可以了。
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/4
* @Description todo
*/
public class ErChaShuDeYouShiTu199_2 {
/**
* 方法1:bfs-队列
* 1.将树每层的最后一个节点取到即可
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public static List rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
LinkedList que = new LinkedList<>();
if (root != null) {
que.push(root);
}
ArrayList result = new ArrayList<>();
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
int size = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = que.removeFirst();
// 将每一层的最后元素放入result数组中
if (i == (size - 1)) {
result.add(node.val);
}
if (node.left != null) {
que.addLast(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
que.addLast(node.right);
}
}
}
return result;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
637.二叉树的层平均值
LeetCode链接 637. 二叉树的层平均值 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述
方法1:bfs+队列
层序遍历的时候计算出每层的平均值即可
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/4
* @Description todo
*/
public class ErChaShuDeCengPingJunZhi637_2 {
/**
* 方法1:bfs+队列
* 层序遍历的时候,计算每一层的平均值即可
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public static List averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {
LinkedList que = new LinkedList<>();
if (root != null) {
que.push(root);
}
ArrayList result = new ArrayList<>();
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
int size = que.size();
double sum = 0;// 统计每一层的和
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = que.removeFirst();
sum += node.val;
if (node.left != null) {
que.addLast(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
que.addLast(node.right);
}
}
result.add(sum / size); // 将每一层均值放进结果集
}
return result;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
429.N叉树的层序遍历
LeetCode链接 429. N 叉树的层序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述
方法1:bfs+队列
不同于二叉树的层序遍历的是:N叉树一个节点有多个孩子,而遍历流程和模板都和二叉树是一样的
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/4
* @Description todo
*/
public class NChaShuDeCengXuBianLi429_2 {
/**
* 方法1:bfs-队列
* 1.二叉树是:处理当前节点的时候,把当前节点的左右子树加入队列中
* 2.N叉树是:处理当前节点的时候,把当前节点的children都加入到队列中
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public List> levelOrder(Node root) {
List> list = new ArrayList<>();
Deque que = new LinkedList<>();
if (root == null) {
return list;
}
que.offerLast(root);
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
int levelSize = que.size();
List levelList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
Node poll = que.pollFirst();
levelList.add(poll.val);
List children = poll.children;
if (children == null || children.size() == 0) {
continue;
}
// 获取当前节点的所有子节点,并加入到队列中
for (Node child : children) {
if (child != null) {
que.offerLast(child);
}
}
}
list.add(levelList);
}
return list;
}
class Node {
public int val;
public List children;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
}
}
515.在每个数行中找到最大值
LeetCode链接 515. 在每个树行中找最大值 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述
方法1:bfs+队列
还是经典的层序遍历,记录每一层的最大值即可
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/4
* @Description todo
*/
public class ZaiMeiGeShuHangZhongZhaoZuiDaZhi515_2 {
/**
* 方法1:bfs+队列
* 层序遍历每行时,记录最大值
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public static List largestValues(TreeNode root) {
LinkedList que = new LinkedList<>();
if (root != null) {
que.push(root);
}
ArrayList result = new ArrayList<>();
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
int size = que.size();
// 取每一层的最大值
int maxValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = que.removeFirst();
maxValue = Math.max(node.val, maxValue);
if (node.left != null) {
que.addLast(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
que.addLast(node.right);
}
}
result.add(maxValue);
// 把最大值放进数组
}
return result;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
方法2:dfs+递归
dfs在递归的时候,传递一个当前层深度,使用HashMap维护一个所在深度的节点最大值.
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/4
* @Description todo
*/
public class ZaiMeiGeShuHangZhongZhaoZuiDaZhi515_3 {
/**
* 记录每层对应的最大值,记录最大深度
*/
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
Integer maxDepth = 0;
/**
* 方法2:dfs+递归
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public List largestValues(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList result = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(root, 1);
// 从map中获取每层的最大深度
for (int i = 1; i <= maxDepth; i++) {
result.add(map.get(i));
}
return result;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode node, int depth) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
// 更新最大深度
maxDepth = Math.max(depth, maxDepth);
// 更新每层的最大值
map.put(depth, Math.max(node.val, map.getOrDefault(depth, Integer.MIN_VALUE)));
// 左右递归
dfs(node.left, depth + 1);
dfs(node.right, depth + 1);
}
public static class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
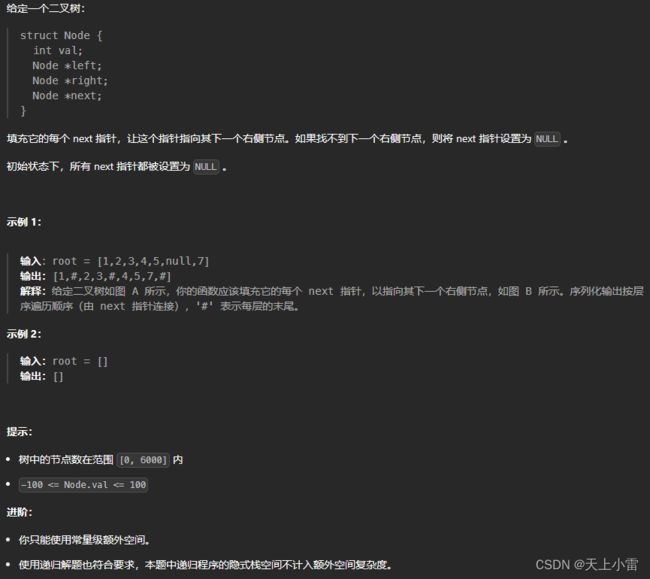
116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
LeetCode链接 116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述
方法1:bfs+队列
能拿到一层所有的节点,就可以将一层所有的节点连接起来
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.LinkedList;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/4
* @Description todo
*/
public class TianChongMeiGeJieDianDeXiaYiGeYouCeJieDianZhiZhen116_2 {
/**
* 方法1:bfs-层序遍历
* 1.看见题目中画出的箭头,应该要想到是层序遍历
* 能拿到一层所有的节点,就可以将一层所有的节点连接起来
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public Node connect(Node root) {
LinkedList queue = new LinkedList<>();
if (root != null) {
queue.addLast(root);
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//当前队列的大小就是本层二叉树所有节点的个数
int size = queue.size();
//当前节点的前一个节点
Node nodePre = null;
//当前节点
Node node;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
//遍历头节点的情况:
if (i == 0) {
nodePre = queue.removeFirst();
node = nodePre;
}
//从第二个节点往后:
else {
//当前节点
node = queue.removeFirst();
//设置上一个节点的next值为当前节点
nodePre.next = node;
//上一个节点后移
nodePre = node;
}
// 左右子节点入队列
if (node.left != null) {
queue.addLast(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.addLast(node.right);
}
//最后一个节点的next设置为null
nodePre.next = null;
}
}
return root;
}
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node next;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
next = _next;
}
}
}
方法2:迭代解法
去串联树中的节点,有两种连接方式
1.两个串联的节点都有一个共同的父节点,通过父节点就可以将两个子节点串联起来,即:
tmp.left.next=tmp.right
2.两个串联的节点的父节点不同,可以先将上一层串联好,再通过父节点的next找到被串联的节点,即:
tmp.right.next=tmp.next.left
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/4
* @Description todo
*/
public class TianChongMeiGeJieDianDeXiaYiGeYouCeJieDianZhiZhen116_3 {
/**
* 方法2:迭代解法
* 去串联树中的节点,有两种连接方式
* 1.两个串联的节点都有一个共同的父节点,通过父节点就可以将两个子节点串联起来,即:
* tmp.left.next=tmp.right
* 2.两个串联的节点的父节点不同,可以先将上一层串联好,再通过父节点的next找到被串联的节点,即:
* tmp.right.next=tmp.next.left
* 参考:https://leetcode.cn/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/solutions/100099/dong-hua-yan-shi-san-chong-shi-xian-116-tian-chong/
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return root;
}
Node pre = root;
// 保持pre在叶子节点是上一行
while (pre.left != null) {
// 开始处理当前行
Node tmp = pre;
// 从左往右处理节点
while (tmp != null) {
// 将tmp节点的左节点和右节点串联起来
tmp.left.next = tmp.right;
// tmp.next不为空,说明上一层已经把tmp.next串联好了
// 将tmp节点的右孩子和tmp.next的左孩子串联起来
if (tmp.next != null) {
tmp.right.next = tmp.next.left;
}
// 继续往右处理
tmp = tmp.next;
}
// 开始处理下一行
pre = pre.left;
}
return root;
}
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node next;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
next = _next;
}
}
}
方法3:dfs+递归
以root为起点,left不断的往右走,right不断的往左走,从而将整个纵深这段串联起来
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/4
* @Description todo
*/
public class TianChongMeiGeJieDianDeXiaYiGeYouCeJieDianZhiZhen116_4 {
/**
* 方法3:dfs+递归
* 以root为起点,left不断的往右走,right不断的往左走,从而将整个纵深这段串联起来
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public Node connect(Node root) {
dfs(root);
return root;
}
private void dfs(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Node left = root.left;
Node right = root.right;
// 以root为起点,left不断的往右走,right不断的往左走,从而
// 将整个纵深这段串联起来
while (left != null) {
left.next = right;
left = left.right;
right = right.left;
}
// 递归的调用左右节点,完成同样的纵深串联
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
}
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node next;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
next = _next;
}
}
}
117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
LeetCode链接 117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述
注意:
117题目给出的是普通的二叉树,而116题目给出的是完美二叉树.对于用bfs层序遍历解决本题的话,和116题的题解是一样的
方法1:bfs+队列
题解和116题解一样
方法2:迭代法
参考:117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/4
* @Description todo
*/
public class TianChongMeiGeJieDianDeXiaYiGeYouCeJieDianZhiZhen117_3 {
/**
* 方法2:迭代解法
* 将一层像链表一样连接起来
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return root;
}
Node cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
// 遍历当前层,为了方便操作,在下一层前添加一个dumpy节点:(访问当前层节点,把下一层的节点串联起来)
Node dumpy = new Node(0);
// pre:下一层节点的前一个节点
Node pre = dumpy;
// 遍历当前层链表
while (cur != null) {
// 当前节点的左子节点
if (cur.left != null) {
// 用next指针把pre和cur.left连接起来
pre.next = cur.left;
// 更新pre:向右移动
pre = pre.next;
}
// 当前节点的右子节点
if (cur.right != null) {
// 用next指针把pre和cur.right连接起来
pre.next = cur.right;
// 更新pre:向右移动
pre = pre.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
// dumpy表示下一层,此处cur=dumpy.next可以跳转到下一层的最左边的节点
cur = dumpy.next;
}
return root;
}
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node next;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
next = _next;
}
}
}
104.二叉树的最大深度
LeetCode链接 104. 二叉树的最大深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述
方法1:bfs+队列
每遍历一层,最大深度就加1
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.LinkedList;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/5
* @Description todo
*/
public class ErChaShuDeZuiDaShengDu104_2 {
/**
* 方法1:bfs-队列
* 1.通过层序遍历,计算有多少层即可
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
LinkedList queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.addLast(root);
int num = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//队里中维护的是每层的所有节点,size就是这层有多少个节点
int size = queue.size();
while (size > 0) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
queue.addLast(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.addLast(node.right);
}
size--;
}
//遍历完一层+1
num++;
}
return num;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
方法2:dfs+递归
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/5
* @Description todo
*/
public class ErChaShuDeZuiDaShengDu104_3 {
/**
* 方法2:dfs+递归
* 1.递归记录左子树对应的最大深度
* 2.递归记录右子树对应的最大深度
* 3.取左右子树的最大值
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
int maxDep = 0;
return dfs(root, maxDep);
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root, int maxDep) {
// baseCase
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
// 左边的最大深度
int left = dfs(root.left, maxDep);
// 右边的最大深度
int right = dfs(root.right, maxDep);
// 取左右两边的最大值,再加上本层
maxDep = Math.max(left, right) + 1;
return maxDep;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
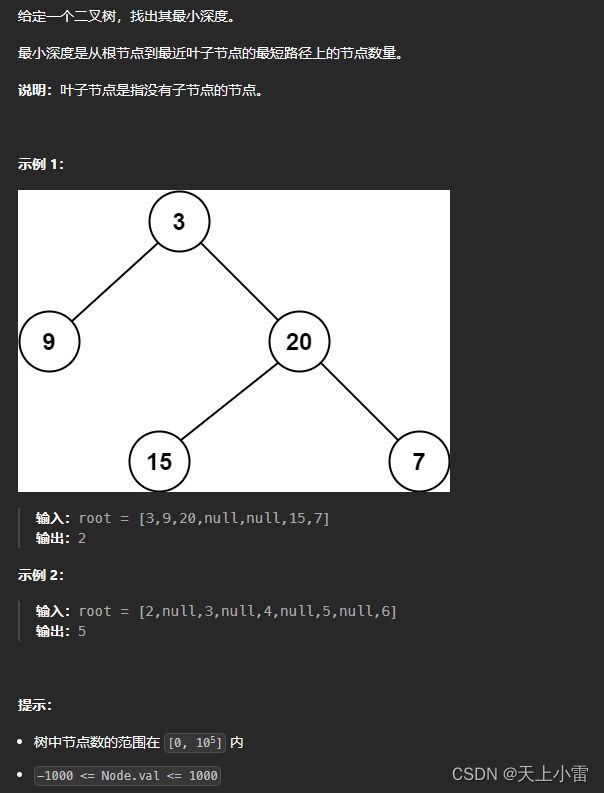
111.二叉树的最小深度
LeetCode链接 111. 二叉树的最小深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述
方法1:bfs+队列
当左右孩子都为null的时候,说明到了最低点,有一个孩子不为null,则不是最低点
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/5
* @Description todo
*/
public class ErChaShuDeZuiXiaoShenDu111_2 {
/**
* 方法2:bfs-队列
* 1.层序遍历
* 2.当左右孩子都为null的时候,说明到了最低点,有一个孩子不为null,则不是最低点
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int depth = 0;
ArrayDeque queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.addLast(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
// 记录最小深度
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.pollFirst();
if (node.left != null) {
queue.addLast(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.addLast(node.right);
}
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
// 当左右孩子都为空的时候,说明是最低点的一层了,退出
return depth;
}
}
}
return depth;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
方法2:dfs+递归
左子树为null,右子树不为null,最小深度就是右子树的最小深度+1;
右子树为null, 左子树不为null,最小深度就是左子树的最小深度+1;
左右子树都不为null,最小深度就是min(左子树最小深度,右子树最小深度)+1
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/5
* @Description todo
*/
public class ErChaShuDeZuiXiaoShenDu111_3 {
/**
* 方法1:dfs-递归,后序遍历
* 1.注意要到达叶子节点
* 2.注意左子树为null,右子树不为null的情况
* 3.注意右子树为null,左子树不为null的情况
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root);
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftMinDep = dfs(root.left);
int rightMinDep = dfs(root.right);
//左子树为null,右子树不为null
if (root.left == null && root.right != null) {
return rightMinDep + 1;
}
//右子树为null,左子树不为null
if (root.right == null && root.left != null) {
return leftMinDep + 1;
}
return Math.min(leftMinDep, rightMinDep) + 1;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
226.翻转二叉树
LeetCode链接 226. 翻转二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述
方法1:dfs+递归
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/5
* @Description todo
*/
public class FanZhuanErChaShu266_2 {
/**
* 方法1: dfs递归
* 1.前序/后序遍历都可以,
* 2.中序不行:
* 因为先左孩子交换孩子,再根交换孩子(做完后,右孩子已经变成了原来的左孩子),
* 再右孩子交换孩子(此时其实是对原来的左孩子做交换)
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
swapChildren(root);
return root;
}
private void swapChildren(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = tmp;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
方法2:bfs+队列
层序遍历
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/5
* @Description todo
*/
public class FanZhuanErChaShu266_3 {
/**
* 方法2:bfs-队列
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
ArrayDeque deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque.offer(root);
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
int size = deque.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = deque.removeFirst();
swapChildren(node);
if (node.left != null) {
deque.addLast(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
deque.addLast(node.right);
}
}
}
return root;
}
private void swapChildren(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = tmp;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
方法3:统一迭代
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/5
* @Description todo
*/
public class FanZhuanErChaShu266_4 {
/**
* 方法3:统一迭代法
* 1.前序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历都可以
* 中序遍历解法
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
Stack st = new Stack<>();
st.push(root);
while (!st.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = st.peek();
if (node != null) {
st.pop();
if (node.right != null) {
st.push(node.right);
}
st.push(node);
st.push(null);
if (node.left != null) {
st.push(node.left);
}
} else {
st.pop();
node = st.peek();
st.pop();
swapChildren(node);
}
}
return root;
}
private void swapChildren(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = tmp;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
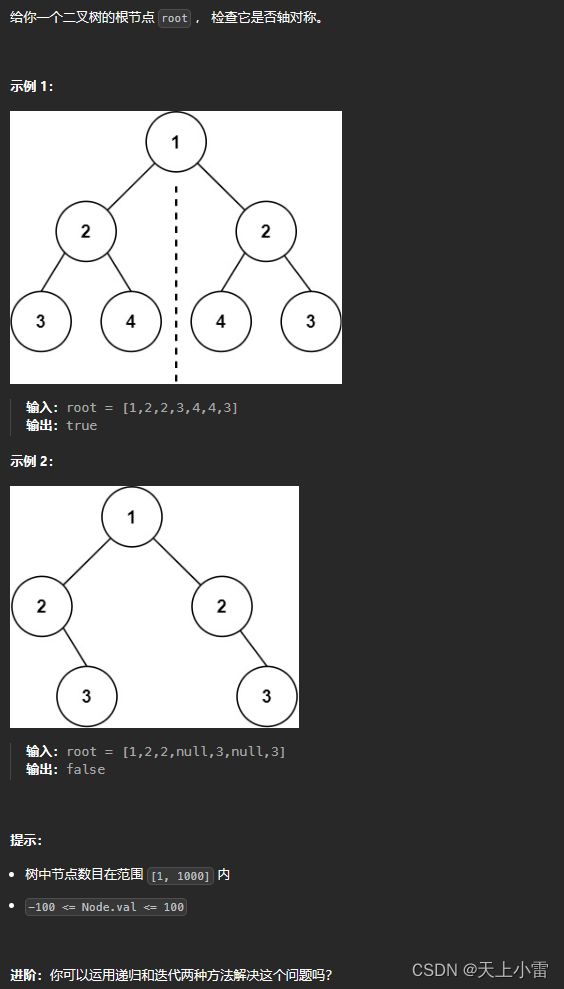
101.对称二叉树
LeetCode链接 101. 对称二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述
实际上是判断root节点的左右两颗子树是否是相互翻转得到的:比较左子树的left和右子树的right是否相等,比较左子树的right和右子树的left是否相等
方法1:dfs+递归
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/5
* @Description todo
*/
public class DuiChenErChaShu101_2 {
/**
* 方法1:dfs-递归
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
return dfs(root.left, root.right);
}
private boolean dfs(TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
//baseCase
//左右树都为null
if (left == null && right == null) {
return true;
}
//左右树一个为null,false
if (left == null || right == null) {
return false;
}
//左右树都不为null,如果值不等,false
if (left.val != right.val) {
return false;
}
//比较left.left 和 right.right , left.right 和 right.left
boolean leftRight = dfs(left.left, right.right);
boolean rightLeft = dfs(left.right, right.left);
return leftRight && rightLeft;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
方法2:bfs+队列
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.LinkedList;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/5
* @Description todo
*/
public class DuiChenErChaShu101_3 {
/**
* 方法2:bfs-队列实现
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return true;
}
LinkedList queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.addLast(root.left);
queue.addLast(root.right);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//从队列中取出两个节点,比较是否相等
TreeNode left = queue.poll();
TreeNode right = queue.poll();
//如果left和right都为null,继续循环
if (left == null && right == null) {
continue;
}
//left和right有一个为null,返回false
if (left == null || right == null) {
return false;
}
//left.val和right.val不等,返回false
if (left.val != right.val) {
return false;
}
//left.left和right.right加入队列,后面会比较
queue.addLast(left.left);
queue.addLast(right.right);
//left.right和right.left加入队列,后面会比较
queue.addLast(left.right);
queue.addLast(right.left);
}
return true;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
方法3:迭代+栈
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/5
* @Description todo
*/
public class DuiChenErChaShu101_4 {
/**
* 方法3:迭代+栈
* 逻辑和队列的逻辑一样,本质上是:
* 把左右两个子树要比较的元素顺序放进一个容器,然后成对成对的取出来进行比较
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return true;
}
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root.left);
stack.push(root.right);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
//从队列中取出两个节点,比较是否相等
TreeNode left = stack.pop();
TreeNode right = stack.pop();
//如果left和right都为null,继续循环
if (left == null && right == null) {
continue;
}
//left和right有一个为null,返回false
if (left == null || right == null) {
return false;
}
//left.val和right.val不等,返回false
if (left.val != right.val) {
return false;
}
//left.left和right.right加入队列,后面会比较
stack.push(left.left);
stack.push(right.right);
//left.right和right.left加入队列,后面会比较
stack.push(left.right);
stack.push(right.left);
}
return true;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
3.小结
二叉树层序遍历的模板:通过队列实现