AVL 树
目录
-
- AVL树
-
- AVL树的结构
- AVL树的插入
- AVL树的验证
- AVL树的性能
- 完整代码
AVL树
二叉搜索树虽可以缩短查找的效率,但如果数据有序或接近有序二叉搜索树将退化为单支树,查找元素相当于在顺序表中搜索元素,效率低下
为了解决上诉问题有这么一种方法:当向二叉搜索树中插入新结点后,如果能保证每个结点的左右子树高度之差的绝对值不超过1(需要对树中的结点进行调整),即可降低树的高度,从而减少平均搜索长度。
一棵AVL树或者是空树,或者是具有以下性质的二叉搜索树:
- 它的左右子树都是AVL树
- 左右子树高度之差(简称平衡因子)的绝对值不超过1(-1/0/1)
AVL树的结构
template<class K,class V>
struct AVLTreeNode
{
AVLTreeNode* _left;
AVLTreeNode* _right;
AVLTreeNode* _parent;
pair<K,V> _kv;
int _bf;//平衡因子
AVLTreeNode(const pair<K,V>& kv)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
,_kv(kv)
,_bf(0)
{}
};
template<class K, class V>
class AVLTree
{
typedef AVLTreeNode<K,V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv);//
protected:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
AVL树的插入
先按照二叉搜索树的方式插入新节点(二叉搜索树的实现)
然后调整节点的平衡因子

bf平衡因子==2 or -2时,需要通过旋转操作来让其正常
有四种旋转情况:
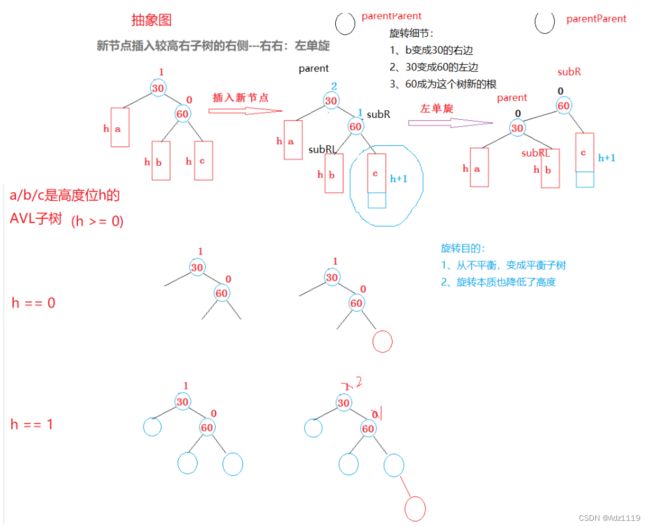
左左的情况和上图类似,需要的是右单旋

当碰到右左的情况,发现左单旋不能解决问题,引出第三种旋转操作,右左双旋:

对应的还有右左的情况,和上图类似
插入代码:
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kv.first > cur->_kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kv.first < cur->_kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
Node* newnode = new Node(kv);
if (parent->_kv.first > kv.first)
{
parent->_left = newnode;
newnode->_parent = parent;
parent->_bf--;
}
else if (parent->_kv.first < kv.first)
{
parent->_right = newnode;
newnode->_parent = parent;
parent->_bf++;
}
else
{
assert(false);
}
//通过平衡因子的变化判断是否需要旋转
while (parent)
{
//cout << "parent-val=" << parent->_kv.first << endl;
//cout << "parent-bf=" << parent->_bf << endl;
if (parent->_bf == 0)
{
//父亲所在子树高度不变,不需要向上更新平衡因子
return true;
}
else if (parent->_bf == 1 || parent->_bf == -1)
{
//父亲所在子树高度变化,可能会影响到上面的树,需要向上更新
if (parent->_parent == nullptr)
;
else if (parent == parent->_parent->_right)
parent->_parent->_bf++;
else if (parent == parent->_parent->_left)
parent->_parent->_bf--;
else
assert(false);
parent = parent->_parent;
}
else if (parent->_bf == 2 || parent->_bf == -2)
{
//平衡因子出现异常,需要进行旋转
if (parent->_bf == 2 && parent->_right->_bf == 1)
{
//右右的情况,需要左单旋
RotateL(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == -2 && parent->_left->_bf == -1)
{
//左左的情况,需要右单旋
RotateR(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == 2 && parent->_right->_bf == -1)
{
//右左的情况,需要右单旋然后左单旋
RotateRL(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == -2 && parent->_left->_bf == 1)
{
//左右的情况,需要左单旋然后右单旋
RotateLR(parent);
}
else
{
cout <<"parent->bf=" << parent->_bf << endl;
cout << "parent->left->bf=" << parent->_left->_bf << endl;
cout << "parent->right->bf=" << parent->_right->_bf << endl;
assert(false);
}
//经过旋转,该子树的高度已经降低,所以不会影响到上面树
break;
}
else
{
assert(false);
}
}
return true;
}
能用else if就用else if,留else来快速判断错误出现位置
AVL树的验证
AVL树是在二叉搜索树的基础上加入了平衡性的限制,因此要验证AVL树,可以分两步:
- 验证其为二叉搜索树
如果中序遍历可得到一个有序的序列,就说明为二叉搜索树 - 验证其为平衡树
- 每个节点子树高度差的绝对值不超过1(注意节点中如果没有平衡因子)
- 节点的平衡因子是否计算正确
public:
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
bool IsBalance()//检查平衡因子是否正确
{
return _IsBalance(_root);
}
protected:
bool _IsBalance(Node* root)//检查左右树高度差,看是不是和平衡因子给的结果一样
{
if (root == nullptr)
return true;
int leftHeight = _Height(root->_left);
int rightHeight = _Height(root->_right);
if (rightHeight - leftHeight != root->_bf)
{
cout <<"root == " <<root->_kv.first<< " 时平衡因子异常:" << root->_bf << endl;
return false;
}
return abs(rightHeight - leftHeight) < 2
&& _IsBalance(root->_left)
&& _IsBalance(root->_right);
}
int _Height(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int leftHeight = _Height(root->_left);
int rightHeight = _Height(root->_right);
return leftHeight < rightHeight ? rightHeight + 1 : leftHeight + 1;
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_kv.first << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
可以先用指定数据测试,没问题了之后使用随机数进行测试,可以通过手动打断点的方式快速定位到出问题的数据。
int main()
{
const int N = 1000;
srand(time(0));
vector<int> v;
v.reserve(N);
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
v.push_back(rand());
cout << v.back() << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//int a[] = { 16, 3, 7, 11, 9, 26, 18, 14, 15 };
//int a[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14 };
AVLTree<int, int> t;
for (auto e : v)
{
//if (e == 5)
//{
// cout << endl;
//}
cout << "Insert:" << e << endl;
t.Insert(pair<int,int>(e,e));
}
t.InOrder();
cout << t.IsBalance() << endl;
return 0;
}
AVL树的性能
AVL树是一棵绝对平衡的二叉搜索树,其要求每个节点的左右子树高度差的绝对值都不超过1,这样可以保证查询时高效的时间复杂度,即log2N,但是如果要对AVL树做一些结构修改的操作,性能非常低下,比如:插入时要维护其绝对平衡,旋转的次数比较多,更差的是在删除时,有可能一直要让旋转持续到根的位置。因此:如果需要一种查询高效且有序的数据结构,而且数据的个数为静态的(即不会改变),可以考虑AVL树,但一个结构经常修改,就不太适合。
完整代码
#include