机器翻译学习1:pytorch官方教程与代码逐行详解
官方教程网址:https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/seq2seq_translation_tutorial.html
代码所需数据源:https://download.pytorch.org/tutorial/data.zip
文章目录
- 1. 机器翻译流程概述
- 2. 代码中的重要模块
- 3. 简化代码与细节解析
- 官方代码
- 更多参考
1. 机器翻译流程概述
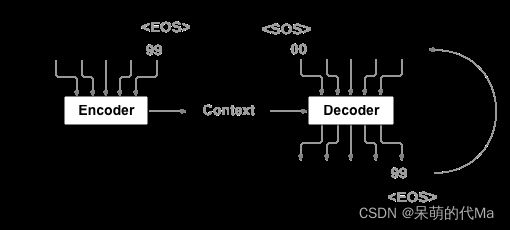
使用encoder-decoder模型的整体流程如下:
- 输入:法语的token,上图为[02,85,03,12,99]
- 输出:英语的token,上图为[42,82,16,04,99]
机器翻译的任何目标就是根据输入的token,预测出输出的token。看似是一个多分类的任务,但是一方面句子长度不定,另一方面错误的分类会导致生成的结果不符合逻辑,因此通常使用Sequence-to-Sequence的模型。
细节上使用的Seq-to-Seq模型示意图如下:
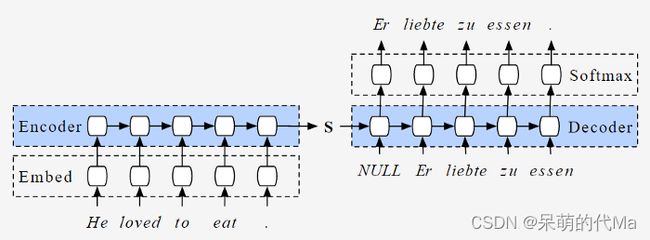
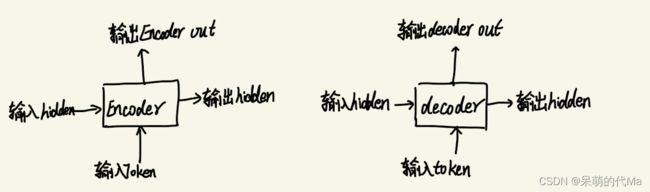
Encoder与Decoder部分的整体都是:两个输入,两个输出;
训练时的整体流程如下图所示:
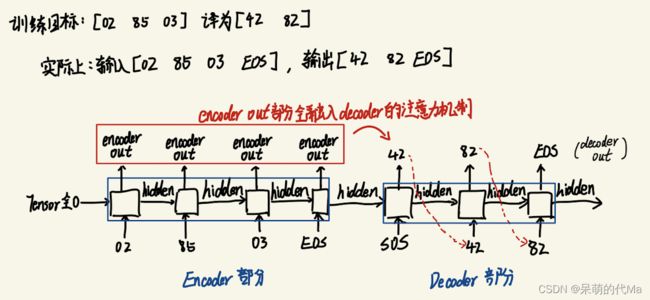
从左到右依次迭代训练,
- 在初始时,使用第一个字的token与全0的tensor作为encoder model的最初输入,然后依次迭代
- encoder model的hidden输出作为下一个encoder或decoder部分的输入,而out输出作为decoder部分计算注意力机制的一个输入
- decoder部分最初,使用encoder的最后一个hidden与SOS对应的token作为输入
- decoder最初输出一个EOS,作为翻译结束
在使用这个模型翻译时:
- 输入的文本转为Token后,在后面加入[EOS],输入到模型中
- 将decoder部分的out作为输出,直到输出一个[EOS],翻译结束(有时为了防止翻译模型走形,也会卡一个翻译最大长度作为阈值)
2. 代码中的重要模块
根据上述的流程,有以下几个模块:
- Lang:语言文本与token相互转换的辅助类
- EncoderRNN:encoder模型
- AttnDecoderRNN:decoder模型
3. 简化代码与细节解析
代码所需数据源:https://download.pytorch.org/tutorial/data.zip
"""
教程:将法语翻译成英语
"""
from io import open
import random
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch import optim
import torch.nn.functional as F
from tqdm import tqdm
import time
from loguru import logger
from translate_utils import normalizeString
# ============ 基本配置 ==============
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
SOS_token = 0 # 输出的起始符
EOS_token = 1 # 输入的终止符
MAX_LENGTH = 10 # 允许输入或输出的最大长度
# 过滤出 "我是","他是" 这种形式的句子(别忘记之前忽略的撇号,比如 "I'm" 这种形式)
eng_prefixes = (
"i am", "i m",
"he is", "he s",
"she is", "she s",
"you are", "you re",
"we are", "we re",
"they are", "they re"
)
# ============ 开始 ==============
class Lang(object):
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
self.word2index = {} # 单词 -> index
self.word2count = {} # 单词 数量统计
self.index2word = {0: "SOS", 1: "EOS"} # index -> 单词
self.n_words = 2 # Count SOS and EOS # 总单词数
def addSentence(self, sentence):
for word in sentence.split(' '):
if word not in self.word2index:
self.word2index[word] = self.n_words
self.word2count[word] = 1
self.index2word[self.n_words] = word
self.n_words += 1
else:
self.word2count[word] += 1
# 文件是 English->其他语言 ,所以这里加上一个 reverse 参数,可以用来获取 其他语言->英语 的翻译对。
def get_data(input_lang_name: str, out_lang_name: str, reverse: bool = False):
"""
用来整理数据用
:param input_lang_name: input的文本名称,自定义
:param out_lang_name: output的文本名称,自定义
:param reverse: 是否需要颠倒文本的顺序
:return: 返回三个值:输入的Lang,输出的Lang,训练文本对
"""
lines = open('data/eng-fra.txt', encoding='utf-8').read().strip().split('\n') # 读取文件
pairs = []
for l in tqdm(lines[:100]): # 读取前100行,按行分割,再将每行分割成语句对
l_p = []
for s in l.split("\t"):
l_p.append(normalizeString(s)) # 过滤内容和长度
pairs.append(l_p)
# Reverse pairs, make Lang instances
# 根据滤出的句子对创建词语列表
if reverse: # 主要看需要从 A语言->B语言
# 本文是从 法语->英语,但是训练数据中时英文在前,法语在后;因此这里需要颠倒一下
pairs = [list(reversed(p)) for p in pairs]
input_lang = Lang(out_lang_name)
output_lang = Lang(input_lang_name)
else:
input_lang = Lang(input_lang_name)
output_lang = Lang(out_lang_name)
# 开始根据已有数据,构建Lang
input_pairs = []
for p in pairs:
if len(p[0].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH and len(p[1].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH and p[1].startswith(eng_prefixes):
input_pairs.append(p)
for pair in input_pairs:
input_lang.addSentence(pair[0])
output_lang.addSentence(pair[1])
return input_lang, output_lang, input_pairs
class EncoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size=256):
super(EncoderRNN, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
# 此处的hidden_size也是embedding_dim
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size)
self.gru = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size)
def forward(self, input_token, hidden):
# 训练时,hidden输入全0
# input维度为(seq_len=1,batch_size=1)
embedded = self.embedding(input_token).view(1, 1, -1)
# 经过embedded,维度为(seq_len=1,batch_size=1,embedding_dim)
output = embedded
# hidden维度为(num_layers*direction_num=1, batch_size=1, hidden_size)
# output的维度为(seq_length=1, batch_size=1, hidden_size)
output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden) # output与hidden都是[1,1,256]个维度
return output, hidden
def initHidden(self):
return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device)
class AttnDecoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, output_size, hidden_size=256, dropout_p=0.1, max_length=MAX_LENGTH):
super(AttnDecoderRNN, self).__init__()
# hidden_size也是embedding_dim
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.output_size = output_size
self.dropout_p = dropout_p
self.max_length = max_length
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(self.output_size, self.hidden_size)
self.attn = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size * 2, self.max_length) # linear 输出 max_length
self.attn_combine = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size * 2, self.hidden_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(self.dropout_p)
self.gru = nn.GRU(self.hidden_size, self.hidden_size)
self.out = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.output_size)
def forward(self, input_token, hidden, encoder_outputs):
# input维度为(seq_len=1,batch_size=1)
# hidden维度为(num_layers*direction_num=1, batch_size=1, hidden_size)
# 经过embedded,维度为(seq_len=1,batch_size=1,embedding_dim),其中embedding_dim=hidden_size
embedded = self.embedding(input_token).view(1, 1, -1)
embedded = self.dropout(embedded)
# attn_weights维度为(batch_size, max_length)
attn_weights = F.softmax(self.attn(torch.cat([embedded[0], hidden[0]], 1)), dim=1)
# encoder_outputs的维度为(max_length, hidden_size)
# attn_applied维度为(1, batch_size=1, hidden_size)
# bmm: input(p,m,n) * mat2(p,n,a) -> output(p,m,a)
attn_applied = torch.bmm(attn_weights.unsqueeze(0), encoder_outputs.unsqueeze(0))
# 此时output维度为(batch_size=1, 2*hidden_size)
output = torch.cat([embedded[0], attn_applied[0]], 1) # torch.cat()用来拼接
# 此时output维度为(seq_len=1, batch_size=1, hidden_size)
output = self.attn_combine(output).unsqueeze(0)
output = F.relu(output)
# 此时output维度为(seq_len=1, batch_size=1, hidden_size)
output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden)
output = F.log_softmax(self.out(output[0]), dim=1)
# 此时output维度为(batch_size=1, output_size)
return output, hidden, attn_weights
def initHidden(self):
return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device)
def indexesFromSentence(lang, sentence):
return [lang.word2index[word] for word in sentence.split(' ')]
def tensorFromSentence(lang, sentence):
indexes = indexesFromSentence(lang, sentence)
indexes.append(EOS_token)
return torch.tensor(indexes, dtype=torch.long, device=device).view(-1, 1)
def tensorsFromPair(input_lang, output_lang, pair):
input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(input_lang, pair[0])
target_tensor = tensorFromSentence(output_lang, pair[1])
return (input_tensor, target_tensor)
def train_once(input_tensor, target_tensor, encoder_model, decoder_model, encoder_optimizer, decoder_optimizer,
loss_model, max_length=MAX_LENGTH):
"""
训练一个例子的翻译任务
:param input_tensor: 输入的index
:param target_tensor: 输出的index
:param encoder_model: encoder部分的模型
:param decoder_model: decoder部分的模型
:param encoder_optimizer: encoder部分的优化器
:param decoder_optimizer: decoder部分的优化器
:param loss_model: loss的方法
:param max_length: 句子容纳的最大长度
:return:
"""
teacher_forcing_ratio = 0.5
encoder_hidden = encoder_model.initHidden() # 这里是第一个encoder的输入
# 优化器清零
encoder_optimizer.zero_grad()
decoder_optimizer.zero_grad()
# 输入与输出
input_length = input_tensor.size(0)
target_length = target_tensor.size(0)
# 预先构造一个全0的encoder
encoder_outputs = torch.zeros(max_length, encoder_model.hidden_size, device=device)
loss = 0
# 开始encoder部分的训练
for ei in range(input_length):
encoder_output, encoder_hidden = encoder_model(input_tensor[ei], encoder_hidden)
encoder_outputs[ei] = encoder_output[0, 0]
decoder_input = torch.tensor([[SOS_token]], device=device)
decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden # 这里是把encoder的最终输出作为decoder的输入
use_teacher_forcing = True if random.random() < teacher_forcing_ratio else False # 随机的判断是否使用teacher forcing修正
if use_teacher_forcing:
# Teacher forcing: Feed the targer as the next input
for di in range(target_length):
decoder_output, decoder_hidden, decoder_attention = decoder_model(decoder_input, decoder_hidden,
encoder_outputs)
loss += loss_model(decoder_output, target_tensor[di])
decoder_input = target_tensor[di] # Teacher forcing
else:
# Without teaching forcing: use its own predictions as the next input
for di in range(target_length):
# 输入是:开始翻译的标识符,encoder的完整输出,encoder部分的每个输出
decoder_output, decoder_hidden, decoder_attention = decoder_model(decoder_input, decoder_hidden,
encoder_outputs)
topv, topi = decoder_output.topk(1)
decoder_input = topi.squeeze().detach() # detach from history as input
loss += loss_model(decoder_output, target_tensor[di])
if decoder_input.item() == EOS_token:
break
loss.backward()
encoder_optimizer.step()
decoder_optimizer.step()
return loss.item() / target_length
def trainIters(input_lang, output_lang, pairs, n_iters, learning_rate=0.01):
"""不断迭代训练"""
# 模型
encoder_model = EncoderRNN(input_lang.n_words).to(device)
decoder_model = AttnDecoderRNN(output_lang.n_words, dropout_p=0.1).to(device)
# 优化器
encoder_optimizer = optim.SGD(encoder_model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
decoder_optimizer = optim.SGD(decoder_model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
training_pairs = [] # 从原始文本中,随机挑选一部分作为训练数据
for i in range(n_iters):
tensor_pair = tensorsFromPair(input_lang, output_lang, random.choice(pairs))
training_pairs.append(tensor_pair)
nll_loss = nn.NLLLoss() # 定义损失函数
logger.info("开始训练模型")
for iter in tqdm(range(1, n_iters + 1)): # 开始迭代训练
training_pair = training_pairs[iter - 1]
input_tensor = training_pair[0] # 输入的index
target_tensor = training_pair[1] # 输出的index
train_once(input_tensor, target_tensor, encoder_model, decoder_model, encoder_optimizer, decoder_optimizer,
nll_loss)
return encoder_model, decoder_model
def evaluate(encoder_model, decoder_model, input_lang, output_lang, sentence, max_length=MAX_LENGTH):
"""
验证模型
:param encoder_model: encoder部分的模型
:param decoder_model: decoder部分的模型
:param input_lang: 输入的文本
:param output_lang: 输出的文本
:param sentence: 待翻译的文本,对应input_lang
:param max_length: 文本的最大长度
:return: 返回两个值: 翻译后的文本 decoded_words,与翻译模型的注意力矩阵decoder_attentions
"""
logger.info("开始验证模型")
with torch.no_grad():
input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(input_lang, sentence)
input_length = input_tensor.size()[0]
encoder_hidden = encoder_model.initHidden()
encoder_outputs = torch.zeros(max_length, encoder_model.hidden_size, device=device)
for ei in range(input_length):
encoder_output, encoder_hidden = encoder_model(input_tensor[ei], encoder_hidden)
encoder_outputs[ei] += encoder_output[0, 0]
decoder_input = torch.tensor([[SOS_token]], device=device) # SOS
decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden # shape:(1,1,256)
decoded_words = []
decoder_attentions = torch.zeros(max_length, max_length)
for di in range(max_length):
decoder_output, decoder_hidden, decoder_attention = \
decoder_model(decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs)
decoder_attentions[di] = decoder_attention.data
topv, topi = decoder_output.data.topk(1)
if topi.item() == EOS_token: # 如果对应的标志是,代表翻译结束,否则继续下去
decoded_words.append('' )
break
else:
decoded_words.append(output_lang.index2word[topi.item()])
decoder_input = topi.squeeze().detach()
return decoded_words, decoder_attentions[:di + 1] # 这里截取是去掉全0的部分
def main():
# ========== 基本设置 ================
input_lang_name = "eng"
out_lang_name = "fra"
# ========== 开始训练 ================
input_lang, output_lang, pairs = get_data(input_lang_name, out_lang_name, True) # 获取数据源
encoder_model, decoder_model = trainIters(input_lang, output_lang, pairs, 222) # 训练模型
# ========== 翻译 ================
check_string = "j ai ans ." # 待翻译的句子,对应的英文是:i m .
decoder_words, decoder_attentions = \
evaluate(encoder_model, decoder_model, input_lang, output_lang, check_string) # 测试效果
print("翻译结果:", " ".join(decoder_words))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
同时还有一个叫做translate_utils.py的工具函数:
import re
import unicodedata
def normalizeString(s):
s = unicode2Ascii(s.lower().strip())
s = re.sub(r"([.!?])", r" \1", s)
s = re.sub(r"[^a-zA-Z.!?]+", r" ", s)
return s
def unicode2Ascii(s):
return ''.join(
c for c in unicodedata.normalize('NFD', s)
if unicodedata.category(c) != 'Mn'
)
官方代码
"""
教程:
将法语翻译成英语
"""
from io import open
import unicodedata
import string
import re
import random
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch import optim
import torch.nn.functional as F
from tqdm import tqdm
import time
import math
from loguru import logger
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
SOS_token = 0
EOS_token = 1
class Lang:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
self.word2index = {}
self.word2count = {}
self.index2word = {0: "SOS", 1: "EOS"}
self.n_words = 2 # Count SOS and EOS # 总单词数
def addSentence(self, sentence):
for word in sentence.split(' '):
if word not in self.word2index:
self.word2index[word] = self.n_words
self.word2count[word] = 1
self.index2word[self.n_words] = word
self.n_words += 1
else:
self.word2count[word] += 1
# Turn a Unicode string to plain ASCII, thanks to
# http://stackoverflow.com/a/518232/2809427
# 文件都是Unicode编码的,我们需要简单得将字符转化为ASCII编码,全部转化为小写字母,并修剪大部分标点符号。
def unicode2Ascii(s):
return ''.join(
c for c in unicodedata.normalize('NFD', s)
if unicodedata.category(c) != 'Mn'
)
# Lowercase, trim, and remove non-letter characters
def normalizeString(s):
s = unicode2Ascii(s.lower().strip())
s = re.sub(r"([.!?])", r" \1", s)
s = re.sub(r"[^a-zA-Z.!?]+", r" ", s)
return s
# 读取数据,我们将文件分割成行,进一步分割成句子对。文件是 English->其他语言 ,所以这里加上一个 reverse 参数,可以用来获取 其他语言->英语 的翻译对。
def readLangs(lang1, lang2, reverse=False):
logger.info("Reading lines...")
lines = open('data/%s-%s.txt' % (lang1, lang2), encoding='utf-8').read().strip().split('\n')
# Split every line into pairs and normalize
pairs = []
for l in tqdm(lines[:100]): # 读取前100行
l_p = []
for s in l.split("\t"):
l_p.append(normalizeString(s))
pairs.append(l_p)
# pairs = [[normalizeString(s) for s in l.split('\t')] for l in lines] # 原始语句
# Reverse pairs, make Lang instances
if reverse:
pairs = [list(reversed(p)) for p in pairs]
input_lang = Lang(lang2)
output_lang = Lang(lang1)
else:
input_lang = Lang(lang1)
output_lang = Lang(lang2)
return input_lang, output_lang, pairs
# 由于样本句子很多,而我们想加速训练。我们会将数据集修剪成相对简短的句子。
# 这里的最大长度是10(包括结束标点)
MAX_LENGTH = 10
# 过滤出 "我是","他是" 这种形式的句子(别忘记之前忽略的撇号,比如 "I'm" 这种形式)
eng_prefixes = (
"i am", "i m",
"he is", "he s",
"she is", "she s",
"you are", "you re",
"we are", "we re",
"they are", "they re"
)
def filterPairs(pairs):
"""的"""
pair_list = []
for p in pairs:
if len(p[0].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH and len(p[1].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH and p[1].startswith(eng_prefixes):
pair_list.append(p)
return pair_list
# 完整的数据准备流程如下:
# 读取文本文件,按行分割,再将每行分割成语句对
# 归一化文本,过滤内容和长度
# 根据滤出的句子对创建词语列表
def prepareData(lang1, lang2, reverse=False):
input_lang, output_lang, pairs = readLangs(lang1, lang2, reverse)
print("Read %s sentence pairs" % len(pairs))
# pairs = filterPairs(pairs)
# 剔除一部分数据
pairs = []
for p in pairs:
if len(p[0].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH and len(p[1].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH and p[1].startswith(eng_prefixes):
pairs.append(p)
print("Trimmed to %s sentence pairs" % len(pairs))
print("Counting words...")
for pair in pairs:
input_lang.addSentence(pair[0])
output_lang.addSentence(pair[1])
print("Counted words:")
print(input_lang.name, input_lang.n_words)
print(output_lang.name, output_lang.n_words)
return input_lang, output_lang, pairs
class EncoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size):
super(EncoderRNN, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
# 此处的hidden_size也是embedding_dim
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size)
self.gru = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size)
def forward(self, input_token, hidden):
# 训练时,hidden输入全0
# input维度为(seq_len=1,batch_size=1)
embedded = self.embedding(input_token).view(1, 1, -1)
# 经过embedded,维度为(seq_len=1,batch_size=1,embedding_dim)
output = embedded
# hidden维度为(num_layers*direction_num=1, batch_size=1, hidden_size)
# output的维度为(seq_length=1, batch_size=1, hidden_size)
output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden) # output与hidden都是[1,1,256]个维度
return output, hidden
def initHidden(self):
return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device)
class DecoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, output_size):
super(DecoderRNN, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_size, hidden_size)
self.gru = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size)
self.out = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
self.softmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, input, hidden):
output = self.embedding(input).view(1, 1, -1)
output = F.relu(output)
output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden)
output = self.softmax(self.out(output[0]))
return output, hidden
def initHidden(self):
return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device)
class AttnDecoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, output_size, dropout_p=0.1, max_length=MAX_LENGTH):
super(AttnDecoderRNN, self).__init__()
# hidden_size也是embedding_dim
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
# ,
self.output_size = output_size
self.dropout_p = dropout_p
self.max_length = max_length
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(self.output_size, self.hidden_size)
self.attn = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size * 2, self.max_length) # linear 输出 max_length
self.attn_combine = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size * 2, self.hidden_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(self.dropout_p)
self.gru = nn.GRU(self.hidden_size, self.hidden_size)
self.out = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.output_size)
def forward(self, input_token, hidden, encoder_outputs):
# input维度为(seq_len=1,batch_size=1)
# hidden维度为(num_layers*direction_num=1, batch_size=1, hidden_size)
# 经过embedded,维度为(seq_len=1,batch_size=1,embedding_dim),其中embedding_dim=hidden_size
embedded = self.embedding(input_token).view(1, 1, -1)
embedded = self.dropout(embedded)
# attn_weights维度为(batch_size, max_length)
attn_weights = F.softmax(self.attn(torch.cat([embedded[0], hidden[0]], 1)), dim=1)
# encoder_outputs的维度为(max_length, hidden_size)
# attn_applied维度为(1, batch_size=1, hidden_size)
# bmm: input(p,m,n) * mat2(p,n,a) -> output(p,m,a)
attn_applied = torch.bmm(attn_weights.unsqueeze(0), encoder_outputs.unsqueeze(0))
# 此时output维度为(batch_size=1, 2*hidden_size)
output = torch.cat([embedded[0], attn_applied[0]], 1) # torch.cat()用来拼接
# 此时output维度为(seq_len=1, batch_size=1, hidden_size)
output = self.attn_combine(output).unsqueeze(0)
output = F.relu(output)
# 此时output维度为(seq_len=1, batch_size=1, hidden_size)
output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden)
output = F.log_softmax(self.out(output[0]), dim=1)
# 此时output维度为(batch_size=1, output_size)
return output, hidden, attn_weights
def initHidden(self):
return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device)
def indexesFromSentence(lang, sentence):
return [lang.word2index[word] for word in sentence.split(' ')]
def tensorFromSentence(lang, sentence):
indexes = indexesFromSentence(lang, sentence)
indexes.append(EOS_token)
return torch.tensor(indexes, dtype=torch.long, device=device).view(-1, 1)
def tensorsFromPair(pair):
input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(input_lang, pair[0])
target_tensor = tensorFromSentence(output_lang, pair[1])
return (input_tensor, target_tensor)
def train(input_tensor, target_tensor, encoder, decoder, encoder_optimizer, decoder_optimizer, criterion,
max_length=MAX_LENGTH):
"""训练本次的翻译任务"""
encoder_hidden = encoder.initHidden()
# 优化器清零
encoder_optimizer.zero_grad()
decoder_optimizer.zero_grad()
# 输入与输出
input_length = input_tensor.size(0)
target_length = target_tensor.size(0)
# 预先构造一个全0的encoder
encoder_outputs = torch.zeros(max_length, encoder.hidden_size, device=device)
loss = 0
# 开始encoder部分的训练
for ei in range(input_length):
encoder_output, encoder_hidden = encoder(input_tensor[ei], encoder_hidden)
encoder_outputs[ei] = encoder_output[0, 0]
decoder_input = torch.tensor([[SOS_token]], device=device)
decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden # 这里是把encoder的最终输出作为decoder的输入
use_teacher_forcing = True if random.random() < teacher_forcing_ratio else False # 随机的判断是否使用teacher forcing修正
if use_teacher_forcing:
# Teacher forcing: Feed the targer as the next input
for di in range(target_length):
decoder_output, decoder_hidden, decoder_attention = decoder(decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs)
loss += criterion(decoder_output, target_tensor[di])
decoder_input = target_tensor[di] # Teacher forcing
else:
# Without teaching forcing: use its own predictions as the next input
for di in range(target_length):
# 输入是:开始翻译的标识符,encoder的完整输出,encoder部分的每个输出
decoder_output, decoder_hidden, decoder_attention = decoder(decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs)
topv, topi = decoder_output.topk(1)
decoder_input = topi.squeeze().detach() # detach from history as input
loss += criterion(decoder_output, target_tensor[di])
if decoder_input.item() == EOS_token:
break
loss.backward()
encoder_optimizer.step()
decoder_optimizer.step()
return loss.item() / target_length
def asMinutes(s):
m = math.floor(s / 60)
s -= m * 60
return '%dm %ds' % (m, s)
def timeSince(since, percent):
now = time.time()
s = now - since
es = s / (percent)
rs = es - s
return '%s (- %s)' % (asMinutes(s), asMinutes(rs))
def trainIters(encoder, decoder, n_iters, print_every=1000, plot_every=1000, learning_rate=0.01):
start = time.time()
plot_losses = []
print_loss_total = 0 # Reset every print_every
plot_loss_total = 0 # Reset every plot_every
encoder_optimizer = optim.SGD(encoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
decoder_optimizer = optim.SGD(decoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
training_pairs = [tensorsFromPair(random.choice(pairs)) for i in range(n_iters)] # 随机挑选一部分
criterion = nn.NLLLoss()
for iter in tqdm(range(1, n_iters + 1)): # 开始迭代训练
training_pair = training_pairs[iter - 1]
input_tensor = training_pair[0] # 输入的index
target_tensor = training_pair[1] # 输出的index
loss = train(input_tensor, target_tensor, encoder, decoder, encoder_optimizer, decoder_optimizer, criterion)
print_loss_total += loss
plot_loss_total += loss
if iter % print_every == 0:
print_loss_avg = print_loss_total / print_every
print_loss_total = 0
print('%s (%d %d%%) %.4f' % (timeSince(start, iter / n_iters),
iter, iter / n_iters * 100, print_loss_avg))
if iter % plot_every == 0:
plot_loss_avg = plot_loss_total / plot_every
plot_losses.append(plot_loss_avg)
plot_loss_total = 0
def evaluate(encoder, decoder, sentence, max_length=MAX_LENGTH):
with torch.no_grad():
input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(input_lang, sentence)
input_length = input_tensor.size()[0]
encoder_hidden = encoder.initHidden()
encoder_outputs = torch.zeros(max_length, encoder.hidden_size, device=device)
for ei in range(input_length):
encoder_output, encoder_hidden = encoder(input_tensor[ei],
encoder_hidden)
encoder_outputs[ei] += encoder_output[0, 0]
decoder_input = torch.tensor([[SOS_token]], device=device) # SOS
decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden
decoded_words = []
decoder_attentions = torch.zeros(max_length, max_length)
for di in range(max_length):
decoder_output, decoder_hidden, decoder_attention = decoder(
decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs)
decoder_attentions[di] = decoder_attention.data
topv, topi = decoder_output.data.topk(1)
if topi.item() == EOS_token:
decoded_words.append('' )
break
else:
decoded_words.append(output_lang.index2word[topi.item()])
decoder_input = topi.squeeze().detach()
return decoded_words, decoder_attentions[:di + 1]
def evaluateRandomly(encoder, decoder, n=10):
for i in range(n):
pair = random.choice(pairs)
print('>', pair[0])
print('=', pair[1])
output_words, attentions = evaluate(encoder, decoder, pair[0])
output_sentence = ' '.join(output_words)
print('<', output_sentence)
print('')
if __name__ == '__main__':
input_lang, output_lang, pairs = prepareData('eng', 'fra', True)
hidden_size = 256
teacher_forcing_ratio = 0.5
encoder1 = EncoderRNN(input_lang.n_words, hidden_size).to(device)
attn_decoder1 = AttnDecoderRNN(hidden_size, output_lang.n_words, dropout_p=0.1).to(device)
trainIters(encoder1, attn_decoder1, 7490, print_every=5000)
更多参考
- 使用Seq2Seq网络和注意力机制进行机器翻译.ipynb:https://github.com/Holy-Shine/Pytorch-notebook/blob/master/RNN-%E8%AF%AD%E8%A8%80%E6%A8%A1%E5%9E%8B/%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8Seq2Seq%E7%BD%91%E7%BB%9C%E5%92%8C%E6%B3%A8%E6%84%8F%E5%8A%9B%E6%9C%BA%E5%88%B6%E8%BF%9B%E8%A1%8C%E6%9C%BA%E5%99%A8%E7%BF%BB%E8%AF%91.ipynb