- 使用AIOps进行更好的事件管理
茵赛飞3D CAD数据转换软件
pagerdutydevops人工智能运维
DevOps为科技界带来了更加协作和高效的工作流程。随着AIOps的集成,自动化更进一步,使用人工智能为团队提供更快的根本原因分析和算法降噪。主要从采用AIOps中受益的主要领域之一是事件管理。AIOps可以帮助DevOps团队自动化工作流程,以实现更智能、更高效的事件管理,从而腾出时间让IT运营团队成员专注于创新以改善用户体验。在本文中,我们将了解AIOps如何从检测和识别到响应改进事件管理,以
- 实时光线追踪技术:Ray Tracing_2024-07-21_02-55-16.Tex
chenjj4003
游戏开发python算法人工智能矩阵线性代数骨骼绑定开发语言
实时光线追踪技术:RayTracing实时光线追踪技术教程基础知识光线追踪原理光线追踪是一种渲染技术,它通过模拟光线在场景中的传播和反射来生成图像。在实时光线追踪中,这一过程被优化以在有限的时间内完成,通常用于游戏和实时动画。其核心原理是逆向追踪,即从观察者(摄像机)发出光线,而不是从光源发出,这样可以减少计算量。示例:光线追踪的基本算法#Python示例代码,展示如何计算光线与场景中物体的交点c
- 图像质量评价学习笔记02:IQA模型性能评价指标(PLCC、SROCC、KROCC、RMSE)
可靠的豆包蟹同志
图像质量评估IQA图像处理计算机视觉人工智能算法
性能好的图像质量评价(IQA)算法,其质量评测分数会与主观质量分数高度一致,IQA有许多评价指标,为了衡量方法测试结果与主观评价之间的一致性,视频质量专家组VQEG(VideoQualityExpertsGroup,目前国际上对视频质量进行标准化及性能测试的权威组织)提出了四个可以验证客观评价结果和主观评价结果之间的紧密程度的四个指标:PLCC、SROCC、KROCC和RMSE,也是目前最常用的I
- X.509数字证书的签名和指纹
汽车通信技术
【付费专栏】车载以太网协议数字证书
X.509是一种非常普遍的数字证书标准,由国际电信联盟(ITU)制定。它定义了证书的格式和一种验证证书有效性的方法。X.509证书的结构遵循特定的语法和编码规则,通常使用ASN.1(AbstractSyntaxNotationOne)进行描述和编码。一个典型的X.509证书通常包含:版本、序列号、签名算法、颁发者、有效期、使用者、公钥、签名、指纹等。其中,版本号表示证书是哪个版本的,不同版本的数字
- 访问者模式【行为模式C++】
GoWjw
设计模式访问者模式
1.概述访问者模式是一种行为设计模式,它能将算法与其所作用的对象隔离开来。访问者模式主要解决的是数据与算法的耦合问题,尤其是在数据结构比较稳定,而算法多变的情况下。为了不污染数据本身,访问者会将多种算法独立归档,并在访问数据时根据数据类型自动切换到对应的算法,实现数据的自动响应机制,并确保算法的自由扩展。访问者模式在实际开发中使用的非常少,因为它比较难以实现并且应用该模式肯能会导致代码的可读性变差
- 策略模式
烟沙九洲
设计模式策略模式java
策略(Strategy)模式属于行为型模式的一种。策略模式的核心思想是定义一系列算法,将每个算法封装起来,并使它们可以互换。策略模式让算法独立于使用它的客户而变化,从而实现了算法族的独立扩展和替换。策略模式指在一个方法中,某些关键步骤的算法依赖调用方传入的策略,传入不同的策略,即可获得不同的结果,大大增强了系统的灵活性。策略模式的核心思想是在一个计算方法中把容易变化的算法抽出来作为“策略”参数传进
- 模板方法模式
烟沙九洲
设计模式模板方法模式java
模板方法(TemplateMethod)模式属于行为型模式的一种。模板方法模式定义了一个操作中的算法骨架,并将一些步骤延迟到子类中实现。模板方法模式的核心思想是:父类定义骨架,子类实现某些细节。模板方法模式允许子类在不改变算法结构的情况下,重新定义算法中的某些特定步骤。Java标准库有很多模板方法模式的应用。比如集合类中的AbstractList、AbstractQueuedSynchronize
- 【论文复现】——基于SIFT特征点结合ICP的点云配准方法
点云侠
点云配准专题开发语言计算机视觉算法3dc++
目录一、论文概述二、代码实现三、结果展示1、初始位置2、配准结果四、实验心得一、论文概述 在点云配准过程中,针对迭代最近点(ICP)算法对点云初始位置依赖性强且迭代速度慢的问题,提出一种基于尺度不变特征变换(SIFT)特征点结合ICP的点云配准方法。首先利用SIFT算法提取待配准点云和目标点云的特征点;接着计算出特征点的快速点特征直方图(FPFH)特征;然后依据该特征使用采样一致性初始配准(SA
- 【重温设计模式】访问者模式及其Java示例
万猫学社
重温设计模式及其Java实现设计模式访问者模式java
访问者模式的基本概念访问者模式,一种行为型设计模式,其基本定义是:允许一个或者多个操作应用到一组对象上,解耦操作和对象的具体类,使得操作的添加可以独立于对象的类结构变化。在面向对象编程中,访问者模式的重要性不言而喻。它将数据操作和数据结构分离,使得在不改变数据结构的前提下,可以添加新的操作,从而增强了系统的灵活性和可扩展性。在访问者模式中,数据结构是稳定的,而操作是易变的。这就像一座博物馆,展品(
- 数字签名与数字证书
TABE_
计算机网络数字签名数字证书
这里写目录标题数字签名数字证书数字证书的原理数字证书的特点如何验证证书机构的公钥不是伪造的数字签名数字签名是非对称密钥加密技术与数字摘要技术的应用,数字签名就是用加密算法加密报文文本的摘要(摘要通过hash函数得到)而生成的内容。发送报文时,发送方用一个哈希函数从报文文本中生成报文摘要,然后用发送方的私钥对这个摘要进行加密生成数字签名,之后将数字签名和报文一起发送给接收方,即数字证书。接收方首先用
- 零基础入门机器学习:用Scikit-learn实现鸢尾花分类
藍海琴泉
机器学习scikit-learn分类
适合人群:机器学习新手|数据分析爱好者|需快速展示案例的学生一、引言:为什么要学这个案例?目的:明确机器学习解决什么问题,建立学习信心。机器学习定义:让计算机从数据中自动学习规律(如分类鸢尾花品种)。为什么选鸢尾花数据集:数据量小、特征明确,适合教学演示。Scikit-learn优势:提供现成算法和工具,无需从头写数学公式。二、环境准备:5分钟快速上手目的:搭建可运行的代码环境,避免卡在工具安装环
- 访问者模式
烟沙九洲
设计模式访问者模式java
访问者(Visitor)模式属于行为型模式的一种。访问者模式主要用于分离算法和对象结构,从而在不修改原有对象的情况下扩展新的操作。它适用于数据结构相对稳定,而操作(行为)容易变化的场景。访问者模式允许在不修改现有类的情况下,为类层次结构中的对象定义新的操作。访问者模式通过将操作封装到一个独立的类(即访问者)中,使得对象结构与操作解耦。访问者模式使用了一种名为双分派(在运行时根据两个对象的类型动态选
- 机器学习--DBSCAN聚类算法详解
2201_75491841
机器学习算法聚类人工智能
目录引言1.什么是DBSCAN聚类?2.DBSCAN聚类算法的原理3.DBSCAN算法的核心概念3.1邻域(Neighborhood)3.2核心点(CorePoint)3.3直接密度可达(DirectlyDensity-Reachable)3.4密度可达(Density-Reachable)3.5密度相连(Density-Connected)4.DBSCAN算法的步骤5.DBSCAN算法的优缺点5
- 软考 中级软件设计师 考点知识点笔记总结 day06
莫问alicia
软考中级软件设计师笔记数据结构算法
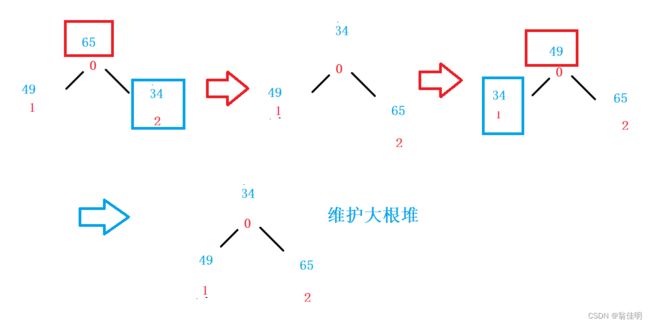
文章目录6、树和二叉树6.1、树的基本概念6.2、二叉树的基本概念6.3、二叉树的遍历6.4、查找二叉树(二叉排序树)BST6.5、构造霍夫曼树+6.6、线索二叉树6.7、平衡二叉树7、图7.1、存储结构-邻接矩阵7.2、存储结构-邻接表7.3、图的遍历7.4、拓扑排序7.5、最小生成树普利姆算法7.6、克鲁斯卡尔算法6、树和二叉树6.1、树的基本概念结点的度:一个结点的度是指该结点拥有的子树数量
- ngx_http_conf_port_t
若云止水
http网络协议网络
定义在src\http\ngx_http_core_module.htypedefstruct{ngx_int_tfamily;in_port_tport;ngx_array_taddrs;/*arrayofngx_http_conf_addr_t*/}ngx_http_conf_port_t;该结构体用于在Nginx配置阶段存储监听端口的配置信息,是listen指令解析后的核心数据结构。它将同一
- 机器学习实战 第一章 机器学习基础
LuoY、
MachineLearning机器学习算法人工智能
第一章机器学习1.1何谓机器学习1.2关键术语1.3机器学习的主要任务1.4如何选择合适的算法1.5开发机器学习应用程序的步骤1.6Python语言的优势1.1何谓机器学习 1、简单地说,机器学习就是把无序的数据转换成有用的信息; 2、机器学习能让我们自数据集中受启发,我们会利用计算机来彰显数据背后的真实含义; 3、机器学习横跨计算机科学、工程技术和统计学等多个学科,需要多学科的
- HTML实现酷炫3D相册
算法与编程之美
编程之美csshtmljscss3javascript
欢迎点击「算法与编程之美」↑关注我们!本文首发于微信公众号:"算法与编程之美",欢迎关注,及时了解更多此系列文章。欢迎加入团队圈子!与作者面对面!直接点击!目录1、创建文件目录2、调背景色3、制作3D相册4、将图片散开,围成一圈。5、绘制透明底盘6、最终效果1、创建文件目录在Hbuilder在新建一个目录,创建css和js文件。图12、调背景色在style块里面给整个页面渲染成黑色调。*{padd
- 蓝桥杯备赛计划
laitywgx
蓝桥杯职场和发展
1-2小时的蓝桥杯PythonB组冲刺日程表(持续1个月,聚焦高频考点):第一周:核心算法突破Day1(周一)学习重点:动态规划(01背包问题)学习资源:AcWing《蓝桥杯辅导课》第8讲(背包问题模板)代码模板速记:#一维01背包模板n,V=map(int,input().split())dp=[0]*(V+1)for_inrange(n):w,v=map(int,input().split()
- 机器学习怎么做特征工程
全栈你个大西瓜
人工智能机器学习人工智能特征工程数据预处理特征变换特征降维特征构造
一、特征工程通俗解释特征工程就像厨师做菜前的食材处理:原始数据是“生肉和蔬菜”,特征工程是“切块、腌制、调料搭配”,目的是让机器学习模型(食客)更容易消化吸收,做出更好预测(品尝美味)。二、为什么要做特征工程?数据质量差:原始数据常有缺失、噪声、不一致问题(如年龄列混入“未知”)。模型限制:算法无法直接理解原始数据(如文本、日期需要数值化)。提升效果:好特征能显著提升模型性能(准确率提升10%~5
- 【机器学习】机器学习四大分类
藓类少女
机器学习机器学习分类人工智能
机器学习的方法主要可以分为四大类,根据学习方式和数据标注情况进行分类:1.监督学习(SupervisedLearning)特点:有标注数据(即训练数据有明确的输入(X)和输出(Y))。学习目标是找到一个映射(f(X)\approxY)。适用于分类和回归问题。主要算法:分类(Classification):逻辑回归(LogisticRegression)支持向量机(SVM)朴素贝叶斯(NaïveBa
- 高频交易:当速度与智慧在金融市场中“飙车”(策略+算法)
西蒙斯.果
pythonnumpypandas
高频交易:当速度与智慧在金融市场中“飙车”高频交易(High-FrequencyTrading,HFT)就像金融市场的“闪电侠”,利用强大的计算机和复杂的算法,在毫秒甚至微秒内完成交易。它的目标是抓住市场中的微小机会,赚取“快钱”。以下是对高频交易策略和算法的详细介绍,带点幽默感,让你在了解金融科技的同时也能会心一笑。---一、高频交易策略:金融市场的“快闪族”1\.做市策略:买卖价差的“中间商”
- Github上神仙级大模型项目:大语言模型(LLM)入门学习路线图,三个月让你从大模型基础到精通!
AI大模型-大飞
github语言模型学习人工智能AI大模型程序员AI
Github项目上有一个大语言模型学习路线笔记,它全面涵盖了大语言模型的所需的基础知识学习,LLM前沿算法和架构,以及如何将大语言模型进行工程化实践。这份资料是初学者或有一定基础的开发/算法人员入门活深入大型语言模型学习的优秀参考。这份资料重点介绍了我们应该掌握哪些核心知识,并推荐了一系列优质的学习视频和博客,旨在帮助大家系统性地掌握大型语言模型的相关技术。大语言模型(LargeLanguageM
- AtCoder备赛冲刺必刷题(C++) | 洛谷 AT_abc396_a Triple Four
热爱编程的通信人
c++算法开发语言
本文分享的必刷题目是从蓝桥云课、洛谷、AcWing等知名刷题平台精心挑选而来,并结合各平台提供的算法标签和难度等级进行了系统分类。题目涵盖了从基础到进阶的多种算法和数据结构,旨在为不同阶段的编程学习者提供一条清晰、平稳的学习提升路径。欢迎大家订阅我的专栏:算法题解:C++与Python实现!附上汇总贴:算法竞赛备考冲刺必刷题(C++)|汇总【题目来源】洛谷:AT_abc396_a[ABC396A]
- 算法及数据结构系列 - 滑动窗口
诺亚凹凸曼
算法及数据结构算法数据结构java
系列文章目录算法及数据结构系列-二分查找算法及数据结构系列-BFS算法算法及数据结构系列-动态规划算法及数据结构系列-双指针算法及数据结构系列-回溯算法算法及数据结构系列-树文章目录滑动窗口框架思路经典题型76.最小覆盖子串567.字符串的排列438.找到字符串中所有字母异位词3.无重复字符的最长子串滑动窗口框架思路/*滑动窗口算法框架*/voidslidingWindow(strings,str
- 数据结构二叉树进阶
z一一m
数据结构数据结构算法
1.根据二叉树创建字符串1.题目2.分析原理要把二叉树元素按照前序顺序取出来,并且以字符串的形式返回,还要添加括号对于左子树和右子树,那么第一步就是向定义一个string类型来接收取出的元素,需要用到to_string函数把整型变成string类型,第二步就是递归来深度遍历了,但是需要判断一下,题目有些情况是省略了括号,有些没有省去,题目例子可以知道左为空右不为空就不能省略括号,左不为空右为空就可
- C/C++数据类型--整型类型
蓝心湄
C/C++数据类型c语言
概念数据类型表示的是数据的身份决定它可以进行什么操作、占用多少空间与数据结构的区别数据类型更倾向于表示数据的身份数据结构表示的是怎么操作数据(是在类型的基础上进行对数据的操作的)C语言允许使用的类型类型的分类算术类型:基本类型和枚举类型纯量类型:算术类型和指针类型组合类型:数组类型和结构体类型整型数据基本整型(int)长度为2字节或4字节短整型(shortint)长度为2字节长整型(longint
- 7种数据结构
就很对
数据结构windows
7种数据结构顺序表sqlite.hseqlite.c单链表linklist.clinklist.h双链表doulinklist.cdoulinklist.h链式栈linkstack.clinkstack.h队列SeqQueue.cSeqQueue.h树tree.c哈希表hash.c顺序表sqlite.h#ifndef__SEQLIST_H__#define__SEQLIST_H__typedefs
- QHDBO基于量子计算和多策略融合的蜣螂优化算法
算法小狂人
算法改进智能优化算法量子计算算法
2.DBO基本的蜣螂算法通过模拟蜣螂在自然界中的四种行为(滚动、产卵、觅食和偷窃)来执行种群位置更新。2.1滚动蜣螂在自然界中,蜣螂必须通过太阳导航,使其球滚动的路线尽可能直线。方程(1)用于原始论文中更新滚动蜣螂的位置:xi(t+1)=xi(t)+α⋅k⋅xi(t−1)+b⋅Δx(1)x_i(t+1)=x_i(t)+\alpha\cdotk\cdotx_i(t-1)+b\cdot\Deltax\
- H800能效架构实战解析
智能计算研究中心
其他
内容概要H800能效架构以异构计算资源调度与动态功耗控制为核心,通过系统级协同设计实现算力密度与能耗优化的双重目标。其核心技术覆盖智能负载分配、电压频率动态调节及热管理三大模块,形成从芯片级到数据中心级的垂直优化链路。在架构设计中,异构资源调度算法通过实时分析任务特征与硬件状态,动态分配CPU、GPU及专用加速器资源,最大化硬件利用率;动态功耗模块则基于负载波动自适应调整供电策略,结合多级电压频率
- 模型优化驱动产业应用创新
智能计算研究中心
其他
内容概要当前模型优化技术的迭代正沿着多维路径快速演进,其核心驱动力在于突破算法性能与产业需求间的适配瓶颈。以自适应学习机制与迁移学习框架为基础的优化策略,显著提升了模型在跨场景应用中的泛化能力,而超参数自动调优技术则通过PyTorch、TensorFlow等主流框架的接口标准化,降低了复杂模型的开发门槛。在部署层面,边缘计算与联邦学习的协同应用不仅缩短了金融预测、医疗影像分析等场景的响应延迟,更通
- Java序列化进阶篇
g21121
java序列化
1.transient
类一旦实现了Serializable 接口即被声明为可序列化,然而某些情况下并不是所有的属性都需要序列化,想要人为的去阻止这些属性被序列化,就需要用到transient 关键字。
- escape()、encodeURI()、encodeURIComponent()区别详解
aigo
JavaScriptWeb
原文:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_4586764e0101khi0.html
JavaScript中有三个可以对字符串编码的函数,分别是: escape,encodeURI,encodeURIComponent,相应3个解码函数:,decodeURI,decodeURIComponent 。
下面简单介绍一下它们的区别
1 escape()函
- ArcgisEngine实现对地图的放大、缩小和平移
Cb123456
添加矢量数据对地图的放大、缩小和平移Engine
ArcgisEngine实现对地图的放大、缩小和平移:
个人觉得是平移,不过网上的都是漫游,通俗的说就是把一个地图对象从一边拉到另一边而已。就看人说话吧.
具体实现:
一、引入命名空间
using ESRI.ArcGIS.Geometry;
using ESRI.ArcGIS.Controls;
二、代码实现.
- Java集合框架概述
天子之骄
Java集合框架概述
集合框架
集合框架可以理解为一个容器,该容器主要指映射(map)、集合(set)、数组(array)和列表(list)等抽象数据结构。
从本质上来说,Java集合框架的主要组成是用来操作对象的接口。不同接口描述不同的数据类型。
简单介绍:
Collection接口是最基本的接口,它定义了List和Set,List又定义了LinkLi
- 旗正4.0页面跳转传值问题
何必如此
javajsp
跳转和成功提示
a) 成功字段非空forward
成功字段非空forward,不会弹出成功字段,为jsp转发,页面能超链接传值,传输变量时需要拼接。接拼接方式list.jsp?test="+strweightUnit+"或list.jsp?test="+weightUnit+&qu
- 全网唯一:移动互联网服务器端开发课程
cocos2d-x小菜
web开发移动开发移动端开发移动互联程序员
移动互联网时代来了! App市场爆发式增长为Web开发程序员带来新一轮机遇,近两年新增创业者,几乎全部选择了移动互联网项目!传统互联网企业中超过98%的门户网站已经或者正在从单一的网站入口转向PC、手机、Pad、智能电视等多端全平台兼容体系。据统计,AppStore中超过85%的App项目都选择了PHP作为后端程
- Log4J通用配置|注意问题 笔记
7454103
DAOapachetomcatlog4jWeb
关于日志的等级 那些去 百度就知道了!
这几天 要搭个新框架 配置了 日志 记下来 !做个备忘!
#这里定义能显示到的最低级别,若定义到INFO级别,则看不到DEBUG级别的信息了~!
log4j.rootLogger=INFO,allLog
# DAO层 log记录到dao.log 控制台 和 总日志文件
log4j.logger.DAO=INFO,dao,C
- SQLServer TCP/IP 连接失败问题 ---SQL Server Configuration Manager
darkranger
sqlcwindowsSQL ServerXP
当你安装完之后,连接数据库的时候可能会发现你的TCP/IP 没有启动..
发现需要启动客户端协议 : TCP/IP
需要打开 SQL Server Configuration Manager...
却发现无法打开 SQL Server Configuration Manager..??
解决方法: C:\WINDOWS\system32目录搜索framedyn.
- [置顶] 做有中国特色的程序员
aijuans
程序员
从出版业说起 网络作品排到靠前的,都不会太难看,一般人不爱看某部作品也是因为不喜欢这个类型,而此人也不会全不喜欢这些网络作品。究其原因,是因为网络作品都是让人先白看的,看的好了才出了头。而纸质作品就不一定了,排行榜靠前的,有好作品,也有垃圾。 许多大牛都是写了博客,后来出了书。这些书也都不次,可能有人让为不好,是因为技术书不像小说,小说在读故事,技术书是在学知识或温习知识,有些技术书读得可
- document.domain 跨域问题
avords
document
document.domain用来得到当前网页的域名。比如在地址栏里输入:javascript:alert(document.domain); //www.315ta.com我们也可以给document.domain属性赋值,不过是有限制的,你只能赋成当前的域名或者基础域名。比如:javascript:alert(document.domain = "315ta.com");
- 关于管理软件的一些思考
houxinyou
管理
工作好多看年了,一直在做管理软件,不知道是我最开始做的时候产生了一些惯性的思维,还是现在接触的管理软件水平有所下降.换过好多年公司,越来越感觉现在的管理软件做的越来越乱.
在我看来,管理软件不论是以前的结构化编程,还是现在的面向对象编程,不管是CS模式,还是BS模式.模块的划分是很重要的.当然,模块的划分有很多种方式.我只是以我自己的划分方式来说一下.
做为管理软件,就像现在讲究MVC这
- NoSQL数据库之Redis数据库管理(String类型和hash类型)
bijian1013
redis数据库NoSQL
一.Redis的数据类型
1.String类型及操作
String是最简单的类型,一个key对应一个value,string类型是二进制安全的。Redis的string可以包含任何数据,比如jpg图片或者序列化的对象。
Set方法:设置key对应的值为string类型的value
- Tomcat 一些技巧
征客丶
javatomcatdos
以下操作都是在windows 环境下
一、Tomcat 启动时配置 JAVA_HOME
在 tomcat 安装目录,bin 文件夹下的 catalina.bat 或 setclasspath.bat 中添加
set JAVA_HOME=JAVA 安装目录
set JRE_HOME=JAVA 安装目录/jre
即可;
二、查看Tomcat 版本
在 tomcat 安装目
- 【Spark七十二】Spark的日志配置
bit1129
spark
在测试Spark Streaming时,大量的日志显示到控制台,影响了Spark Streaming程序代码的输出结果的查看(代码中通过println将输出打印到控制台上),可以通过修改Spark的日志配置的方式,不让Spark Streaming把它的日志显示在console
在Spark的conf目录下,把log4j.properties.template修改为log4j.p
- Haskell版冒泡排序
bookjovi
冒泡排序haskell
面试的时候问的比较多的算法题要么是binary search,要么是冒泡排序,真的不想用写C写冒泡排序了,贴上个Haskell版的,思维简单,代码简单,下次谁要是再要我用C写冒泡排序,直接上个haskell版的,让他自己去理解吧。
sort [] = []
sort [x] = [x]
sort (x:x1:xs)
| x>x1 = x1:so
- java 路径 配置文件读取
bro_feng
java
这几天做一个项目,关于路径做如下笔记,有需要供参考。
取工程内的文件,一般都要用相对路径,这个自然不用多说。
在src统计目录建配置文件目录res,在res中放入配置文件。
读取文件使用方式:
1. MyTest.class.getResourceAsStream("/res/xx.properties")
2. properties.load(MyTest.
- 读《研磨设计模式》-代码笔记-简单工厂模式
bylijinnan
java设计模式
声明: 本文只为方便我个人查阅和理解,详细的分析以及源代码请移步 原作者的博客http://chjavach.iteye.com/
package design.pattern;
/*
* 个人理解:简单工厂模式就是IOC;
* 客户端要用到某一对象,本来是由客户创建的,现在改成由工厂创建,客户直接取就好了
*/
interface IProduct {
- SVN与JIRA的关联
chenyu19891124
SVN
SVN与JIRA的关联一直都没能装成功,今天凝聚心思花了一天时间整合好了。下面是自己整理的步骤:
一、搭建好SVN环境,尤其是要把SVN的服务注册成系统服务
二、装好JIRA,自己用是jira-4.3.4破解版
三、下载SVN与JIRA的插件并解压,然后拷贝插件包下lib包里的三个jar,放到Atlassian\JIRA 4.3.4\atlassian-jira\WEB-INF\lib下,再
- JWFDv0.96 最新设计思路
comsci
数据结构算法工作企业应用公告
随着工作流技术的发展,工作流产品的应用范围也不断的在扩展,开始进入了像金融行业(我已经看到国有四大商业银行的工作流产品招标公告了),实时生产控制和其它比较重要的工程领域,而
- vi 保存复制内容格式粘贴
daizj
vi粘贴复制保存原格式不变形
vi是linux中非常好用的文本编辑工具,功能强大无比,但对于复制带有缩进格式的内容时,粘贴的时候内容错位很严重,不会按照复制时的格式排版,vi能不能在粘贴时,按复制进的格式进行粘贴呢? 答案是肯定的,vi有一个很强大的命令可以实现此功能 。
在命令模式输入:set paste,则进入paste模式,这样再进行粘贴时
- shell脚本运行时报错误:/bin/bash^M: bad interpreter 的解决办法
dongwei_6688
shell脚本
出现原因:windows上写的脚本,直接拷贝到linux系统上运行由于格式不兼容导致
解决办法:
1. 比如文件名为myshell.sh,vim myshell.sh
2. 执行vim中的命令 : set ff?查看文件格式,如果显示fileformat=dos,证明文件格式有问题
3. 执行vim中的命令 :set fileformat=unix 将文件格式改过来就可以了,然后:w
- 高一上学期难记忆单词
dcj3sjt126com
wordenglish
honest 诚实的;正直的
argue 争论
classical 古典的
hammer 锤子
share 分享;共有
sorrow 悲哀;悲痛
adventure 冒险
error 错误;差错
closet 壁橱;储藏室
pronounce 发音;宣告
repeat 重做;重复
majority 大多数;大半
native 本国的,本地的,本国
- hibernate查询返回DTO对象,DTO封装了多个pojo对象的属性
frankco
POJOhibernate查询DTO
DTO-数据传输对象;pojo-最纯粹的java对象与数据库中的表一一对应。
简单讲:DTO起到业务数据的传递作用,pojo则与持久层数据库打交道。
有时候我们需要查询返回DTO对象,因为DTO
- Partition List
hcx2013
partition
Given a linked list and a value x, partition it such that all nodes less than x come before nodes greater than or equal to x.
You should preserve the original relative order of th
- Spring MVC测试框架详解——客户端测试
jinnianshilongnian
上一篇《Spring MVC测试框架详解——服务端测试》已经介绍了服务端测试,接下来再看看如果测试Rest客户端,对于客户端测试以前经常使用的方法是启动一个内嵌的jetty/tomcat容器,然后发送真实的请求到相应的控制器;这种方式的缺点就是速度慢;自Spring 3.2开始提供了对RestTemplate的模拟服务器测试方式,也就是说使用RestTemplate测试时无须启动服务器,而是模拟一
- 关于推荐个人观点
liyonghui160com
推荐系统关于推荐个人观点
回想起来,我也做推荐了3年多了,最近公司做了调整招聘了很多算法工程师,以为需要多么高大上的算法才能搭建起来的,从实践中走过来,我只想说【不是这样的】
第一次接触推荐系统是在四年前入职的时候,那时候,机器学习和大数据都是没有的概念,什么大数据处理开源软件根本不存在,我们用多台计算机web程序记录用户行为,用.net的w
- 不间断旋转的动画
pangyulei
动画
CABasicAnimation* rotationAnimation;
rotationAnimation = [CABasicAnimation animationWithKeyPath:@"transform.rotation.z"];
rotationAnimation.toValue = [NSNumber numberWithFloat: M
- 自定义annotation
sha1064616837
javaenumannotationreflect
对象有的属性在页面上可编辑,有的属性在页面只可读,以前都是我们在页面上写死的,时间一久有时候会混乱,此处通过自定义annotation在类属性中定义。越来越发现Java的Annotation真心很强大,可以帮我们省去很多代码,让代码看上去简洁。
下面这个例子 主要用到了
1.自定义annotation:@interface,以及几个配合着自定义注解使用的几个注解
2.简单的反射
3.枚举
- Spring 源码
up2pu
spring
1.Spring源代码
https://github.com/SpringSource/spring-framework/branches/3.2.x
注:兼容svn检出
2.运行脚本
import-into-eclipse.bat
注:需要设置JAVA_HOME为jdk 1.7
build.gradle
compileJava {
sourceCompatibilit
- 利用word分词来计算文本相似度
yangshangchuan
wordword分词文本相似度余弦相似度简单共有词
word分词提供了多种文本相似度计算方式:
方式一:余弦相似度,通过计算两个向量的夹角余弦值来评估他们的相似度
实现类:org.apdplat.word.analysis.CosineTextSimilarity
用法如下:
String text1 = "我爱购物";
String text2 = "我爱读书";
String text3 =
![]()