Sentinel规则
一、服务熔断测试
例子:
application.properties配置文件
server.port=8083 spring.application.name=order #spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.server-addr=http://192.168.44.64:80 spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.server-addr=localhost:8848 spring.cloud.sentinel.transport.port=9999 spring.cloud.sentinel.transport.dashboard=localhost:8888 spring.cloud.sentinel.web-context-unify=false
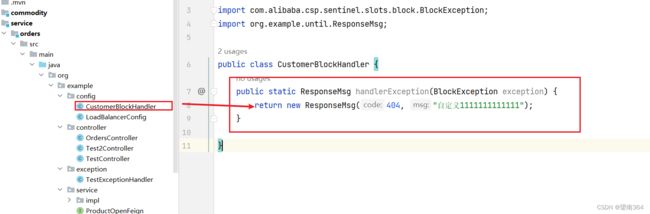
自定义业务类CustomerBlockHandler
public class CustomerBlockHandler {
public static ResponseMsg handlerException(BlockException exception) {
return new ResponseMsg(404, "自定义1111111111111");
}
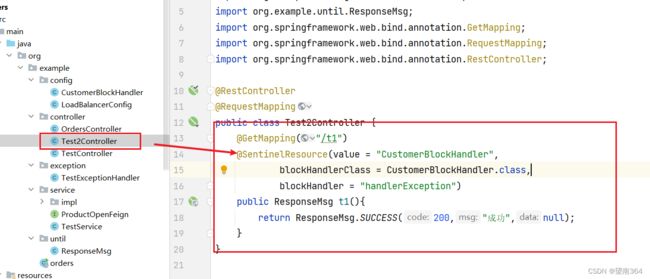
}controller类
@RestController
@RequestMapping
public class Test2Controller {
@GetMapping("/t1")
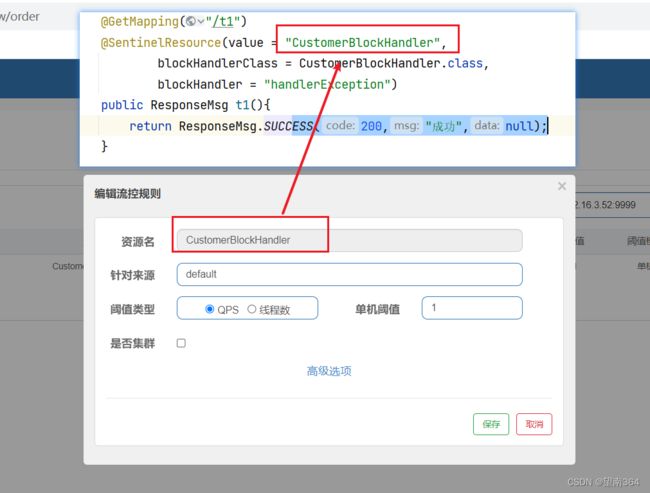
@SentinelResource(value = "CustomerBlockHandler",
blockHandlerClass = CustomerBlockHandler.class,
blockHandler = "handlerException")
public ResponseMsg t1(){
return ResponseMsg.SUCCESS(200,"成功",null);
}
}
Sentinel配置
二、配置流控效果
1. 快速失败(默认)
直接失败,抛出异常,不做任何额外的处理,是最简单的效果
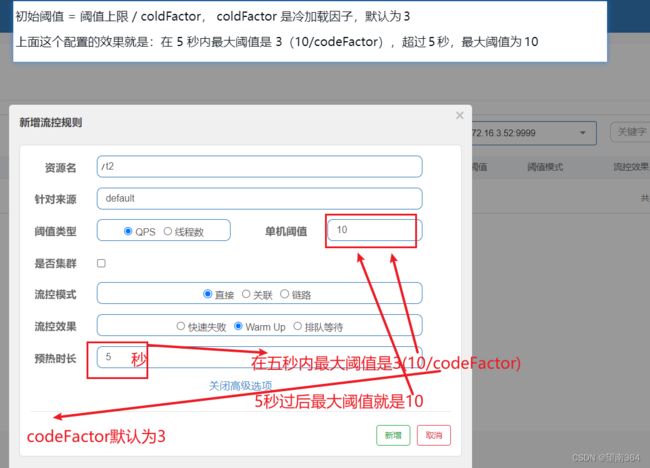
2. Warm Up
它从开始阈值到最大QPS阈值会有一个缓冲阶段,一开始的阈值是最大QPS阈值的1/3,然后慢慢.增长,直到最大阈值,适用于将突然增大的流量转换为缓步增长的场景
例子:
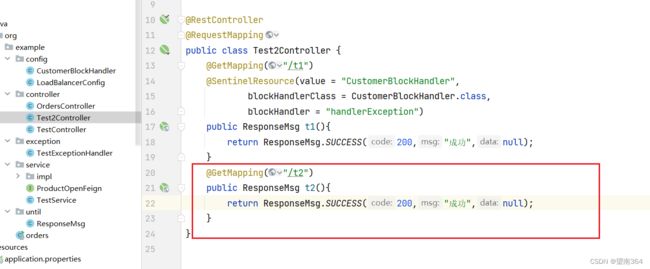
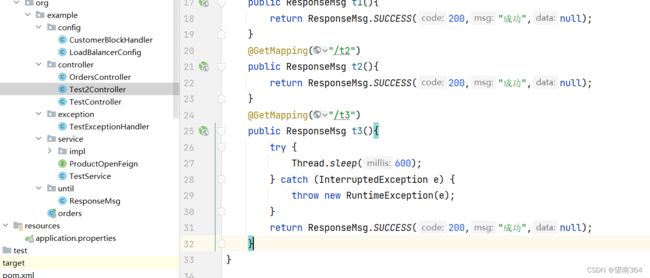
Controller类
@GetMapping("/t2")
public ResponseMsg t2(){
return ResponseMsg.SUCCESS(200,"成功",null);
}Sentinel配置
设置阈值为 10,预热时间是 5 秒,逐渐增加到阈值上限,所以会有一个初始阈值
初始阈值 = 阈值上限 / coldFactor, coldFactor 是冷加载因子,默认为3
上面这个配置的效果就是:在 5 秒内最大阈值是 3(10/codeFactor),超过5秒,最大阈值为10
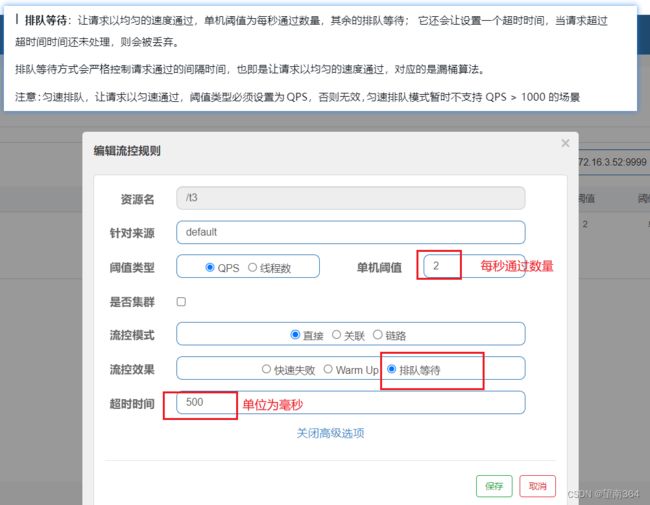
3. 排队等待
让请求以均匀的速度通过,单机阈值为每秒通过数量,其余的排队等待; 它还会让设置一个超时时间,当请求超过超时间时间还未处理,则会被丢弃
排队等待方式会严格控制请求通过的间隔时间,也即是让请求以均匀的速度通过,对应的是漏桶算法。
注意:匀速排队,让请求以匀速通过,阈值类型必须设置为QPS,否则无效,匀速排队模式暂时不支持 QPS > 1000 的场景
例子:
Controller
@GetMapping("/t3")
public ResponseMsg t3(){
return ResponseMsg.SUCCESS(200,"成功",null);
}Sentinel配置
当阈值设为 2 的时候,则代表一秒匀速的通过 2 个请求,也就是每个请求平均间隔恒定为 1000 / 2 = 500 ms,每一个请求的最长等待时间(maxQueueingTimeMs)为 0.5s 。
三、降级规则
降级规则就是设置当满足什么条件的时候,对服务进行降级
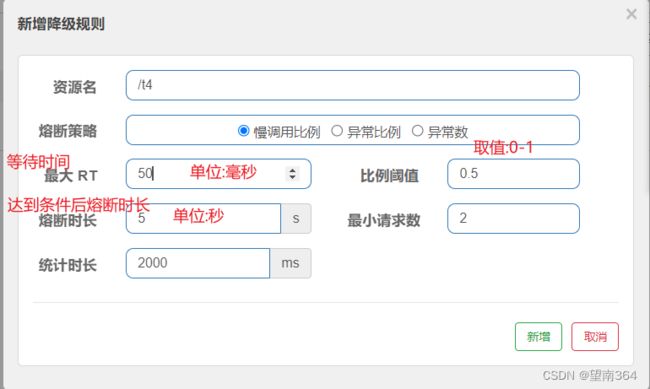
慢调用比例
例子:
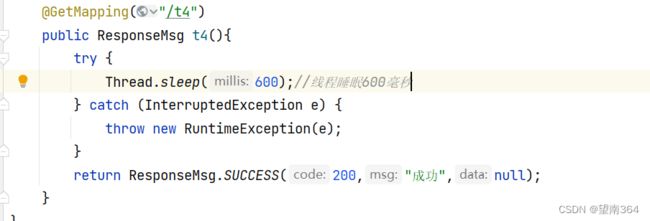
Controller
@GetMapping("/t4")
public ResponseMsg t4(){
try {
Thread.sleep(600);//线程睡眠600毫秒
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return ResponseMsg.SUCCESS(200,"成功",null);
}Sentinel配置
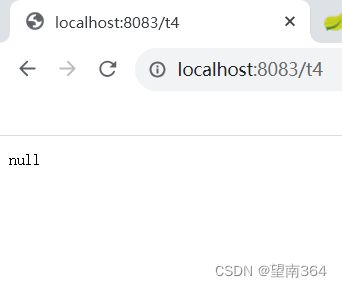
测试
这样在5秒内查询的结果一直为空
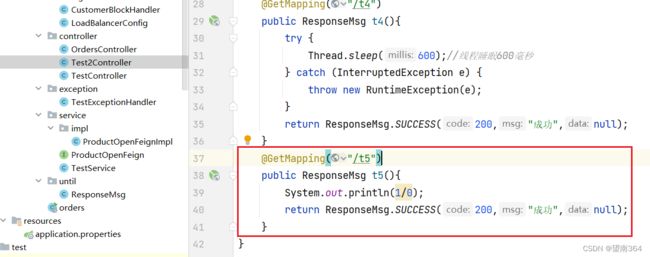
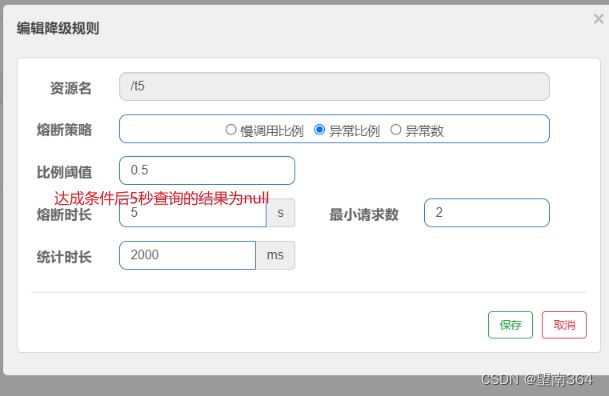
异常比例
当资源的每秒请求量>=5,并且每秒异常总数占通过量的比值超过阈值之后,资源进入降级状态,即在接下的时间窗口智能,对这个方法的调用都会自动地返回。异常比率的阈值范围是[0.0,1.0],代表0%~100%
例子:
Controller
@GetMapping("/t5")
public ResponseMsg t5(){
System.out.println(1/0);
return ResponseMsg.SUCCESS(200,"成功",null);
}Sentinel配置
测试
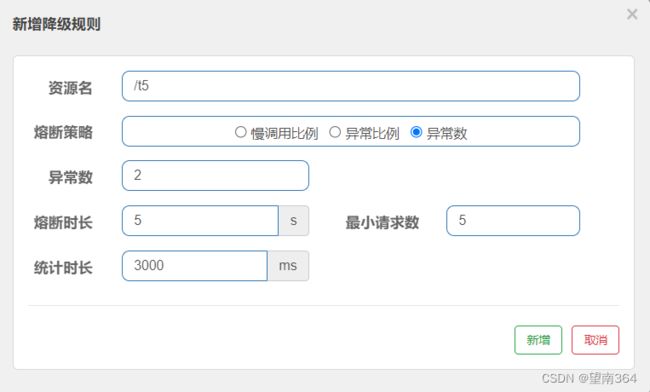
异常数
跟异常比例基本上一样
例子:
Controller
@GetMapping("/t5")
public ResponseMsg t5(){
System.out.println(1/0);
return ResponseMsg.SUCCESS(200,"成功",null);
}Sentinel配置
测试
四、热点规则
热点参数流控规则是一种更细粒度的流控规则, 它允许将规则具体到参数上。
热点规则普通使用
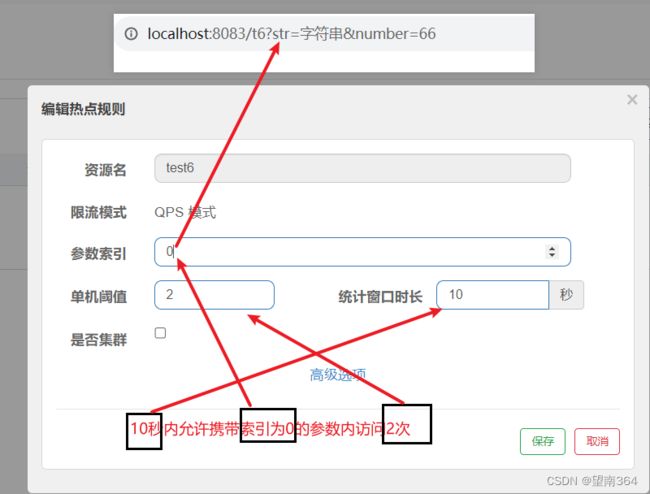
Controller
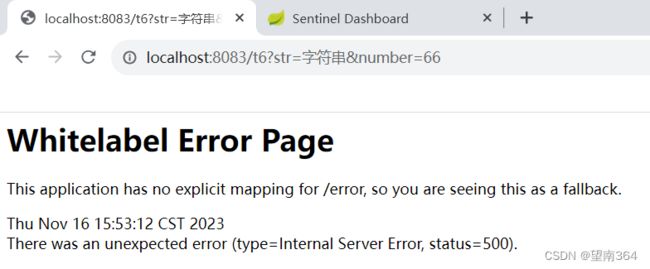
@GetMapping("/t6")
@SentinelResource(value = "test6")
//注意这里必须使用这个注解标识,热点规则不生效
public ResponseMsg t6(String str , Integer number){
return ResponseMsg.SUCCESS(number,"成功",str);
}Sentinel配置
测试
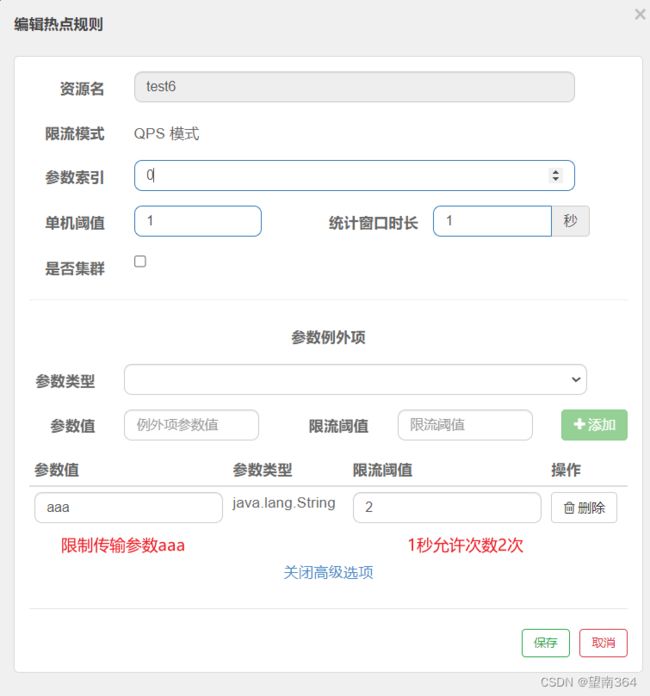
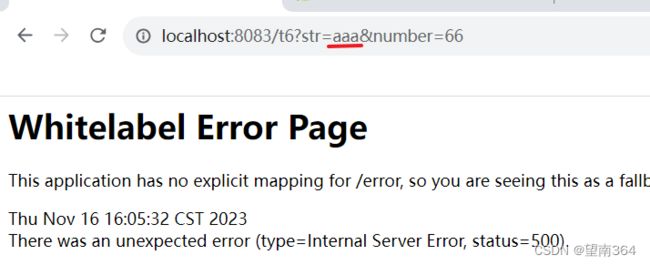
热点规则增强使用
controller
跟上面的普通使用一样
@GetMapping("/t6")
@SentinelResource(value = "test6")
//注意这里必须使用这个注解标识,热点规则不生效
public ResponseMsg t6(String str , Integer number){
return ResponseMsg.SUCCESS(number,"成功",str);
}Sentinel配置
测试
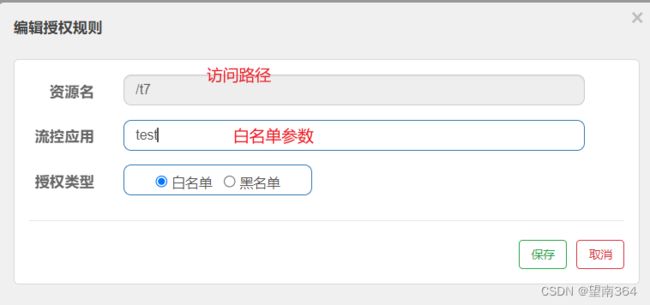
五、授权规则
很多时候,我们需要根据调用来源来判断该次请求是否允许放行,这时候可以使用 Sentinel 的来源 访问控制的功能。来源访问控制根据资源的请求来源(origin)限制资源是否通过: 若配置白名单,则只有请求来源位于白名单内时才可通过; 若配置黑名单,则请求来源位于黑名单时不通过,其余的请求通过
例子:
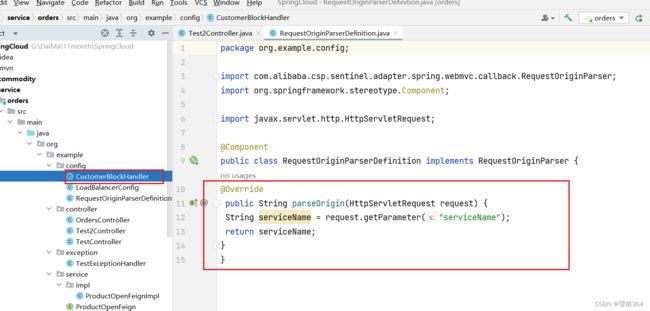
自定义来源处理规则
@Component
public class RequestOriginParserDefinition implements RequestOriginParser {
@Override
public String parseOrigin(HttpServletRequest request) {
String serviceName = request.getParameter("serviceName");
return serviceName;
}
}
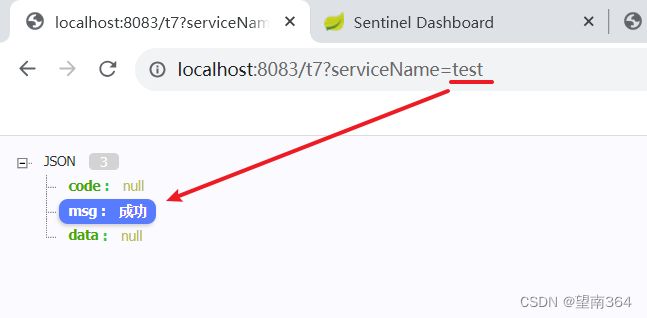
Controller
@GetMapping("/t7")
public ResponseMsg t7(String str , Integer number){
return ResponseMsg.SUCCESS(number,"成功",str);
}Sentinel配置
测试
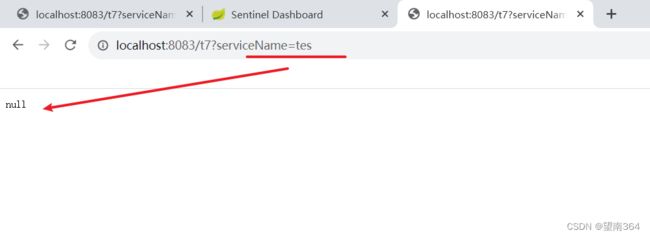
黑名单同样如此 只不过携带的参数是设置的参数将被拦截
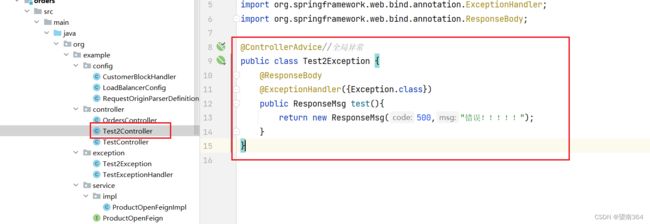
六、全局异常的返回
异常配置类
@ControllerAdvice//全局异常
public class Test2Exception {
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler({Exception.class})
public ResponseMsg test(){
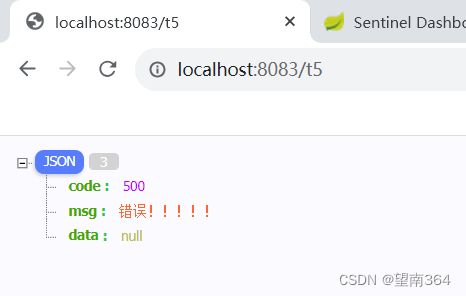
return new ResponseMsg(500,"错误!!!!!");
}
}controller
@GetMapping("/t5")
public ResponseMsg t5(){
System.out.println(1/0);
return ResponseMsg.SUCCESS(200,"成功",null);
}测试
七、Sentinel规则持久化
以通过Dashboard来为每个Sentinel客户端设置各种各样的规则,但是这里有一个问题,就是这些规则默认是存放在内存中,极不稳定,所以需要将其持久化。
方法一
添加到nacos里面
在配置文件application中添加以下内容
spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.ds1.nacos.data-id=${spring.application.name}
spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.ds1.nacos.data-type=json
spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.ds1.nacos.server-addr=localhost:8848
spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.ds1.nacos.group-id=DEFAULT_GROUP
spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.ds1.nacos.rule-type=flow
在nacos中为cloudalibaba-sentinel-service(可以在配置文件自定义)服务添加对应配置。
[
{
"resource": "/rateLimit/customerBlockHandler",#/rateLimit/customerBlockHandler
"limitApp": "default",
"grade": 1,
"count": 1,
"strategy": 0,
"controlBehavior": 0,
"clusterMode": false
}
]
resource: 资源名称;
imitApp: 来源应用;
grade: 阈值类型,0表示线程数,1表示QPS;
count: 单机阈值;
strategy: 流控模式,0表示直接,1表示关联,2表示链路;
controlBehavior: 流控效果,0表示快速失败,1表示。Warm Up,2表示排队等待。
clusterMode: 是否集群。
方法二
使用文件
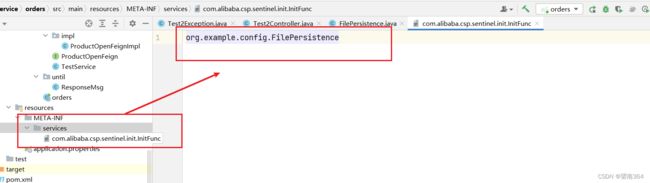
先创建一个FilePersistence类
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.command.handler.ModifyParamFlowRulesCommandHandler;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.*;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthorityRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthorityRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.param.ParamFlowRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.param.ParamFlowRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.transport.util.WritableDataSourceRegistry;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.TypeReference;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
public class FilePersistence implements InitFunc {
@Value("${spring.application.name}")
private String appcationName;
@Override
public void init() throws Exception {
String ruleDir = System.getProperty("user.home") + "/sentinel-rules/" + appcationName;
String flowRulePath = ruleDir + "/flow-rule.json";
String degradeRulePath = ruleDir + "/degrade-rule.json";
String systemRulePath = ruleDir + "/system-rule.json";
String authorityRulePath = ruleDir + "/authority-rule.json";
String paramFlowRulePath = ruleDir + "/param-flow-rule.json";
this.mkdirIfNotExits(ruleDir);
this.createFileIfNotExits(flowRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(degradeRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(systemRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(authorityRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(paramFlowRulePath);
// 流控规则
ReadableDataSource> flowRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
flowRulePath,
flowRuleListParser
);
FlowRuleManager.register2Property(flowRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource> flowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
flowRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerFlowDataSource(flowRuleWDS);
// 降级规则
ReadableDataSource> degradeRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
degradeRulePath,
degradeRuleListParser
);
DegradeRuleManager.register2Property(degradeRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource> degradeRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
degradeRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerDegradeDataSource(degradeRuleWDS);
// 系统规则
ReadableDataSource> systemRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
systemRulePath,
systemRuleListParser
);
SystemRuleManager.register2Property(systemRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource> systemRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
systemRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerSystemDataSource(systemRuleWDS);
// 授权规则
ReadableDataSource> authorityRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
authorityRulePath,
authorityRuleListParser
);
AuthorityRuleManager.register2Property(authorityRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource> authorityRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
authorityRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerAuthorityDataSource(authorityRuleWDS);
// 热点参数规则
ReadableDataSource> paramFlowRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
paramFlowRulePath,
paramFlowRuleListParser
);
ParamFlowRuleManager.register2Property(paramFlowRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource> paramFlowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
paramFlowRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
ModifyParamFlowRulesCommandHandler.setWritableDataSource(paramFlowRuleWDS);
}
private Converter> flowRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference>() {
}
);
private Converter> degradeRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference>() {
}
);
private Converter> systemRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference>() {
}
);
private Converter> authorityRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference>() {
}
);
private Converter> paramFlowRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference>() {
}
);
private void mkdirIfNotExits(String filePath) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdirs();
}
}
private void createFileIfNotExits(String filePath) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
}
private String encodeJson(T t) {
return JSON.toJSONString(t);
}
} 写上刚才的配置类位置
这样每次设置的配置项目重启都不会清空了