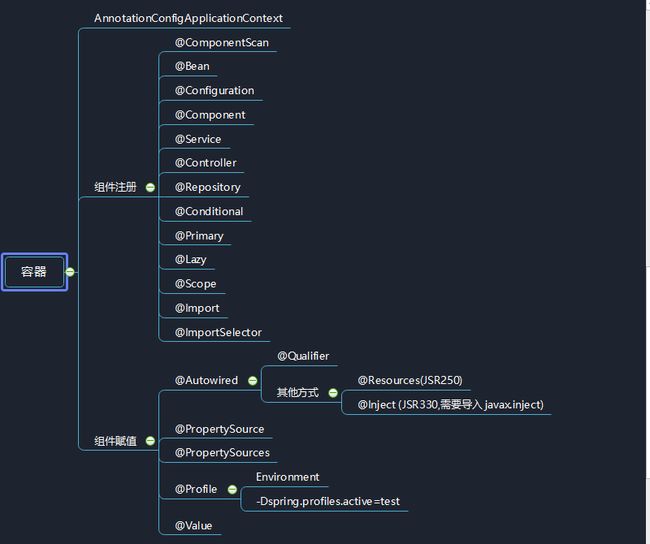
深入学习Spring IOC组件注册
@Configuration配置spring并启动spring容器
@Configuration用于定义配置类,标注在类上,相当于把该类作为spring的xml配置文件中的
实例说明:
配置类
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
public MyConfig() {
System.out.println("TestConfig容器初始化!!!!");
}
}
相当于xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
</beans>
测试类
public class TestConfig {
@Test
public void test(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyConfig.class);
}
}
运行结果
TestConfig容器初始化!!!!
@Configuration&@Bean给容器中注册组件
@Bean标注在方法上,相当于xml配置配置中的
代码实例说明:
注册类
public class ConfigurationBean {
public void start() {
System.out.println("容器初始化开始!!!!!");
}
}
配置类
@Configuration
public class MyConfiguration {
//可以指定bean 的名称,也可以指定注入容器之前加载的方法
@Bean()
public ConfigurationBean configurationBean(){
return new ConfigurationBean();
}
}
相当于xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="configurationBean" class="zfcoding.bean.ConfigurationBean" ></bean>
</beans>
测试方法
@Test
public void ConfigurationTest(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyConfiguration.class);
ConfigurationBean configurationBean=(ConfigurationBean) applicationContext.getBean("configurationBean");
System.out.println(configurationBean);
}
运行结果:
容器初始化开始!!!!!
zfcoding.bean.ConfigurationBean@77be656f
说明几点:
(1)、@Bean注解标注在方法上,如果未通过@Bean指定bean的名称,则默认与标注的方法名相同;
(2)、@Bean注解标注在方法上,如果想通过@Bean指定bean的名称,例如 @Bean(“configurationBean1”),那么容器中实例化bean的名称为configurationBean1;
@Bean 指定初始化和销毁的方法及@Scope ,@Lazy
容器bean管理的生命周期:
我们可以自定义初始化和销毁的方法,容器在bean进行到当前生命周期的时候来调用我们自定义的初始化和销毁的方法。
@Bean 中指定初始化和销毁的方法。
@Bean(initMethod = “init”,destroyMethod = “destory”)
xml
<bean id="student" class="zfcoding.bean.Student" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory"></bean>
@Scope
默认情况下: singleton 单实例(默认值),ioc容器启动会调用方法创建对象放到ioc容器当中。以后每次获取直接获取对象。
prototype :多实例,ioc容器启动并不会调用方法创建对象放到容器当中。,而是每次获取的时候才会调用方法创建对象,调用一次创建一次。
@Lazy 懒加载,
针对单实例bean,默认在容器启动的时候创建对象
懒加载:容器启动不创键对象,第一次使用Bean创建对象,并初始化。
实例说明:
public class Student {
public Student() {
System.out.println("Student容器加载开始!!!!");
}
//对象创建完成,并赋值好,调用初始化方法......
public void init() {
System.out.println("Student.init()初始化开始.....");
}
//销毁针对(单实例),容器关闭的时候调用。
//多实例(@Scope("prototype")):容器不会管理这个bean,容器也不回调用销毁的方法。
public void destory() {
System.out.println("Student.destory().........");
}
}
@Configuration
public class MyConfigStudent {
//@Lazy
//@Scope("prototype")
@Bean(value = "student",initMethod = "init",destroyMethod = "destory")
public Student student(){
return new Student();
}
}
测试类一
public class MyConfigStudent