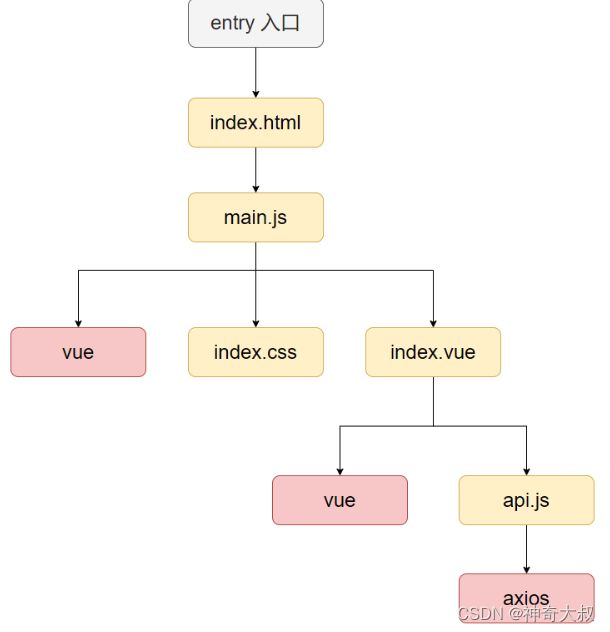
vite 依赖预构建-依赖扫描
文章目录
- 依赖预构建的目的
- 需要预构建的模块
- 依赖扫描方式
-
- 树的深度遍历
- 子节点的处理
- 遍历的具体实现
- esbuild插件编写
- 源码解析
-
- 依赖扫描的入口
- js模块
- 非js模块
- bare import
- html、vue 类型模块
- 虚拟模块加载对应的 script 代码
- 扫描结果
依赖预构建的目的
- 目的是为了兼容 CommonJS 和 UMD,以及提升性能。
需要预构建的模块
- 只有 bare import(裸依赖)会执行依赖预构建
- bare import:一般是 npm 安装的模块,是第三方的模块,不是我们自己写的代码,一般情况下是不会被修改的,因此对这部分的模块提前执行构建并且进行缓存,有利于提升性能。
- monorepo下的模块不会被预构建,部分模块虽然是 bare import,但这些模块也是开发者自己写的,不是第三方模块,因此 Vite 没有对该部分的模块执行预构建。
// vue 是 bare import
import vue from "vue"
import xxx from "vue/xxx"
// 以下不是裸依赖,用路径去访问的模块,不是 bare import
import foo from "./foo.ts"
import foo1 from "/foo.ts"
- vite的判断
依赖扫描方式
-
树的深度遍历
-
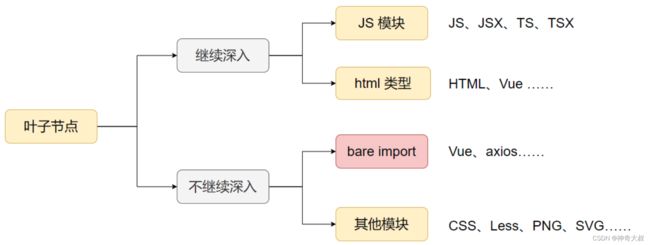
当前节点不需要继续深度的情况
- 当遇到 bare import 节点时,记录下该依赖,就不需要继续深入遍历
- 遇到其他 JS 无关的模块,如 CSS、SVG 等,因为不是 JS 代码,因此也不需要继续深入遍历
- 当所有的节点遍历完成后,记录的 bare import 对象,就是依赖扫描的结果。
-
子节点的处理
- bare import
- 通过模块id,模块 id 不为路径的模块,就是 bare import。遇到这些模块则记录依赖,不再深入遍历
- 在解析过程中,将裸依赖保存到 deps 对象中,设置为 external
- 其他 js 无关的模块
- 可以通过模块的后缀名判断,例如遇到 *.css 的模块,无需任何处理,不再深入遍历。
- 在解析过程中,设置为 external
- js 模块
- 将代码转成 AST,获取其中 import 语句引入的模块,或者正则匹配出所有 import 的模块,然后继续深入遍历这些模块
- html、vue 类型模块
- 需要把这部分 JS 代码提取出来,然后按 JS 模块进行分析处理,继续深入遍历这些模块。这里只需要关心 JS 部分,其他部分不会引入模块。
- 在解析过程中,将这些模块加载成 JS
- 非es module模块,不做处理
- 每个外联 script:src=‘xxx/xxx’;会直接转换为 import 语句,引入外部 script
- 每个内联 script,及直接在script中写内容,其内容将会通过虚拟模块被引入。
- 虚拟模块:是模块的内容并非直接从磁盘中读取,而是编译时生成。多个内联的 script 标签,其内容无法处理成一个 js 文件 (因为可能会有命名冲突等原因),既然无法将多个内联 script,就只能将它们分散成多个虚拟模块,然后分别引入了
- 如:src/main.ts 是磁盘中实际存在的文件,而 virtual-module:D:/project/index.html?id=0 在磁盘中是不存在的,需要借助打包工具(如 esbuild),在编译过程生成。
- bare import
-
-
遍历的具体实现
- 用 esbuild 工具打包,因为打包过程本质上也是个深度遍历模块的过程
- 深入遍历模块:正常解析模块(esbuild 默认行为),返回模块的文件真实路径
- 不用继续深度遍历的节点:esbuild 可以在解析过程,指定当前解析的模块为 external
则 esbuild 不再深入解析和加载该模块。
- 最终 dep 对象中收集到的依赖就是依赖扫描的结果
- 用 esbuild 工具打包,因为打包过程本质上也是个深度遍历模块的过程
esbuild插件编写
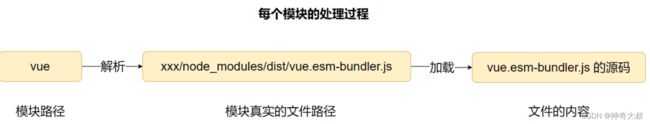
- 每个模块都会经过解析(resolve)和加载(load)的过程:
解析:将模块路径,解析成文件真实的路径。例如 vue,会解析到实际 node_modules 中的 vue 的入口 js 文件
加载:根据解析的路径,读取文件的内容
const plugin = {
name: 'xxx',
setup(build) {
// 定制解析过程,所有的 http/https 的模块,都会被 external
build.onResolve({ filter: /^(https?:)?\/\// }, ({ path }) => ({
path,
external: true
}))
// 定制解析过程,给所有 less 文件 namespace: less 标记
build.onResolve({ filter: /.*\.less/ }, args => ({
path: args.path,
namespace: 'less',
}))
// 定义加载过程:只处理 namespace 为 less 的模块
build.onLoad({ filter: /.*/, namespace: 'less' }, () => {
const raw = fs.readFileSync(path, 'utf-8')
const content = // 省略 less 处理,将 less 处理成 css
return {
contents,
loader: 'css'
}
})
}
}
-
通过 onResolve、onLoad 定义解析和加载过程
-
onResolve 的第一个参数为过滤条件,第二个参数为回调函数,解析时调用,返回值可以给模块做标记,如 external、namespace(用于过滤),还需要返回模块的路径
-
onLoad 的第一个参数为过滤条件,第二个参数为回调函数,加载时调用,可以读取文件的内容,然后进行处理,最后返回加载的内容。
源码解析
依赖扫描的入口
import { build } from 'esbuild'
export async function scanImports(config: ResolvedConfig): Promise<{
deps: Record<string, string>
missing: Record<string, string>
}> {
// 将项目中所有的 html 文件作为入口,会排除 node_modules
let entries: string[] = await globEntries('**/*.html', config)
// 扫描到的依赖,会放到该对象
const deps: Record<string, string> = {}
// 缺少的依赖,用于错误提示
const missing: Record<string, string> = {}
// esbuild 扫描插件,这个是重点!!!
// 它定义了各类模块(节点)的处理方式。
const plugin = esbuildScanPlugin(config, container, deps, missing, entries)
// 获取用户配置的 esbuild 自定义配置,没有配置就是空的
const { plugins = [], ...esbuildOptions } =
config.optimizeDeps?.esbuildOptions ?? {}
await Promise.all(
// 入口可能不止一个,分别用 esbuid 打包
entries.map((entry) =>
// esbuild 打包
build({
absWorkingDir: process.cwd(),
write: false,
entryPoints: [entry],
bundle: true,
format: 'esm',
// 使用插件
plugins: [...plugins, plugin],
...esbuildOptions
})
)
)
return {
deps,
missing
}
}
esbuildScanPlugin
function esbuildScanPlugin(
config: ResolvedConfig,
container: PluginContainer,
depImports: Record<string, string>,
missing: Record<string, string>,
entries: string[]
): Plugin
//config:Vite 的解析好的用户配置
//container:这里只会用到 container.resolveId 的方法,这个方法能将模块路径转成真实路径。
//例如 vue 转成 xxx/node_modules/dist/vue.esm-bundler.js。
//depImports:用于存储扫描到的依赖对象,插件执行过程中会被修改
//missing:用于存储缺少的依赖的对象,插件执行过程中会被修改
//entries:存储所有入口文件的数组
- esbuild 默认能将模块路径转成真实路径,为什么还要用 container.resolveId ?因为 Vite/Rollup 的插件,也能扩展解析的流程,例如 alias 的能力,我们常常会在项目中用 @ 的别名代表项目的 src 路径。因此不能用 esbuild 原生的解析流程进行解析。
container.resolveId
- 这个方法能将模块路径转成真实路径,并进行缓存
const seen = new Map<string, string | undefined>()
const resolve = async (
id: string,
importer?: string,
options?: ResolveIdOptions
) => {
const key = id + (importer && path.dirname(importer))
// 如果有缓存,就直接使用缓存
if (seen.has(key)) {
return seen.get(key)
}
// 将模块路径转成真实路径
const resolved = await container.resolveId(
id,
importer && normalizePath(importer),
{
...options,
scan: true
}
)
// 缓存解析过的路径,之后可以直接获取
const res = resolved?.id
seen.set(key, res)
return res
}
js模块
- esbuild 能够分析出 js 文件中的依赖,并进一步深入处理这些依赖。
非js模块
// external urls
build.onResolve({ filter: /^(https?:)?\/\// }, ({ path }) => ({
path,
external: true
}))
// external css 等文件
build.onResolve(
{
filter: /\.(css|less|sass|scss|styl|stylus|pcss|postcss|json|wasm)$/
},
({ path }) => ({
path,
external: true
}
)
// 省略其他 JS 无关的模块
bare import
build.onResolve(
{
// 第一个字符串为字母或 @,且第二个字符串不是 : 冒号。如 vite、@vite/plugin-vue
// 目的是:避免匹配 window 路径,如 D:/xxx
filter: /^[\w@][^:]/
},
async ({ path: id, importer, pluginData }) => {
// depImports中已存在
if (depImports[id]) {
return externalUnlessEntry({ path: id })
}
// 将模块路径转换成真实路径,实际上调用 container.resolveId
const resolved = await resolve(id, importer, {
custom: {
depScan: { loader: pluginData?.htmlType?.loader }
}
})
// 如果解析到路径,证明找得到依赖
// 如果解析不到路径,则证明找不到依赖,要记录下来后面报错
if (resolved) {
if (shouldExternalizeDep(resolved, id)) {
return externalUnlessEntry({ path: id })
}
// 如果模块在 node_modules 中,则记录 bare import
if (resolved.includes('node_modules')) {
// 记录 bare import
depImports[id] = resolved
return {
path,
external: true
}
}
// isScannable 判断该文件是否可以扫描,可扫描的文件有 JS、html、vue 等
// 因为有可能裸依赖的入口是 css 等非 JS 模块的文件,如import 'xx.less'
else if (isScannable(resolved)) {
// 真实路径不在 node_modules 中,则证明是 monorepo,实际上代码还是在用户的目录中
// 是用户自己写的代码,不应该 external
return {
path: path.resolve(resolved)
}
} else {
// 其他模块不可扫描,直接忽略,external
return {
path,
external: true
}
}
} else {
// 解析不到依赖,则记录缺少的依赖
missing[id] = normalizePath(importer)
}
}
)
html、vue 类型模块
const htmlTypesRE = /\.(html|vue|svelte|astro)$/
// html types: 提取 script 标签
build.onResolve({ filter: htmlTypesRE }, async ({ path, importer }) => {
// 将模块路径,转成文件的真实路径
const resolved = await resolve(path, importer)
if (!resolved) return
// 不处理 node_modules 内的
if (resolved.includes('node_modules'){
return
}
return {
path: resolved,
// 标记 namespace 为 html
namespace: 'html'
}
})
- 加载过程
- 读取文件源码
- 正则匹配出所有的 script 标签,并对每个 script 标签的内容进行处理
- 外部 script,改为用 import 引入
- 内联 script,改为引入虚拟模块,并将对应的虚拟模块的内容缓存到 script 对象。
最后返回转换后的 js
// 正则,匹配例子:
const scriptModuleRE = /(]*type\s*=\s*(?:"module"|'module')[^>]*>)(.*?)<\/script> /gims
// 正则,匹配例子:
export const scriptRE = /(]*>|>))(.*?)<\/script> /gims
build.onLoad(
{ filter: htmlTypesRE, namespace: 'html' },
async ({ path }) => {
// 读取源码
let raw = fs.readFileSync(path, 'utf-8')
// 去掉注释,避免后面匹配到注释
raw = raw.replace(commentRE, '')
const isHtml = path.endsWith('.html')
// scriptModuleRE:
// scriptRE:
// html 模块,需要匹配 module 类型的 script,因为只有 module 类型的 script 才能使用 import
const regex = isHtml ? scriptModuleRE : scriptRE
// 重置正则表达式的索引位置,因为同一个正则表达式对象,每次匹配后,lastIndex 都会改变
// regex 会被重复使用,每次都需要重置为 0,代表从第 0 个字符开始正则匹配
regex.lastIndex = 0
// load 钩子返回值,表示加载后的 js 代码
let js = ''
let scriptId = 0
let match: RegExpExecArray | null
// 匹配源码的 script 标签,用 while 循环,因为 html 可能有多个 script 标签
while ((match = regex.exec(raw))) {
// openTag: 它的值的例子: