springboot启动bean加载处理器ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 一(@ComponentScan注解)
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 是spring加载bean的重要入口,我们先来看下该类的关系图

可以看到它实现了接口BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,这个类的作用就不在这里展开了。
那ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 是怎么加载bean信息的呢?
- 首先会在当前容器中加载有 @Configuration注解的类,我们当前是基于springboot的,我们知道SpringApplication中的run方法中会传入一个source类(一般就是启动类),这个类会加载到spring bean容器中
- 定义个ConfigurationClassParser,进行解析,在构造方法中会定义componentScanParser=ComponentScanAnnotationParser(后续扫描工作的员工)
- 调用ConfigurationClassParser中的parse进行解析,参数是springboot的source类,然后调用方法doProcessConfigurationClass会依次对**@PropertySource、 @ComponentScan、@Import、@ImportResource、@Bean**注解进行解析并导入类。
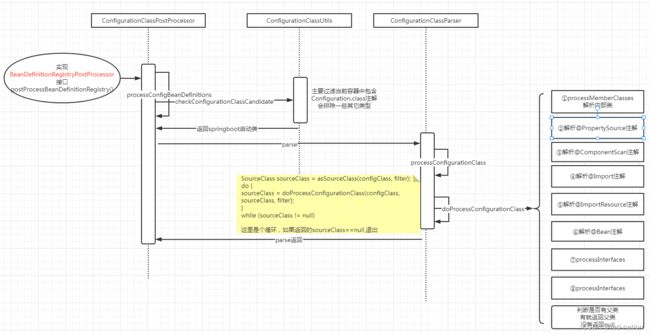
为啥首先将@ComponentScan呢,一般我们在springboot启动类上加的注解是@SpringBootApplication,而该注解包含了@ComponentScan
下面就进入本文的重点@ComponentScan工作流程。我们先看下源码执行
@Nullable
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(
ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass, Predicate<String> filter)
throws IOException {
// Process any @PropertySource annotations
...
// Process any @ComponentScan annotations
Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&
!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
if (bdCand == null) {
bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();
}
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
}
// Process any @Import annotations
// Process any @ImportResource annotations
// Process individual @Bean methods
...
// No superclass -> processing is complete
return null;
...
}
}
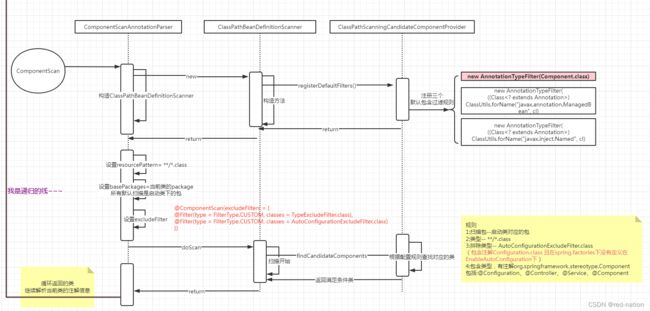
方法获取当前类的@ComponentScans, @ComponentScan注解信息,然后进入ComponentScanAnnotationParser的parse的方法,该方法会构建一个ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner类信息并读取注解中的信息进行赋值,该类的重要组成信息看下
- 设置resourcePattern 默认"**/*.class"
- 设置includeFilters(包含),注解默认是空,但是会在构造方法中添加3个类型,主要关注new AnnotationTypeFilter(Component.class)
- 设置excludeFilters(排除),注解默认两个类型
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class),要对该注解进行讲解下,看下他的排除规则:包含Configuration注解信息 且 在spring.factories中定义了,并且key=org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration会排除
public class AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter implements TypeFilter, BeanClassLoaderAware {
private ClassLoader beanClassLoader;
private volatile List<String> autoConfigurations;
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader beanClassLoader) {
this.beanClassLoader = beanClassLoader;
}
@Override
public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory)
throws IOException {
return isConfiguration(metadataReader) && isAutoConfiguration(metadataReader);
}
private boolean isConfiguration(MetadataReader metadataReader) {
// 包含Configuration注解信息
return
metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata().isAnnotated(Configuration.class.getName());
}
private boolean isAutoConfiguration(MetadataReader metadataReader) {
// 在spring.factories中定义了,并且key=org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration
return getAutoConfigurations().contains(metadataReader.getClassMetadata().getClassName());
}
protected List<String> getAutoConfigurations() {
if (this.autoConfigurations == null) {
this.autoConfigurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(EnableAutoConfiguration.class,
this.beanClassLoader);
}
return this.autoConfigurations;
}
}
然后进入doScan方法进行扫描,我们来总结下当前的定义的规则
- 扫描包–启动类对应的包
- 类型-- **/*.class
- :排除类型-- AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class(包含注解Configuration.class 且在spring.factories下定义在EnableAutoConfiguration下)
- 包含类型,有注解org.springframework.stereotype.Component包括:@Configuration、@Controller、@Service、@Component
public class ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner extends ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider {
...
protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified");
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
//这里就是按照我们定义的规则进行扫描并返回BeanDefinition集合
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) {
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate);
candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry);
if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName);
}
if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate);
}
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName);
definitionHolder =
AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder);
registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
...
}
返回满足条件的BeanDefinition信息后进行注册bean定义。然后我们要回到当初进行解析@ComponentScan的入口
@Nullable
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(
ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass, Predicate<String> filter)
throws IOException {
// Process any @PropertySource annotations
...
// Process any @ComponentScan annotations
Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&
!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
if (bdCand == null) {
bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();
}
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
// 会对返回的bean进行重新解析,解析的对象就是当前类,是个递归,这样我们第一次扫描的bean如果又包含类似@ComponentScan注解的又会包含进来
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
}
// Process any @Import annotations
// Process any @ImportResource annotations
// Process individual @Bean methods
...
// No superclass -> processing is complete
return null;
...
}
}
至此@ComponentScan已解析完,该左右总结来说就是定义一个启动类,读取该类的注解信息(@Configuration、@Controller、@Service、@Component),例如默认情况我们会在启动类包下,如果我们定义一个类上包含了(@Component(xxx.xx))就会加载该包下的类,满足条件的加载到spring容器,然后递归进行扫描。