搜索引擎ElasticSearch分布式搜索和分析引擎学习,SpringBoot整合ES个人心得
ElasticSearch
Elasticsearch是一个基于Lucene的搜索服务器。它提供了一个分布式多用户能力的全文搜索引擎,基于RESTful web接口。Elasticsearch是用Java语言开发的,并作为Apache许可条款下的开放源码发布,是一种流行的企业级搜索引擎。Elasticsearch用于云计算中,能够达到实时搜索,稳定,可靠,快速,安装使用方便。官方客户端在Java、.NET(C#)、PHP、Python、Apache Groovy、Ruby和许多其他语言中都是可用的。根据DB-Engines的排名显示,Elasticsearch是最受欢迎的企业搜索引擎,其次是Apache Solr,也是基于Lucene
如京东,淘宝
Lucene是一个Java语言的搜索引擎类库,是Apache公司的顶级项目,由DougCutting于1999年研发。官网地址: https:// lucene.apache.org/
重要性:
- 分布式的实时文件存储,每个字段都被索引并可被搜索
- 实时分析的分布式搜索引擎
- 可以扩展到上百台服务器,处理PB级结构化或非结构化数据
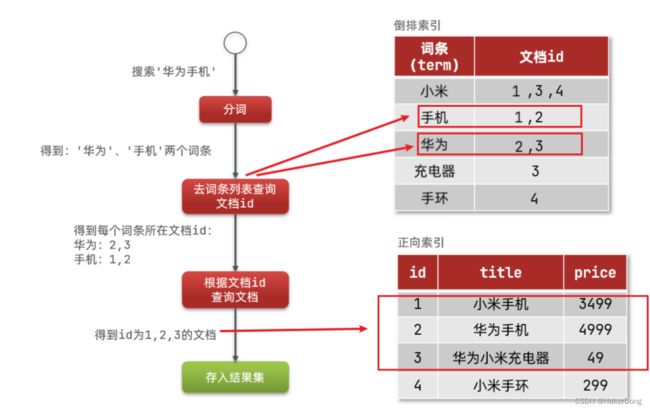
倒排索引
倒排索引的概念是基于MySQL这样的正向索引而言的
正向索引
但如果是基于title做模糊查询,只能是逐行扫描数据,流程如下:
- 用户搜索数据,条件是title符合“
%手机%” - 逐行获取数据,比如id为1的数据
- 判断数据中的title是否符合用户搜索条件
- 如果符合则放入结果集,不符合则丢弃。回到步骤1
逐行扫描,也就是全表扫描,随着数据量增加,其查询效率也会越来越低。当数据量达到数百万时,就是一场灾难。
倒排索引
倒排索引中有两个非常重要的概念:
- 文档Document:用来搜索的数据,其中的每一条数据就是一个文档。例如一个网页、一个商品信息
- 词条Term:对文档数据或用户搜索数据,利用某种算法分词,得到的具备含义的词语就是词条。例如:我是中国人,就可以分为:我、是、中国人、中国、国人这样的几个词条
创建倒排索引是对正向索引的一种特殊处理,流程如下:
- 将每一个文档的数据利用算法分词,得到一个个词条
- 创建表,每行数据包括词条、词条所在文档id、位置等信息
- 因为词条唯一性,可以给词条创建索引,例如hash表结构索引
倒排索引的搜索流程如下(以搜寻“华为手机”为例)
- 用户输入条件 “华为手机” 进行搜索。
- 对用户输入内容分词,得到词条: 华为 、 手机 。
- 拿着词条在倒排索引中查找,可以得到包含词条的文档id:1、2、3。
- 拿着文档id到正向索引中查找具体文档
虽然要先查询倒排索引,再查询倒排索引,但是无论是词条、还是文档id都建立了索引,查询速度非常快!无需全表扫描。
正向和倒排
- 正向索引是最传统的,根据id索引的方式。但根据词条查询时,必须先逐条获取每个文档,然后判断文档中是否包含所需要的词条,是根据文档找词条的过程。
- 而倒排索引则相反,是先找到用户要搜索的词条,根据词条得到保护词条的文档的id,然后根据id获取文档。是根据词条找文档的过程
正向索引
优点:
- 可以给多个字段创建索引
- 根据索引字段搜索、排序速度非常快
缺点:
- 根据非索引字段,或者索引字段中的部分词条查找时,只能全表扫描
倒排索引
优点:
- 根据词条搜索、模糊搜索时,速度非常快
缺点:
- 只能给词条创建索引,而不是字段
- 无法根据字段做排序
ES的一些概念
elasticsearch中有很多独有的概念,与mysql中略有差别,但也有相似之处
文档和字段
elasticsearch是面向**文档(Document)**存储的,可以是数据库中的一条商品数据,一个订单信息。文档数据会被序列化为json格式后存储在elasticsearch中:
而Json文档中往往包含很多的字段(Field),类似于数据库中的列
索引和映射
索引(Index),就是相同类型的文档的集合。
例如:
- 所有用户文档,就可以组织在一起,称为用户的索引;
- 所有商品的文档,可以组织在一起,称为商品的索引;
- 所有订单的文档,可以组织在一起,称为订单的索引;
因此,我们可以把索引当做是数据库中的表。
数据库的表会有约束信息,用来定义表的结构、字段的名称、类型等信息。因此,索引库中就有映射(mapping),是索引中文档的字段约束信息,类似表的结构约束。
MySQL和ElasticSearch
我们统一的把mysql与elasticsearch的概念做一下对比
ES环境安装
ES环境需要ES和分词器
环境搭建步骤:
- windows版ES下载:网址https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/elasticsearch
- 下载分词器(4IK分词器):https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases
- 解压缩ES,并且在解压缩的plugins创建ik文件夹
- 将4IK分词器解压后的所有文件拷贝到创建的ik文件夹下
启动ES:
- 找到ES文件夹下的bin文件夹,双击文件 elasticsearch.bat(弹出窗口不要关闭)
- 浏览器访问localhost:9200能看到json代表启动成功
4IK分词器
作用:
- 创建倒排索引时对文档分词
- 用户搜索时,对输入的内容分词
IK分词器的模式:
- ik_smart:智能切分,粗粒度
- ik_max_word:最细切分,细粒度
索引库操作
索引库就类似数据库表,mapping映射就类似表的结构。
我们要向es中存储数据,必须先创建“库”和“表”。
mapping映射属性
mapping是对索引库中文档的约束,常见的mapping属性包括:
type:字段数据类型,常见的简单类型有:
- 字符串:text(可分词的文本)、keyword(精确值,例如:品牌、国家、ip地址)
- 数值:long、integer、short、byte、double、float
- 布尔:boolean
- 日期:date
- 对象:object
index:是否创建索引,默认为true
analyzer:使用哪种分词器
properties:该字段的子字段
Eg:
{
"age": 18,
"weight": 70.2,
"isMarried": false,
"info": "apesourceJavaEE王讲师",
"email": "[email protected]",
"score": [99.1, 99.5, 98.9],
"name": {
"firstName": "师傅",
"lastName": "王"
}
}
对应的每个字段映射(mapping):
- age:类型为 integer;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
- weight:类型为float;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
- isMarried:类型为boolean;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
- info:类型为字符串,需要分词,因此是text;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;分词器可以用ik_smart
- email:类型为字符串,但是不需要分词,因此是keyword;不参与搜索,因此需要index为false;无需分词器
- score:虽然是数组,但是我们只看元素的类型,类型为float;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
- name:类型为object,需要定义多个子属性
- name.firstName;类型为字符串,但是不需要分词,因此是keyword;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
- name.lastName;类型为字符串,但是不需要分词,因此是keyword;参与搜索,因此需要
- index为true;无需分词器
创建索引库和映射
基本语法:
- 请求方式:PUT
- 请求路径:/索引库名,可以自定义
- 请求参数:mapping
格式:
{
"mappings":{
"properties":{
"age":{
"type":"integer"
},
"isMarried":{
"type":"boolean"
},
"name":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"ik_smart"
},
"info":{
"type":"text",
"index":"false"
},
"pet":{
"properties":{
"dog":{
"type":"text"
},
"cat":{
"type":"text"
}
}
}
}
}
}
Postman测试创建索引库和映射
查询索引库
基本语法:
- 请求方式:GET
- 请求路径:/索引库名
- 请求参数:无
格式:
GET /索引库名
eg:postman发送GET请求:localhost:9200/teachers
修改索引库
倒排索引结构虽然不复杂,但是一旦数据结构改变(比如改变了分词器),就需要重新创建倒排索引,这简直是灾难。因此索引库一旦创建,无法修改mapping。
虽然无法修改mapping中已有的字段,但是却允许添加新的字段到mapping中,因为不会对倒排索引产生影响。
语法说明:
PUT /索引库名/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"新字段名":{
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
eg:postman发送PUT请求:localhost:9200/teachers/_mapping
删除索引库
语法:
- 请求方式:DELETE
- 请求路径:/索引库名
- 请求参数:无
格式:
DELETE /索引库名
postman发送DELETE请求:localhost:9200/teachers
总结:
- 创建索引库:PUT /索引库名
- 查询索引库:GET /索引库名
- 删除索引库:DELETE /索引库名
- 添加字段:PUT /索引库名/_mapping
文档操作
新增文档
语法:
POST /索引库名/_doc/文档id
{
"字段1": "值1",
"字段2": "值2",
"字段3": {
"子属性1": "值3",
"子属性2": "值4"
},
// ...
}
eg:
POST请求:localhost:9200/teachers/_doc/1
{
"info":"java程序开发工程师",
"age":"23",
"name":"詹姆斯高斯林",
"pet":{
"拉布拉多":"旺财",
"英短":"小老弟"
}
}
查询文档
根据rest风格,新增是post,查询应该是get,不过查询一般都需要条件,这里我们把文档id带上。
语法:
GET /{索引库名称}/_doc/{id}
查看数据:
GET请求:localhost:9200/teachers/_doc/1
localhost:9200/teachers/_doc/1
删除文档
删除使用DELETE请求,同样,需要根据id进行删除
语法:
DELETE /{索引库名}/_doc/id值
eg:
DELETE请求
localhost:9200/teachers/_doc/1
修改文档
- 全量修改:直接覆盖原来的文档
- 增量修改:修改文档中的部分字段
全量修改
全量修改是覆盖原来的文档,其本质是:
- 根据指定的id删除文档
- 新增一个相同id的文档
**注意:**如果根据id删除时,id不存在,第二步的新增也会执行,也就从修改变成了新增操作了
语法:
PUT /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id
{
"字段1": "值1",
"字段2": "值2",
// ... 略
}
eg:
postman发送PUT请求:localhost:9200/teachers/_doc/1
{
"info":"python程序开发工程",
"name":"吉多范罗苏姆",
"age":"22",
"pet":{
"拉布拉多":"旺财",
"英短":"小老弟"
}
}
全量修改
增量修改是只修改指定id匹配的文档中的部分字段
语法:
POST /{索引库名}/_update/文档id
{
"doc": {
"字段名": "新的值",
}
}
eg:
postman发送POST请求:localhost:9200/teachers/_update/1
{
"doc":{
"name":"詹姆斯高斯林再牛逼也进不了谷歌"
}
}
总结:
- 创建文档:POST /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id { json文档 }
- 查询文档:GET /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id
- 删除文档:DELETE /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id
- 修改文档:
- 全量修改:PUT /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id { json文档 }
- 增量修改:POST /{索引库名}/_update/文档id { “doc”: {字段}}
RestAPI
ES官方提供了各种不同语言的客户端,用来操作ES。这些客户端的本质就是组装DSL语句,通过http请求发送给ES。官方文档地址:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/client/index.html
其中的Java Rest Client又包括两种:
- Java Low Level Rest Client
- Java High Level Rest Client
主要介绍Java High Level Rest Client
数据库建表语句
CREATE TABLE `tb_hotel` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '酒店id',
`name` varchar(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '酒店名称;例:7天酒店',
`address` varchar(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '酒店地址;例:航头路',
`price` int(10) NOT NULL COMMENT '酒店价格;例:329',
`score` int(2) NOT NULL COMMENT '酒店评分;例:45,就是4.5分',
`brand` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '酒店品牌;例:如家',
`city` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '所在城市;例:上海',
`star_name` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '酒店星级,从低到高分别是:1星到5星,1
钻到5钻',
`business` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商圈;例:虹桥',
`latitude` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '纬度;例:31.2497',
`longitude` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '经度;例:120.3925',
`pic` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '酒店图片;例:/img/1.jpg',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
mapping映射分析
酒店数据的索引库结构:
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"name":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"address":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": false,
"copy_to": "all"
},
"price":{
"type": "integer"
},
"score":{
"type": "integer"
},
"brand":{
"type": "keyword",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"city":{
"type": "keyword",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"starName":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"business":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"location":{
"type": "geo_point"
},
"pic":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"all":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
几个特殊字段说明:
location:地理坐标,里面包含精度、纬度
all:一个组合字段,其目的是将多字段的值 利用copy_to合并,提供给用户搜索
地理坐标说明:
copy_to说明:
JAVA中使用ES
初始化RestClient
在elasticsearch提供的API中,与elasticsearch一切交互都封装在一个名为RestHighLevelClient的类中,必须先完成这个对象的初始化,建立与elasticsearch的连接。
在Spring Boot中使用ES三步骤:
-
引入es的RestHighLevelClient依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.elasticsearch.clientgroupId> <artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-clientartifactId> dependency> -
因为SpringBoot默认的ES版本是7.6.2,所以我们需要覆盖默认的ES版本
<properties> <java.version>1.8java.version> <elasticsearch.version>7.12.0elasticsearch.version> properties> -
初始化RestHighLevelClient
将RestHighLevelClient注入容器,可以写配置类,也可以写在启动类中
@Bean public RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient(){ RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder( HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200") )); }
创建索引库
-
准备索引库映射字符串
public class HotelConstants { public static final String MAPPING_TEMPLATE = "{\n" + " \"mappings\": {\n" + " \"properties\": {\n" + " \"id\": {\n" + " \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" + " },\n" + " \"name\":{\n" + " \"type\": \"text\",\n" + " \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\",\n" + " \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" + " },\n" + " \"address\":{\n" + " \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" + " \"index\": false\n" + " },\n" + " \"price\":{\n" + " \"type\": \"integer\"\n" + " },\n" + " \"score\":{\n" + " \"type\": \"integer\"\n" + " },\n" + " \"brand\":{\n" + " \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" + " \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" + " },\n" + " \"city\":{\n" + " \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" + " \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" + " },\n" + " \"starName\":{\n" + " \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" + " },\n" + " \"business\":{\n" + " \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" + " },\n" + " \"location\":{\n" + " \"type\": \"geo_point\"\n" + " },\n" + " \"pic\":{\n" + " \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" + " \"index\": false\n" + " },\n" + " \"all\":{\n" + " \"type\": \"text\",\n" + " \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\"\n" + " }\n" + " }\n" + " }\n" + "}"; } -
索引库的操作
@SpringBootTest class SpringbootEs01ApplicationTests { private RestHighLevelClient client; @BeforeEach void setUp(){ this.client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder( HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200") )); } @AfterEach void tearDown() throws Exception{ this.client.close(); } // 判断索引库是否存在 @Test void testExistsHotelIndex() throws Exception { GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest("hotels"); boolean exists = client.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.err.println(exists ? "索引库已经存在":"索引库不存在"); } // 创建索引库 @Test void createHotelIndex() throws Exception{ // 创建Request对象 CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("hotels"); // 准备请求的参数:DSL语句 request.source(HotelConstants.MAPPING_TEMPLATE, XContentType.JSON); // 发送请求 client.indices().create(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT); } // 删除索引库 @Test void delteHotelIndex() throws Exception{ // 创建Request对象 DeleteIndexRequest request = new DeleteIndexRequest("hotels"); // 发送请求 client.indices().delete(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT); } }
总结
JavaRestClient操作elasticsearch的流程基本类似。核心是client.indices()方法来获取索引库的操作对象
索引库操作的基本步骤:
- 初始化RestHighLevelClient
- 创建XxxIndexRequest。XXX是Create、Get、Delete
- 准备DSL( Create时需要,其它是无参)
- 发送请求。调用RestHighLevelClient#indices().xxx()方法,xxx是create、exists、delete
文档操作
演示在juint单元测试中进行,准备
@SpringBootTest
public class HotelDocumentTests {
// 核心对象
private RestHighLevelClient client;
// 需要从数据库中查数据存入es,装配业务
@Autowired(required = false)
private IHotelService service;
@BeforeEach
void setUp(){
this.client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200")
));
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown() throws Exception{
this.client.close();
}
}
-
从数据库中新增一条数据到ES
@Test void addDocument() throws Exception{ // 从数据库查询一条数据 Hotel hotel = service.getById(395434); System.out.println(hotel); // 转换为文档类型 HotelDoc hotelDoc = new HotelDoc(hotel); // 将文档类型转为JSON格式 String json = JSON.toJSONString(hotelDoc); // 准备request请求对象 IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("hotels").id(hotelDoc.getId().toString()); // 准备JSON文档 request.source(json, XContentType.JSON); // 发送请求 client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); } -
从ES中删除一条数据
@Test void deleteDocument() throws Exception{ // 准备删除请求Request DeleteRequest request = new DeleteRequest("hotels", "395434"); client.delete(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT); } -
修改ES中的数据
修改有两种方式:
- 全量修改:本质是先根据id删除,再新增
- 增量修改:修改文档中的指定字段值
- 在RestClient的API中,全量修改与新增的API完全一致
@Test void updateDocument() throws Exception{ // 准备修改请求UpdateRequest UpdateRequest request = new UpdateRequest("hotels", "395434"); // 准备请求参数(要修改的数据内容) request.doc( "name","W酒店", "city","西安", "price","2000", "starName","五星级" ); } -
批量新增数据到ES中
@Test void addAllDocument() throws Exception{ // 数据库全查 List<Hotel> hotels = service.list(); // 准备请求 BulkRequest bulkRequest = new BulkRequest(); // 准备参数 for(Hotel hotel : hotels){ // 类型转化 HotelDoc hotelDoc = new HotelDoc(hotel); // 请求添加数据 bulkRequest.add(new IndexRequest("hotels").id(hotelDoc.getId().toString()).source(JSON.toJSONString(hotelDoc),XContentType.JSON)); } // 发送请求 client.bulk(bulkRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT); }
总结
文档操作的基本步骤:
- 初始化RestHighLevelClient
- 创建XxxRequest。XXX是Index、Get、Update、Delete、Bulk
- 准备参数(Index、Update、Bulk时需要)
- 发送请求。调用RestHighLevelClient#.xxx()方法,xxx是index、get、update、delete、bulk
- 解析结果(Get时需要)
查询文档操作
Elasticsearch提供了基于JSON的DSL(Domain Specific Language)来定义查询。常见的查询类型包括:
==查询所有:==查询出所有数据,一般测试用(不会显示出所有,自带分页功能)。例如:match_all
==全文检索(full text)查询:==利用分词器对用户输入内容分词,然后去倒排索引库中匹配。例如:
- match_query:单字段查询
- multi_match_query:多字段查询,任意一个字段符合条件就算符合查询条件
==准确查询:==根据精确词条值查找数据,一般是查找keyword、数值、日期、boolean等类型字段。例如
- ids:id查询
- range:根据值的范围查询
- term:根据词条精确值查询
==地理(geo)查询:==根据经纬度查询。例如:
- geo_distance
- geo_bounding_box
==复合(compound)查询:==复合查询可以将上述各种查询条件组合起来,合并查询条件。例如:
-
bool
-
function_score
-
查询一条数据
@Test void getDocumentById() throws Exception{ // 准备查询请求GetRequest GetRequest getRequest = new GetRequest("hotels", "395434"); // 发送请求,得到响应 GetResponse response = client.get(getRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); // 解析响应结果 String json = response.getSourceAsString(); HotelDoc hotelDoc = JSON.parseObject(json,HotelDoc.class); System.out.println(hotelDoc); } -
解析对象方法
// 解析对象方法 public void show(SearchResponse response){ // 解析响应 SearchHits searchHits = response.getHits(); long total = searchHits.getTotalHits().value; System.out.println("总计查询数据:"+total+"条"); SearchHit[] hits = searchHits.getHits(); for(SearchHit hit :hits){ /// 获取文档source String json = hit.getSourceAsString(); // 反序列化 HotelDoc hotelDoc = JSON.parseObject(json, HotelDoc.class); System.out.println("hotelDoc="+hotelDoc); } } -
全查
@Test void findAllDocument() throws IOException{ // 准备request SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotels"); // 2.准备DSL,QueryBuilders构造查询条件 request.source().query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery()); // 3.发送请求 SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); show(response); } -
全文索引----查询all字段内容中含有如家的
@Test void testMacth() throws IOException{ // 准备请求 SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotels"); // 准备DSL request.source(). query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("all","如家")); // 发送请求 SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); show(response); } -
全文索引----多字段查询
@Test void testMultiMatchQuery()throws IOException { // 准备请求 SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotels"); // 准备DSL request.source() .query(QueryBuilders.multiMatchQuery("上海","name","city")); // 发送请求 SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); show(response); } -
精确查询1
// term:根据词条精准查询(字段等值查询) @Test void testTerm() throws IOException{ // 准备请求 SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotels"); // 准备DSL request.source() .query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("brand","希尔顿")); // 发送请求 SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); show(response); } -
精确查询2
// range范围查询 @Test void testRange() throws IOException { // 准备请求 SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotels"); // 准备DSL request.source() .query(QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("price").gte(200).lte(300)); // 发送请求 SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); show(response); } -
精确查询3
// ids查询 @Test void testIds() throws IOException { // 准备请求 SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotels"); // 准备DSL request.source() .query(QueryBuilders.idsQuery().addIds("395434","3532")); // 发送请求 SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); show(response); } -
复合查询
// bool复合查询 @Test void testBool() throws IOException{ // 准备请求 SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotels"); // 准备条件 /*-- 方式1 ----*/ // BoolQueryBuilder boolQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.boolQuery(); // boolQueryBuilder.must(QueryBuilders.termQuery("city","北京")); // boolQueryBuilder.filter(QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("price").lte(500)); // // 准备DSL // request.source().query(boolQueryBuilder); /*---- 方式2 ----*/ request.source() .query(QueryBuilders.boolQuery() .must(QueryBuilders.termQuery("city","北京")) .filter(QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("price").lte(500))); // 发送请求 SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); show(response); } -
自定义分页规则
// 自定义分页方式 @Test void testPageAndSort() throws IOException{ int page = 1; //页码 int size = 5; //步长 String searchName="希尔顿"; // 查询条件 // 准备请求 SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotels"); if (searchName == null){ request.source().query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery()); }else { request.source().query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("brand",searchName)); } // 自定义分页 request.source().from((page-1)*size).size(size); // 自定义排序 request.source().sort("price", SortOrder.DESC); SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); show(response); }
总结
SpringBoot中整合ES的实现步骤 :
-
导pom文件ES的坐标
<properties> <java.version>1.8java.version> <elasticsearch.version>7.12.0elasticsearch.version> properties> -
写ES配置类
@Configuration public class ElasticSearchConfig { @Bean public RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient(){ return new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder( HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200") )); } } -
写ES映射Mapping
-
建立ES索引库
public void createEs() throws IOException { GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest("employee"); // 判断索引库是否存在 boolean exists = restHighLevelClient.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); // 如果不存在建库 if(!exists){ // 创建Request对象 CreateIndexRequest createIndexRequest = new CreateIndexRequest("employee"); // 准备请求的参数DSL语句 createIndexRequest.source(EmployeeConstants.MAPPING_TEMPLATE, XContentType.JSON); // 发送请求 restHighLevelClient.indices().create(createIndexRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT); } } -
把数据库中的数据添加到ES中
public void addAllEmployee() throws Exception{ // 数据库全查 List<Employee> list = employeeService.list(); // 准备请求 BulkRequest bulkRequest = new BulkRequest(); for(Employee e : list){ bulkRequest.add(new IndexRequest("employee").id(e.getId().toString()).source(JSON.toJSONString(e),XContentType.JSON)); } // 发送请求 restHighLevelClient.bulk(bulkRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT); } -
业务中查询ES,修改添加删除数据库同步ES
-
写解析
// 解析对象方法 public void show(SearchResponse response){ // 解析响应 SearchHits searchHits = response.getHits(); long total = searchHits.getTotalHits().value; System.out.println("总计查询数据:"+total+"条"); SearchHit[] hits = searchHits.getHits(); for(SearchHit hit :hits){ /// 获取文档source String json = hit.getSourceAsString(); // 反序列化 HotelDoc hotelDoc = JSON.parseObject(json, HotelDoc.class); System.out.println("hotelDoc="+hotelDoc); } }
注意:操作ES需要装配核心对象RestHighLevelClient