链表常见面试题-c语言实现,单链表相关面试题(C语言实现)
在这里给出一些关于单链表常见的面试题。
一、 给定单链表,检测是否有环。
1.题目分析
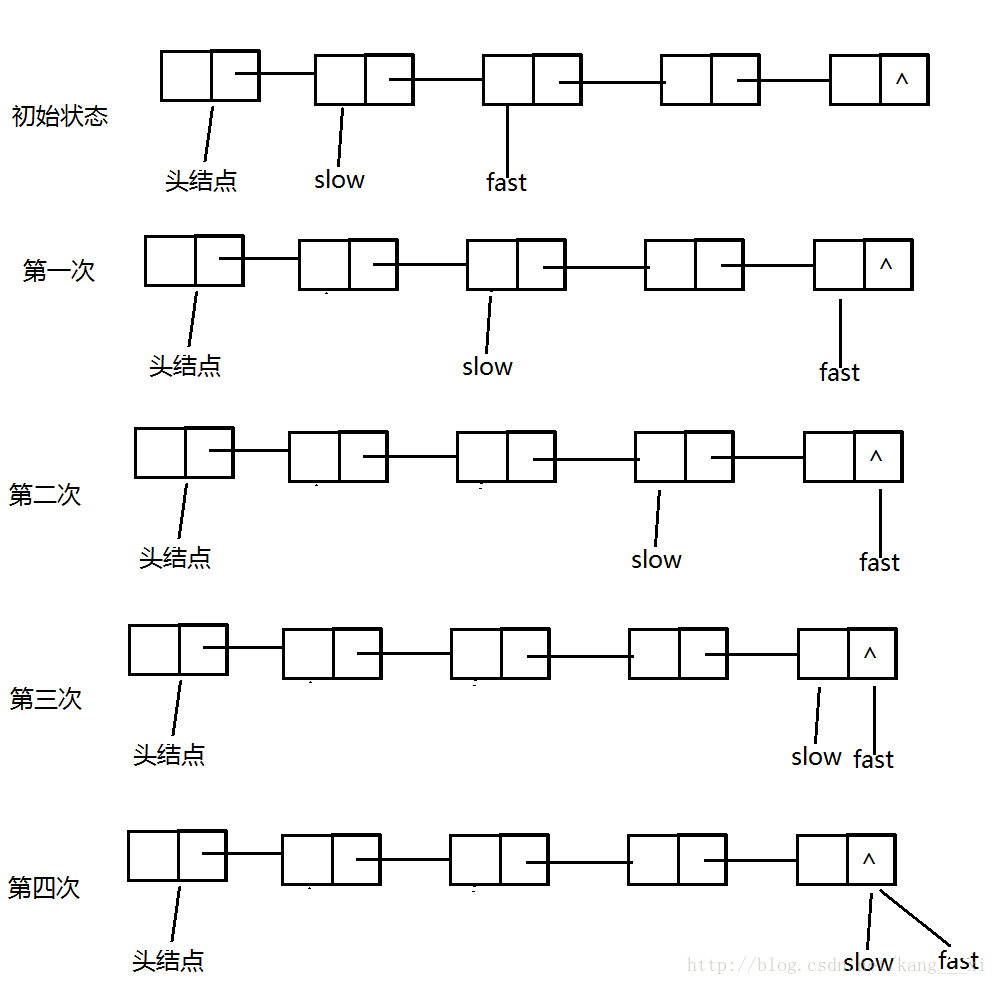
仔细读题目发现还是有难度的,很多人刚开始会理解成就是判断一个单链表是否为循环链表,这样的理解是错的。题目的意思是指给出一条单链表,判断其中是否含有环,如“6”字型单链表就含有环。
明白题目意思以后我们来说明解题思路,假设给定的单链表中有n个节点,我们可以利用两个指针fast和slow来求解问题。fast指针每次走两步,而slow指针每次走一步,下面分两种情况来说明。
第一种情况是链表中没有环,即普通的单链表,按上面的规则fast和slow一直往链表后面走,这时候会特殊情况,就是fast指针本应该每次走两步,但走完一步以后就走到了链表的尾部,此时fast指针为NULL,不再往后走;而slow指针每次走一步,这种情况下也会走到链表尾部,slow指针变为NULL,两者相等,而且这两个指针最后都变为NULL。
在第三次中fast走了一步以后就到了链表尾部,所以不再向后走,此时就静待slow的到来,看来这次的龟兔赛跑兔子没有中间睡懒觉,哈哈。
第二种情况就是链表中有环,以“6”字型链表进行说明。此时在链表进入环之前,fast指针和slow指针走过的路程都是一样的;在进入环以后两者肯定会相遇,下面给出数学证明:
2.代码实现
#ifndef JUDGE_CIRCLE_H_
#define JUDGE_CIRCLE_H_
typedef struct Node
{
int iData;
struct Node *pNext;
}Node, *List;
void InitList(List plist); //初始化单链表
bool JudgeCircle(List plist); //判断链表是否含环
#endif
#include "JudgeCircle.h"
#include
#include
void InitList(List plist)
{
if (NULL == plist) //安全性检查,下同
{
return;
}
plist->pNext = NULL;
}
bool JudgeCircle(List plist)
{
Node *pFast, *pSlow;
pSlow = plist->pNext; //共同的起点
pFast = plist->pNext;
if (pFast != NULL)
{
pFast = pFast->pNext;
}
while (pFast != pSlow)
{
pSlow = pSlow->pNext; //走一步
if (pFast != NULL)
pFast = pFast->pNext;
if (pFast != NULL)
{
pFast = pFast->pNext;
}
}
if (pSlow == pFast && pSlow != NULL)
{
return true;
}
else if (pSlow == pFast && pSlow == NULL)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
int main(void)
{
Node head;
InitList(&head);
Node no1;
no1.iData = 1;
no1.pNext = NULL;
Node no2;
no2.iData = 2;
no2.pNext = NULL;
Node no3;
no3.iData = 3;
no3.pNext = NULL;
Node no4;
no4.iData = 4;
no4.pNext = NULL;
Node no5;
no5.iData = 5;
no5.pNext = NULL;
Node no6;
no6.iData = 6;
no6.pNext = NULL;
head.pNext = &no1;
no1.pNext = &no2;
no2.pNext = &no3;
no3.pNext = &no4;
no4.pNext = &no5;
no5.pNext = &no6;
no6.pNext = NULL;
if (JudgeCircle(&head))
{
printf("The list is a circle.\n");
}
else
{
printf("The list isn't a circle.\n");
}
return 0;
}
二、 给定两个单链表(head1, head2),检测两个链表是否有交点,如果有返回第一个交点
1.题目分析
这个题目相对比较简单,这里直接说出解题思路。
分别获取两个单链表的长度,求出两个单链表的长度差,假设单链表head1的长度为5,单链表head2的长度为3,两者的长度差为2。知道长度差以后,用一个指针指向长的那个单链表(这个例子中是指向head1),这个指针先往后走长度差步(这个例子中是2步);用一个指针指向head2,然后指向这两个链表的指针同时往后走,每次走一个节点,每走一步就要判断这两个指针的next域是是否一样,且不为NULL。如果一样且不为空,则此时找到两个链表的交点,反之。
2.代码实现
#ifndef JUDGE_CIRCLE_H_
#define JUDGE_CIRCLE_H_
typedef struct Node
{
int iData;
struct Node *pNext;
}Node, *List;
void InitList(List plist);
Node* BuyNode(int iVal);
void TailInsert(List plist, int iVal);
int GetListLen(List plist);
void PrintList(List plist);
void MergeList(List pDest, List pSrc);
Node* JudgeY(List pLhs, List pRhs);
#endif
#include "JudgeCircle.h"
#include
#include
void InitList(List plist)
{
if (NULL == plist) //安全性检查,下同
{
return;
}
plist->pNext = NULL;
}
//申请一个值为iVal的节点,并返回其内存地址
Node* BuyNode(int iVal)
{
Node* pNew = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
pNew->iData = iVal;
pNew->pNext = NULL;
return pNew;
}
void TailInsert(List plist, int iVal)
{
if (NULL == plist)
{
return;
}
Node *pTail;
for (pTail = plist; pTail->pNext != NULL; pTail = pTail->pNext)
{
NULL;
}
Node *pNew = BuyNode(iVal);
pTail->pNext = pNew;
}
int GetListLen(List plist)
{
if (NULL == plist)
{
return -1;
}
int iCount = 0;
for (Node *pTemp = plist->pNext; pTemp != NULL; pTemp = pTemp->pNext)
{
++iCount;
}
return iCount;
}
void PrintList(List plist)
{
for (Node *pTemp = plist->pNext; pTemp != NULL; pTemp = pTemp->pNext)
{
printf("%5d", pTemp->iData);
}
printf("\n");
}
void MergeList(List pDest, List pSrc)
{
if (NULL == pDest || NULL == pSrc)
{
return;
}
找到pDest的最后一个节点,然后将pSrc链接到后面
Node *pTail;
for (pTail = pDest; pTail->pNext != NULL; pTail = pTail->pNext)
{
NULL;
}
pTail->pNext = pSrc->pNext;
}
Node* JudgeY(List pLhs, List pRhs)
{
int iLhsLen = GetListLen(pLhs);
int iRhsLen = GetListLen(pRhs);
Node *pList1 = pLhs->pNext;
Node *pList2 = pRhs->pNext;
int iDiff = iLhsLen - iRhsLen;
if (iDiff > 0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < iDiff; ++i)
{
pList1 = pList1->pNext;
}
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < iDiff; ++i)
{
pList2 = pList2->pNext;
}
}
while (pList1 != NULL)
{
if (pList1->pNext == pList2->pNext)
{
return pList1->pNext;
}
pList1 = pList1->pNext;
pList2 = pList2->pNext;
}
return NULL;
}
int main(void)
{
Node head1, head2, head3;
InitList(&head1);
InitList(&head2);
InitList(&head3);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
TailInsert(&head1, i);
}
PrintList(&head1);
for (int i = 5; i < 10; ++i)
{
TailInsert(&head2, i);
}
PrintList(&head2);
for (int i = 5; i < 10; ++i)
{
TailInsert(&head3, i + 5);
}
PrintList(&head3);
MergeList(&head1, &head3);
PrintList(&head1);
MergeList(&head2, &head3);
PrintList(&head2);
Node *p = JudgeY(&head1, &head2);
if (p != NULL)
{
printf("%d\n", p->iData);
}
else
{
printf("Not cross.");
}
return 0;
}
三、只给定单链表中某个结点p(并非最后一个结点,即p->next!=NULL)指针,删除该结点。
1.题目分析
办法很简单,首先是放p中数据,然后将p->next的数据copy入p中,接下来删除p->next即可。
2.代码实现
//删除链表中指定节点p
void DeleteNode(List plist, Node *p)
{
if(NULL == plist)
{
return;
}
Node *pTemp = p->pNext;
p->iData = pTemp ->iData;
p->pNext = pTemp ->pNext;
free(pTemp);
pTemp = NULL;
}
四、只给定单链表中某个结点p(非空结点),在p前面插入一个结点。
1.题目分析
办法与前者类似,首先分配一个结点q,将q插入在p后,接下来将p中的数据copy入q中,然后再将要插入的数据记录在p中。
2.代码实现
void InsertNode(Node *p, Node *q)
{
q->pNext = p->pNext;
p->pNext = q;
int iTemp = p->iData;
p->iData = q->iData;
q->iData = iTemp;
}
五、给定单链表头结点,删除链表中倒数第k个结点。
1.题目分析
使用两个节点p1,p2,p1初始化指向头结点,p2一直指向p1后第k个节点,两个结点平行向后移动直到p2到达链表尾部(NULL),然后根据p1删除对应结点。
2.代码实现
//查找倒数第K个节点
Node* SearchTailK(List plist, int k)
{
if (NULL == plist)
{
printf("The list is valid.\n");
return false;
}
if (k < 1 || k > GetLength(plist))
{
printf("The delete position is valid.\n");
return false;
}
Node *p1 = plist;
int iCount;
for (iCount = 0; iCount < k - 1; ++iCount)
{
p1 = p1->next;
}
Node *p2 = plist;
while (p1->next != NULL)
{
p2 = p2->next;
p1 = p1->next;
}
return p2;
}
//删除倒数第K个节点
bool DeleteTailK(List plist, int k)
{
if (NULL == plist)
{
printf("The list is valid.\n");
return false;
}
if (k < 1 || k > GetLength(plist))
{
printf("The delete position is valid.\n");
return false;
}
Node *pTemp = SearchTailK(plist, k);
Node *pPre = NULL;
for (pPre = plist; pPre->next != pTemp; pPre = pPre->next)
{
NULL;
}
pPre->next = pTemp->next;
free(pTemp);
return true;
}